How the study is performed
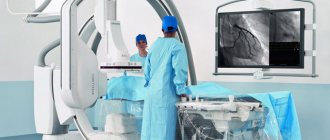
Cerebral angiography is performed in the operating room of the cath lab department. The patient's head is gently fixed to the table with a special tape passing through the frontal area. This is necessary to eliminate head movements during the examination and obtain a high-quality “unblurred” image.
In the department, before transportation to the operating room, premedication is carried out using a mild sedative and an antiallergic drug.
The puncture site in the area of the femoral artery through which the examination is carried out must first be shaved the day before and treated with an antiseptic in the operating room. The examination is performed under local anesthesia. Through a small incision with a diameter of 2.0-3.0 mm, a catheter is inserted into the mouth of the arteries of the brain, through which contrast is injected, and the image is recorded on a computer. If there is pathology of the cerebral vessels, this will be reflected in the resulting image. After completion of the study, a pressure aseptic bandage is applied to the puncture site. For 12 hours after the examination, it is necessary to remain in bed in a position with the lower limb extended on the side where the intervention was performed. After completing the study, it is recommended to drink at least 0.5-0.7 liters of clean water to ensure rapid removal of the contrast from the body.
Angiography of cerebral arteries
Angiography of the arteries of the brain (cerebral angiography) is a study in which a special substance containing iodine (contrast) is introduced into the lumen of the arteries of the brain through a thin, flexible and long tube (catheter), and an image of the vessels of the brain is obtained using X-rays.
How the study is performed
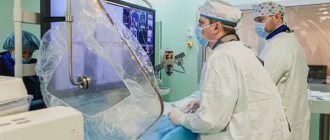
Cerebral angiography is performed in the operating room of the cath lab department. The patient's head is gently fixed to the table with a special tape passing through the frontal area. This is necessary to eliminate head movements during the examination and obtain a high-quality “unblurred” image.
In the department, before transportation to the operating room, premedication is carried out using a mild sedative and an antiallergic drug.
The puncture site in the area of the femoral artery through which the examination is carried out must first be shaved the day before and treated with an antiseptic in the operating room. The examination is performed under local anesthesia. Through a small incision with a diameter of 2.0-3.0 mm, a catheter is inserted into the mouth of the arteries of the brain, through which contrast is injected, and the image is recorded on a computer. If there is pathology of the cerebral vessels, this will be reflected in the resulting image. After completion of the study, a pressure aseptic bandage is applied to the puncture site. For 12 hours after the examination, it is necessary to remain in bed in a position with the lower limb extended on the side where the intervention was performed. After completing the study, it is recommended to drink at least 0.5-0.7 liters of clean water to ensure rapid removal of the contrast from the body.
How to prepare for the test
Before the study, be sure to inform your doctor about the presence of:
- allergies to strawberries, shellfish, seafood or iodine-containing substances;
- history of bleeding of unknown origin;
- an allergic reaction to a contrast agent in the past;
- pregnancy.
Before the study, it is necessary to exclude food and liquid intake for 4-8 hours. Before the examination, you need to remove all jewelry, decorations and costume jewelry to prevent their contours from interfering with the resulting image.
How will you feel during the study?
When contrast is administered, you may feel a short-term burning sensation in the groin, heat in the face and head. After the examination, small hematomas (hemorrhages) may remain in the area of the puncture site, which resolve within a few days.
Why is the research being done?
Cerebral angiography is used to detect or exclude pathologies of the blood vessels of the brain, such as:
- abnormal blood vessels (vascular malformation);
- aneurysms;
- narrowing of the arteries of the brain;
- vasculitis.
The study is also used for:
— confirmation of the presence and location of a brain tumor;
— assessment of the artery of the head and neck before surgery;
- determining the presence of blood clots in the vessels of the brain, which can cause a stroke.
In some cases, this procedure is used to clarify the diagnosis after abnormalities have been identified according to MRI or CT. Contrast that extends beyond the outline of a blood vessel may be a sign of internal bleeding. Narrowing of the arteries may indicate cholesterol deposits, spasms, or hereditary diseases. Abnormally developed blood arteries may be associated with brain tumors, intracranial bleeding, aneurysm (bulging of the artery wall), or arteriovenous malignancy.
Cerebral angiography is also performed to prepare for x-ray surgery to eliminate malformation, aneurysm or thrombosis of cerebral vessels.
Possible complications:
- development of an allergic reaction to the contrast agent;
- subcutaneous hemorrhage (hematoma) at the puncture site;
- damage to the artery or artery wall.
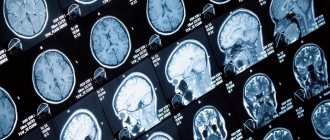
| Angiography of cerebral arteries (normal) | Pathological formation in the parietal region on the right (arteriovenous malformation) |
How to prepare for the test
Before the study, be sure to inform your doctor about the presence of:
- allergies to strawberries, shellfish, seafood or iodine-containing substances;
- history of bleeding of unknown origin;
- an allergic reaction to a contrast agent in the past;
- pregnancy.
Before the study, it is necessary to exclude food and liquid intake for 4-8 hours. Before the examination, you need to remove all jewelry, decorations and costume jewelry to prevent their contours from interfering with the resulting image.
What are the limitations and contraindications for MR angiography?
Despite a number of advantages, Magnetic resonance angiography has some contraindications, such as:
- claustrophobia
- mental disorders with the inability to remain in a lying position for a long time at rest
- pregnancy
- the presence of metal prostheses (implants) in the patient’s body (for example, artificial heart valves, joints, pacemakers)
- performing artificial ventilation of the lungs
A significant disadvantage of the study is its long duration, ranging from 40 to 90 minutes.
Why is the research being done?
Cerebral angiography is used to detect or exclude pathologies of the blood vessels of the brain, such as:
- abnormal blood vessels (vascular malformation);
- aneurysms;
- narrowing of the arteries of the brain;
- vasculitis;
The study is also used for:
- confirmation of the presence and location of a brain tumor;
- assessment of the head and neck artery before surgery;
- determining the presence of blood clots in the vessels of the brain, which may cause a stroke.
In some cases, this procedure is used to clarify the diagnosis after abnormalities have been identified according to MRI or CT. Contrast that extends beyond the outline of a blood vessel may be a sign of internal bleeding. Narrowing of the arteries may indicate cholesterol deposits, spasms, or hereditary diseases. Abnormally developed blood arteries may be associated with brain tumors, intracranial bleeding, aneurysm (bulging of the artery wall), or arteriovenous malignancy.
Cerebral angiography is also performed to prepare for x-ray surgery to eliminate malformation, aneurysm or thrombosis of cerebral vessels.
In what cases can vascular MR angiography be used?
A doctor may recommend MR angiography as a diagnostic procedure for the following diseases and conditions:
- Obliterating atherosclerosis and endarteritis of the vessels of the lower extremities (narrowing and blockage of the arteries of the lower extremities)
- Atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries (narrowing and blockage of the carotid, vertebral and subclavian arteries, brachiocephalic trunk)
- Diseases that affect the arteries of internal organs, including the kidneys and intestines.
- Aneurysm is a pathological dilation of a vessel, for example, the abdominal aorta.
- Aortic dissection (dissection)
- Arterial thrombosis and embolism - an acute violation of the patency of the arteries, as a result of their sudden blockage by blood clots
- Extravasal compression syndrome (external compression) of the vessel
- Control of the performed surgical intervention
Contraindications for diagnostics
Angiography using a tomograph is performed according to indications at any age.
Unfortunately, some diseases may be contraindications for MRA diagnostic procedures. This type of diagnosis cannot be performed :
- in the presence of infectious or inflammatory diseases;
- in acute periods of mental illness;
- with existing heart failure;
- in case of allergy to iodine and iodine-containing drugs (when conducting a study using a contrast agent);
- with decompensated liver or kidney failure;
- if the patient’s body contains implants made of metal alloys, spoke-shaped structures for osteosynthesis, metal dentures;
- with an implanted pacemaker or insulin pump;
- in case of blood clotting disorders;
- in patients weighing more than 150 kg;
- during pregnancy and lactation.
It should be noted that structures made of titanium, copper, and ceramics located on the body (or inside it) are not contraindications to the procedure. All other metals (or alloys of them) under the influence of a magnetic field can move and cause damage to tissues and organs. If the patient has a fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia), the examination is performed under general anesthesia.
Operating principle of an MRI machine
The essence of the operation of the resonant device used for MRI of the neck and other parts of the human body is to produce electromagnetic waves during the procedure. After entering the body, they collide with hydrogen atoms, where they are activated. As a result, a resonance occurs between the chemical element and the radiation. After the process is completed, hydrogen returns to its original state. The received data is transferred to a special computer, which is connected to the device. On the screen, specialists can see a detailed image and characteristics of various pathologies inside that cannot be noticed during a routine examination or using other diagnostic methods. At the end of the appointment, the patient receives several images printed on wide-format film or the results are recorded on a removable drive. Using pictures of the required area, the doctor can identify the level of progression of the disease and the clear location of the inflammatory process.
The search service “Unified Recording Center” offers its professional services for individual selection of the most suitable option for undergoing MRI testing of the neck and other areas. With our help, you can find out: information about the nearest clinics specializing in such tests, the cost of the procedure, the number of available places for the current and upcoming ones, as well as many other useful information. In addition, using our search system, you can independently make an appointment with any specialist you like. To do this, you will need to enter some information and wait a couple of seconds, the system itself will select acceptable options for you. If you have any additional questions or difficulties, please contact our operators at the hotline number, which you will find at the top of the site.
3. Risks of analysis and what can affect the result?
Risks of angiography of the brain and neck vessels
After the dye is injected, you may feel nauseous and nervous. These symptoms go away quickly. Some people are allergic to the dye. Tell your doctor if you experience dizziness, nausea, or itching after the dye is injected.
The dye can worsen the condition of the kidneys if they are sick. The dye may also cause fetal harm in pregnant women. Consult your doctor before the procedure.
What can affect angiography?
Pregnancy, curvature of blood vessels as a result of atherosclerosis or with age, and the inability to remain in a quiet position may interfere with angiography.