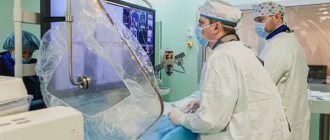
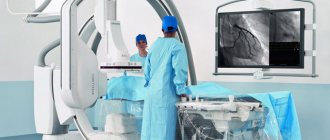
Carotid angiography is an invasive X-ray imaging procedure of the carotid arteries that is performed through a catheter inserted into a blood vessel in the arm or leg. A contrast agent is injected through the catheter, which is opaque to X-rays and therefore shows the internal lumen of the carotid arteries. This procedure is the gold standard for visualization of the carotid and cerebral vessels.
Preparing for the study
- Preparation for the study involves shaving the access site (usually the groin area).
- You should tell your doctor about any allergic reactions you have.
- If you are diabetic, tell your doctor so your medications can be adjusted on the day of the test.
- Tell your doctor if you are allergic to anything, especially iodine, shellfish, X-ray contrast, latex, or rubber products (such as rubber gloves).
- It is advisable to drink enough fluids before the examination to reduce the possible effects of contrast on the kidneys.
Why CT angiography of the brain is the best diagnostic method
The main advantage of this method is its safety. Radiation exposure during the examination is minimal. Unlike classical angiography, CT is a more gentle diagnostic method. Long-term preparation with a hospital stay is not required. In addition, during the procedure, patients do not experience discomfort or negative emotions.
At the same time, the significance of CT angiography of the brain and neck is very high. Using this examination, the specialist examines the walls of the blood vessels of the neck, brain and adjacent tissues layer by layer. For more convenient decryption, all data is recorded on removable media. The patient can additionally show the images to any doctor to get a second opinion.
After research
Tell your doctor or nurses if you feel:
- Itching, dry throat
- Nausea
- Chest discomfort
- Vision problems
- Weakness in one or more limbs
At the end of the study, you will be transferred to a ward. It is necessary to remain in bed for several hours. The doctor will periodically examine the access site and assess the general condition. If there are no problems, then discharge can be made the next day.
How is it carried out?
MRI angiography of cerebral vessels is performed under local anesthesia. It involves puncture of the wrist artery and installation of an introducer. It is a thin sterile plastic tube through which thin catheters are inserted. With their help, a diagnostic specialist will inject a contrast agent into distant vessels. At the multidisciplinary CELT clinic, specialists do everything to ensure that the patient does not experience pain during this procedure. Once the examination is completed, the introducer is removed from the arm and a pressure bandage is applied to the wrist. 30 minutes after the MRI, the patient is allowed to stand up, move independently and eat. If no deviations are found during the examination, within three to four hours after the examination they are given a transcript of the examination and a disc with the recording - and sent home. If pathologies are detected, our specialists will suggest appropriate surgical intervention, which can be carried out on the same day or the next.
Possible complications of carotid angiography
Complications are rare - the risk is 0.5%. The most dangerous are complications from the brain. They can develop as a result of the effect of contrast or when pieces of plaque are torn off during catheter insertion. Complications include:
- Transient ischemic attack - short-term disturbance of cerebral circulation
- Ischemic stroke is a persistent disorder of cerebral circulation
- Bleeding from the arterial access site
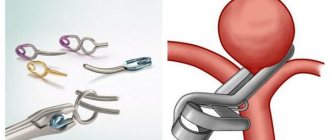
- Carotid artery dissection with thrombosis
- Allergic reaction to contrast
Timely diagnosis of complications allows you to minimize their consequences.
Perform MSCT angiography of cerebral vessels in St. Petersburg
Computed tomography (MSCT) of cerebral vessels can be done at Medical in St. Petersburg. The procedure helps in identifying pathologies and prevents the development of serious diseases. The diagnostic cost includes:
- Examination using an expert-class computed tomograph Aquilion Lightning TSX-035A (Canon Japan).
- A detailed, comprehensive conclusion made based on the images by a highly qualified radiologist. The description of the study is checked by the chief physician.
- 24/7 access to your personal account to view all your research and conclusions.
- Internal quality control of research.
- 100% guarantee of photo quality.
- Detailed information about prices can be found in the “Prices” section.
- You can find out about the benefits and ongoing promotions in the “Promotions” section.
Med is open every day from 9-00 to 21-00, so you can sign up for CT angiography of the cerebral arteries at a time convenient for you. You can also ask the radiologist your questions and get a free consultation. The procedure lasts approximately 20-30 minutes, as a modern tomograph of the latest generation quickly visualizes the structures of the brain arteries.
Angiography, vasography, vascular MRI - what's the difference?
There is practically no difference. The essence of all manipulations is a contrast study of vessels, arteries and veins, which allows medical workers to make a conclusion about the state of the anatomical structures and tissues in the area under study.
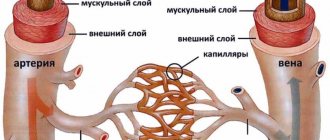
Angiography is the collective name for manipulations (radiography, ultrasound diagnostics, fluoroscopy, MRI) used for contrast examination of blood vessels.
Vasography is a similar collective name for contrast X-ray examination of veins, which can be carried out using various technological means.
Contraindications for diagnosis
There is a category of patients for whom magnetic resonance venography of the brain is contraindicated. Limitations include;
- metal clips on the arteries in the head;
- pacemaker for the heart;
- ferromagnetic, electrical implants in the middle ear;
- insulin pumps, implanted nerve stimulators;
- some types of dental posts;
- pregnancy 1st and 2nd trimester.
Pregnancy is a relative contraindication to the procedure. In the same group: prosthetic heart valves (non-magnetic), metal clips on the vessels of the peritoneum and pelvis.
Patients with chronic renal failure and nursing mothers should not undergo examinations using contrast. If the contrast agent is not tolerated by the patient’s body, MRI will also have to be abandoned.
Arteriovenous malformation
The condition is manifested by an abnormal plexus of veins and arteries. The external appearance of the formation resembles a tumor. Malformation leads to disruption of the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the brain.
If the formation reaches a significant size, then it becomes the cause of defective functioning of the organ. Gradually, the veins stretch and weaken, which is ultimately complicated by hemorrhage.
The problem can only be dealt with surgically. In the absence of timely treatment, malformation leads to irreversible changes.
Signs of pathology depending on its type:
- Hemorrhagic. It is characterized by a sharp headache, paralysis of the limbs, weakness, difficulties in perceiving sounds and images.
- Torpidnaya. It is characterized by severe pain sensations that occur in a certain area of the brain. Long-term pathology leads to impairment of speech, thinking and visual functions.
The risk of complications from arteriovenous malformation increases in older people and pregnant women.
MRI of the cerebral arteries: for what symptoms is it done?
Indications for MRI of the cerebral arteries may include the following symptoms:
- frequent, severe headaches;
- dizziness, loss of coordination;
- head injuries and bruises;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- speech disorder;
- cognitive impairment;
- noise in ears;
- sudden deterioration of vision.
When such conditions occur, patients most often turn to a neurologist. After asking the patient about troubling symptoms, the doctor may prescribe a number of examinations, including an MRI of the arteries of the brain.
MR image of cerebral arteries
The study can be carried out not only to diagnose the disease, but also to determine the effectiveness of treatment for various pathologies.
MRI of the arteries of the head - indications and contraindications
MRI of the cerebral arteries is prescribed to identify a number of diseases:
- dissection of the walls of blood vessels;
- cerebral hemorrhages;
- senile dementia;
- congenital vascular pathologies;
- vascular malformations;
- arterial stenosis;
- atherosclerosis;
- thrombosis;
- cerebral ischemia;
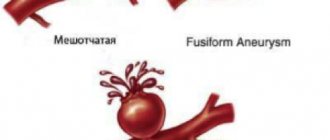
- aneurysm (expansion of artery walls);
- neoplasms.
Like any other diagnostic procedure, magnetic resonance imaging has its contraindications.
Modern tomograph Philips Intera 1.5 T
The examination cannot be carried out in the following cases:
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- the patient has a pacemaker, neurostimulator, vascular clips or medical devices and products made of ferromagnetic materials;
- the patient's weight is more than 130 kilograms;
- waist circumference more than 150 centimeters;
- inability to maintain a stationary position for various reasons;
- children under 5 years of age.
If you suspect possible contraindications, you must inform your doctor about them, who will help determine whether the procedure is possible in each specific case.
If it is necessary to use a contrast agent, you must ensure that there are no previous severe allergic reactions. MRI of the cerebral arteries usually does not need to be performed with contrast, but if such a need arises, you need to make sure there is no pregnancy.
Indications
A doctor's referral is required to examine the brain using cerebral angiography. This diagnostic method is not carried out only at the request of the patient.
The main indications are:
- suspicion of the presence of a cerebral aneurysm (sac-like bulging of the artery wall);
- determining the degree of narrowing of the lumen of the vessel by atherosclerotic plaques (narrowing of more than 75% significantly aggravates blood circulation in the brain and is an indication for surgical intervention);
- control of the location of clips pre-installed on the vessels;
- diagnosis of arteriovenous malformation (pathological connections between arteries and veins; usually congenital);
- suspicion of the presence of tumors, while the angiogram visualizes a change in the normal vascular pattern at the site of the tumor;
- visualization of the arteries of the brain during volumetric processes in it (tumors, cysts) in order to establish the location of the vessels relative to each other;
- suspicion of the presence of a brain angioma (a benign tumor formed by the vascular wall);
- lack of information when using other neuroimaging methods (CT, MRI), but in the presence of patient complaints and symptoms of the disease.
MRI of cerebral arteries with contrast
In most cases, modern high-field tomographs will help provide a detailed picture of the structure of the arteries and veins of the brain. But sometimes doctors resort to improving image quality by introducing a special coloring agent - contrast. This is done in order to see a clearer picture when damage or changes in the arteries may be very small in size.
Modern contrast agents are made from the metal gadolinium and are safe. The drug is administered intravenously and stains damaged tissue. In this case, the patient usually does not feel anything unusual. In rare cases, a feeling of warmth may occur at the injection site or area of examination.
Contrast drugs practically do not cause allergies and do not require a preliminary allergy test if the patient has not previously experienced acute allergic reactions or severe renal failure.
How to prepare?
- It is necessary to inform the doctor about the presence of allergies and concomitant diseases. Your doctor may recommend that you stop taking NSAIDs or blood thinners before the procedure.
- It is recommended not to eat or drink 8-12 hours before the procedure
- Women should always inform their doctor and radiologist if there is a possibility that they are pregnant. Many types of imaging are contraindicated during pregnancy, and the use of CT angiography is possible only when there are compelling clinical indications and minimizing the risk to the fetus.
If you are breastfeeding after the procedure, you should avoid breastfeeding your baby for 24 hours after the procedure.
What diseases can MRI of the head veins help diagnose?
The procedure allows us to identify pathological phenomena of blood flow. During the diagnostic process, areas of ischemia and infarction are visualized. The doctor is able to state the development of the following diseases:
- sinus thrombosis;
- anomalies, damage to the vascular system of the brain;
- aneurysms,
- cerebral vasculitis.
To get an MRI at Babushkinskaya, just call us or use the feedback form. Within the walls of our Center you can always count on timely delivery of research results. Accurate diagnosis will allow us to solve the problem in time and return you to a full life.
Make an appointment
Advantages
Annual attachment
Experienced doctors
Multidisciplinary clinic
Regular promotions
Free with annual membership!
more details
Several years ago, specialists could not even imagine that with the help of instrumental methods they would be able to make a diagnosis without characteristic signs in the early stages of the disease. Venography of the brain, performed by doctors at our clinic, helps evaluate the venous bed and the condition of individual structures.
The procedure is indicated for diagnosis and verification of the results of previously organized treatment. The same technique is applicable in drawing up a surgical intervention scheme for the development of certain diseases.
Contraindications
Carrying out both indirect and direct cerebral angiography has a number of contraindications:
- Allergy to iodine and iodine-containing substances. In this condition, the contrast can be replaced with gadolinium. If there is an allergy to other contrast components, it is necessary to completely abandon this examination method.
- Kidney and liver failure in the stage of decompensation. These conditions lead to impaired removal of contrast from the body.
- Severe chronic diseases.
- Acute inflammatory diseases, as the symptoms of infection may worsen.
- Age up to two years, as radiation impairs the growth and development of the child.
- The period of pregnancy and breastfeeding, since X-ray radiation has a detrimental effect on the fetus.
- Mental illnesses during exacerbation.
- Bleeding disorders (hemophilia, thrombocytopenic purpura), which increases the possibility of bleeding after contrast administration.