Types of lumboischialgia
According to the method of progression, lumboischialgia is divided into 2 forms:
- acute – characterized by acute lumbago that occurs for the first time;
- chronic - pain (they are nagging and dull) appears periodically and systematically, periods of exacerbation are replaced by remission.
Depending on the affected area, lumbago with sciatica occurs:
- unilateral – pathology covers the right or left side of the body;
- bilateral, or bilateral - inflammation spreads to both sides.
Depending on the cause, lumbar sciatica is distinguished:
- vertibral, or vertebrogenic – caused by diseases of the spine:
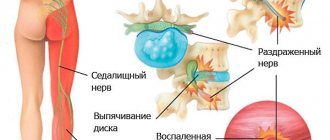
- discogenic – develops with intervertebral hernia;
- spondylogenic – caused by osteochondrosis;
- nonvertebrogenic – not associated with diseases of the spine:
- angiopathic - provoked by disruptions in the blood circulation of the lower back and lower extremities;
- myofascial – a consequence of damage to muscles and fascia;
- caused by pathologies of the peritoneal organs;
- caused by problems in the hip joints;
- idiopathic - the cause cannot be determined.
Diagnosis of piriformis syndrome
To recognize piriformis syndrome, methods such as:
- Certain manual tests
- Neurological tests
- Infiltration of the piriformis muscle with novocaine with assessment of the resulting positive changes
Recognizing piriformis syndrome is not difficult, it is much more difficult, but it is absolutely necessary to find out its true cause. The idea that piriformis syndrome may be the final diagnosis is another myth.
Examination of the piriformis muscle itself can be difficult, so if there is no indication of damage to it, it is examined last.
If piriformis syndrome is confirmed, the study begins with an MRI of the lumbar spine and ultrasound of the pelvic organs. An X-ray examination of the hip joint can then be performed to possibly detect coxarthrosis at an early stage.
Causes of pathology
The disease develops when the sciatic nerve is pinched, injured or inflamed.
A variety of factors can cause this situation:
- injury to the back area;
- radicular syndrome;
- chronic diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia, arthrosis, osteoporosis, spondylitis, scoliosis, protrusion);
- benign or malignant neoplasms in the spinal column;
- infections affecting nerve trunks;
- inflammation of the back muscles;
- inflammatory processes in the blood vessels of the sacrum;
- pathologies of the hip joint;
- diseases of the abdominal organs;
- prolonged sitting;
- unsuccessful injections into the epidural cavity;
- postoperative complications.
They increase the risk of developing the disease and provoke relapses in the chronic form:
- hypothermia of the body;
- prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position;
- long work at the computer;
- improper performance of exercises during sports;
- increased physical activity;
- constant work in the garden (sometimes lumboischialgia is called summer residents’ disease);
- poor posture;
- age-related degenerative processes in the spine;
- excess weight;
- frequent stressful situations;
- depression;
- pregnancy;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking.
Piriformis syndrome
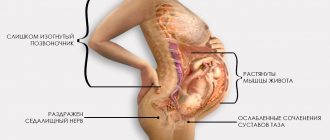
When a muscle is damaged, dystrophic changes rarely occur; contractures and myotonic phenomena are more common. All unpleasant sensations in this syndrome are associated with infringement by the inflamed and spasmodic piriformis muscle of the sciatic nerve, pudendal nerve, posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh, inferior gluteal nerve, gluteal artery and vessels of the sciatic nerve.
The pain syndrome is localized in the gluteal region and can spread to the groin, upper thigh, and even lower leg. Aching, pulling pain can occur in the buttock, sacroiliac and hip joints. It intensifies when walking, in a long standing position, and when the hip is adducted. The pain subsides somewhat when lying down or sitting with legs apart.
When the sciatic nerve and its vessels are compressed, the pain has a pronounced vegetative nature: sensations of chilliness, burning, and stiffness occur. Short-term spasms of the vessels of the leg are possible, leading to intermittent claudication - the patient is forced to stop, sit down or lie down when walking; the skin of the leg turns pale; After rest, the patient can continue walking, but soon the same attack recurs.
Often, tonic tension of the piriformis muscle is combined with a similar condition of other pelvic floor muscles. With piriformis syndrome, there are almost always mild sphincter disorders: a short pause before urination begins.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of lumboischialgia is acute lumbago (sharp pain of a shooting nature) in the buttocks and back of the legs, radiating to the lower extremities. The pain is provoked by sudden movements, lifting heavy objects, sneezing, coughing. Attacks can last several minutes or several days.
The patient may experience other symptoms:
- decreased or loss of sensitivity in the skin of the buttocks and affected leg;
- stiffness in the lower back;
- muscle tension;
- pain when standing on your leg;
- cramps in the calf muscle;
- numbness of the toes;
- pallor of the skin in the sacral area;
- increased body temperature;
- chills and fever;
- weakness in the legs;
- indigestion;
- difficulty and pain in urination and defecation;
- itching, burning or subcutaneous throbbing.
If left untreated, blood circulation is impaired. Over time, lumbago with sciatica can cause urinary and fecal incontinence, sexual dysfunction, cause a decrease in muscle mass in one limb, and lead to disability.
Characteristic
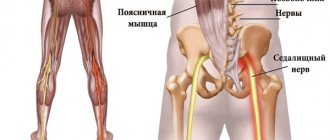
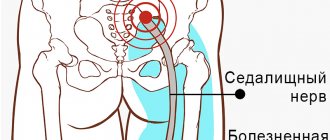
The largest nerve in the body is formed outside the spinal canal (in the pelvic area). The nerve goes through the gluteal opening, is closed by the muscle, then goes down to the back of the thigh, moving to the lower leg.
In the popliteal region it is divided into the medial thick tibial branch and the fibular lateral branch. They pass along the leg, then approach the foot and hand (phalanxes).
It is thanks to the sciatic nerve that full mobility of the legs and the activity of the small pelvis are ensured.
When a problem such as sciatica appears, it is important to begin diagnosis and treatment as quickly as possible, otherwise you may end up with disability.
Diagnostics
The doctor will be able to draw preliminary conclusions by studying the medical history and examining the affected area.
To confirm the diagnosis, determine the cause of the disease and determine the condition of the tissues, he refers the patient for diagnostics:
- radiography;
- ultrasonography;
- densitometry;
- computed or magnetic resonance imaging;
- blood test for infections and autoimmune diseases;
- analysis for tumor markers (if a tumor is suspected).
Orthopedic products for the treatment of sciatic nerve
Both with neuritis and with muscular-ligamentous pain after defeating an exacerbation, it is important to eliminate the cause. Pay attention to how you walk, sleep and sit. Orthopedic insoles and special pillows for sitting and sleeping help to correct unfavorable factors.
A special feature of our stores is our specially trained consultants. They will help you choose the best set of orthopedic products, taking into account the doctor’s recommendations and the manifestations of the problem. All stores have the possibility of plantoscopy, and in many also computer diagnostics of the feet, which are the foundation for the whole body.
Treatment methods
Treatment of lumboischialgia consists of two stages: medication and complex.
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating muscle spasms and relieving pain. The patient must be prescribed bed rest (for a couple of weeks). In this case, the bed should be flat and firm. For particularly severe pain, it is recommended to use a corset.
Drug treatment includes taking:
- anti-inflammatory medications – relieve inflammation, relieve pain;
- analgesics – relieve pain;
- muscle relaxants - eliminate muscle spasms;
- vasodilators - activate blood circulation and accelerate metabolism;
- diuretics – have a diuretic effect, eliminate swelling, remove toxins from the body;
- antidepressants – relieve depression, nervousness, fears;
- vitamin complexes - provide the body with useful substances, accelerate regeneration, help restore nerve structures and improve conductivity.
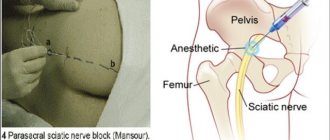
Local agents (ointments, creams and gels) that improve blood circulation and have an analgesic effect will help increase the effectiveness of treatment. For severe, unremitting pain, blockades with novocaine or glucocorticosteroids are made.
Under no circumstances should you massage or knead the sore area, as this can lead to a significant deterioration in your well-being.
After the pain disappears, they move on to the second stage, aimed at eliminating the cause of the pathology.
For complex therapy the following is used:
- physiotherapeutic procedures (shock wave therapy, ultra-high frequency therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis, ionization, Bernard currents, laser therapy, magnetotherapy, electrotherapy, diathermy, reflexology, ozone therapy, muscle relaxation, paraffin baths) - effectively relieve inflammation and pain, restore the functionality of the lower back;
- physical therapy – special exercises are selected to relieve pinched nerves.
Additionally, you can use traditional medicine recipes.
In difficult cases (for example, if lumboischialgia is combined with an intervertebral hernia), surgical intervention is resorted to.
Shock wave therapy treatment
Among physiotherapeutic procedures, shock wave therapy is the most effective.
During the procedure, the affected tissues are exposed to acoustic shock waves of a given frequency, which are generated by a special sensor. The therapy has a complex effect on all components of the pathological process: destroys salt deposits, increases blood flow in capillaries tens (and sometimes hundreds) times, normalizes metabolism, improves cell nutrition, eliminates muscle spasms and inflammation, relieves pain, and restores spinal mobility . In addition, it activates the body’s own forces, contributing to its restoration and return to a full life.
Quite often, when drug treatment fails, shock wave therapy leads to complete recovery, making it a worthy alternative to injections and avoiding surgical treatment.
To increase the effectiveness of the procedure, individual parameters are selected on the device for each patient, taking into account the general condition of the body and associated pathologies.
The full course of treatment includes 8-10 weekly procedures.
Techniques and features of various types of massage for sciatica
Classic manual massage
A relaxing massage during an exacerbation helps to warm up painful areas, improve lymph and blood circulation, which helps reduce pain. Usually, even after the first session, patients feel relief.
General massage technique:
- The patient lies on his stomach and is as relaxed as possible.
- The painful area is warmed up by stroking.
- The massage uses circular and ridge-like movements, without putting pressure on the affected areas.
- Finish the massage with light strokes.
, the entire back or also the leg (for lower sciatica) is massaged in the same way . During pain, intense exposure should be avoided: vibrations, tapping, strong rubbing. All this will only increase the spasm, and will not make the patient’s life easier.
Any massage for sciatica should be done with caution due to the proximity of the spinal cord to the site of inflammation. Ideally, even a relaxing massage is best left to a professional, but if there are no contraindications or spinal injuries, loved ones can help with it at home.
Therapeutic massage, which is performed during remission and is much more intense, should only be performed by a specialist.
Video: “Massage for sciatica at home”
Vacuum (cupping) massage
Did you know that...
Next fact
Vacuum treatment is primarily aimed at eliminating lymph circulation disorders in the affected area . Its normalization has a very beneficial effect on the condition of tissues and accelerates recovery. In addition, cupping immediately relieves pain.
The method of placing cups for medicinal purposes, which has long been used by people, is also a kind of vacuum massage. For sciatica, you can “place cupping” to alleviate the patient’s condition and activate lymph flow.
How to place jars correctly:
- The patient lies on his stomach. To prepare the tissues, it is better to slightly warm up the lower back with stroking and a light relaxing massage.
- Place small glass jars, first freeing them from oxygen with a burning “torch” (cotton wool wound around a metal object and soaked in alcohol). It is better that the jars are special for medical purposes. In the absence of them, you can get by with small ones, such as mayonnaise ones (without sharp edges).
- Cover with a light blanket.
- The duration of the procedure is from 10 to 20 minutes. Then the jars no longer hold so tightly, and they are removed.
- After cupping, you can do a light soothing massage with stroking. It is better for the patient to lie under a blanket for at least half an hour.
You should not use large jars, this can lead to injury. It is best to place jars before bed.
Precautionary measures:
- Do not use synthetic materials for ignition: only natural cotton wool and alcohol should be used. This is important to avoid additional tissue intoxication in an already unhealthy area.
- Do not use bottles instead of jars or jars that are too large. This won't help, it will only hurt.
To perform a vacuum massage, in which cups are moved over the skin, some skill may be required. It is good if it is carried out by a specialist, but if desired, the technique can be mastered.
This massage can be done with glass jars, but it is better to purchase a special silicone one, which is much more convenient because it does not require ignition.
The sequence of such a procedure:
- The skin in the affected area is lubricated with massage oil, quite generously.
- The jar is set on fire if it is glass or the air is released by compression if it is silicone. Apply to the area where there is pain.
- Perform movements on the skin with the cup: straight, spiral, s-shaped. The movements are slow and during them the can should not lag behind the skin. If this happens, install it again.
- After the procedure, it is better for the patient to wrap up his lower back and keep warm for some time.
This massage may be a little painful, but it should not hurt too much. Duration 5-15 minutes.
Acupressure (acupressure)
Massage of active points is recognized as a very effective method of treating sciatica, but it is difficult to master and is not suitable as self-treatment . Here you need to understand well what this or that point on the body is responsible for.
The procedure is carried out in several stages:
- First, the point of greatest pain is identified by palpating the area along the sciatic nerve.
- Massage the found point and the entire painful area.
- They massage the buttocks.
- Finally, massage the meridian points of the bladder.
Acupressure of known points for the treatment of sciatica does not harm and can be used as self-help.
Usually 4 points are massaged:
- Find the point of greatest pain in the sacral region. To do this, move the muscle away from the bone using rotational movements. This is the point at which inflammation begins.
- At the bottom of the buttock there is a gluteal fossa, in which the 2nd point is located.
- The next one is under the knee, on the back of the joint.
- The lowest point is at the junction of the foot and shin, in the center.
Pay attention to which points are massaged for sciatica
Massage these points clockwise and back, or simply pressing with your thumb, for 30 seconds to 5 minutes.
Honey massage
Honey massage is difficult to classify as relaxing due to some pain , which patients report. However, the effect is only on the skin, without deeply affecting the muscles. For this reason, it is also acceptable in the acute stage of sciatica, as a good method for activating blood circulation in the tissues.
For such a massage you will need high-quality honey. The technique is not particularly difficult, it can be done at home, but, like any type of massage, it is still better to entrust it to a professional, if possible.
Sequencing:
- Apply a tablespoon of honey to the lower back, which is best warmed slightly.
- Let the honey absorb (2-3 minutes).
- Rub the remaining honey into the skin.
- Make light pats with your palms. During them, your hands will stick to the skin, and this moment causes pain. It is important not to overdo it and listen to the patient’s feelings.
- You need to finish the massage after a white coating appears on the skin.
- Remove plaque with a cloth soaked in warm water and wrap the patient’s lower back.
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of lumboischialgia, it is recommended:
- eat rationally;
- move more often;
- exercise;
- perform exercises that strengthen the back muscles and stretch the muscles;
- when doing physical work, use the principles of biomechanics;
- balance the load with the body’s capabilities;
- fight excess weight;
- promptly treat diseases of the spine, blood vessels and digestive system;
- don't get too cold.
Manual therapy of the spine: features
The fundamental principle of manual therapy is deep muscle work in tandem with dosed effects on various parts of the spine, as well as ligaments and joints. The use of such a technique allows you to: unblock pinches of varying intensity; restore mobility of the spine; realign vertebrae (displaced); block the development of hernias and protrusions, and in some cases, achieve their regression. It should be noted that treating the spine using manual techniques can enhance the effects of medications prescribed by a doctor, and in some cases, reduce their use to a minimum or even eliminate it completely.
Manual therapy (Simferopol) is justified if a person has the following problems: osteochondrosis; pain of various etiologies (chronic or acute) in some parts of the spine; chronic overexertion; compression neuropathies; joint pain or limited mobility.
After a course of procedures (the duration and intensity is determined by the doctor), pain completely goes away, posture improves, as well as joint mobility.