- What does a brain CT scan show?
- CT with contrast
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Preparing for the examination
- How is the procedure performed?
- Decoding the results
- Is the examination safe?
- How often can you do it
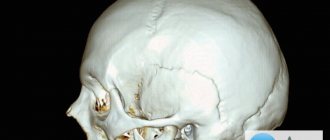
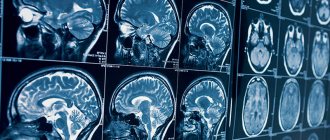
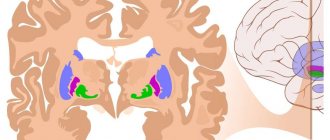
CT scan of the brain is a high-tech, informative examination method that allows you to obtain detailed and clear images of the structures of the brain, blood vessels, nerves, bones of the cranial vault, and soft tissues of the head.
Computed tomography allows you to obtain black and white images, which are layer-by-layer sections of the brain and its surrounding structures. The thickness of the sections can be about 1 mm. This makes it possible to detect even small tumors and other pathological changes that occur in the brain at the earliest stages of the development of the disease.
What does a brain CT scan show?
The images can reveal signs of the following pathological processes::
- cerebral edema of varying severity;
- displacement of brain structures such as ventricles, etc.;
- hemorrhages in the brain tissue, even minimal in size;
- hematomas of various locations: epidural (located between the bones of the skull and the dura mater), and subdural (located between the dura and arachnoid membranes);
- brain cysts;
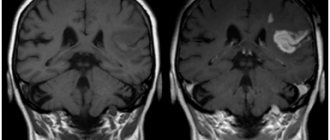
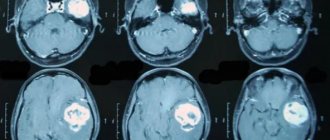
- tumors of the brain and meninges;
- inflammatory processes: arachnoiditis, encephalitis, abscess, pus between the meninges.
Modern computed tomographs have special modes that allow you to examine the vessels of the problem area of the body and build a three-dimensional color image of the arteries and veins. This examination is called CT angiography of the brain.
CT angiography allows you to examine the condition of vessels with a diameter of more than 1 mm and identify pathological changes in the blood supply to the brain:
- protrusions of vessel walls (aneurysms);
- malformations (congenital abnormalities of vascular development);
- atherosclerotic changes in the walls of blood vessels;
- thrombosed and embolized areas of blood vessels;
- narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels;
- kinks of blood vessels;
- proliferation of blood vessels by a tumor.
A CT scan of the brain and cerebral vessels can be performed in one clinic visit, but this will be two studies in one.
Other ways to examine the head
MRI
MRI of the head
– the main alternative to computed tomography. The magnetic resonance scanning method allows a better assessment of the chemical composition of the tissues of the brain and skull bones. If the task is to study in detail the physical state of the head and brain, it is better to conduct a CT scan. MRI, unlike CT, is a safe procedure, during which there is no negative effect on the patient’s body.
Radiovisiography
This type of study, such as radiovisiography, is used only to identify pathologies or dysfunctions of the patient’s dental system. It will report in detail on the condition and structure of the teeth, but will not show the condition of the brain or skull bones.
X-ray
Radiography today is also used to diagnose the condition of the head and brain. Most often it is prescribed if we are not talking about a complex oncological disease of the brain, hydrocephalus or stroke. X-rays are prescribed, for example, if you need to visualize minor injuries to the skull, the level of its deformation, detect foreign bodies and estimate their size. X-ray can be called the primary diagnostic procedure, after which a CT or MRI is prescribed for a more detailed study.
Computed tomography of the brain with contrast
Native (performed without contrast) CT scan of the brain allows one to obtain informative images of bones, as well as hematomas and areas of hemorrhage. Neoplasms, blood vessels, and soft tissues of the head will not be visible on native images. To increase the information content of the examination, special contrast agents based on iodine are used, which “stain” individual anatomical structures and tissues valuable for diagnosis.
For contrast-enhanced computed tomography, contrast is administered intravenously immediately before the study begins or as a bolus throughout the scan. For bolus administration of contrast, a special device is used - an injector, which delivers the drug into the blood at a constant speed.
CT scan of brain vessels is performed only with contrast.
Cost difference
These types of scanning are comparable in price.
| Service | Price | Discounts | Phone number for appointment |
| CT scan of the brain | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of cerebral vessels | from 4400 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT tear ducts | from 2800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the larynx | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the nose | from 2600 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT ear | from 2100 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the thyroid gland | from 2800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the skull | from 2900 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of neck vessels | from 4400 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| Service | Price | Discounts | Phone number for appointment |
| CT scan of one part of the spine (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT joint (knee, elbow, shoulder, hip, ankle, wrist) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the jaw joint | from 1300 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of ribs | from 4200 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the hand | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the foot | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the pelvis | from 2500 rub. | 372-65-26 | |
| CT scan of the bones of the hip, face, leg | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| Service | Price | Discounts | Phone number for appointment |
| CT scan of the throat and larynx | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the heart and coronary vessels | from 9900 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the lungs and mediastinal organs | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the retroperitoneum (kidneys and adrenal glands, urinary tract, soft tissues and lymph nodes) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the abdomen (liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the pelvis in men (prostate, bladder, ureters, rectum) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the pelvis in women (uterus, vagina and appendages, ovaries, bladder, ureters, rectum) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT colonoscopy | from 4000 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT virtual bronchoscopy | from 4500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the urinary system (kidneys, bladder, urinary tract) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT pancreas | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the pelvis and abdomen | from 4400 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT urography | from 4400 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the mammary glands | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT soft tissue (one area) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT soft tissue of the neck | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| Service | Price | Discounts | Phone number for appointment |
| CT angiography of cerebral vessels | from 4500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of neck vessels | from 4500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the thoracic aorta | from 5800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the abdominal aorta | from 5800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of limb vessels | from 9800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the coronary vessels of the heart | from 9500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the pulmonary arteries | from 4500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the renal arteries | from 5800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the pelvic arteries | from 5800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the iliac artery | from 5800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the brain | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of cerebral vessels (arteries) | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland (without contrast) | 3500 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast | from 7500 rub. | from 6990 rub. | |
| MRI of the brain and pituitary gland | 6800 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the brain and cerebral vessels | 6600 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the paranasal sinuses | 2900 rub. | 2690 rub. 2100 rub. in the Armed Forces | 2990 rub. 2100 rub. in the Armed Forces |
| MRI of the central nervous system (MRI of the brain, MRI of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral region) | 13200 rub. | 9590 rub. | 10790 rub. |
| Contrast administration (based on patient weight) | from 3000 to 5000 rub. | only during the daytime | from 3000 to 5000 rub. |
| Recording an MRI examination on film | 500 rub. | 450 rub. | 450 rub. |
| Duplicate photo | 800 rub. | 800 rub. | 800 rub. |
| Duplicate description of MRI study | 300 rub. | 300 rub. | 300 rub. |
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| Shoulder MRI | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| MRI of the elbow joint | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| MRI of the knee joint | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| MRI of the ankle | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| MRI of the hip joints | 5000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| Appointment with an orthopedist | 1800 rub. | free after MRI | free after MRI |
| First aid program for joints (8 studies + appointment with an orthopedist + MRI of the joint) | 13000 rub. | 7500 rub. | 7500 rub. |
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the cervical spine or cervical vessels | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the thoracic spine | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the lumbosacral spine | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the craniovertebral junction | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the sacroiliac joints | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| MRI of the coccyx | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of two parts of the spine | 6600 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of three parts of the spine | 9900 rub. | 6900 rub. | 7900 rub. |
| MRI of the central nervous system (MRI of the brain, MRI of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral region) | 13200 rub. | 9590 rub. | 10890 rub. |
| Appointment with a neurologist | 1800 rub. | free after MRI | free after MRI |
| Comprehensive body diagnostics (MRI of the thoracic spine, MRI of the lumbar spine, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the bladder, consultation with a neurologist, consultation with a therapist) | 11700 rub. | 7000 rub. |
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of cerebral vessels (MR angiography) | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of neck vessels (MR angiography of the neck) | 3500 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the brain and cerebral vessels | 6800 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| Comprehensive examination of the vessels of the brain and neck | 6600 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MR arteriography | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
Indications for CT scan of the brain
You can get a referral from your doctor for an examination in the following cases::
- head injury;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- violation of higher brain functions such as speech, memory;
- convulsions;
- fainting;
- neurological signs of damage to parts of the brain if symptoms appeared for the first time or began to progress over time.
Indications for CT angiography of cerebral vessels:
- suspicion of the presence of congenital vascular anomalies (malformations);
- syndrome of compression of blood vessels by a space-occupying formation (tumor);
- proliferation of blood vessels by a cancerous tumor.
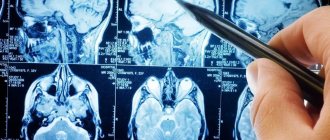
Interpretation of CT images
After completing the procedure, the radiologist receives the images immediately, and it may take him about 30-40 minutes to interpret them. The specialist compares the structures of the brain in different parts of the brain, assesses the size of the brain, identifies pathological areas and their exact location. A CT scan can also help identify fluid accumulation in certain areas of the brain. When a tumor is detected, the radiologist assesses its size. This can be done by direct signs of head tomography, such as darkening in the images, or indirect signs, for example, general cerebral edema. After deciphering the results, the images are given to the patient. He is also given recommendations on which specialist should continue examination or begin treatment: surgeon, oncologist, neurologist, dentist, and so on.
Contraindications for computed tomography of the brain
Absolute contraindications include:
- pregnancy at any stage;
- patient weight over 120 kg.
Relative contraindications:
- age up to 12 years;
- allergy to drugs containing iodine;
- feeding the baby with breast milk;
- chronic renal failure;
- multiple myeloma.
If the examination is planned to be carried out using a contrast agent, then the:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- insufficiency of kidney and liver function;
- intolerance to iodine-based drugs.
When is a brain CT scan prescribed?
Computer scanning in native mode is carried out when:
- head injuries;
- dental research;
- acute cerebrovascular accidents;
- lesions that cause the patient to lose consciousness;
- convulsive syndrome.
A diagnostic examination using computer equipment with the introduction of a contrast component, called angiography, is necessary for:
- clarification of the area of stenosis;
- study of aneurysms;
- the likelihood of developing an ischemic stroke;
- analysis of vascular patency.
How to do a CT scan of the brain
The patient is placed on the moving table of the CT scanner in the supine position. The head is fixed with a special pillow and a belt so that the patient remains completely still during the examination. The clarity and information content of the resulting images depends on this.
A contrast agent can be administered before the examination begins or after native images are taken. If a bolus injection of the drug is planned, a special catheter is inserted into the patient’s vein, to which a thin tube from the injector is connected.
The machine table together with the patient is moved inside the tomograph and the examination begins.
The best examination results are obtained by spiral computed tomography of the brain, when the scanner continuously moves around the human body. One revolution of the scanner produces one image of a tissue section of the area under study.
When the examination is completed, the doctor checks the quality of the images obtained. If all the images are clear and detailed, then the table along with the patient is pulled out of the tomograph capsule, and the patient is allowed to stand up.
To make our explanation more clear, we have prepared a video about what a CT scan of the brain shows.
Pros of CT
Screening tomography has special advantages in comparison with other brain diagnostic methods. The main advantages are:
- non-invasiveness - the procedure is painless due to the absence of the need to use surgical or other medical instruments (the patient’s discomfort can arise exclusively when using a contrast reagent and only when it is administered intravenously through a catheter);
- high accuracy of data - layer-by-layer examination of the head helps to identify changes in the structure of its parts in the early stages of development, and the use of an additional amplifier further increases the information content;
- speed - the study takes place as quickly as possible, since it usually lasts about 60 minutes (after an hour the patient receives the results);
- minimal radiation exposure - the dosage of X-rays with CT is much lower than with radiography, so the study is allowed to be performed more often
Additional advantages of diagnostic tomography:
- the ability to obtain information about bones and soft structures simultaneously;
- reducing the amount of contrast agent, which reduces the risk of complications;
- allowed for patients with metal implants in the body, which is mainly a contraindication to MRI.
Another advantage of the technique is the possibility of conducting diagnostics for people who are afraid of being in confined spaces. To do this, they use open-type devices that do not close completely, which allows the patient to feel comfortable throughout the entire examination period. The disadvantages include the inability to conduct research during pregnancy, preparation for the procedure with contrast, as well as exposure to radiation on the body, albeit in a minimal amount.
Is a CT scan of the brain harmful?
CT scanners use X-rays to obtain images of tissue slices on the patient's body. The radiation dose that the patient receives during the examination is 1.4±0.4 mSv. For comparison, the permissible annual radiation exposure from background radiation is 3-4 mSv. One such examination will not cause harm to the patient. But one should take into account the fact that performing several such procedures in a short time can lead to radiation sickness. In this regard, for computed tomography, restrictions have been introduced on the volume of one examination and the frequency of procedures.
Diagnostic advantages and disadvantages of brain MRI
The strength of MRI is the fact that the magnetic resonance imaging scanner is able to record even the most minor changes in soft tissue, so it has better sensitivity:
- to differentiate gray and white matter of the brain;
- for studying the cerebellum, posterior fossa and temporal lobes;
- to record the consequences of vascular lesions of the brain, such as thrombosis, embolism, even if they are small;
- differential diagnosis of tumor formations;
- detection of a cyst, hematoma or ischemic tissue damage;
- for pathological disorders caused by diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and senile dementia.
Magnetic resonance diagnostics is prescribed if it is necessary to find out the cause:
- frequent fainting and dizziness;
- frequently recurring severe headaches;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- progressive loss of vision and hearing;
- to conduct preoperative diagnostics and ensure high-quality monitoring of the effectiveness of treatment measures.
Pros of MRI
The advantages of MRI are:
- high information content and accuracy of results;
- absolute safety for health, since the doctor does not use X-rays;
- when using MRI of the brain with contrast, a hypoallergenic substance is used, which almost never causes a negative reaction in the patient;
- no complications;
- the opportunity to conduct a full examination even for pregnant women without fear of harming the fetus;
- the earliest possible diagnosis of diseases even at the stage of absence of symptoms characteristic of the pathology.
It should be noted that today there is an extremely limited list of brain pathologies that cannot be determined using magnetic resonance. MRI is the gold standard in medicine for a comprehensive examination of the brain.
Previous NextCons of MRI
The disadvantages of the study include the peculiarities of the interaction of the magnetic field with metal objects and electronic devices, which excludes access to MRI in patients:
- with artificial heart valves and stimulators;
- working insulin pumps;
- surgical staples, pins, prostheses;
- any metal objects that can move under the influence of a powerful magnetic field.
The accuracy of the resulting images may be compromised for those with tattoos made with metal-containing inks.
In most cases, dentures, braces and crowns will not cause interference (artifacts) on MRI images. The small closed space of the magnetic resonance imaging scanner, the duration of the diagnosis, the need to remain still and the presence of loud sounds can be an obstacle to the examination of patients suffering from claustrophobia and people with nervous and mental disorders. Sign up for diagnostics
If in doubt, sign up for a free consultation or consult by phone
+7
Where to get a head CT scan?
On our search service you will find a detailed list of diagnostic institutions. We present only verified data about each clinic in the city. To select a medical center you must:
- Select an organization using the search system by districts and metro stops.
- Study the information about each clinic presented on the service.
- Contact a call center representative.
To make an appointment for a tomography, call the hotline. Resource managers work every day. With them you will get a free consultation, find out where is the closest place to get a CT scan and book a place with a radiologist with a bonus of up to 1,000 rubles.
Which is better to choose: CT or MRI of the brain?
As a result of the high risks associated with CT scanning, patients are interested in what can replace tomography. MRI is considered one of the alternative options. Magnetic testing is one of the safest tests in medicine today. It works by generating a magnetic field and radio waves, which is harmless to the body.
The sensors built into the device easily capture the patient’s body responses to these forces and transmit the data to the PC. On a computer, information is processed and formed into three-dimensional images. However, MRI is usually used to check soft tissue, but dense areas are less clearly visible on the images. Because of this, the technology is not used in skeletal diagnostics.
MRI screening is necessary for the study of cerebral tumors, ischemic lesions, inflammation and degenerative diseases. The results help in identifying the consequences of injuries, strokes, and infectious reactions. CT and MRI are two complementary methods. Each study has special specifics and is prescribed in certain cases. Often, doctors prescribe two procedures to patients at once to get a clear picture of the disease.
How should you prepare for a CT scan?
The study is carried out only on an empty stomach. A few hours before the session, the patient needs to drink approximately 2 liters of plain water. Before starting the tomography, notify the radiologist about the presence of chronic diseases, medications used, as well as allergic reactions and other characteristics of the body.
Before entering the diagnostic room, you need to put jewelry, electronic devices and other items that may impede the operation of the device into the storage room. It is important to bring your creatinine and TSH test results with you to your appointment if you are scheduled to have a contrast agent test.
What are the contraindications to CT?
Most patients tolerate the study well and particularly appreciate its painlessness. However, brain CT has limitations. The following conditions have been added to this category:
- Carrying a child. Screening is not carried out to prevent the development of pathologies in the fetus after receiving a dose of radiation.
- Patient obesity. If a person weighs more than 200 kg, tomography is not performed for technical reasons - the patient simply cannot fit into the scanner.
- Mental disorders. These diseases are accompanied by inappropriate behavior of the patient, which causes difficulties in diagnosis.
- Allergy to contrast. Individual intolerance to the dye leads to refusal of testing with an additional enhancer and the appointment of an alternative diagnostic method.
- Kidney or liver failure. CT with contrast is contraindicated, since drug removal requires stable operation of the excretory system, which is not important for such diseases.
CT diagnostic services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| MSCT angiography of cerebral arteries | 12 000 |
| MSCT of the pituitary gland | 6 000 |
| MSCT of the skull bones with three-dimensional reconstructions | 8 000 |
| MSCT of the skull bones | 6 500 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions