After a person has at least once been in a state of severe alcoholic intoxication, due to the consumption of large quantities of alcoholic beverages, he begins to be interested in the question: will the organs and their functions be restored? It is especially important whether brain cells are able to recover after quitting alcohol. The same question is asked by a person undergoing rehabilitation after treatment for chronic alcohol addiction.
There are times, especially on holidays, when a person, without meaning to, drinks a very large dose of alcohol in a short time. It is clear that you should not expect pleasant sensations after this. People who suffer the most are those who are not used to drinking alcoholic beverages, or who do so rarely and in small portions. They will have headaches from drinking alcohol for a long time.
Research shows that only five percent of ethanol leaves the body naturally, that is, through sweating and urination.
The rest of it is broken down in the body, and it will take some time to remove all the breakdown products of ethanol from the body. It also depends on the physical condition of the person, what age he is, and his gender. And of course, what drinks did he drink and in what quantities.
Destructive effects of ethanol on brain cells
There is no doubt that ethanol destroys brain cells. This is evidenced by gait disturbances, inhibition of reactions, and memory disorders. As soon as ethanol stops entering the body, functions are gradually restored.
Everyone knows that alcohol is harmful to health. It all starts with a violation of consciousness, and can lead to the fact that a person becomes disabled forever. There are some factors that help determine how much damage is done to brain cells and what effect ethanol has on them.
These include:
- how often a person drinks alcohol and in what quantities;
- at what age did he start drinking alcohol, and when did he become dependent on alcohol?
- what gender is the person, how old is he, is he educated, is there a genetic predisposition to alcohol addiction, and have there been any cases of chronic alcoholism among relatives;
- what physical condition the person is in;
- whether fetal alcohol syndrome has been observed in humans.
Disorder of consciousness for a short time, which occurs after drinking alcohol, occurs much more often than doctors previously claimed. Such a result can be defined as a possible consequence of alcohol intoxication, which does not depend on whether the person has symptoms of chronic alcohol dependence or how old he is.
Scientists conducted an experiment trying to identify the negative effects of ethanol on brain cells associated with short-term consciousness disorders. More than seven hundred students participated in the experiment. They all answered the same question: has it ever happened to you when, waking up in the morning, after a night of alcoholic outpourings, you were unable to remember what you did in the evening and where you were?
More than half of the youth already had experience of drinking alcoholic beverages, and answered in the affirmative: yes, after drinking a large amount of alcohol they experienced memory disorders. Forty percent of them said this had happened in the past year, and nine percent of respondents had consumed alcoholic beverages in the past two weeks and experienced brain fog.
Content:
- Effect on the central nervous system.
- Alcohol harms the heart.
- Pathologies of the digestive tract: 3.1. Alcoholic liver damage. 3.2. Pancreatitis. 3.3. Gastritis.
Everyone probably knows how harmful systematic alcohol consumption is to the body, including those who drink regularly. Doctors confirm that drunkenness negatively affects the functioning of all internal organs without exception. And when visiting a doctor in the later stages of addiction, the problem is not so much getting rid of the patient’s painful craving for alcohol, but rather restoring the body after many years of intoxication. What exactly are the harms of alcohol?
Is it possible to prevent the development of severe pathologies?
The effect of alcohol on the female brain?
Complications caused by drinking alcoholic beverages are more serious in the fairer sex than in men.
It has been experimentally proven that ethanol behaves much more aggressively towards the cells of a woman’s body than towards the cells of a man. Organs and their functions are more susceptible to the negative effects of alcohol. The destruction of the liver, damage to the heart muscle and cells of the nervous system occurs faster.
Having carried out a comparative analysis of the results of studies of the human brain using MCT, scientists have established the fact that the negative effects of ethanol manifest themselves in the fact that the brain decreases in size.
The degree of such a decrease is the main indicator that organic changes are present in the brain cells. And the longer the experience of drinking alcohol, the higher these indicators.
In addition, the results of the experiments showed that both women and men who suffer from alcohol addiction face certain problems when they have to learn something or remember any information. All this occurs due to frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Note that the male representatives who participated in such an experiment had twice as much experience of regular consumption of large amounts of alcohol than the fairer sex.
It turns out that the negative effects of ethanol on both the male and female brains manifest themselves in the same ways. But it is necessary to take into account that women took exactly half as much alcohol. From all this we conclude that ethanol has a stronger effect on the female brain.
In contrast, two articles were recently published in an American publication discussing the role of gender in the effects of ethyl alcohol on the body.
The authors came to the opposite conclusion, that is, according to them, ethanol has the same effect on everyone without exception. This means that experiments of this kind need to be continued in order to find out the specific effects of ethyl alcohol on a woman’s brain cells.
Short-term effects of alcohol consumption
Let's take a closer look at what happens when a person sits down to have a glass or two.
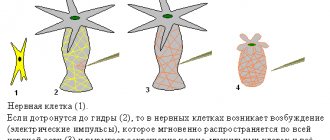
Problems go away. The membranes of dopamine receptors are the most sensitive to the invasion of alcohol.
Dopamine, an excitatory neurotransmitter, regulates our motor activity and is responsible for the ability to experience positive emotions. A small dose of alcohol does not yet have any effect on the coordination of movements, but it already provokes dopamine activation: a person’s mood improves, and the illusion arises that everything is fine, regardless of the real picture of the world. It is not surprising that with such effects you want to drink more. But at some point, other chemical processes turn on, and the reverse process begins - sadness and causeless melancholy roll in. Stress goes away. If you continue to drink alcohol, the GABA system, gamma-aminobutyric acid, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter, will join the reaction. The process of releasing glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter, is suppressed by alcohol. In simple words, the thoughts, speech, and movements of a drunk person slow down. This is the same psychostimulating effect that alcoholics artificially induce to “relieve stress.” The work of the brain and nervous system is slowed down: a person feels, notices and remembers less.
Price is beyond the control of all mediators. When the dose of ethanol exceeds 250 grams, the effect of alcohol on the nervous system is characterized by the failure of all mediator systems. And since we are all different, the effect of intoxication manifests itself differently in everyone: some become aggressive, others cry bitterly, and others demonstrate sexual preoccupation. The negative effect of alcohol on nerve cells is simultaneously accompanied by dehydration of the brain. For this reason, during a hangover, a person experiences severe headaches, dizziness and other neurological symptoms.
Thiamine deficiency and Korsakoff-Wernicke disease
If a person systematically drinks alcohol, without control over the amount he drinks, and this lasts for quite a long time, then he has every chance of developing brain dysfunction or damage to his cells. Moreover, this can be caused by the consumption of large amounts of alcohol, or there may be serious disturbances in the liver due to chronic alcohol dependence.
For example, most people suffering from chronic alcohol addiction have a lack of thiamine in their bodies, or as it is also called vitamin B1. It may be lacking due to poor nutrition, metabolic disorders in the body and, of course, due to the abuse of alcoholic beverages. It plays an indispensable role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. It supports the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system, digestive tract, and nervous structures.
Most people suffering from chronic alcohol addiction are deficient in vitamin B1. And this can lead to such a serious illness as Korsakoff-Wernicke syndrome, or more precisely, Wernicke syndrome and Korsakoff syndrome.
Wernicke's disease is characterized by paralysis of the eye muscles, disturbance of consciousness and impaired coordination of movements. Sometimes a patient with a similar syndrome cannot independently find the door of the room to leave, he cannot move without someone else's help. If at least one of the signs of the disease appears, you need to urgently seek medical help.
Most people suffering from alcohol dependence, along with Wernicke's syndrome, experience Korsakoff's syndrome, which is also called alcohol paralysis. With this disease, memory impairment is observed, when he forgets everything that happened to him before the disease, but can describe in great detail the events that took place several years before.
In addition, he remembers well everything that happens to him after his illness. The patient begins to invent non-existent events, or talk about those that really happened, but at the same time greatly distorts the facts. All this is accompanied by disorientation. The patient ceases to navigate the world around him and himself. Sometimes, even after seeing his reflection in the mirror, the patient does not realize that it is him.
Call us now:
+7 (812) 454-00-50
Prices for Ultramed clinic services
Is it possible to drink if you have certain diseases?
The presence of illness makes its own adjustments to the nuances of drinking alcohol. Different types of alcoholic beverages can be beneficial or harmful for various pathologies, ailments, and diseases of the blood vessels and brain.
- After the concussion . A concussion is a mechanical action, a kind of bruise that has an effect similar to alcohol intoxication (poisoning). A concussion is accompanied by changes in blood pressure, dizziness, loss of coordination and even orientation, nausea, and vomiting. Therefore, you should not add stress after a concussion with alcohol. Violation of this rule can lead to increased headaches, hypertensive crisis, vasospasm and cerebral edema, stroke, and coma. How much exactly should you not drink? Until complete recovery.
- For a stroke . Good red wine and cognac, consumed in small doses, really cleanse and strengthen blood vessels, and also prevent atherosclerosis and stroke. However, immediately after the occurrence of a stroke, in no case should you aggravate the condition, which is characterized by loss of consciousness, hemorrhage, sometimes paralysis, etc.
- For atherosclerosis . A small and periodically taken dose of high-quality alcohol helps reduce the level of “harmful” cholesterol and stimulates the production of “good” cholesterol in the liver, dissolves fatty deposits on the walls of blood vessels, cleanses the blood and improves blood circulation. Exceeding the recommended dose leads to the opposite effect.
- With hypoxia . Brain hypoxia occurs at the first signs of intoxication, the degree of which dictates the amount of harm from hypoxia. Alcohol is the direct culprit of oxygen starvation. However, in the hangover stage, a minimal dose of ethanol can save you from a stroke.
- With a cyst . This is a benign neoplasm. But it can lead to disruption of some parts of the brain. Therefore, the cyst should not be disturbed. That is, any negative processes are dangerous: the slightest increase in pressure, blood thickening, etc. Alcohol is not advisable until the disease is cured.
- With a tumor . Oncology is a mysterious disease. Despite the fact that some alcoholic drinks have an anti-cancer effect, as they contain a large amount of antioxidants, you should not provoke an existing disease by placing additional stress on the diseased organ. Moreover, even a healthy drink cannot be the decisive factor in the cure.
You should also avoid drinking alcohol before MRI and other diagnostic procedures.
Is it possible to restore brain cells?
It was believed that a person is born with a specific number of brain cells, and if they are somehow damaged, then they cannot be restored. Scientists believed that neurons under the influence of ethyl alcohol were destroyed and no longer function. in order to restore their activity it is necessary to strengthen the remaining nerve cells, since there is no possibility of adding new ones. But in the second half of the last century, scientists discovered that the formation of new neurons is possible. This process is called neurogenesis. After this discovery, scientists developed a new approach to the treatment of disorders of brain cells.
Pathologies of the digestive tract
The harm of alcohol to the liver and other organs of the gastrointestinal system is felt even after a single episode of drinking abuse. But systematic drunkenness is fraught with severe, often irreversible changes. This:
- alcoholic liver disease;
- pancreatitis;
- gastritis.
In these diseases, the absorption of thiamine and other vitamins, macro- and microelements, vital for the full functioning of cells, is impaired. This further aggravates the addict’s health condition.
Alcoholic liver damage
At the initial stage
Alcohol addiction
develops steatosis of the liver parenchyma - fatty infiltration of cells.
This process is reversible in most cases, but only under the condition of a categorical refusal of alcohol and supportive therapy.
If a person continues to drink, degenerative processes progress:
areas of hepatocyte necrosis are replaced by connective tissue, and severe inflammation begins. At the stage of liver cirrhosis, health can only be restored through organ transplantation surgery.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatic pathology is usually diagnosed after 5–8 years of systematic drinking. A typical manifestation of the disease is pain radiating to the side in the epigastric region, which can last for several days.
Discomfort increases with non-compliance with the diet and drinking alcohol. Also characteristic are bowel movements, weight changes, and diabetes due to damage to pancreatic cells.
Gastritis
The course is severe, there is a high risk of gastric ulcer with perforation of the intestinal wall and internal bleeding. Symptoms of the pathology are aggravated by uncontrolled drinking and poor diet.
We can talk endlessly about the dangers of alcohol, since the listed syndromes and diseases are not all that an addict may encounter. The only way to avoid severe pathologies
(many of which are incurable) -
contact a narcologist in time
and overcome the craving for alcohol.
Literature:
- Sivolap Yu.P. Alcohol abuse and pharmacotherapy of alcoholism. Lecture. — First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov, Moscow, 2005.
- Shabanov P.D. Fundamentals of Narcology. - St. Petersburg: Lan Publishing House, 2002. - 560 p.
- Pyatnitskaya I. N. General and private narcology A guide for doctors. - M.: OJSC "Publishing House" Medicine", 2008. - 640 p.
- Entin G.M., Goffman A.G., Muzychenko A.P., Krylov E.N. Alcohol and drug addiction. Practical guide for doctors. — M.: MEDPRACTIKA-M. - 2002. - 328 p.
Need some advice?
OR CALL A DOCTOR
CALL!
+7