Catatonia (or catatonic syndrome) is an acute psychopathic disorder that causes a variety of speech, behavioral and motor disturbances. It may occur in the form of lethargy, stupor or psychomotor agitation. Catatonic behavior requires emergency medical care in a specialized clinic. In the inpatient mental health center “Leto”, patients in a similar condition are provided with round-the-clock supervision by experienced and highly qualified medical personnel, constant monitoring of their psycho-emotional and physical condition, timely emergency care and correction of medical prescriptions.
What is catatonia
Catatonia, or catatonic syndrome, is a condition in which a person becomes unresponsive to external stimuli and loses the ability to move and speak normally.
Until the beginning of the 20th century, it was believed that this only happened in schizophrenia. But then scientists found out Catatonia: pathophysiology, diagnosis and modern approaches to treatment that more than 50% of cases of catatonia appear in bipolar disorder, about 10–15% occur in schizophrenia, and 21% are not associated with mental illness at all.
Catatonia is similar Catatonia is the evolution of views and modern ideas (literature review) on mental disorders and other diseases, so it is difficult to recognize. For example, with it, as with a stroke, a person may respond with incomprehensible phrases or stop talking altogether. Urgent help is needed in both cases, but it will be different.
Catatonia can develop rapidly or gradually over several days. In the first case, the symptoms are usually strong and obvious; pressure or temperature surges are added to motor and speech disorders. This can lead, for example, to a stroke. In the second option, the symptoms are barely noticeable, and this is the most dangerous: in 3–4 days complications may appear: Catatonia or the person will die.
Imagine a grandmother who suffers from dementia. She often sits on the edge of the bed and looks out the window. But suddenly she spends the whole day like this. Then the grandmother stops talking and reacting to others, but continues to sit. Then she refuses food and water.
The body is exhausted, and 2-3 days after the first symptoms appear, blood clots form in the legs from a long immobile position. At some point they break off and clog the vessel. The man dies. But they would have been able to save him if dangerous symptoms had been noticed on the first day.
Locked up in solitary confinement
Psychiatrist Anna Konoreva says that catatonia is not a separate disease. Previously, it was considered a subtype or one of the manifestations of schizophrenia. But modern research shows that it occurs only in 10-15% of people with such a mental disorder, but in patients with bipolar disorder - in 20-50% of cases: stupor, mutism, waxy flexibility and other symptoms most often appear in them mixed or manic period.
Several years ago, Lina was diagnosed with type 1 bipolar disorder, which is characterized by mania. All this time she takes medication and visits a psychotherapist. But the selected treatment gives half the result.
Sometimes a girl, unnoticed by herself, flies into an extremely joyful mood, manages to redo all her affairs and come up with as many new ones, spend a lot of money and sleep with two different people on the same day. And sometimes you find yourself at an emotional low, and even the thought of brushing your teeth hurts. Catatonia manifests itself in a mixed state, between these two extremes.
“In the morning I wake up in a great mood, as if I’m floating above the earth, and I succeed in everything. And already during the day I start to hate myself and don’t want to do anything.
But since I need to put my energy somewhere, I work through force - and at the same time I get very angry. Several times such a swing was slowed down by a stupor: my plugs were knocked out, and I froze. When this happened in front of my ex, I felt him trying to bring me to consciousness, squeezing my hand, hitting my cheeks, but I couldn’t budge and answer him anything,” Lina recalls.
In addition to bipolar disorder, catatonia sometimes accompanies other affective disorders - for example, depression: people susceptible to this form of the disease perform actions very slowly, look at one point and rarely blink. In common parlance, such a patient is called a “vegetable,” and in medical theory, a person in a vegetative state.
But despite their immobility, inside these people experience the same depressive symptoms. This is how a woman who managed to get out of it describes her condition:
“My limbs felt like they were filled with concrete, my body was rejecting food. Chewing and swallowing was extremely difficult. And everything that came into my mouth tasted like sawdust.
My brain turned off all functions except suffering.
I could barely move or speak. And everyone who looked at me did not even suspect that I was going through - they saw only a shell. It was like I was in solitary confinement and couldn’t tell anyone how bad I felt.”
Why does catatonia occur?
Catatonia was first described in detail in 1874, but its causes have not yet been established. Scientists have several theories about catatonia: pathophysiology, diagnosis and modern approaches to treatment, which approximately explain what changes in the body lead to the appearance of symptoms of catatonia.
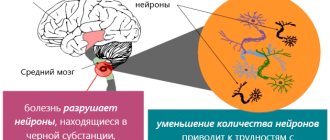
Some researchers believe that the problem lies in a disruption in the transmission of nerve impulses in those areas of the brain that are responsible for muscle contractions. Others associate catatonia with a change in the balance of neurotransmitters - substances that are produced by neurons in the brain and are involved in transmitting signals from cell to cell and many biochemical processes. Still others blame the excess or lack of certain hormones of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, the production of antibodies to brain proteins.
Such disturbances in the functioning of the body appear in many diseases:
- psychiatric Borisova P. O. Nosological dilemma and clinical polymorphism of the phenomenon of catatonia. , for example bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, autism, depression, anorexia nervosa;
- endocrine: Cushing's syndrome, hyperthyroidism, Sheehan's syndrome and others;
- neurological, for example epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, brain tumors, dementia;
- metabolic - this is when substances accumulate in the body that have a bad effect on the brain: this happens with Wilson-Konovalov disease, an increase and decrease in sodium concentration in the blood, kidney failure and other diseases;
- autoimmune, for example systemic lupus erythematosus, antiphospholipid syndrome;
- Catatonia caused by psychoactive substances: alcohol, antipsychotics, sedatives, drugs;
- infectious Catatonia: HIV, typhoid fever, tuberculosis, meningoencephalitis, herpes and others;
- vascular, for example thrombosis of the arteries and veins of the brain, stroke, cerebral hemorrhage.
What is catatonic disorder of organic nature?
Catatonic disorder in organic pathology is relatively rare and is recorded in approximately 1/10 patients suffering from encephalitis.
What causes catatonic disorder of organic nature?
The clinical picture of catatonia is most often found in brainstem encephalitis, as well as Jacob-Kretzfeldt disease. The occurrence of catatonia always indicates an increase in the severity of the process.
Symptoms of catatonic disorder of organic nature
In the foreground are the symptoms of the underlying pathology, which is usually detected neurologically. Catatonic syndrome contains typical manifestations of stupor: catalepsy, absence of voluntary reactions to a common stimulus when reacting to a paradoxically insignificant stimulus (Pavlov's symptom), immobility, mutism, cogwheel symptom, air cushion; as well as agitation: chaotic, undirected psychomotor agitation, which suddenly interrupts stupor. However, there is also atypia associated with an organic background, atonic stupors are frequent, in which muscle tone is reduced, catalepsy can be accompanied by tremor, tremor of the eyelids is noticeable, and the air cushion symptom can be confused with meningeal symptoms. The temperature is often elevated to 40 degrees, which is due to the underlying disease. Catatonia may be preceded by delirium or disorders of consciousness follow after the disappearance of the clinical picture of this syndrome.
Clinical example: Patient G., 34 years old, was examined in an infectious diseases clinic and diagnosed with tick-borne encephalitis. Stays within the bed and does not answer questions. Floating movements of the eyeballs, a sign of a cogwheel on the right, but catalepsy is noted on all extremities. Tremor of the fingers, performs stereotypical chewing actions. Negativism, when trying to open the mouth, clenches the teeth more strongly, grinds the teeth (bruxism). The condition is preceded by chaotic psychomotor agitation against the background of hyperthermia (temperature 39 degrees). In a state of excitement, she left the house and was found in the forest, sitting on the grass.
Diagnosis of catatonic disorder of organic nature
Diagnosis is based on identifying symptoms of the underlying pathology and atypical catatonia.
Differential diagnosis
The condition should be differentiated from neuroleptic malignant syndrome, catatonic schizophrenia, dissociative and depressive stupor, and catatonic disorders in the postpartum period.
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome is caused by hypodopaminergy, it is accompanied by hyperthermia, muscle rigidity, transformation of stupor into amentia and coma, autonomic disorders and impaired vascular permeability. The occurrence of the syndrome is facilitated by: organic background, intercurrent somatic disorders, agitation, dehydration, increased dosage or rate of administration of antipsychotics, combined use of antipsychotics.
Currently, catatonic schizophrenia occurs in the form of microcatatonia, accompanied by negative emotional-volitional disorders. Catatonic disorder in schizophrenia is accompanied by emotional-volitional negative manifestations characteristic of schizophrenia.
Dissociative stupor follows immediately after stress and manifests itself more clearly in the presence of strangers; in solitude it often disappears.
Depressive stupor is characterized by facial expressions of depression, answers in a quiet voice against the background of periodic mutism, dilated pupils, tachycardia. It also follows stress or at the height of depression, which can be identified in the anamnesis.
Treatment of catatonic disorder of organic nature
Treatment should take into account the therapy of the underlying disease, as well as the use of intravenous tranquilizers (Relanium, Sibazon). Frenolone and small doses of teralen are recommended. The use of antipsychotics should be extremely careful and in small doses.
What are the symptoms of catatonia?
Catatonia has many symptoms. In the DSM-5 reference book, which is used by psychiatrists all over the world, 12 main Catatonia are identified. But doctors add other symptoms to them:
- Remaining motionless (stupor).
- Long-term maintenance of the posture given to the body (catalepsy). If you plant or stand a person, he will not move.
- Prolonged silence (mutism). The person does not respond, even if addressed by name. On the contrary, he will most likely turn away.
- Changing the position of the limbs, like a plasticine figurine (wax flexibility). Some patients easily obey and can follow any command, like robots.
- Passive and strong resistance to any attempts to change the position of the arms and legs (negativism). Sometimes it is physically impossible to bend or straighten the limbs.
- Maintaining an awkward posture (posing). For example, a person can bend over on the bed without touching the pillow with his head, as if hanging in the air.
- Pretentiousness of movements (manneriness). Someone with catatonia may gesticulate strangely and inappropriately.
- Repetitive monotonous movement (stereotypy). Remember how in horror films the possessed constantly sway, tap their fingers, or move their mouths creepily. Most likely they are having an episode of catatonia.
- Excessive arousal without external stimuli. A person can rush around the room, show aggression, and rush at others.
- Involuntary movements of the lips and eyebrows. Grimaces that are not made to amuse others.
- Repeating someone else's words (echolalia). Moreover, speech often becomes incoherent, monotonous, words and phrases are spoken continuously, sometimes for a very long time.
- Copying other people's movements (echopraxia).
Additionally, symptoms may occur Neznanov N. G., Kuznetsov A. V. Clinical and psychopathological aspects of the pathomorphosis of catatonic disorders associated with disruption of the autonomic nervous system. With catatonia, the temperature rises, thirst increases, saliva flows, blood pressure rises and the pulse quickens. Patients often refuse water and food.
When a doctor makes a diagnosis, he looks for a combination of several signs. But medical attention is needed even if one symptom appears. Otherwise, you can miss not only catatonia, but also a stroke, the onset of schizophrenia, a complication of meningitis or another disease.
Classification
The types of catatonia differ depending on whether it is stupor or excitement.
Catatonic excitement has various forms:
• Pathetic excitement has the most striking symptom of increased speech and a very obvious increasing motor agitation. The speech of such individuals has a pathetic character, but often carries little semantic load. With this type of excitement in catatonia, there are elements of foolishness, as in hebephrenia. Exaltation can reach significant severity, along with impulsiveness.
• The second type of agitation is impulsive catatonia. This manifestation of a form of catatonia is more dangerous; it contains cruelty and a tendency towards excessive aggressive tendencies. This condition is highly harmful to the environment and to the individual himself. In addition, excitement is expressed through accelerated speech with elements of echolalic inclusions. Echolalia and echopraxia are manifested in movements and facial expressions. The activity that manifests itself in movements gradually develops into choreiform activity. The randomness of movements is very alarming to the environment, since it is not possible to predict the moment of danger. Silent excitement in catatonia is manifested by mutistic manifestations along with aggression, which unreasonably spills out onto the environment.
Stupor with catatonia also has several varieties:
• Negativistic stupor is manifested by passive resistance with silence and prolonged freezing. With this type of stupor there is a very high resistance to absolutely everything. But you can cheat, because if you forbid doing something, then the individual can do it. Often they are forbidden to eat so that they can eat at least a little.
• Cataleptic stupor is characterized by almost complete immobility with an absolute lack of contact. Disinhibition often occurs at night, while the patient is available for relatively productive contact.
• Stupor with the severity of numbness is the most elaborate in its manifestations, since the individual simply freezes in strange, specific poses.
Oneiric catatonia is a pathology that, in addition to classical catatonia, has manifestations of oneiroid. Oneiric catatonia is accompanied by hallucinations, in which the individual experiences scene-like, kaleidoscopic hallucinations. Oneiric catatonia is based on clouding of consciousness of the same type.
Lucid catatonia is considered a milder type compared to others. It proceeds against the background of preserved consciousness, which appears like “windows,” that is, in a flickering manner. Lucid catatonia has a less serious degree of pathology precisely because of clear or periodically clear consciousness.
How is catatonia treated?
If a person cannot move or does not respond to calls to him, an ambulance must be called. If the symptoms are mild, it is important to go to a therapist as soon as possible.
From the words of relatives or by analyzing a medical record, the doctor will determine whether there are mental illnesses, alcohol addiction or other pathologies that can cause catatonia. And if necessary, he will send you to a psychiatrist.
He will prescribe medication or electroconvulsive therapy as quickly as possible.
If there is no danger to the patient’s life, the Catatonia examination will help find the causes of catatonia:
- general blood analysis;
- biochemical research;
- analysis of blood electrolytes;
- liver function tests;
- or MRI of the brain.
An electroencephalogram will be performed if there is a suspicion of a brain tumor or seizures.
What medications are prescribed
To eliminate catatonia, the psychiatrist uses strong prescription medications. Taking them on your own is dangerous.
First of all, they give drugs Catatonia: pathophysiology, diagnosis and modern approaches to treatment from the group of second-generation anxiolytics based on benzodiazepine. They reduce muscle spasms, calm, and help remove the symptoms of catatonia. Benzodiazepines are effective Systematic review of catatonia treatment in 66–100% of patients.
If these drugs do not help, the treatment regimen is changed. Sometimes alternative drugs with sedative, anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects provide the best effect. For example, lithium drugs Catatonic syndrome: From detection to therapy will not allow a recurrence of an attack of catatonia.
Medicines from the group of neuroleptics are prescribed Catatonia: pathophysiology, diagnosis and modern approaches to treatment rarely: it is impossible to guess how the patient’s body will react. On the one hand, drugs can relieve muscle spasms. But at the same time, they can cause neuroleptic malignant syndrome. This is a condition when the temperature and blood pressure rise and the symptoms of catatonia intensify.
In what cases is electroconvulsive therapy used?
Electroconvulsive therapy is a treatment that uses electric current through the brain. It suppresses areas that emit abnormal impulses and helps relieve muscle spasms and cramps.
Is electroconvulsive therapy an evidence‑based treatment for catatonia? A systematic review and meta-analysis if benzodiazepines are ineffective or if the patient can Is electroconvulsive therapy an evidence-based treatment for catatonia? A systematic review and meta‑analysis to die.
Sometimes, after using electroconvulsive therapy, attacks of catatonia completely stop. But there is a risk. Is electroconvulsive therapy an evidence‑based treatment for catatonia? A systematic review and meta‑analysis of side effects: headache, amnesia, confusion.
Catatonic state: general description
The syndrome was first described at the end of the 19th century by the German psychiatrist K. Kahlbaum, and for a long time it was considered as a separate disease, and doctors noted that even despite intensive treatment, there is a high probability of an unfavorable, progressive course. At the beginning of the 20th century, catatonic disorders were described exclusively as one of the typical symptoms of schizophrenia, and only in the early 2000s was the connection of such a disorder not only with other mental, but also with somatic diseases established and proven.
What is “catatonia” in simple words? The pathology is accompanied by severe movement disorders from complete immobility to acute agitation. At the same time, patients do not react at all to speech addressed to them and aggressively perceive attempts to calm them down.
The pathogenetic mechanisms of the occurrence of catatonic symptoms are not completely known today. There are several hypotheses for its development:
- disturbances in the production and metabolism of neurotransmitters, mainly γ-aminobutyric acid, and to a lesser extent, dopamine;
- organic lesions of individual foci of the brain, in particular, the orbitofrontal cortex, basal ganglia;
- neuroendocrine changes caused by pheochromocytoma, thyrotoxicoma, hypoparathyroidism (however, endocrinopathies are only one of the provoking factors in the development of affective catatonic syndrome);
- an autoimmune inflammatory process affecting the central nervous system.
How successfully is catatonia treated?
The sooner catatonia is treated, the better for the patient. Quick help helps to avoid complications and save life.
But not everyone recovers. According to Catatonia statistics, 12–40% of patients are successfully cured. The prognosis is poor in children and adolescents with schizophrenia, as well as in older adults. They may require Catatonia ongoing psychiatric care.
If a person has long suffered from kidney failure, alcoholism, Parkinson’s disease or other pathology, then the disturbances in brain function are already chronic. Therefore, at any moment, catatonic syndrome can recur. Catatonic syndrome: From detection to therapy. In order not to be late with help, you need to remember the dangerous symptoms and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Treatment
Treatment of catatonic syndrome is a difficult process, this is due to the polyetiological origin of the pathological process, as well as the fact that it can be provoked by certain types of substances. Often, for this disorder, drugs of the benzodiazepine group are used, in particular Lorazepam, Phenazepam, Nozepam, Gidazepas, Dorozepam. Severe forms of catatonic syndrome are indicative of ECT, and the voltage of the effect is correctly selected with the help of a good specialist. The procedure itself, if done correctly, is not very traumatic, but can produce remission for a long time.
A gentle approach is important with antipsychotic drugs due to the possible worsening of catatonic symptoms. In addition, the disorder has a tendency to worsen if it is not treated correctly. The neuroleptic, which was developed for catatonic symptoms, Mazeptil, has an excellent effect, but is difficult to obtain in pharmacy production.
Patients with catatonic syndrome are more prone to neuroleptic syndrome due to the presence of organic lesions in the brain; this pathology is deadly. That is why it makes sense for such individuals to prescribe all dosages at the lowest possible dose. Neuroleptics are indicated for treatment-resistant catatonic syndrome: Soleron, Adagio, Rispaxol, Eglonil, Olanzapine.
Effective in some forms of disorder, especially in the presence of affective inclusions - mood stabilizers. These include: Carbamazepine, Lithium carbonate, Lamotrigine, Lithium salt, Valprocom. In some cases, sleeping pills are used: Zolpidem, Zolpiclone. Often, especially in combination with dementia, it is important to use NMDA receptor antagonists: Memox, Mema, Memantine, Amantadine.
For the correct application of therapeutic approaches, it is important to exclude the presence of concomitant neurological and even somatic disorders, which can significantly affect the course of the disease. Often, with the stuporous form of the disease, intensive care observation is necessary, since due to negativism and immobilization, the patient does not feed on his own and may die from hunger and disease
Often, even tube feeding is not enough and resuscitators switch to parenteral administration of all necessary fluids and nutrients.
For malignant neuroleptic syndrome, which masquerades as catatonic syndrome, muscle relaxants are used, for example, Sodium Datrolene. Dopamine agonists are also relevant: Bromocriptine.
How to avoid getting catatonia
Scientists have not yet learned how to prevent catatonia, like other mental illnesses or brain tumors. But, taking into account the causes of the syndrome, we can advise the following:
- Reduce alcohol consumption, and if you have symptoms of addiction, get treatment.
- Never use drugs.
- Don't ignore symptoms of depression.
- Do not take sleeping pills, sedatives, or antipsychotics without a specialist’s prescription. Catatonia: pathophysiology, diagnosis and modern approaches to treatment.
- See a doctor if you have headaches, dizziness, or spots in your eyes.
- Treat kidney and liver diseases in a timely manner.
- Avoid casual sex to protect yourself from HIV and syphilis.
- Monitor your weight and avoid stress so as not to worsen the condition of your blood vessels.
- Pregnant women should register on time and follow the doctor’s recommendations so that the birth goes smoothly.
- Try not to injure your head.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Catatonia often develops together with a mental illness such as schizophrenia.
However, most often catatonia, also called “stress psychosis,” is caused by organic brain lesions, such as tumors. Also, the disease often develops together with organic, intoxication, infectious, somatic, withdrawal, and other psychoses. The disease is present in a large number of patients with autism and occurs after traumatic brain injury, epilepsy, severe infectious diseases, a number of cases of drug addiction, as well as when taking psychoactive substances.
Motor signs of catatonia, according to experts, are caused by a deficiency of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Also, many experts believe that the development of symptoms may be associated with dopamine blockade.
Diagnosis of catatonic syndrome
All patients with suspected catatonia should undergo EEG testing as a screening for other neurological conditions. It tends to exhibit epileptiform activity in nonconvulsive status epilepsy and slowing in cases of encephalopathy.
The EEG in catatonia is usually normal unless there is an underlying condition that may be causing the abnormality.
Given that catatonia can develop in the context of a wide range of neurological conditions, brain imaging, preferably MRI, is recommended. In cases of catatonic stupor, immobility usually allows these tests to be carried out easily.
Laboratory studies should include a complete blood count, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, muscle and liver enzymes, thyroid function tests, electrolytes, blood glucose, and urinalysis to evaluate associated conditions, causes, or complications of catatonia.
Marked dehydration is not uncommon in catatonic patients and should be addressed.
Vital signs should be assessed frequently because hypertension and fever (often accompanied by elevated creatine phosphokinase, decreased serum iron, and leukocytosis) may herald the occurrence of malignant catatonia or neuroleptic malignant syndrome if the patient has been receiving antipsychotic medications.
Unfortunately, the nature of catatonia makes certain aspects of physical and neurological examination impossible. Components of the neurological examination that can typically be assessed include pupillary response, eye movements, corneal reflex, response to pain, presence of drooling, immediate response to threat, response to light or sound, tendon reflexes, and plantar response.
Symptoms and manifestations of catatonic syndrome
According to the DSM-5, at least three of the twelve symptoms must be present to diagnose catatonia. These include the following signs:
- Catalepsy: passive induction of postures held against gravity.
- Waxy flexibility: characterized by the patient freezing for a long time in the position he has adopted or given to him, even if it is very uncomfortable.
- Stupor: lack of psychomotor activity and reaction to the environment.
- Agitation: does not depend on external stimuli.
- Grimacing: distortion of facial expression.
- Mutism: complete silence of the patient or minimal verbal response.
- Negativism: the patient's resistance or non-response to external stimuli, such as instructions.
- Posturing: spontaneously and actively holding a pose or position that goes against the force of gravity.
- Mannerism: extreme or strange caricatures of various actions and movements, spontaneous movements.
- Stereotypy: frequent, repetitive movements for no reason.
- Echolalia: frequent repetition of other people's words.
- Echopraxia: imitation of other people's movements.
- Proboscis sign: contraction of the muscles around the mouth, which consists of
- the lips are constantly extended forward with the jaws tightly clenched. Characteristic of catatonic stupor with numbness.
- Babinski's sign: extensor reflex of the big toe.
Other common symptoms include rigidity (lack of response or resistance to stimuli) or automatic obedience. If catatonia is associated with schizophrenia, the stupor may continue for a long period of time. This is in contrast to catatonia associated with other psychiatric conditions, where there may be long-term remissions.