- Location and functions of the facial nerve
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Otogenic neuritis of the facial nerve
- Folk remedies
- Possible complications
- Prevention
Pathology of the facial nerve is registered annually in 2–3 people out of 10 thousand people. It occurs due to various reasons, the nature of which largely determines the treatment of facial neuritis. Taking into account the anatomical connection of this formation and the ENT organs, with neuritis of the facial nerve the patient needs to consult not only a neurologist, but also an ENT doctor.
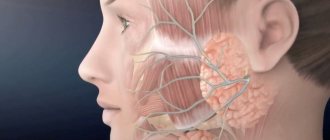
Location and functions of the facial nerve
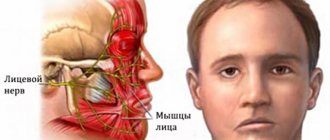
The facial nerve controls muscle movements in this anatomical region. This gives a person the opportunity to smile, express emotions with facial expressions, cry, and wink. Facial neuritis can lead to severe physical disability that is poorly tolerated psychologically. Although in most cases the symptoms of the disease gradually disappear, this requires long-term rehabilitation.
The facial nerve is the seventh of 12 paired cranial nerves. Each person has 2 facial nerves, corresponding to the right and left halves of the face. This nerve is adjacent to the eighth nerve, the auditory nerve, and passes through the structures of the middle ear, the mastoid process, and the parotid salivary gland, where it splits into many small branches.
Causes
Facial neuritis occurs under the influence of the following etiological factors:
- in 15% of patients this is damage to the branches of the nerve during surgical interventions on the middle ear, mastoid process, and also associated with otitis media and other lesions of the hearing organ, for example, cholesteatoma;
- in rare cases, the disease is caused by infection - herpes virus (Hunt syndrome), mumps, polio, influenza, as well as Lyme disease, transmitted through tick bites;
- in 75% of cases, the cause of neuritis of the facial nerve cannot be determined; in this case, they speak of Bell's palsy, which worsens after hypothermia and colds.
Other causes include head trauma, surgery on the salivary gland, and removal of an acoustic neuroma.
1.General information
Cochlear neuritis is a collective diagnosis that generalizes the condition of hearing loss due to damage to the auditory nerve; The terms “sensorineural hearing loss” and “sensorineural hearing loss” are also widely used (in some cases as a synonym, in others as a designation of an axial symptom).
Unlike the vast majority of diagnoses ending in “-itis,” cochlear neuritis does not imply the dominant etiopathogenetic significance of infectious and inflammatory processes. Some authors, defining the scope and content of this concept, generally insist on the non-infectious nature of the lesion; in other sources the significance of the inflammatory factor is veiled, etc. Generally speaking, the formulation “cochlear neuritis” refers to those diagnoses that are perceived and interpreted (even by specialists) more on an intuitive than on a rational level. The English term “Auditory neuropathy” seems to be somewhat more successful.
One way or another, hearing loss caused by lesions of auditory neural conductors is widespread: according to modern data, this is the most common cause of partial or complete hearing loss. At the same time, epidemiological estimates published in different sources differ significantly. As a first approximation and taking into account WHO reports, the total number of hearing impaired people in the world is at least 300 million people. According to other sources, this figure is even higher and reaches 10% of the world's population, of which 125 million people are actually disabled (three quarters of them are residents of the poorest countries). In Russia, the number of socially significant hearing loss is estimated at 13 million people, with at least a million being children and adolescents.
Thus, partial or complete hearing loss is one of the global health problems, and its severity is dramatically aggravated by the fact that today there are no truly effective methods for treating cochlear neuritis as the dominant etiopathogenetic factor of hearing loss.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Symptoms
Manifestations of the disease occur acutely, within a few hours, for a maximum of 3 days. The gradual appearance of signs is most typical of compression of the nerve by a tumor growing from the surrounding tissue.
Depending on the severity, neuritis of the facial nerve is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- movements of the facial muscles are weakened, up to barely noticeable, disruption of conjugate contractions of symmetrical areas of the face;
- facial asymmetry, even disfiguring;
- difficulty closing the eyes; in severe cases, the palpebral fissures do not close completely;
- disorders of swallowing, chewing, speech;
- when the disease is complicated by keratitis, vision loss gradually develops;
- taste disturbance, weakening or strengthening of sound sensations;
- lacrimation;
- with simultaneous damage to the trigeminal nerve - severe pain in the facial area.
Signs of intoxication and fever are uncharacteristic and usually occur due to the infectious nature of neuritis of the facial nerve.
Diagnostics
Treatment of facial nerve neuritis is prescribed after an examination, which includes:
- general blood and urine tests, blood glucose levels;
- if the infectious nature of the disease is suspected (Lyme disease, HIV infection, syphilis and others) - appropriate serological tests;
- if sarcoidosis or brucellosis is suspected, chest X-ray;
- in the case of a prolonged course (more than 3 weeks), if damage to the brain stem or cerebellopontine angle is suspected, MRI is prescribed, and if the pathological process is localized in the area of the temporal bone, computed tomography is more informative;
- Electroneuromyography is used to assess the effectiveness of treatment;
- If a nerve tissue infection is suspected, a lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid examination are performed.
If the patient has already been diagnosed with ear diseases, or has discharge from the ear canal or hearing loss, he should definitely consult an ENT doctor.
Facial neuritis is differentiated from Lyme disease, Ramsay Hunt syndrome, Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
The most typical manifestations of cochlear neuritis, in addition to hearing loss itself, are sensations of constant extraneous noise in the head and asymmetrical hearing loss. Some patients also experience a complex of vestibular disorders (dizziness, coordination and balance disorders, unsteadiness of gait, etc.).
Obviously, any hearing loss, incl. caused by cochlear neuritis, is a socially significant problem, since it leads to disruptions in communication and social functioning, requires the use of hearing aids, in many cases limits or excludes professional suitability, and provokes the development of psychological disorders of the depressive register.
The degree of functional failure of the auditory analyzer is established in a series of audiometric, tuning fork and other similar tests. Otoscopy and microotoscopy are performed; Electrocochleagraphy, vestibulometric studies, consultations (and corresponding examinations) of specialized specialists, and a battery of laboratory tests are also prescribed.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Treatment
Treatment of facial nerve neuritis is carried out on an outpatient basis. The exception is cases of illness associated with ear pathology that require surgical intervention.
- At home, it is necessary to spare the organs of vision. Due to incomplete closure of the eyelids, the cornea of the eye quickly dries out, so it must be constantly moistened with special drops, wear dark glasses during the day, and cover the eyes with a bandage at night.
- The basis of treatment for facial neuritis is glucocorticoid preparations (prednisolone), which are often supplemented with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs.
- If facial neuritis is caused by damage to the part of the nerve that runs in the labyrinth, middle ear or mastoid process, then only surgery will bring the best results.
- In severe cases, accompanied by paralysis of facial muscles, microsurgical neurological operations are performed to stitch or transplant nerves.
Reconstructive surgeries that are performed on patients with severe cases of facial neuropathy:
- movement of the branches of the hypoglossal nerve to the distal end of the facial nerve;
- transposition of the temporal muscle to the corner of the mouth, which allows you to learn how to raise its corner;
- transplantation of a muscle flap from the thigh while preserving the nerve branches;
- plastic surgery – brow lift, face lift, partial lip resection, eyelid correction.
Otogenic neuritis of the facial nerve
Neuritis of the facial nerve, which occurs secondary to serious diseases of the middle ear, requires urgent surgery. During the intervention, the doctor relieves excess pressure on the nerve (decompresses it) by removing part of the bone wall of the nerve canal that runs in the middle ear. Subsequently, treatment of the underlying disease is prescribed, as a result of which the function of the affected facial nerve is also restored.
If the pathology develops at an early stage of acute otitis media, a decision may be made on conservative treatment of facial neuritis:
- vitamin therapy with ascorbic acid and group B preparations (Milgamma);
- decongestants (furosemide);
- glucocorticoids for rapid relief of inflammation and pain;
- after acute manifestations subside, actovegin, solcoseryl, and other drugs that affect the metabolism of nervous tissue are prescribed;
- If conservative treatment is ineffective, different types of surgical interventions are prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic methods are included in the complex of restorative treatment measures:
- therapy with UHF, quartz radiation, laser;
- electrophoresis with B vitamins, lidase;
- acupuncture and massage, especially performed on the inside of the cheek;
- applications of therapeutic mud, ozokerite, paraffin;
- physical therapy aimed at restoring the activity of the muscles of the lower part of the face.
Folk remedies
At home, you can use traditional medicine recipes to warm up and relieve inflammation:
- three times a day for 20 days, warm the sore side with a bag of warm table salt;
- massage your face with essential oil of fir or cedar twice a day for two weeks;
- 3 times a day for 2 weeks, make warm compresses with linden blossom infusion or gruel from fresh black elderberries;
- 3 times a day for 15 days, rub with a composition consisting of equal parts of horseradish juice and olive oil;
- before going to bed, make compresses from fresh wormwood leaves for 30 minutes;
- make compresses from cottage cheese and honey: mix 4 parts of low-fat cottage cheese and 1 part of linden honey, wrap in gauze and apply to the affected half of the face for 1 hour, wrap with a scarf; do 2 compresses a day for 2 weeks.
Of course, folk recipes cannot replace drug therapy, much less surgery. However, they are not prohibited from being used to speed up recovery in complex treatment.
Diagnosis of neuritis
Specialists at the CELT Pain Clinic pay special attention to differentiating neuritis from:
- multiple sclerosis;
- brain tumors;
- circulatory disorders in the brain.
Facet blockade
- Cost: 10,500 rub.
- Duration: 15-30 minutes
- Hospitalization: 2 hours in hospital
More details
In addition to examination and history taking, electroneuromyography can be used. Thanks to it, you can assess the degree of nerve damage and predict how the disease will progress.
Possible complications
Treatment of facial neuritis cannot be delayed. The later therapy is started, the greater the likelihood of developing complications:
- With a long course of the disease, the patient develops a persistent contracture of the facial muscles on the affected side: the muscles are involuntarily tense, contracted, and involuntary movements are possible. Recovery from such a complication is extremely difficult.
- The appearance of the face can change greatly: immobile muscles create a significant cosmetic defect.
- Persistent disturbances of taste.
- Corneal ulcers, infection, cataract formation, blindness.
- Constant spasm of the muscles of the face or eyelid.
Causes of neuritis
In order to correctly prescribe treatment for neuritis, it is necessary to correctly identify the causes that caused it. These are bacteria and viruses, as well as:
- intoxication due to poisoning with alcoholic beverages, medications, food;
- nerve compression;
- injury.
The reasons may lie in a number of diseases:
- diabetes;
- rheumatism;
- metabolic disease;
- excess body weight.
Prevention
Taking into account the main causes of the disease, its prevention includes protection from colds, hypothermia, as well as timely treatment of diseases of the ENT organs. It is useful to harden the body, treatment in sanatoriums on the seashore, and a diet rich in B vitamins.
After suffering from facial neuritis, self-massage of the face with essential oil of fir or cedar is useful to prevent recurrence of the disease. It can be done at night during the cold season.
The paid services department of NIKIO invites patients with neuritis and neuropathies of the facial nerve for treatment. The patient is examined by an experienced doctor; a consultation with a candidate or doctor of medical sciences is possible. The clinic uses modern physiotherapy equipment. If necessary, the patient undergoes surgery to quickly restore the function of the damaged nerve.
Forecast and prevention of neuritis
In young patients with good regeneration, nerve inflammation responds well to therapeutic measures. In older people, treatment is longer due to the fact that it is often necessary to treat concomitant diseases. If you ignore the problem, paralysis and contractures may develop.
General preventive recommendations:
- balanced diet;
- timely treatment of any ailments (not only neurological);
- hardening;
- vaccination according to schedule.
Rehabilitation after neuritis should be carried out annually. The doctor prescribes various preventive procedures: radon baths, water procedures, massage, etc. Social rehabilitation of patients with neuralgia and neuritis is aimed at restoring ability to work, mobility of the limbs, and getting rid of pain. The patient regains the opportunity to lead a normal lifestyle without experiencing limitations in motor functions.