- Location and functions of the facial nerve
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Otogenic neuritis of the facial nerve
- Folk remedies
- Possible complications
- Prevention
Pathology of the facial nerve is registered annually in 2–3 people out of 10 thousand people. It occurs due to various reasons, the nature of which largely determines the treatment of facial neuritis. Taking into account the anatomical connection of this formation and the ENT organs, with neuritis of the facial nerve the patient needs to consult not only a neurologist, but also an ENT doctor.
Location and functions of the facial nerve
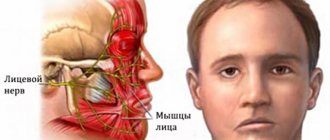
The facial nerve controls muscle movements in this anatomical region. This gives a person the opportunity to smile, express emotions with facial expressions, cry, and wink. Facial neuritis can lead to severe physical disability that is poorly tolerated psychologically. Although in most cases the symptoms of the disease gradually disappear, this requires long-term rehabilitation.
The facial nerve is the seventh of 12 paired cranial nerves. Each person has 2 facial nerves, corresponding to the right and left halves of the face. This nerve is adjacent to the eighth nerve, the auditory nerve, and passes through the structures of the middle ear, the mastoid process, and the parotid salivary gland, where it splits into many small branches.
Features of massage for other diseases of the facial nerve
Properly selected manipulations, taking into account indications and contraindications, help:
- improve local blood circulation;
- eliminate muscle spasms;
- will restore facial activity;
- correct speech defects that have arisen under the influence of pathology.
The speed of obtaining therapeutic results depends on timely seeking medical help.
Facial nerve paresis
To solve the problem, experts use rubbing in the form of semicircles with constant stroking. Vibration and ultrasonic therapy methods show good effectiveness for paresis.
Neuralgia of the facial nerve
Requires separate techniques:
- stroking the face and back of the head;
- rubbing the shoulders, neck until the dermis becomes slightly red;
- small vibrating movements in the area of the cheekbones and forehead;
- weak effect on the skin of the nose, eyebrows, nasolabial triangle.
Important! A professional massage therapist will be able to enhance metabolic processes, blood circulation in the problem area, and accelerate the removal of decay products.
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
The pathology requires treatment of the facial, head, and cervical-collar areas. Massage of the trigeminal nerve on the face and these areas leads to:
- normalization of blood circulation;
- lymph outflow;
- stable nutrition of tissues.
The course is conducted with the utmost care. If the rules are violated, a new attack is possible due to the impact of trigger areas.
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Causes
Facial neuritis occurs under the influence of the following etiological factors:
- in 15% of patients this is damage to the branches of the nerve during surgical interventions on the middle ear, mastoid process, and also associated with otitis media and other lesions of the hearing organ, for example, cholesteatoma;
- in rare cases, the disease is caused by infection - herpes virus (Hunt syndrome), mumps, polio, influenza, as well as Lyme disease, transmitted through tick bites;
- in 75% of cases, the cause of neuritis of the facial nerve cannot be determined; in this case, they speak of Bell's palsy, which worsens after hypothermia and colds.
Other causes include head trauma, surgery on the salivary gland, and removal of an acoustic neuroma.
Causes of the disease
The causes of acute facial neuritis have not been proven in the scientific research world. However, doctors identify factors that provoke the development of a disease leading to a pathological condition:
- Cytomegalovirus (herpes) – often it is genetic in nature, is found in the body of most people and does not manifest itself in any way until the immune system fails. In a dormant state, the virus is located in nerve cells, in its active form it comes out (lips, nose, corners of the mouth, genitals, they are removed with antiviral drugs), and can cause severe inflammation of the facial nerve and its swelling. Other skin diseases caused by viruses - lichen, dermatitis, contribute to the appearance of neuritis.
- Frequent exposure to the cold. When the body becomes hypothermic, the level of immune defense first decreases. With neuritis of the facial nerve, even a draft can lead to spasm and disruption of the functioning of blood vessels and muscle fibers. Against the background of a lack of heat, nerve nutrition is disrupted and inflammation occurs.
- Alcohol abuse. Such drinks contain alcohol, which damages brain cells and the facial nerve.
- Increased pressure. Due to jumps in upper and lower blood pressure, intracranial pressure increases, as a result of which the center of the facial nerve is affected. Such conditions lead to a risk of stroke.
- Carrying a child. The main danger awaits a woman in the first trimester of pregnancy. At this time, various hormonal changes occur in the body's systems, including the nervous system, preparing for the birth of the baby.
- Malignant neoplasms of the brain. The tumor develops and increases in size, pinching the nerve and disrupting the functioning of impulses.
- Traumatic effects in the brain area. At the site of impact, the facial nerve ruptures, which contributes to the accumulation of water, internal swelling of tissues and bones is formed, and the inflammatory process moves along the structure of the nerve.
- Tooth infection. When treating teeth, incorrect actions by the doctor or infectious diseases entering the tissue cause inflammation.
- Previously suffered diseases of the ENT organs. Other viruses in otitis, sinusitis, spread to nearby tissues, they cause damage to the nerve in the temple.
- The disease is diabetes mellitus. Disruption of metabolic processes leads to the appearance of inflammation due to the occurrence of polyneuropathy.
- Presence of atherosclerosis. Fatty plaques that form as a result of the disease clog the capillaries that supply the nerve with blood.
- Stressful and depressive conditions. When a person suffers morally, the protective functions of his body weaken, then he becomes susceptible to infections and viruses that provoke nervous diseases.
The main cause of the disease is pathogenic agents, namely viruses and bacteria. Risk factors are exogenous and endogenous.Exogenous ones include:
1. Poisoning of the body with alcohol, drugs, low-quality products. 2. Nerve compression. This is possible during surgery. 3. Injuries. In this case, post-traumatic neuritis is diagnosed.
Endogenous ones include:
1. Diseases of the endocrine system. 2. Obesity. 3. Diabetes. 4. Rheumatism. 5. Hereditary predisposition. 6. Problems with metabolism. 7. Otitis media.
The main manifestation of neuritis is pain along the nerve and in the area that it innervates. Decreased sensitivity, numbness, and impaired movement may occur.
Symptoms
Manifestations of the disease occur acutely, within a few hours, for a maximum of 3 days. The gradual appearance of signs is most typical of compression of the nerve by a tumor growing from the surrounding tissue.
Depending on the severity, neuritis of the facial nerve is accompanied by the following symptoms:
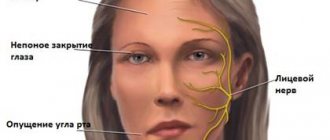
- movements of the facial muscles are weakened, up to barely noticeable, disruption of conjugate contractions of symmetrical areas of the face;
- facial asymmetry, even disfiguring;
- difficulty closing the eyes; in severe cases, the palpebral fissures do not close completely;
- disorders of swallowing, chewing, speech;
- when the disease is complicated by keratitis, vision loss gradually develops;
- taste disturbance, weakening or strengthening of sound sensations;
- lacrimation;
- with simultaneous damage to the trigeminal nerve - severe pain in the facial area.
Signs of intoxication and fever are uncharacteristic and usually occur due to the infectious nature of neuritis of the facial nerve.
Diagnostics
Treatment of facial nerve neuritis is prescribed after an examination, which includes:
- general blood and urine tests, blood glucose levels;
- if the infectious nature of the disease is suspected (Lyme disease, HIV infection, syphilis and others) - appropriate serological tests;
- if sarcoidosis or brucellosis is suspected, chest X-ray;
- in the case of a prolonged course (more than 3 weeks), if damage to the brain stem or cerebellopontine angle is suspected, MRI is prescribed, and if the pathological process is localized in the area of the temporal bone, computed tomography is more informative;
- Electroneuromyography is used to assess the effectiveness of treatment;
- If a nerve tissue infection is suspected, a lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid examination are performed.
If the patient has already been diagnosed with ear diseases, or has discharge from the ear canal or hearing loss, he should definitely consult an ENT doctor.
Facial neuritis is differentiated from Lyme disease, Ramsay Hunt syndrome, Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome.
Treatment
Treatment of facial nerve neuritis is carried out on an outpatient basis. The exception is cases of illness associated with ear pathology that require surgical intervention.
- At home, it is necessary to spare the organs of vision. Due to incomplete closure of the eyelids, the cornea of the eye quickly dries out, so it must be constantly moistened with special drops, wear dark glasses during the day, and cover the eyes with a bandage at night.
- The basis of treatment for facial neuritis is glucocorticoid preparations (prednisolone), which are often supplemented with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs.
- If facial neuritis is caused by damage to the part of the nerve that runs in the labyrinth, middle ear or mastoid process, then only surgery will bring the best results.
- In severe cases, accompanied by paralysis of facial muscles, microsurgical neurological operations are performed to stitch or transplant nerves.
Reconstructive surgeries that are performed on patients with severe cases of facial neuropathy:
- movement of the branches of the hypoglossal nerve to the distal end of the facial nerve;
- transposition of the temporal muscle to the corner of the mouth, which allows you to learn how to raise its corner;
- transplantation of a muscle flap from the thigh while preserving the nerve branches;
- plastic surgery – brow lift, face lift, partial lip resection, eyelid correction.
Otogenic neuritis of the facial nerve
Neuritis of the facial nerve, which occurs secondary to serious diseases of the middle ear, requires urgent surgery. During the intervention, the doctor relieves excess pressure on the nerve (decompresses it) by removing part of the bone wall of the nerve canal that runs in the middle ear. Subsequently, treatment of the underlying disease is prescribed, as a result of which the function of the affected facial nerve is also restored.
If the pathology develops at an early stage of acute otitis media, a decision may be made on conservative treatment of facial neuritis:
- vitamin therapy with ascorbic acid and group B preparations (Milgamma);
- decongestants (furosemide);
- glucocorticoids for rapid relief of inflammation and pain;
- after acute manifestations subside, actovegin, solcoseryl, and other drugs that affect the metabolism of nervous tissue are prescribed;
- If conservative treatment is ineffective, different types of surgical interventions are prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic methods are included in the complex of restorative treatment measures:
- therapy with UHF, quartz radiation, laser;
- electrophoresis with B vitamins, lidase;
- acupuncture and massage, especially performed on the inside of the cheek;
- applications of therapeutic mud, ozokerite, paraffin;
- physical therapy aimed at restoring the activity of the muscles of the lower part of the face.
Massage technique
To treat neuropathy, 2 main massage techniques are used:
- Spot;
- Stroking.
Acupressure on certain points of the human body, which are recognized as biologically active zones, is called acupressure. For neuritis, apply gentle pressure movements to the following points:
- Above the eyebrows;
- Above the eyes;
- On the temples;
- Under the cheekbones;
- On the wings of the nose;
- In front of the ears;
- In the dimple on the chin.
Each point is massaged for 10-15 seconds. In this case, both sides of the face “participate” in the massage: the sick and healthy.
Note!
There should be no pain during massage movements. Therefore, all movements should be soft.
Acupressure is performed in front of a mirror to control the response of facial muscles to the massage effect. If it is performed by another person, the patient is placed on a hard surface.
After 3-4 minutes of massage, the stroking movements are replaced with rubbing ones. Light pinching is also included in the process.
The total duration of the massage effect should not exceed 10 minutes.
Folk remedies
At home, you can use traditional medicine recipes to warm up and relieve inflammation:
- three times a day for 20 days, warm the sore side with a bag of warm table salt;
- massage your face with essential oil of fir or cedar twice a day for two weeks;
- 3 times a day for 2 weeks, make warm compresses with linden blossom infusion or gruel from fresh black elderberries;
- 3 times a day for 15 days, rub with a composition consisting of equal parts of horseradish juice and olive oil;
- before going to bed, make compresses from fresh wormwood leaves for 30 minutes;
- make compresses from cottage cheese and honey: mix 4 parts of low-fat cottage cheese and 1 part of linden honey, wrap in gauze and apply to the affected half of the face for 1 hour, wrap with a scarf; do 2 compresses a day for 2 weeks.
Of course, folk recipes cannot replace drug therapy, much less surgery. However, they are not prohibited from being used to speed up recovery in complex treatment.
Massage techniques
For neuritis, several massage techniques are used, as well as a set of special exercises. Regardless of the chosen technique, the main movements are performed in the directions of the massage lines. The use of amplification techniques, as well as tapping and effleurage, is prohibited.
Segmental
Carrying out segmental massage aims not only to strengthen facial muscles, but also to relieve swelling and congestion in the nerve canal, as well as improve the conductivity and excitability of nerve endings. The massage technique for neuritis includes several techniques:
- vibrating soft movements;
- light stroking massage with fingertips;
- trituration;
- stroking.
All movements of the massage therapist should be light, without pressure. If there are no concomitant inflammatory diseases, then additional use of a vibrating massager is possible.
A segmental massage session for the treatment of neuritis begins with massaging the forehead. The forehead is stroked with an open palm from the central point to the temples, after which it is carried out with light rubbing. Vertical strokes are carried out from the eyebrows to the hairline. After stroking, apply light pressure with your fingers from the central point to the temples. Then they repeat the strokes and move on to vibrational patting of the entire surface of the forehead.
After the forehead, massage the area around the eyes. Using your fingers, they pass from the outer corner of the eye along the lower edge to the inner one. Use the middle and index fingers to lightly touch the upper eyelid. Then, with pointed circular movements, massage the outer edge of the eye socket, the lower edge towards the inner corner of the eye and the area above the eyebrows.
Move on to massaging the lower jaw, nose and lips. Usually the massage begins with the healthy half of the face, and gradually moves to the affected half. Techniques for this area are carried out using the index and middle finger along lines from the middle of the chin to the wings of the nose, along the sides of the nose to the bridge of the nose, along the back of the nose to its tip. Sequence of techniques:
- horizontal rubbing;
- vertical rubbing;
- point pressure;
- light point pressure;
- stroking;
- pincer-like stroking.
Finish the session by massaging the cheeks. The entire area is stroked with the palm of the hand, then rubbed linearly. Next they do:
- circular acupressure;
- forceps massage;
- zigzag stroking;
- point pressure with fingertips;
- tingling;
- light patting;
- horizontal active stroking.
All techniques alternate with soft relaxing strokes. The use of segmental massage in the treatment of neuritis requires a gradual increase in the load on the muscles. The first introductory sessions are always carried out in a gentle mode, selecting the optimal force of influence.
Spot
Acupressure facial massage is a simple but effective technique that is also suitable for independent use. The technique uses the impact of the surface of the fingers on biologically active points on the body, which are the projection of organs and systems. For neuritis of the facial nerve, massage is performed at the following points:
- between the eyebrows. The point is massaged for several minutes for pain, fatigue, or decreased concentration;
- below the inner edge of the eyebrows. The area is massaged to relieve nasal congestion, nerve pain and improve vision;
- above the corners of the lips. The points are massaged to relieve symptoms of stress;
- on the back of the neck along the spine. Massaging the points helps eliminate the symptoms of nerve inflammation, get rid of headaches, eye pain, and migraines;
- 2 cm above the auricle. Massage of the point relieves headaches and helps with neuritis of the auricular nerve.
After the massage, it is recommended to rest for a few minutes and do 2-4 breathing exercises . Do not perform acupressure if you have high blood pressure or chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Self-massage
At home, self-massage of the face is carried out using the classical method. Facial massage consists of several basic techniques:
- circling with fingertips;
- circling with fingertips;
- tingling.
All techniques are performed first on the muscles of the healthy half of the face.
The session begins with pinching at the base of the nose, gradually moving along the eyebrow line to the temples. Then pinching passes along the lower jaw from the midpoint of the chin to the bottom of the ears. Next, the face is massaged in circular movements with minimal pressure. Massage techniques affect the side of the nose, forehead, hairline area, temples, and chin. Then intense circular movements are made through the cheekbones to the temples. With slight reinforcement, they pass along the sides of the nose to the lower edge of the cheekbones and to the ears. Next, the pads of the middle fingers are pressed to the inner corners of the eyes and slowly move them towards the ears. The forehead is massaged with circular, slow and sliding movements.
The session is completed by massaging the entire surface of the head and face. They pass from the temples behind the ears to the back of the head, massaging the forehead, chin, cheeks, and the front surface of the neck with light pressure.
Possible complications
Treatment of facial neuritis cannot be delayed. The later therapy is started, the greater the likelihood of developing complications:
- With a long course of the disease, the patient develops a persistent contracture of the facial muscles on the affected side: the muscles are involuntarily tense, contracted, and involuntary movements are possible. Recovery from such a complication is extremely difficult.
- The appearance of the face can change greatly: immobile muscles create a significant cosmetic defect.
- Persistent disturbances of taste.
- Corneal ulcers, infection, cataract formation, blindness.
- Constant spasm of the muscles of the face or eyelid.
Prevention
Taking into account the main causes of the disease, its prevention includes protection from colds, hypothermia, as well as timely treatment of diseases of the ENT organs. It is useful to harden the body, treatment in sanatoriums on the seashore, and a diet rich in B vitamins.
After suffering from facial neuritis, self-massage of the face with essential oil of fir or cedar is useful to prevent recurrence of the disease. It can be done at night during the cold season.
The paid services department of NIKIO invites patients with neuritis and neuropathies of the facial nerve for treatment. The patient is examined by an experienced doctor; a consultation with a candidate or doctor of medical sciences is possible. The clinic uses modern physiotherapy equipment. If necessary, the patient undergoes surgery to quickly restore the function of the damaged nerve.
Prevention of neuropathy
No one is immune from the appearance of unpleasant and painful symptoms of neuropathy. Inflammatory processes, brain diseases and even ordinary hypothermia can cause the appearance of one of the forms of neuralgia: inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. To avoid illness, you need to adhere to the rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- Eat rationally and balanced;
- Temper the body;
- Exercise;
- Avoid hypothermia and sudden temperature fluctuations;
- Do not use air conditioning for a long time in hot weather.
It is also important to consult a doctor in a timely manner to prescribe adequate treatment for diseases of the ear, nose and throat. During treatment, follow all doctor's recommendations and strict bed rest.