Today, ultrasound diagnostics is rightfully considered one of the safest and most informative. It is applicable in various fields of medicine, and is also used to determine abnormalities in the vascular system. If there is a need to study blood vessels, TCDG is used, which stands for transcranial Dopplerography of cerebral vessels.
Transcranial Dopplerography of cerebral vessels: what is it?
TCD is based on ultrasonic waves and the Doppler effect. Ultrasound waves are reflected from moving red blood cells and vessel walls, and with the help of a special sensor and software, the pulses are converted into an image that is displayed on a computer screen.
TCD of cerebral vessels will determine the condition of the main arteries, which are responsible for supplying the brain with oxygen, as well as other large arteries and vessels. Thanks to this, it will be possible to assess the condition of the vessels and determine the speed and intensity of blood flow in them.
What does the study reveal?
Transcranial Dopplerography of cerebral vessels provides reliable data on the state of blood vessels and blood flow and allows for a correct diagnosis.
Ultrasound ultrasound helps to identify:
- vasospasms and increased intracranial pressure, which cause headaches;
- cervical artery stenosis;
- thrombus formation;
- pathological tortuosity of the vessel;
- deviations in the condition of the vertebral arteries;
- deviations in the venous blood flow of vessels in the head and neck, etc.
Transcranial Doppler ultrasound of an infant is performed to analyze the condition of blood vessels and prescribe timely treatment if the child was born prematurely and has low weight, developmental defects, cerebral hernia, brain pathologies detected during pregnancy, intrauterine infections, etc. Most often, instead, at an early age, when the bones of the skull are still quite thin and there is a fontanel, neurosonography is performed.
Older children are prescribed the procedure if they experience headaches and dizziness, moodiness, restlessness, fatigue, poor sleep, or the presence of diseases that directly affect the quality of cerebral circulation (diabetes mellitus, vasculitis, arterial hypertension.
Indications for transcranial Doppler ultrasound
There are many reasons why you may need to undergo Doppler ultrasound. Transcranial Dopplerography of cerebral vessels
may show a large number of deviations from the norm.
Vascular malformation
It is a congenital disease that affects the development of the vascular system. Manifests itself in the form of plexuses of abnormal vessels of various sizes. It is dangerous because it can cause subarachnoid hemorrhage of a non-traumatic nature. Among other things, steal syndrome may develop, and malformations may begin to compress the brain tissue.
Cerebral circulatory disorders
TCD is used quite often to examine cerebral vessels. It may be necessary to identify the cause of problems with cerebral circulation. They may consist of the formation of blood clots, loops and kinks in blood vessels. Often the cause is: the formation of narrowings, aneurysms or embolism.
Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the neck and head
It consists of damage to areas of blood vessels by atherosclerotic plaques, which either significantly narrow the lumen of the vessel or clog it completely. In advanced cases, treatment is performed surgically. TCD is used to examine vessels because it allows one to determine not only the presence of plaques, but also their size and location.
Encephalopathy
Occurs in chronic cerebral vascular diseases that slowly progress. This disease combines cognitive impairment, disruptions in the emotional and motor spheres.
Decoding the research results
Transcranial Doppler ultrasound helps to identify many organic or functional disorders:
- thrombosis of various etiologies;
- stenosis;
- vasculitis;
- aneurysms;
- signs of hypertensive or atherosclerotic angiopathy;
- congenital vascular pathologies;
- vasospasms of various nature;
- signs of venous stagnation.
Thrombosis and embolism are characterized by partial or complete blocking of the lumen of the vessel. Moreover, the lower the degree of residual blood flow, the more pronounced the clinical manifestations. In this case, ultrasound reveals a formation of varying echogenicity, often without clear contours, located in the lumen of the vessel. Above the site of thrombosis, signs of ischemia of varying severity are observed. Also, the presence of an obstruction to blood flow explains the occurrence of turbulent blood movement.
Stenosis is most often a consequence of past inflammatory processes. The study reveals a concentric narrowing of the lumen of the vessel. The thickness of the vascular wall in this place is increased.
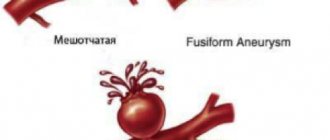
Aneurysms are visualized as a sac-like deformation of the vessel. Their shape may be different. The walls of the aneurysmal sac are much thinner than the walls of a healthy vessel.
The most common congenital pathologies are:
- arterial or arteriovenous aneurysms;
- arteriosinus anastomosis;
- arteriovenous malformations or shunts.
These pathologies are life-threatening, since, in addition to affecting hemodynamics (speed, nature of blood flow), they can lead to the development of hemorrhages and death. The study reveals pathological communications between arteries and veins, increased pressure in various parts of the vascular system, and the presence of turbulent blood flow.
Vasospasms of the cerebral arteries can be a consequence of organic pathology of brain structures (substantia nigra, medulla oblongata, cortical centers for regulating vascular tone), taking medications or dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. In this case, only the spasmodic vessel is visualized. Objective signs of ischemia are rarely detected.
Additionally, watch the video of how this brain study looks on the monitor:
Research methodology
It is important not only to understand what it is - TCD of cerebral vessels, but also to know how such a procedure is carried out. During this procedure, the patient will need to lie on his back, at which time the doctor will apply a special gel to the area being examined, after which he will apply a sensor and move it along the course of the arteries. You may need to breathe more frequently and also turn your head in certain ways. Unpleasant sensations during TCD to examine the cerebral vessels are excluded; the patient only feels the pressure of the sensor.
What vessels can be studied using TCD?
The position of the acoustic window will determine the list of blood vessels that can be examined. There are only three windows:
- temporal;
- orbital;
- suboccipital.
Examination of the brain using the TCD method using a temporal window will allow you to examine the internal carotid artery, middle, anterior and posterior cerebral arteries. Involves examination through the temporal region.
Orbital window - scanning the arteries through the orbits of the eyeballs. Allows you to assess the condition of the ophthalmic artery and the internal carotid siphon.
The suboccipital window involves ultrasound examination through the junction of the occiput with the spine. The basilar artery is examined, as well as the intracranial segments of the vertebral blood vessels.
Neurosonography and TCD
If you do not know what kind of examination TCD and neurosonography
, then you should understand that it applies to infants. In fact, this is an ultrasound of the child’s brain, which is completely safe and allows you to see the early manifestations of various abnormalities.
Comparison of TCD with other studies
The following methods are widely used in the diagnosis of cerebral blood flow disorders: transcranial Doppler sonography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). There is no clear answer to the question of which technique is preferable. After all, each study has certain advantages and disadvantages.
TCD and MRI are absolutely safe diagnostic procedures for humans. In the first case, ultrasound is used, in the second - magnetic fields.
However, MRI has the following contraindications: the presence of metal plates and prostheses, a pacemaker. Also, during tomography, a contrast agent is used to clearly visualize brain structures. Therefore, MRI is not prescribed for patients with gadolinium allergy. CT is a study of blood vessels using x-rays. Therefore, the method is not used in pregnant women and children under 5 years of age.
If we compare techniques in terms of information content, then the most accurate is MRI with contrast.
However, the study is expensive and takes about 40 minutes. TCD and CT scans require no more than 20 minutes. Therefore, in emergency situations, these methods are preferred.
What does transcranial Doppler sonography show?
After you have learned what TCD is, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the data that will become known as a result of the procedure. The following will be taken into account:
- vein or artery wall thickness, diameter;
- minimum and maximum blood flow speed, its nature;
- resistive and ripple indices.
Each of these indicators may indicate the presence or absence of disease.
The speed of blood flow through the arteries
A TCD examination may show an abnormality, which is a deterioration in blood flow. The cause may be the presence of blood clots or plaques, as well as other problems that can be identified through duplex testing.
Venous drainage from the cranial cavity
There can be many reasons for this phenomenon; they may include severe traumatic brain injuries, the occurrence of tumors that compress blood vessels and/or brain tissue. Often, outflow occurs against the background of a stroke and its consequences, with a decrease or underdevelopment of the network of blood vessels.
Degrees of development of the collateral network of brain vessels
TCD examination can reveal underdevelopment of the blood vessel network. It often causes problems with blood supply to the brain. All detected violations are recorded in the conclusion.
Kinds
There is a temporal, orbital, and occipital examination. The name directly depends on the area where the information is read.
To ensure that intracranial blood flow studies are complete, another ultrasound option is additionally performed - transcranial duplex scanning. This qualitative research technique displays the vessel in two-dimensional mode, which allows one to obtain information about the condition (stiffness-elasticity), thickness and integrity of the vessel walls, its lumen and location, and monitor hemodynamic properties. Information, in this case, is provided as color cartograms or in spectral analysis mode. In color mode, the data characterizes blood flow and is qualitative in nature. The spectral mode makes it possible to objectively assess the presence and severity of hemodynamic disorders or the absence thereof.
The procedure, like all types of ultrasound, is non-invasive, absolutely painless and takes no more than 15-40 minutes.
Going through the procedure
You can sign up for transcranial Doppler ultrasound at the Orange Medical Center by phone or by leaving a request on the website. The procedure does not require any additional preparation, so it can be performed on the day of the appointment. In adult patients, the occipital part of the head, areas of the temporal bone and orbit are examined, in children - the fontanel area. When scanning vessels located outside the skull, the neck area is examined.
TKDG is carried out for a fee. You can see the cost of the procedure in the price list on the website or check at the reception. Since Doppler sonography of the brain is prescribed when serious neurological pathologies are suspected, in most cases it is part of a comprehensive examination. In this case, the cost of diagnostics may increase.