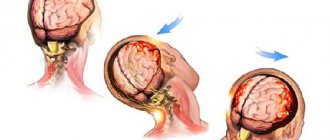
Symptoms and warning signs after a stroke
You can get a strong blow to the back of the head when practicing martial arts.
Injury to the back of the head can be accompanied by a decrease in the quality of visual function, since this area is connected to the optic nerves. In some cases, loss of consciousness or a feeling of numbness in the extremities (especially the lower ones) is provoked. This sign is explained by a possible concussion. It is not recommended to neglect a bruise of the occipital part. In medicine, there are cases where damage made itself felt after many years.
Symptoms may vary depending on the degree of injury and the exact location of the injury. With minor damage to soft tissue, a hematoma forms. A strong blow to the back of the head usually causes a concussion (ICD-10 code S06.0).
The main signs of mild damage are:
- drowsiness;
- pain;
- diplopia;
- loss of consciousness.
In case of severe trauma, a person experiences:
- loss of consciousness;
- headache;
- nausea;
- noise in ears;
- fear of light and sounds;
- nystagmus;
- asthenia;
- change in heart rate;
- sweating;
- sleep disorders.
Serious damage can be caused by hitting the back of your head against a wall or ice. The injury is characterized by clouding of consciousness, short-term loss of speech and paralysis of facial muscles. The person may feel very dizzy.
If someone hits a child on the back of the head and he has a headache, this is particularly dangerous.
Invisible strikes for urban self-defense
How to knock out an opponent on the street, what can be vitally important for you and your loved ones? As you know, a knockout blow is a blow that the opponent does not see. That is, an invisible blow. “Invisible” does not mean super-fast or supernatural that cannot be captured on camera. "Invisible" means unnoticeable, unexpected, unusual.
Here we will cover some invisible strikes. This article will be useful for both experienced athletes and those who have never practiced martial arts - because good physical shape or sparring is not required to deliver these blows. They are simple, but have repeatedly proven their effectiveness in war and on the street.
First, let's figure out what kind of blow can be invisible. If you are not one of “those”, then you have already guessed that any blow can be invisible. Even a tornado kick (with a turn in a jump), provided that the enemy is drunk to death, or is blind from the notorious handful of sand or a pinch of salt. But in this case, of course, such delights are optional.
Second question. An invisible strike implies a surprise attack. Is it possible to unexpectedly beat an opponent on the street? Will this be interpreted as an attack on a civilian? No - provided that the aforementioned citizen has clearly stated his plans for the evening, which include your untimely death. After this, preventative measures (aka “giving back in advance”) are possible. The second point is that if the enemy has not made any such statements, but you see that he (they) approached for a reason, it is your right to decide what to do. If you think too much and for too long about the possible consequences, you may receive an invisible blow. Your life is your decision .
Having dealt with the moral and legal side of the issue, we move on to the scientific justification.
As you know, a person mainly uses frontal vision, that is, he fixes his gaze on something specific. In the worst, extreme case, this is known as tunnel vision, which sometimes occurs in extreme situations, which is very disruptive, since the person can only see the enemy standing in front. Therefore, he may get hit on the side of the head.
More rarely, a person uses peripheral vision, and, as a rule, it is poorly developed in people, which is also bad from a combat, self-defense point of view. But this is the subject of a separate article. It turns out that a person’s field of vision is limited. Roughly speaking, our field of vision is a circle that extends 180 degrees on the sides, as well as above and below. In fact, it is smaller, and this is not a circle, but a “spot” of an individual shape for each person, but such a description is enough for understanding. The main thing here is to understand what an invisible blow is, how to deliver it, and how to protect yourself from such an “unexpected attack.” It is impossible to describe all the details in such a brief instruction as an article.
So, if you are standing almost close to your opponent, he cannot see the blows you throw from below. Let's list them.
1. Hit to the shin. A blow to the shin is quite traumatic, but it is not a knockout blow - this blow is needed to shock and move on to another action. Well, only if you don’t know how to break a bone with one such blow, which is possible with enough training. If you can, then you don’t need invisible blows. The blow is not applied with your toes, since, firstly, you may miss, and secondly, you will break them, and not the opponent’s leg. Hit with the middle of the inner rib of the foot - like they kick the ball in yard football. This way you will definitely hit the target. When striking, never look down! The enemy will automatically follow your gaze and see everything. Look into his eyes, or even better, behind his back - so you won’t even look at him, wasting your energy, and if something happens, you will control the situation. Be sure to practice this strike with a partner, so that you first understand that such strikes are not visible at close range. Also train on thin trees about the thickness of your mid-shin.
2. A hard blow to the groin. This blow is delivered with the fingertips, with the palm facing the opponent with the back side (the outer side, where the knuckles are). You hit like a whip, bitingly, as if shaking your hand. Naturally, in this case, all the above conditions are met - do not look at the point of impact, stand close to the enemy, do everything sharply and quickly.
3. Strike with the heel of your hand to the jaw. This is a sabotage, traumatic blow.
Apply it when your life and health are in danger. Because this blow, in turn, threatens the same enemy. It's similar to an uppercut, but it's thrown with the palm of your hand instead of the fist. In the lower jaw. The hand goes as close as possible to the enemy’s body so that he does not notice anything until the last moment. And in general, blows should not be sweeping - this way they are less noticeable. After striking, leave the striking hand in place, and with the other grab him by the back of the head and throw him to the ground, holding his head with both hands. 4. Continuation of attacks. It is clear that one blow to the shin or groin may not be enough. In general, these are rather distracting blows that you need in order to bring the enemy to the desired position. So to speak, to stir up his defenses, to tear him apart. - Continuation of the blow to the shin: a knee strike to the groin, the aforementioned strike with the heel of the palm to the jaw from below; simple side elbow strike.
- Continuation of the blow to the groin: if the enemy is bent over, we hit him with the “edge of the fist” or with the same heel of the palm on the back of his head from top to bottom. Add a knee to the face.
Methodological recommendations Naturally, it is necessary to practice all these technical actions. In pairs, and on projectiles (on “paws”, on the same trees). You need to start with simple things and move on to more complex ones. That is: first practice all the described strikes separately, then put them together in combinations, and practice them in turn.
What should you do to avoid such a sudden blow? Observe the first universal principle of (y)personal safety - distance control . Which means - don’t let strangers (especially in a conflict situation, especially on the street) closer than arm’s length. It is clear that there is public transport, there are shops, there are elevators. But we are talking about those cases where this is possible. If you are forced to stand closely with someone, observe the 2nd principle of personal safety - visual control . Don't get distracted, stay alert. Develop your peripheral vision, don't be fooled. What to do if “someone is wrong”, you get excited and push forward, pushing with your chest or horns? Remember the 3rd universal principle of street safety - behavior control . Learn to manage your emotions, be more restrained and cool-headed. Don't let your opponents (especially if they're some kind of "handbag slayers") drive you crazy.
Someone might say - if we are talking about the fact that I strike first, then why do I need these techniques? For example, I’m a boxer, and I can cut down an opponent with a left and then a right! Firstly, even an experienced athlete would benefit from learning some “tricks,” especially since they help maintain his health. If an athlete is experienced, then he understands how fragile our metacarpal bones are. If we hit with the heel of our palm, we won’t get injured and there won’t be any marks left – which is also in our favor. “What fight? Look at your hands, I didn’t hit anyone!” How many people know that you can hit with the heel of your palm? Not everyone. Already a plus.
In addition, the article is also intended for those who have not done anything, but want to stand up for themselves. What should we do with teenagers, women, old people, people with disabilities? It’s precisely such “mean tricks” that can help them, because for a typical aggressor they don’t seem to pose a threat, “you can show off,” so the blow can become doubly sudden and effective.
Diagnostic methods
The degree of damage is assessed using MRI images.
In order to diagnose damage caused by trauma to the occipital part, it is necessary to consult a neurologist. The specialist will evaluate the biomechanics of the cervical spine, determine range of motion and muscle tone.
Clinical diagnosis is based on examination results. If it is impossible to clarify it, additional procedures are carried out. MRI, CT and echoencephalography are usually prescribed.
First aid
If a person hits the back of their head, it is recommended to apply a cold compress to the affected area. You can use ice wrapped in a cloth or a bottle filled with cold water. You need to keep the compress for 15-20 minutes, then take a half-hour break and repeat the procedure. It is extremely important to monitor your pulse and breathing. If blood appears, the wound should be disinfected and bandaged.
A severe concussion is accompanied by poor circulation and severe hematomas around the eyes. The injured person should be kept at rest. The victim may feel sick, so it is necessary to turn him on his right side so that the vomit can come out freely and air can enter the lungs. It is recommended to tilt your head back slightly and tilt your face closer to the floor. Limbs should be placed at an angle of 90 degrees to prevent fractures during convulsions. It is necessary to call an ambulance and not take any action until the doctor arrives.
It is not recommended to give painkillers, as they interfere with the diagnosis of the injury.
Head injury: symptoms, first aid, consequences
Head contusions are injuries that most often result from a fall or blow from a blunt object. Often such injuries occur in young people.
Even when there are no symptoms, it is not recommended to ignore head injuries, since they can pose a danger to human health and life.
Injuries can cause a fracture of the base of the skull, concussion and other unpleasant complications, which is why it is necessary to know what to do in case of a head injury and, if necessary, provide first aid.
Classification
The injury can be open, that is, damage to the skin is observed, and blood vessels are also affected. If the injury is penetrating, then the dura mater of the brain is affected, sometimes a fracture of the base of the skull is diagnosed - one of the most dangerous injuries.
With closed injuries, the skin is not injured. The following groups of brain damage have been identified:
- A concussion is a mild degree of traumatic brain injury, the manifestations of which disappear after a few days, there are no symptoms of vascular damage, and functional disorders are reversible. A bruise is a more severe injury and may cause brain damage. Manifested by such symptoms as nausea, vomiting, pale skin, tissue swelling, pain.
- compression of the affected area of the brain (foreign object, hematoma, air, bone fragment);
- hemorrhage in the subarachnoid space (the cavity between the arachnoid and pia mater);
- diffuse damage.
A severe brain contusion can result from a combined injury.
With a head injury, there are 2 types of bruises:
- Brain contusion.
- Contusion of the soft tissues of the head.
Sometimes the injury is accompanied by hemorrhage. This is often accompanied by fractures of the bone tissue of the skull.
Types of damage are identified depending on location:
- contusion of the back of the head;
- damage to the temporal region;
- bruise of the frontal part of the head;
- damage to the parietal lobe.
Changes that occur in the brain as a result of a bruise are divided into primary and secondary. Primary ones are caused by the injury itself, and secondary ones are caused by deterioration of tissue nutrition and increased intracranial pressure, the appearance of edema, and hematomas.
In case of serious injuries, contusion of several areas of the brain is sometimes diagnosed.
When a child bruises the soft tissues of the head, a lump appears. However, as a result of the blow, brain injuries are also possible, the consequences of which can appear in adulthood, after 40 years or later. Therefore, even if a lump simply appears after a blow, it is recommended to seek medical help.
Symptoms
What can happen to the brain after a stroke? The brain, by inertia, sharply shifts in the opposite direction, so it is damaged not only at the site of the impact, but also on the opposite side, this causes vascular spasms and swelling. Due to edema, intracranial pressure increases.
A severe head injury is often accompanied by fractures of the skull bones, which worsen the person’s condition; the risk of developing an infection in the affected area also increases. In any case, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Symptoms of a head injury are determined by the location and force of the blow:
- A mild bruise is characterized by pain that subsides after a few hours. When the subcutaneous vessels are damaged, a hematoma forms. The victim complains of constant drowsiness, double vision and darkening of the eyes, and sometimes fainting occurs. Symptoms disappear after a few weeks;
- moderate injuries are accompanied by prolonged fainting (several hours), severe headaches, inhibited reactions and impaired awareness of what is happening. Speech is unclear and slow;
- for fractures of the skull bones, the main clinical symptoms are dizziness, vomiting, and nosebleeds;
- contusion of the back of the head is manifested by blurred vision, dizziness, loss of consciousness and general weakness.
In case of serious injury, patients are unconscious for a long time (up to several days), and coma may occur. There is a disturbance in speech, breathing and swallowing, and the pupils may vary in size. Partial or complete memory loss cannot be ruled out.
First aid for head injury
For a head injury, first aid consists of the following:
- put cold on the site of the impact, this will make it possible to reduce pain and swelling, keep it for several hours, but avoid hypothermia.
- the victim must be laid on a horizontal surface, which will make it possible to avoid another fall due to weakness and dizziness;
- regardless of the severity of the condition, take the victim to the hospital or call an ambulance; exclude the intake of water, food and medications;
- in case of hematoma, apply a compressive bandage;
- Warming compresses with alcohol can only be used after a few days.
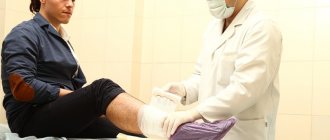
First aid for a head injury can be provided by anyone, but qualified medical assistance will still be required.
If a child suffers a head injury, first aid must be provided; it must also be taken into account that the symptoms in children may not appear as pronounced as in adults.
Treatment
Some people self-medicate for a head injury, which is not recommended, especially if there is even the slightest suspicion of a concussion or hemorrhage. How to treat a head injury is determined by the doctor; the methods depend on the nature of the injury and its location.
Drug treatment
Medicines are prescribed to reduce symptoms:
- analgesics – to reduce pain;
- medications to regulate the functioning of the autonomic nervous system;
- sleeping pills to normalize sleep;
- nootropic drugs are prescribed to prevent complications, as well as to restore brain function;
- diuretics;
- anticonvulsants - prescribed in more severe cases in the presence of seizures.
For topical use, ointments are used that have a strengthening effect on blood vessels, relieve swelling and help eliminate hematomas. During the rehabilitation period after injury, doctors prescribe physiotherapeutic measures.
A specialist will tell you how to treat a bruise at home. For this, compresses made from tincture of ginseng, lemongrass, and eleutherococcus are recommended.
Surgical intervention
In severe cases, surgical treatment is indicated, for example, for a head injury from a fall, if it is accompanied by damage to the integrity of the brain structures.
Most often, operations are prescribed for damage to the temporal and frontal lobes of the brain. Craniotomy is performed by drilling a hole through which dead tissue is removed. During the postoperative period, the patient should be under the supervision of doctors.
In case of a head injury due to a fall, treatment is prescribed based on the diagnosis. If the injury is not dangerous, then the following recommendations must be followed:
- bed rest for several days;
- adhere to the instructions of the treating specialist and ensure that you take prescribed medications;
- during the rehabilitation period, exclude physical activity;
- if the left side of the brain is injured, then it is better to lie on the right side, and vice versa;
- during the recovery period, it is better to avoid using gadgets and TV or limit such leisure activities to a minimum;
- Long walks in the fresh air are necessary.
If the back of the head is bruised, bruises and bumps also cannot be ignored, especially if unpleasant symptoms appear. In such cases, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid unpleasant complications.
Consequences of a bruise
Complications can be different, it depends on the location and severity of the injury. Minor injuries resolve on their own in a short period of time. In case of serious injuries, the development of the following complications cannot be ruled out:
- waking coma (apallic syndrome) - patients are conscious, but they are not able to react to what is happening, and are absolutely indifferent to the people and objects around them. There is a reaction only to pain;
- paresis – partial loss of motor function.
- brain cyst;
- brain abscess - the formation of a cavity with pus during the development of the inflammatory process;
- ICH, or intracranial hypertension syndrome, is increased intracranial pressure;
- constant headache - does not go away for six months or more;
- meningitis is an inflammatory process in the membranes of the brain;
- development of secondary epilepsy;
- death or disability cannot be excluded in case of severe injuries;
Consequences of a bruise on the back of the head:
- decreased performance and concentration;
- deterioration in sleep quality;
- depression;
- regular dizziness;
- the appearance of hallucinations;
- weather dependence.
If you hit the back of your head during a fall, the consequences of the impact can be serious, so it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination.
The success of therapeutic measures depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and treatment and the severity of the injury.
General practitioner with 10+ years of experience. Graduated from Bukovina State Medical University in 2008 with a degree in general medicine.
Treatment methods
Heparin ointment is used to resolve the hematoma.
Treatment at home is justified in cases of minor injury. Experts recommend the use of external agents Heparin, Traumeel gel or Dolobene gel. In accordance with the instructions, ointments are applied 2-3 times a day.
A hematoma in the occipital region is eliminated with cold compresses. If a lump forms, it is recommended to use Troxevasin or Gepatrombin ointment.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to reduce the time spent watching TV or spending time in front of a computer monitor, and avoid physical activity. This regime should be followed for a month. It is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air.
In case of a concussion, the pathology must be treated in a hospital setting under the supervision of a neurologist, surgeon and traumatologist. The duration of rehabilitation for a child is 1 month, and for an adult - 2 weeks. It is extremely important to maintain bed rest and avoid bright lights and loud sounds.
To eliminate headaches, analgesics Ibuprofen, Noofen, Nimesulide, Maxigan are prescribed.
In some cases, the patient experiences sleep disturbance or drowsiness, sudden mood swings and memory loss. To improve the general condition, sedatives Adaptol, Novopassit, Persen are prescribed, as well as drugs that help optimize blood circulation in the brain. This series includes Piracetam, Cavinton, Sermion, Trental, Cinnarizine, Instenon. Neuroprotectors Cerebrolysin, Actovegin, Gliatilin, Mexidol, Neurox are also used. To improve memory, nootropics Phezam, Selank, Phenotropil are prescribed.
In order to optimize the functionality of the nervous system, it is recommended to take B vitamins Milgamma, Neuromultivit, Benevron BF, Neurobion, as well as vitamins containing magnesium Magne B6, Magnelis B6.
For constant apathy, a course of antidepressants Tsitol, Stimuloton, Fluoxetine is recommended. Treatment is carried out under the strict supervision of a neurologist.
Massage
Massage helps improve blood circulation and normalize the functions of the neck and brain.
Procedures are prescribed for impaired motor functions after a severe brain injury. First of all, the back is massaged, then the limbs and abdomen. Stroking, rubbing and kneading are used. The duration of exposure is 10-20 minutes. The course includes 15-20 procedures.
For mild to moderate concussion, massage can be done 2-3 days after the injury. The back of the head, neck and forearms are warmed up while the patient is sitting. Then the back and shoulder blades are rubbed. Also, during the first 3-5 days, cryomassage is used, which involves the use of liquid nitrogen. The duration of the procedure is 5 minutes. The course includes 8-10 procedures.
Physiotherapy and spa treatment
Physiotherapeutic methods are indicated for severe bruises. They serve as an adjunct to drug treatment. Helps optimize cerebral circulation and metabolism.
Among the main procedures it should be noted:
- electrophoresis with vasodilators and cerebral circulation stimulants;
- galvanization of the brain and its segments;
- transcerebral UHF therapy;
- laser therapy;
- oxygen baths.
Patients who have suffered a mild form of concussion, after two months from the onset of the disease, can be sent to climatic and balneological resorts in Kislovodsk, Pyatigorsk, Essentuki, Solnechnogorsk.
Resort rehabilitation is not indicated in the acute phase of the disease, in the presence of contraindications and mental disorders.
Treatment with folk remedies
Ginseng root in the form of a decoction helps normalize blood circulation in the brain.
To speed up therapy, they often resort to using traditional medicine recipes. For example, it is recommended to add aloe juice to medications. Stimulation of blood circulation is facilitated by an infusion based on string, St. John's wort or ginseng. If apathy is present, taking valerian or motherwort is indicated.
Before using traditional medicine, you should consult a doctor. A specialist can choose the appropriate combination of medications and herbs.
Nutrition
When restoring the nervous system, honey, potato or cabbage juice, and flax oil are useful. It is recommended to include nuts and dried fruits in your diet. Nutrition should be varied, but not heavy. You should consume more citrus fruits and drink plenty of water.
It is necessary to completely eliminate alcoholic beverages, caffeine, and nicotine.
First aid for head injury
If a head injury occurs, it is important to immediately begin rehabilitation measures at home, which will help prevent serious complications - intracranial hemorrhages, swelling and dislocation of brain structures.
If a person falls and hits their head hard, the consequences can range from a mild concussion to coma and death. Statistics show that the prevalence of head injuries is about 200 cases per 100 thousand population annually. For 30% of patients, brain damage is fatal.
Every year, severe head injuries and associated disorders of vital and brain functions lead to the death of 1.5 million people in the world. Another 2.5 million people become disabled.
Definition
A head injury occurs when a person falls or hits the skull with a hard object; the condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate treatment.
Even weak blows to the skull area lead to an increase in the permeability of the blood-brain barrier, the development of autoimmune reactions in the tissues of the central nervous system, and neurodegenerative changes.
If you hit the back of the head, forehead, or temple hard, the tissues of the brain and skull will be damaged, which can be hidden from view during a visual inspection when there are no violations of the integrity of the skin. A fracture of the bone structures of the skull is a life-threatening disorder, which is always accompanied by a change in the morphological structure of the brain matter.
A dent on the forehead, crown or back of the head after a blow is a reason to suspect a fracture of the cranial bones. Other signs to look out for include softening of the bone structures of the skull, progressive loss of motor coordination and other reactions. If you shake your head, it is important not to make sudden movements, which can aggravate the dysfunction of the brain.
If struck, a person may be seriously injured. As a result of a skull fracture, pneumocephalus (air entering the cranial cavity) often develops. A common complication of head injury is damage to the cranial nerves. The condition is accompanied by paresis of the facial muscles and visual impairment.
Often the pathology is combined with damage to the spinal column in the cervical region. Airway obstruction (obstruction) is a common cause of early death in TBI.
Head injuries in 90% of cases are accompanied by loss of consciousness, which correlates with a decrease in the tone of the muscles located in the pharynx.
A decrease in tone leads to a displacement of the tongue and soft palate, which causes a violation of the patency of the respiratory system.
Types of injuries
Taking into account the nature of the damage, concussion, contusion of brain tissue or compression of the brain are distinguished. Considering the severity of the injuries received, a distinction is made between concussion of the brain (mild contusion), moderate contusion of brain tissue, and severe trauma. A wound that appears on the head when you fall, get knocked, or are attacked occurs:
- Open (damaged skin).
- Closed (skin without damage; subcutaneous soft tissues, bone and medulla undergo pathological changes in morphological structure).
- Penetrating (characterized by a violation of the integrity of the meninges).
Depending on the location of the pathological focus, contusion of the occipital area, frontal, temporal, parietal lobe is distinguished.
Features of head injury in childhood
The bone tissue of a child under 12 years of age contains a large amount of water, has a fibrous structure, and is characterized by a low content of calcium salts. The bones of the skull in childhood are soft and flexible. After a blow, a dent may appear on the child’s head; the brain matter is damaged more often due to strong mechanical impact on the skull than in adult patients.
If a child falls and hits his head, he may have a headache, an increase in body temperature, and vomiting, which suggests the need to urgently take the following actions: lay the child in a horizontal position and call a doctor. Even if the baby remains conscious, it is important to pay attention to changes in his behavior.
Affected children usually lose their appetite. They become inactive and complain of double vision. If a child feels sick after hitting his head, and signs such as apathy, lethargy, weakness, drowsiness and dizziness appear, he needs urgent medical attention.
Causes
If you have a headache after a fight, it is better to immediately seek medical help. Contusion of the brain and bone structures of the skull occurs due to a direct blow to the skull area, mechanical impact with acceleration, and compression of the cranial structures. Common situations associated with injury:
- Road accidents.
- Falling from height.
- Industrial injuries.
- Traumatic injuries as a result of a fight or attack.
- Sports activities.
Depending on the strength of the traumatic impact, damage of varying degrees of severity occurs - reversible disorders (concussions of the brain) and irreversible (foci of crushed brain structures).
The crush site is a variable area of the cerebral hemispheres, in the area of which the meninges are ruptured and particles of alternative brain matter are present.
The crush site is characterized by a functional and structural change in the nervous tissue (neurons, gliocytes, nerve fibers, synapses) and elements of the vascular system, in the area of which multiple hematomas appear. Bruises of the skull are usually accompanied by the formation of foci of hemorrhage.
The crush site in the acute period of TBI manifests itself clinically as an intracranial space-occupying process (hematoma, tumor) and contributes to the progression of hypertensive-dislocation syndrome. As a result, life-threatening conditions associated with pinching and compression of the brain stem may develop.
Symptoms
Injuries in the skull area are differentiated based on severity. In accordance with this classification, they are divided into mild, moderate and severe forms. Symptoms depend on the severity of the damage. A mild form, known as a concussion, is accompanied by symptoms:
- Darkness, loss of consciousness (lasts several seconds, minutes).
- Disorientation in space and time, confusion of thoughts.
- Amnesia (memory loss) of retrograde or anterograde type.
- Pain in the head area (intense, bursting, acute), dizziness.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Noise, buzzing in the ears.
- Pain in the eye orbits.
Neurological deficit of focal type is absent or mildly expressed. A strong blow to the back of the head during a fall or as a result of mechanical impact from the outside in adults and children is associated with serious consequences. Moderate injuries are accompanied by symptoms:
- Prolonged loss of consciousness (lasts several minutes or hours).
- Lethargy, inability to adequately navigate time and space.
- Amnesia of retrograde and anterograde type.
- Diffuse type headache.
- Meningeal symptoms (muscle rigidity in the occipital region, pathological reflexes of Brudzinsky, Kernig, state of stupor, stupor, paresis and paralysis, paresthesia - sensitivity disorder, numbness, tingling in the area of the limbs, face).
- Psychomotor agitation.
Additional signs of damage to nervous tissue depend on the localization of the site of impact during a head injury; taking into account the focal symptoms, the doctor decides what to do.
Focal symptoms include impaired motor coordination, pyramidal signs (pathological foot and hand reflexes, reactions of oral automatism, clonus - rapid, involuntary contractions of muscle groups, synkinesis - involuntary friendly contraction of a limb in response to voluntary movement of a symmetrical limb).
Some patients experience damage to the bone structures of the skull - most often the vault and base, which is accompanied by the appearance of subgaleal hematomas (accumulation of blood in the space located between the periosteum and the aponeurosis - a tendon plate formed from collagen fibers). Bleeding from the wound often occurs.
In the absence of a violation of the integrity of the cranial bones and soft tissues of the head, sometimes there is a leakage of a mixture of blood and cerebrospinal fluid from the physiological openings of the head - the nasal and auditory passages, from the pharynx. If a TBI is accompanied by liquorrhea (random leakage of cerebrospinal fluid), it is considered open.
After a strong blow, which provokes severe damage to the nervous tissue, an acute, debilitating headache appears and dizziness occurs. The patient does not regain consciousness for a long time. Signs noted: severe impairment of respiratory function and cardiac activity. Other symptoms:
- Heart rhythm disturbances (tachycardia, bradycardia).
- Increased blood pressure values.
- Difficulty breathing associated with obstruction of the respiratory system.
In the acute period, primary brainstem symptoms develop - horizontal, slow, unassociated movement of the eyeballs, dilation or contraction of the diameter of the bilateral pupils, unstable changes in muscle tone, decerebrate rigidity (increased tone of the extensor muscles, decreased tone of the flexor muscles).
Primary brainstem symptoms that develop with a strong blow to the head include a decrease in deep reflexes (tendon, articular, periosteal), which correlates with the serious condition of the victim and necessitates the need to correct vital functions.
Neurological deficit is manifested by general cerebral signs - severe depression of consciousness up to coma. In victims who have developed an intracranial hematoma as a consequence of a blow to the head, there is a short-term clear interval (temporary improvement in condition), after which a sharp deterioration occurs.
In addition to severe bradycardia (less than 40-50 beats per minute), symptoms such as unilateral mydriasis (pupil dilation), hemiparesis of collateral (lateral) localization, convulsive attacks of local (local) or generalized (widespread) type are detected. After a strong blow to the head, the body temperature may rise, which is due to various reasons:
- Stressful effects on the body.
- The development of the inflammatory process due to pathogens (bacteria, viruses) entering the wound.
- Shock due to injuries.
- Intoxication of the body as a result of the formation of decay products of damaged tissue.
If after a blow you have a headache and your body temperature has risen, you need to consult a doctor and do a comprehensive examination, which will help to find out the exact causes of the disorders.
Diagnostics
Timely, correct diagnosis significantly improves the prognosis for severe head injuries; the doctor identifies the nature and extent of the damage and determines what to do. Priority methods of instrumental diagnostics are CT and MRI. During neuroimaging, the exact localization of the pathological focus, the presence of intracranial hematomas, and the extent of the pathological process are detected.
To assess the state of consciousness, the criteria of the Glasgow scale are used. In a hospital setting, a blood test is done to determine the concentration of glucose and electrolytes, blood clotting indicators. In some cases, lumbar puncture is indicated (confirmation of the presence of intracranial bleeding, exclusion of infectious lesions of the central nervous system).
First aid
In case of a head injury, which is accompanied by loss of consciousness and severe neurological deficit, it is necessary to immediately call emergency doctors. First aid for a mild blow to the head that provoked a concussion is to do the following:
- Place the victim in a horizontal position.
- Perform sanitation (cleaning) of the oral cavity (without raising the head and flexing the spinal column in the cervical region).
- Turn your head to the side to avoid vomit entering your respiratory tract.
- If there is an open wound, treat it with antiseptic treatment and apply a bandage to stop the bleeding.
- Until the doctors arrive, do not let the victim sleep, constantly talking to him.
If there are no visible injuries affecting the soft tissues and bone of the skull, a cooling compress (ice wrapped in a towel, cloth soaked in cold water) can be applied to the site of the injury. Exposure to cold reduces pain, prevents the formation of hematomas and the development of perifocal edema.
First aid for a severe head injury, which is accompanied by a disorder of respiratory function and cardiac activity, involves artificial heart massage and ventilation of the lungs (mouth-to-mouth breathing).
Treatment methods
In case of a mild concussion, the patient is advised to rest in bed. If you hit the back of your head or any other part of your head, the first thing to do is call an ambulance. The doctor will assess the severity of the condition and, if necessary, carry out rehabilitation measures, which include:
- Tracheal intubation.
- Air duct insertion.
- Connection to a ventilator.
- Administration of plasma replacement solutions (Polyglukin, Rotsdex, Reogluman).
- Dehydration therapy (Lasix, Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone).
If necessary, surgical intervention is performed, during which intracerebral and meningeal hematomas are removed and impaired blood flow is restored.
Consequences of a head injury
The consequences of a strong blow to the back of the head can be expressed in sleep disturbances, visual dysfunction, deterioration in performance and cognitive abilities, and the development of depression. A simple hit to the head with a ball can lead to serious consequences:
- Chronic headaches.
- Hydrocephalic syndrome, persistent increase in intracranial pressure.
- Paresis, paralysis.
- Brain abscess.
- Epileptic seizures, convulsive syndrome.
The consequences of strong blows to the head with a fist often manifest themselves in the form of intracranial bleeding, swelling of brain tissue, dislocation of brain structures, which can ultimately lead to disability or death.
A head injury, regardless of severity, can have serious health consequences. For any head injury, it is necessary to undergo a diagnostic examination and receive adequate treatment.
Possible consequences and complications
After a brain injury, it is necessary to check your vision.
The consequences of a blow to the back of the head during a fall in an adult and a child are dangerous and can be irreversible. Therefore, even with the slightest damage, it is important to contact a specialist in a timely manner.
The main complications include:
- the formation of visual-spatial agnosia (a person has a failure to perceive the left side of space);
- absent-mindedness;
- forgetfulness;
- irritability;
- decreased performance;
- sleep disorder;
- depressive disorder;
- hallucinations;
- clouding of consciousness;
- blurred vision;
- dependence on weather conditions;
- constant headaches;
- noise in ears;
- dizziness;
- decreased concentration.
Displacement of the occipital bone can cause circulatory problems in the brain.
Displacement of the occipital bone often provokes insufficiency of blood flow in the arteries of the spinal column. The person may lose coordination. The segment determines the topography of the temporal zones, and they, in turn, determine the location of the lower jaw. Therefore, one of the complications of the injury may be its sagging or displacement to the side.
Tension of the muscular system under the occipital area contributes to compression of the lymphatic vessels, which causes a violation of the outflow of lymph and swelling in the chin area. Too much damage can cause death.
What to do if you have a bruise on the back of your head
If a head injury occurs, it is important to immediately begin rehabilitation measures at home, which will help prevent serious complications - intracranial hemorrhages, swelling and dislocation of brain structures.
If a person falls and hits their head hard, the consequences can range from a mild concussion to coma and death. Statistics show that the prevalence of head injuries is about 200 cases per 100 thousand population annually. For 30% of patients, brain damage is fatal.
Every year, severe head injuries and associated disorders of vital and brain functions lead to the death of 1.5 million people in the world. Another 2.5 million people become disabled.