Neurologists and otorhinolaryngologists at the Yusupov Hospital often have to consult patients whose main complaint is tinnitus.
Patients describe their sensations in different ways. The noise may resemble ringing, squeaking, buzzing, crackling, rumble, buzzing, rustling, hissing. Its intensity also varies.
Often tinnitus is combined with symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, unsteadiness of gait, darkening of the eyes, and headaches.
Let's look at the most common causes of tinnitus.
Description of the phenomenon
Tinnitus or ringing in the ears is a very common condition, affecting approximately one in five adults. Usually it is only an inconvenience, but sometimes it can interfere with the ability to concentrate and sleep well. As a result, the patient experiences constant stress, which has a negative impact on his personal relationships and work.
This condition often accompanies hearing loss, although it does not cause deafness in itself. Many people with tinnitus have excellent hearing. Sometimes they develop increased sensitivity to sounds - hyperacusis, so they are forced to take measures to limit external noise.
In some cases, the pathology disappears after eliminating its cause, for example, otitis media or ear plug. However, often even after treatment, ear noise persists.
Practical advice
If you experience ringing in the ears, and even more so it bothers you and interferes with your activities, you should not delay in contacting a specialist for professional help, otherwise you may miss the progression of a serious disease that may be accompanied by ringing in the ears. Only a specialist - an otorhinolaryngologist will be able to accurately determine the cause of tinnitus and plan subsequent treatment. By the way. Following the advice of your doctor is a prerequisite for effective relief from an unpleasant symptom. Take care of your body and health, be happy!
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 142 votes
Share article on social networks
Why is there noise in my ears?
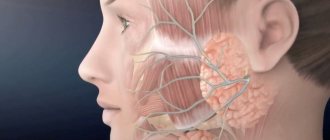
The causes of tinnitus may be associated with damage to parts of the auditory system - the outer, middle, inner ear or brain. There are several theories explaining what happens in the body with this pathology:
- spontaneous electroacoustic emission, that is, the spontaneous generation of electrical signals in the cochlea of the inner ear, which are perceived as tinnitus;
- damage to the organ of Corti with dysfunction of the auditory cells of the cochlea;
- dissonance between healthy and damaged cells of the organ of Corti, which can be caused by the normal aging process;
- increased activity in the posterior cochlear nuclei of the brain caused by exposure to too much external noise;
- auditory plasticity, that is, activation of nerve centers in response to hearing loss due to damage to the cochlea;
- the formation of new connections between the neurons of the auditory nerves when they are damaged, compressed by a tumor or hemorrhage, and the generation of impulses in them in the absence of external sound;
- damage to the trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal and other cranial nerves, activating the so-called oto-somatic interaction;
- increased activity of the limbic and autonomic nervous systems due to increased sensitivity to the first episode of tinnitus.
Thus, tinnitus is a complex process that requires accurate diagnosis using modern equipment and competent treatment.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
You can completely get rid of tinnitus only after treating the underlying disease that caused the discomfort. Therefore, if extraneous sounds appear for no reason, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor. To reduce discomfort until the cause of the disorder is identified, mild herbal sedatives and soothing herbal teas are recommended. In some cases, self-massage of the ears helps: rubbing movements, pressing with your palms on the ears.
Conservative therapy
Since tinnitus is caused by various causes, treatment regimens are selected strictly individually, taking into account the underlying disease and concomitant pathology. A prerequisite for the effectiveness of therapy is the elimination of provoking factors (refusing loud music on headphones, changing jobs, avoiding noisy parties and visiting nightclubs). Etiotropic therapy includes antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antihistamines, angioprotectors, other groups of drugs, and their combinations. For the symptomatic treatment of tinnitus, use:
- Sedatives
. Herbal and synthetic drugs reduce the excitability of the brain and the speed of nerve impulses. Medicines also normalize the emotional state. - Antidepressants
. Medicines are effective for constant noise, which is caused by chronic diseases, Meniere's disease. The drugs affect centers in the brain and increase the concentration of serotonin. - Tranquilizers
. Indicated for severe ringing or buzzing in the ears, leading to insomnia and reducing performance. The effectiveness of the drugs is due to their sedative and hypnotic effects.
Experimental treatment
Tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT) is an innovative direction that is a type of cognitive behavioral therapy. The program involves individual sessions using psychotherapeutic methods, during which a person is taught ways to relax and techniques for switching attention. A component of the treatment is individually selected sound therapy. The patient is asked to listen to a pleasant noise (the splashing of waves, the rustling of leaves, the sound of rain). Over time, the brain learns to block these sounds, while the perception of pathological noise decreases.
Surgery
If humming, ringing, or tinnitus are associated with purulent inflammatory diseases, it is necessary to open and drain the tympanic cavity, which significantly speeds up the healing process. If tumors of the auditory analyzer are detected as the main cause of the disorder, they are removed with mandatory cytomorphological examination. Treatment of malignant neoplasms involves a combination of surgery with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In aneurysms, the affected vessel is clipped.
Kinds
There are the following types of noise in the ear:
- subjective: the patient hears noise that does not come from the external environment, it is associated with irritation of the auditory nerve;
- pulsating: the patient hears a buzzing, ringing, clicking or other loud sound that coincides with his heartbeat;
- objective: a rather rare phenomenon associated with the patient’s increased sensitivity to external sounds or vibration of various parts of the body.
Depending on the cause of the noise, it is divided into the following types:
- associated with damage to the vascular system;
- caused by damage to the outer or middle ear;
- muscular;
- neurosensory (peripheral and central), associated with the pathology of auditory cells and pathways.
Additionally, doctors distinguish 3 degrees of noise: with the first, the patient notes sound sensations only upon active questioning, with the second, he considers it not the main problem with hearing, and with the third, tinnitus becomes the main complaint.
Prevention methods
The essence of treatment comes down not only to eliminating uncomfortable extraneous sounds, but to treating the disease that directly caused these noises.
An individual treatment plan is prescribed for each patient. For example:
- If it has been determined that the cause of the noise is an inflammatory process, the doctor prescribes antibacterial drugs and local therapy (for example, darsonvalization of the collar area).
- If the hum is due to the presence of a cerumen plug, then the only treatment method will be to remove it by lavage, aspiration or curettage.
- For constant stress, which can provoke noise, antidepressants are prescribed. Additionally, they may prescribe massage, acupuncture, herbal medicine, and aromatherapy. A good treatment method would be to visit a sauna or bathhouse if there are no medical contraindications.
- In hypertensive crises, medications are prescribed to normalize blood pressure.
- If otosclerosis is detected, operations aimed at prosthetics of the auditory ossicle are performed.
- When working in rooms with high noise levels, it will be necessary to use earplugs that will reduce the impact of external noise on the hearing organs.
- If there are displacements in the cervical vertebrae, it is necessary to restore the spine and pay attention to muscle tension.
Alternative medicine methods also influence a good recovery outcome. For example:
- Magnetic therapy is the use of a static magnetic field or an alternating magnetic field;
- reflexology is a treatment method that uses influence on biologically active points located on the skin;
- laser therapy - the use of radiation in the optical range, the source of which is a laser;
- physical exercise;
- massages.
In cases of damage to the auditory nerve, the only way to relieve the patient from unpleasant noise is to use a hearing aid, which improves the perception of sounds in a noisy background.
Currently, hearing aids help make sounds more intelligible and the speech of other people understandable.
Causes of tinnitus
The causes of tinnitus are usually associated with some kind of disease of the hearing organs or nervous system.
- The most common cause of tinnitus is hearing loss. Due to age-related changes, injuries, and the effects of medications, the sensitive cells of the cochlea are damaged. They do not send electrical signals to the brain, and it begins to produce its own impulses, as if compensating for the lack of external stimuli.
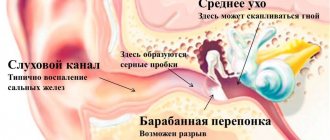
- Diseases of the outer and middle ear can cause noise: cerumen plug, otitis media, narrowing of the ear canal, tumor of the tympanic cavity.
- Exposure to loud noise is a very common cause of not only hearing loss, but also tinnitus. Every person should be aware of the damaging effects of loud music and the noise of operating machinery and protect themselves from such influence. Another cause of pathology is barotrauma.
- More than 200 medications can cause this symptom, most often aspirin, aminoglycoside antibiotics (gentamicin, kanamycin) and quinine derivatives. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ethacrynic acid, platinum derivatives, ACE inhibitors and other drugs can cause noise. Exposure to methyl alcohol and benzene is also dangerous.
- Meniere's disease is a disease accompanied by transient dizziness, ringing and congestion in the ears, and temporary hearing loss.
- Acoustic neuroma is a tumor that affects the nerve pathway leading from the cochlea to the brain centers, and causes noise and hearing loss on one side.
- Pulsatile noise is usually associated with pathology of the circulatory system. It is observed during pregnancy, anemia, thyrotoxicosis, arteritis, and also with increased intracranial pressure; In addition, vascular murmur appears with heart defects, vascular development anomalies, and stenosis of the ear arteries.
- The causes of objective tinnitus may be diseases of the temporomandibular joint, pathology of the muscles of the soft palate, middle ear, or gaping of the eustachian tube in the nasopharynx.
- Diseases that can cause tinnitus: hepatitis, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, instability or osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as well as various hereditary anomalies (Chiari, Gardner-Turner, Klippel-Feil, Pence, Hunt, Konigsmark-Hollender-Berlin syndromes).
The causes and treatment of this pathology are complex, and only a highly qualified otolaryngologist can understand the problem comprehensively.
Symptoms
Manifestations of tinnitus include a variety of sounds heard by the patient. It could be ringing, buzzing, the sound of a roaring aircraft engine, hissing, whistling, clicking. It may be constant or appear only occasionally.
If you experience noise in the ear, you should consult a doctor. This may be associated not only with pathology of the hearing aid, but also be a manifestation of hypertension, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, anemia and other diseases.
With infectious diseases of the ear, noise may be accompanied by pain and discharge from the ear canal.
When noise is combined with dizziness, urgent medical attention is required, as this may be a manifestation of Meniere's disease or cerebrovascular accident.
With brain tumors, this complaint intensifies at the height of a headache attack. With a tumor located in the posterior cranial fossa, the noise increases with changes in body position.
Diagnostics
To identify the causes of ear noise, the following diagnostic tests are used:
- complete physical examination, medical history, examination of the head and neck, determination of cranial nerve function;
- hearing test (subjective audiography);
- objective audiological examination: method of studying the auditory brainstem response (ABR) and extratympanic electrocochleography;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the skull;
- endoscopic nasopharyngoscopy to identify the causes of muscle noise;
- microotoscopy;
- in some cases – diagnosis of hypertension, hyperthyroidism and other therapeutic diseases;
- according to indications - spinal puncture with determination of intracranial pressure.