The brain often plays a very cruel joke on us. Two people experienced the same event, but their stories differ. What is this - amnesia or a simple lie? However, everything is not as simple as it seems. Memories tend to become distorted. For example, replacing some events with others. In science, this problem is called confabulation, or paramnesia, when a person, in addition to basic memories, has false ones. As a result, it is very difficult to distinguish truth from fiction. Let's figure out what's going on here in this post.
How memories are formed
Our memory is the response of a certain group of neurons to some stimuli. They are formed due to constant changes and connections between themselves. Thus, from birth, our brain never stops working. Neurons wander from image to image and create certain thoughts.
The response is synaptic plasticity, which is permanent changes in the strength of connections (synapses) between brain cells. They may be stronger or weaker depending on how long ago they were activated. Active connections can strengthen, and unused connections, on the contrary, weaken and disappear.
Memory is divided into two categories:
- Short-term. Allows you to hold a thought for about a minute. This is necessary in order to remember a phone number, car number or a person’s last name.
- Long-term. Responsible for long lasting memories.
Long-term memory, in turn, is divided into procedural memory, which is responsible for actions, and declarative memory, which is responsible for consciously recalling information.
All memories are based on declarative memory. It can be activated visually or verbally. For example, you need to remember the names of the football team or restore your shopping list.
Declarative memory is divided into the following categories:
- Semantic. Operates with meanings and concepts. For example, what is a computer or a ball.
- Episodic. Refers to events. For example, when did you have your wedding or how long ago did you go on a catamaran?
Our memory is the reactivation of a specific group of neurons, formed by constant changes in the strength of connections between them. Reactivates a combination of neurons “synaptic plasticity”.
The contact between neurons is called synapses. He may be stronger or weaker. That is, all the connections used can become stronger. However, unused neurons weaken and disappear completely. The connection between two neurons becomes stronger when neuron A sequentially activates neuron B, causing it to fire an action potential. Neurons communicate with each other using electrical events called action potentials and chemical events called neurotransmitters. As a result of changes, additions or death of synapses, our memory is formed.
However, recent studies on elderly mice have proven that due to the hippocampus (a part of the brain), neurogenesis increases, that is, new neurons appear and our memory is restored.
I remember everything that was not with me!
Pseudo-reminiscence is literally translated from ancient Greek as “false memory.” Or a “memory” of something that never actually happened to this person.
This pathology is exclusively a product of the human brain - a type of hallucination. But hallucinations that occurred not with perception, but with its memory due to organic pathology of the brain, or as a result of the development of paraphrenic or paranoid syndrome.
Combinations of pseudo-reminiscences with truly actual memory disorders (hypomnesia and amnesia) are not uncommon.
Main causes of false memory
Research into false memory has recently begun. The founders of this trend were, oddly enough, hypnotists Pierre Janet, Richard Kraift-Ebing and others. Moreover, the latter demonstrated such a phenomenon as age regression. He immersed a person in hypnosis, and he reproduced his childhood.
Scientists immediately divided into two camps. Some believed that the hypnotized person was actually reproducing memories of his childhood. However, there were those who believed that he was simply playing some role, that is, he wanted everything to be that way. It was the work of Kreift-Ebing that gave rise to controversial discussions.
However, the real causes of memory disorders are unknown. From a medical point of view, paramnesia most often occurs in people with damage to the front part of the brain (frontal lobes).
Doctors identify the following causes of false memories:
- traumatic brain injury with Korsakov's syndrome during an exacerbation;
- cerebrovascular accident (ischemia, hemorrhagic strokes with vascular damage);
- Korsakoff's syndrome (as a result - an acute lack of vitamin B1 due to an unhealthy lifestyle or the formation of malignant tumors);
- amnestic cerebral atherosclerosis (consequences - disorientation and memory impairment);
- vascular dementia (occurs as a result of single cerebral infarctions);
- various diseases associated with memory impairment (Parkinson's, Pick's, Alzheimer's, Huntington's, senile dementia, psychotic forms of senile dementia);
- paranoid psychosis with delusions of persecution, accompanied by hallucinations;
- severe form of poisoning with alcohol, drugs, poisons, carbon monoxide;
- abscesses and tumors in the brain.
Unfortunately, false memories occur in healthy people. This is the conscious replacement of bad moments with good events. That is, a simple form of self-defense. Some people who have lost loved ones sincerely believe that they are still alive and are somewhere abroad.
Cognitive psychology professor Elizabeth Loftus has conducted research trying to understand the plasticity of human memories. She showed videos of disasters lasting 5-30 seconds and asked to fill out a report. The question was: “How fast were the cars in the video moving at the moment they crashed into each other?” However, the question was framed differently for individual groups. For example, they replaced the word “crashed” with “touched”, “hit”, “crashed”, “knocked”.
Depending on one word, the subjects changed their readings. For example, the word "crashed" made the event more terrifying, and people thought the cars were moving much faster.
In other experiments the effect was the same. The subjects provided a large amount of false evidence. For example, they claimed that some part of the car was broken or broken. Although in the video she was intact.
Thus, the cause of false memory can be not only mental disorders. It is very easy to distort facts if you insert the right words into sentences.
Fantasies of shameless flight
Confabulations - a term literally translated as “pre-composition”, unites a whole group of memory illusions, which can be:
- ecmnestic (anchored on past events);
- mnemonic (based on the present moment);
- fantastic (with the addition of imaginary fragments to actual events);
- delusional (with the addition of nonsense of ordinary or fantastic content);
- oneiric (oneiric or delirious origin);
- spontaneous (spontaneous, for example, with Korsakoff psychosis);
- induced (or suggested - in case of Alzheimer's disease).
The peculiarity of the phenomenon is embellishment-distortion uncontrollably, to the point of pathology, played out by the fantasy of an event that actually happened in the past, which now becomes a false memory.
“Diving” into the past, consciousness returns, proudly dragging behind it “to the surface” of the present time some insignificant event that happened in the past, unrecognizable, to the point of brilliance, remade by the unrestrained play of the imagination.
Confabulations arise as a result of:
- psychoses of various origins;
- paraphrenia;
- Korsakoff's syndrome;
- schizophrenia with delusional manifestations;
- exit from the twilight state of consciousness.
Types of false memories
We create some false memories ourselves. Sometimes they are imposed on us. However, all distorted reality has its own nuances.
For example, pseudoreminiscence (a type of false memory) differs from contabulation (implausible stories). Although the symptoms are very similar. If in the first case, a person who has experienced a trauma or insult for a long time begins to remember it as if it had happened quite recently. In the second case, flashbacks are decorated with made-up stories. These fantasies are typical of alcoholics, drug addicts or patients diagnosed with schizophrenia. As a result, false memory is divided into several categories.
For reasons of origin:
- delusional false memories that are not associated with mental disorders and are characterized by obsessions of the person himself;
- suggested - appear after certain prompts or leading questions;
- mnestic - replace certain gaps in the memory of the past or present;
- oneiric - occur due to intoxication of the body or brain damage;
- expansive - associated with delusions of grandeur (for example, a person sincerely believes that he is Napoleon Bonaparte).
According to provoking factors:
- spontaneous (primary) paramnesia. It arises on its own. Most often it goes in parallel with dementia, and all memories are fictitious;
- provoked (secondary) confabulation. Response to memory impairment.
They occur not only in the form of dementia, but also as amnesia. There are cases when false memories appear as a short-term phenomenon due to experienced stress.
By content:
- amnestic - a person loses a sense of reality and relates himself to the past (for example, the patient may think that he is still 12 years old);
- mnemonic - false memories about current events (they can relate to everyday life or professional activities);
- fantastic - contain numerous unreal, made-up stories, similar to detective stories or science fiction films.
At one time, the mind game played a cruel joke on some celebrities. Marilyn Monroe claimed that she was raped at age 7. However, in different interviews she named new names of the rapist.
Marlene Dietrich believed that her music teacher raped her. The police began to investigate and found out that such a person existed in reality and he really taught music. Fortunately for him, when Marlene was 16, the teacher lived in another city.
Thus, doctors first try to find out the cause and type of memory and only then begin to work with the patient.
Principles in neuroscience
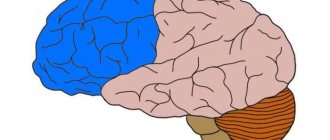
Neuroscience believes that the hippocampus and amygdala are responsible for reworking memories. By scanning the brain with fMRI and observing how areas work, it can be determined whether overwriting has occurred or not.
Location of the hippocampus in the human brain
As practice shows, a person does not always agree with what is imposed on him. Under pressure, he can admit anything, but will remain unconvinced. This is easy to prove. After repeated testing, but without pressure, the initial memory does not change.
If the subject begins to sincerely believe in an obsession, he will insist on it in any situation. That is, the original memory disappeared, and a new one appeared in its place. This phenomenon interested neuroscientists from Great Britain and Israel (source). Using fMRI, they decided to find out which parts of the brain are involved in memory distortion.
30 volunteers took part in the experiment. They were divided into groups of 5 people. Each group was shown a 40-minute video about catching illegal immigrants. All subjects were explained that the purpose of the experiment was to study memory and at the end everyone would be asked questions. Therefore, everyone was asked not to discuss the plot with each other.
After three days, the subjects answered 400 questions (true/false). Each participant had to choose an option and indicate how confident he was in the correctness of his judgments.
As a result, an average of 69% of people answered correctly (medium to high confidence). When subjects indicated this degree, 80% of them were right.
Four days later the experiment was repeated. However, now the subjects were scanned with fMRI and monitored for changes in the cerebral cortex. The questions were repeated, but now they were trying to manipulate the participants. They were allowed to rely on public opinion. That is, sometimes they showed how other subjects answered.
The questions were divided into three groups, to which the subject answered correctly and confidently.
- Manipulation. 80 questions were fabricated. He was shown a 2.5-second question with two options (true/false), followed by photographs of people and their answers, followed by a blank screen and the previous photograph.
- No manipulation. 25 questions were without other people's opinions and were marked with crosses.
- Improving trust. The remaining questions were accompanied by correct answers from other subjects or a combination of correct and incorrect opinions.
Manipulation turned out to be the most effective. About 68.3% of subjects, under the influence of others' opinions, distorted their own reality. This was not amnesia, not forgetting, since only in 15.5% of cases in the absence of manipulation the answers were incorrect.
In the third experiment, which was carried out a week later, the subjects were asked the same questions. However, this time everyone was told that the past answers were randomly generated by a computer. This time, 59.2% returned to the original option. However, 40.2% still answered the same as in the second test. That is, stable conformism completely replaced the memories of the subjects.
fMRI allows you to record areas of the brain that are actively working at a certain moment and therefore require additional oxygen flow.
The images showed that the brain is active in the following situations:
- Nonconformism. When a person answers correctly regardless of the opinions of others.
- Public conformism. When the opinions of others initially influenced the answer, but then the subject returned to the initial option.
- Persistent error. Memories are replaced by false ones.
- Control. No manipulation.
What does psychotherapy think about this?
Unlike neuroscience, in psychology everything happens a little differently. The main mechanism of false memories is cognitive dissonance, when we perceive and analyze any information based on previous experience. This refers to all of psychology as a whole: values, beliefs, morals, character, etc. Simply put, if something does not agree with something, a person tries to explain to himself what happened in other words.
For example, when studying sects, some facts emerged. When the promised apocalypse did not occur, one half realized that they had been deceived. The other half continued to believe in the idea despite the lies.
In the 1990s, Mavrodi directly said on television that he had deceived everyone. However, many did not want to admit it. Some people continued to have a portrait of the “great schemer” hanging on their wall.
That is, a person does not want and cannot accept the truth. Memories are stored in our memory in the form of certain image patterns. They are constantly changing and adjusted to new information.
Thus, each mechanism of false memories can be described:
- Inflation of the imagination. A person remembers a fictitious event as if it were real.
- Interference. Sorted memories get mixed up and often people become victims of stereotypes. For example, in the USA the first suspicion falls on a black person. In the early 1990s, under the influence of American and Chinese militants, our compatriots thought that all Asians knew karate techniques.
- Hindsight bias. Consciousness tends to perceive initially predictable results, that is, information that is already known, but previously the person doubted it.
- A false sense of knowledge or uncritical perception of information. That is, some image pops up in your head, but who or what it is is hard to remember. Thus, the media, esotericists and sub-psychologists manipulate consciousness. They repeat the same information many times until the person begins to believe it.
- Conformity of memory. Changes in memory under the influence of society.
- Emotional distortion. Real events that take on new colors under the influence of emotions or stress. For example, psychologist F. Shapiro had a case when a client sincerely believed that she was raped by the devil. However, it turned out that she was actually raped, but it was an acquaintance of her father who was wearing a hat with horns.
Misrecognition
False recognition is the erroneous recognition of persons or objects, areas, premises, or even oneself (for example, a person does not recognize himself in the reflection). With severe memory impairment, recognition of family and friends is impaired. Most often found in schizophrenia.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yj2A57269nQ
The occurrence of paramnesia is often caused by a person’s increased suggestibility, infantilism of the psyche, certain emotional characteristics and lack of criticality, therefore the prevention of this condition is greatly facilitated by personal growth and work with a psychotherapist.
How false memories affect work
Apart from extreme cases and pathologies, false memories do not create problems. Valerie F. Reyna, a researcher in the field of psychology, believes that as we age, we rely more on semantic memory than on reproductive memory. A form of memorization allows us to make safer decisions and reduces risk.
This phenomenon explains the Allais paradox, named after the economist and Nobel laureate Maurice Allais.
The subjects are given a choice - the probability of receiving money and the final amount.
Experiment No. 1
| Situation | Probability 1 | Probability 2 | Probability 3 |
| A | 100%, £1 million. | — | — |
| IN | 10%, £2.5 million. | 89%, £1 million. | 1%, nothing |
Experiment No. 2
| Situation | Probability 1 | Probability 2 | Probability 3 |
| WITH | 10%, 5 million | 90%, nothing | — |
| D | 11%, 1 million | 89%, nothing. | — |
Allais found that subjects do not like to take risks and choose the safest option. In experiment No. 1, situation A is most often chosen. In the second experiment, situation C is chosen. That is, a person artificially reduces risk and prefers absolute reliability.
One example of the Allais paradox in the film "The Matrix"
Valerie Reyna relates this paradox to rewritten memories as follows. Unlike real memories, false memories allow you to deal with stress and create a certain comfort zone, that is, they also minimize risk.
For example, students who read the same textbook may have differences of opinion. The whole problem is that we are used to thinking about the ideality of our brain. However, it is not. In any case, dying neurons will be filled with something. In this case, semantic memory will help adapt to the new reality. Just don't confuse false memories with dementia.
Progression of the disease can lead to the following complications:
- sensory disturbance;
- partial or complete paralysis;
- development of dementia;
- complete loss of memory;
- disability.
Paramnesia - the taste of a non-existent life
Paramnesia (“parallel”, false memories) is a common attribute of neurological and mental diseases.
But this is not necessarily the case. In one form or another, it can also be characteristic of creative and artistic individuals (or simply overly sensitive and impressionable).
It is also characteristic of ages “specially created” for it – children’s and old age. Ages when there is still – or no longer – enough strength to create in matter.
A separate category is the disabled. Not disabled people from childhood - with unawakened feelings and brains - but disabled adults who have already learned the power of life, and then, for one reason or another, lose it irrevocably.
The cause of the condition may also be chronic, ongoing intoxication (both as a result of alcoholism, and as a result of a chronic infection, for example, with tuberculosis).
In a word, paramnesia is the essence and destiny of those powerless to create physical life. But only those who already know (or still remember) its taste.
And on the basis of this memory and knowledge they create a new life - a life based on false memory. With myself (not realized in true life) in all the main roles.
But there are a great many main roles. This means that there must be no less options for “plot development” in order to be able to play them all.
And they exist. Here they are.
How to distinguish false memories from real ones
On our own, we will not be able to distinguish truth from lies, since we do not have a value judgment. Only a few realize that their memories are false. However, it is very difficult to prove this without outside help.
A psychotherapist will also not be able to make an accurate diagnosis without preliminary research. He needs to know the personality type, conditions and nature of growing up.
Brain scans using MRI or ultrasound may show physical damage. However, deception has no material embodiment. Therefore, the only way is differential diagnosis.
To do this, deliberate substitution of memories is used:
- The Diz-Rodriguere-McDermott paradigm. They let you listen to a recording that contains several lists of words related thematically. If the subject names a word that is not there, this is a sign of confabulation.
- Recognition and memory tasks. The therapist shows the pictures several times. Some appear only once. Then they are asked to select the images that were shown to the test taker. If he selects pictures that were not there or were shown only once, this indicates false memories.
- Memory tasks. Famous tales must be told. If there are disagreements with the source, then there is a possibility of memory substitution.
To identify memory pathologies, you first need to contact a psychiatrist, who can write a referral to another specialist (psychotherapist or neuropsychiatrist).
Treatment in clinics
Since the problem of false memories is not fully understood, there are no exact treatment methods yet. Doctors prescribe medications to strengthen the blood vessels of the brain, improve blood supply and metabolism of its structures. Vitamin-mineral complex and antioxidants are used as additional preparations.
After the diagnosis is established, the underlying disease is first treated. If the pathology does not disappear, medications are prescribed to reduce the progression of the disease.
Hypnotherapy, relaxation techniques, qigong, and yoga are used as psychological influences. However, without the patient's cooperation, treatment is impossible. Timely consultation with a doctor can improve memory and correct the patient’s condition.
Prevention
It is not possible to completely get rid of false memories. However, we can improve memory and reduce the risk of replacement.
In this case, doctors recommend:
- give up or reduce consumption of alcohol and tobacco;
- monitor your blood pressure to avoid stroke;
- exercise carefully to avoid head injuries;
- undergo regular examination by a neurologist and treat emerging diseases;
- eat healthy (using a balanced amount of vitamins and minerals).
To train your memory, psychologists recommend doing simple exercises: learning poetry, repeating the multiplication tables, comparing facts and reading information from different sources.
Treatment
Currently, there is no specific drug treatment that could restore memory processes, since there is no proven and tested pharmacological agent.
Indirect treatment methods are mainly used, among which the following are worth noting:
- treatment of underlying mental illness;
- the use of nootropics that restore brain structures, these include nootropil, phenotropil and many others.
- stabilization of blood circulation in the main brain structures;
- psychotherapy;
- diagnosis and exclusion of traumatic situations in a person’s life, elimination of stress.
Treatment must be carried out under conditions of clinical observation; constant registration of all changes is necessary. Treatment depends on the specific features of the underlying pathology that the person suffers from. In addition to nootropics that accelerate the functioning of nerve cells, vitamins and antioxidants are prescribed
It is also important to ensure and create a favorable environment around the patient. The patient should be limited from any factors that provoke stress.
Differential diagnosis
Paramnesia is a short-term phenomenon of memory loss. The psyche can thus protect consciousness from the consequences of negative experiences. That is, it deliberately blocks bad memories.
Often manifestations of paramnesia intersect with delusional states. Delusion is also an implausible perception of reality. However, delirium is practically untreatable and is caused by mental disorders.
To diagnose paramnesia, a psychiatrist must conduct a thorough examination. Simple tests (ECG, MRI of the brain) will not help in this case. An incorrect diagnosis can forever plunge the psyche into a state of persistent disorder. And there are quite a lot of similar cases known.
We all come from childhood. Perhaps this phrase is perfectly suited for the treatment and prevention of paramnesia. The task of the attending physician is to eliminate from the patient’s life experiences that contribute to the occurrence of paramnesia.
Family help is also invaluable. Relatives should be nearby and support a mentally ill person in every possible way. It is worth noting that people of art (artists, painters, musicians, etc.) are more susceptible to such conditions.
Classification
Confabulation as a symptom is observed in various psychopathologies. Accordingly, in each specific case there is a different etiology, different depth and severity of memory impairment, and different accompanying symptoms. As a result, the manifestations of such a disorder are also quite different.
For this reason, in psychology and psychiatry, confabulations are divided into two main groups, in which the patients’ fiction differs both in its content and in its original origin.
By content
Mnemonic.
False memories affect everyday life or professional activities in the current time. Ecmnestic confabulation most often accompanies progressive amnesia in middle-aged and elderly patients.
False memories are associated with the past: from youth to childhood. There is no idea of real age and present time.
Fantastic. Such memory deception is a typical symptom of paraphrenic syndrome - a combination of affect with delusions of grandeur, influence and persecution. False memories differ from all previous forms in their scale of unreality: from historical events of the distant past to the no less distant future. Often this type of confabulation runs parallel to paraphrenic delirium.
By origin
Suggested is the most common form. It is expressed by a laconic and expected answer to the question posed. No matter how absurd the tips are, the patient does not notice the catch.
Spontaneous - the patient tells impressive stories invented on the spot. He answers the question posed incorrectly, while embellishing his answer as much as possible in order to impress the listener.
Oneiric - caused by a violation of consciousness of the productive type. Fictional memories relate to the subject of psychosis experienced in schizophrenia, oneiric syndrome, hallucinations or epilepsy.
Occasionally occurs in organic, infectious or intoxication psychosis.
Expansive - fictitious facts are associated with delusions of grandeur and obsessions, when the patient considers himself a genius, extremely rich and even a titled person.
Replacement mnestic - confabulation is expressed by replacing memory gaps with events of both past years and the present.
Delusional - does not refer to clouding and memory impairment. Arises as a result of the patient's delusional ideas. Typical of the paranoid syndrome of schizophrenia.
What is the danger?
A person who accumulates unfinished gestalts concentrates within himself a great feeling of dissatisfaction (did not say, did not finish, did not live some moment to the end). In a word, he did not complete a separate process of his life. This leads to a person’s constant return to a certain situation, to a loss of energy and resources. You experience and replay this situation again and again, imposing other people’s roles on your loved ones.
Symptoms of incomplete gestalt are decreased performance, constant tension, unreasonable feelings of anxiety, irritation, psychological discomfort, and insomnia. More serious consequences: a deep feeling of dissatisfaction with life, neuroses, chronic stress, depression, somatic illnesses.
Symptoms of mnemophobia
The severity of symptoms in mnemophobia depends on the individual characteristics of the body and psyche, on the level of stress tolerance, tendency to anxiety, and also on the duration of the phobic disorder. As with all phobias, the symptoms of mnemophobia manifest themselves at the somatic, mental, cognitive and behavioral levels.
At the somatic level, mnemophobia is manifested by the following symptoms:
- fainting and dizziness;
- headaches and migraines;
- tremor;
- increased, uneven pulse;
- feeling of suffocation, shortness of breath;
- heart pain, chest spasms;
- gastrointestinal disorders, colic, abdominal pain;
- increased sweating;
- constant feeling of thirst;
- nausea, vomiting that does not bring relief;
- blurred vision, “circles”, “dots” before the eyes;
- frequent deurination.
On a psychological level:
- Obsessive anticipation of a new anxiety attack.
- Pessimistic view of the future.
- Inability to switch from thoughts about memories to anything else.
- Acceptance of unreal images and events as real, occurring in the present period of time.
- Depersonalization – separation from one’s own self, loss of a clear sense of self
- Fear of losing your mind.
- Fear of not being able to control your actions and behavioral reactions.
- Distraction of attention.
- Decreased efficiency of thought processes and intellectual work.
At the cognitive level:
The individual is prone to hypochondria - fixation and exaggeration of physical ailments.
The following behavioral reactions are characteristic of mnemophobia:
- An uncontrollable desire to flee when faced with negative circumstances reminiscent of the past.
- Insomnia, drowsiness, sleep phase disturbance.
Heal old wounds and traumas
This may require either a psychotherapist or independent practice. The simplest thing you can do with this load of trauma is to burn them. Try to write down in a notebook for a week or two everything that stirs your soul and everything that emerges of its own accord with someone’s words or actions. It is best to carry a notebook with you everywhere so as not to miss a single negative emotion.
Remember all the bad things that happened in childhood and adolescence and carefully write down all the hurtful words and negative emotions that you experienced then. And after a couple of weeks, burn all this writing somewhere in a forest park and scatter the ashes. You are almost free. However, there are other healing options.
Focus on your present
It's not as hard as it seems
Pay attention to what you want right now, or what you are wearing. Ask yourself the question: what is your joy and what is most valuable to you at this moment?
Try to do this whenever you are carried back into the past, both into the terrible and the beautiful.
Accept that everything goes away
Both bad and beautiful. It is normal that one stage ends and the next begins. Moreover, the next one may be even more beautiful than the previous one.
Don't hold back your emotions if the past was terrible.
It doesn't matter how much time has passed since the tragic events. You have the right to talk about it, and even shout it out. If you want to send the past to hell, you must release it with your emotions.
Make plans for the future
Don't even be afraid of wanting to make your dream come true. Write down in detail your plan to achieve any of your goals and to realize your desires. This will definitely help you focus on the present and even enjoy it.
Send love and forgiveness to your past
If you constantly scold yourself for your mistakes, actions and misdeeds, as well as wrong choices, then you will live in the past all your life. It’s better to convince yourself that in your past you acted exactly as you could and based on your capabilities, experience and level of development in general at that time.
You may have committed the offense because you were scared, did not feel any support, were unsure or confused, that is, you succumbed to the emotions that were then a natural reaction to what happened.
Think about what you learned then and what good this situation brought to you today. Show your past self love and sympathize with this person. Speak to your then self the words you needed and talk about what you have learned over the years.
Try to forgive the people from that time
Perhaps now you are blaming not yourself, but your parents, children from a parallel class who bullied you, or the first man. What to do with them? Forgive too, just as you forgave yourself. Now they are also different, and you constantly think about people who no longer exist. Perhaps they also learned from their mistakes, and at that time they simply did not know how to act differently.
Instead of thinking about how to take revenge on the offender and about how the earth generally bears such people, live your life. And if this is truly a hopelessly bad person, retribution will definitely find him.
Thank your past for wisdom
Even if the situation was terrible, you got through it and became better, more experienced and wiser. This is the only thing worth thanking your terrible past for.
You can reflect on your thoughts and write down exactly what you learned from this situation, person, or your own action. Write it all down in a few bullet points.
Make a note of how your life changed after what happened, what you comprehended and realized after this story. These are the pearls of wisdom, and the rest is river silt and garbage that can be thrown away without regret.
Get to work
And not only her. If you spend too much time dwelling on your past, you may simply have too much free time. And he can be occupied with more sensible things. Find a job that you enjoy and devote all your days to it.
If you still have enough strength after this, including heavy thoughts about the past, devote your evenings to hobbies. Enjoying the present, you will not notice how you let go of the past and there will be very little of it in your life. Being active in the present will help you let go of the past.
Don't forget about the good
You only need to let go of the bad things from the past. But good memories and your achievements from the past are proof that you can have a good life and you are capable of much. All this should be preserved.
Pathogenesis
Memory processes are realized with the participation of modality-specific centers of the cortex, where information is received from analyzers, and non-specific structures - the hippocampus, thalamus optica, and cingulate gyrus. Specific (according to the modality of analyzers) cortical sections interact with speech zones, as a result of which memory moves to a more complex level of organization - it becomes verbal-logical. The selectivity of memory is ensured by the activity of the frontal lobes, and the general ability to remember and reproduce is ensured by the brainstem and reticular formation.
Memory disorders are characterized by dysfunctional brain structures. With a decrease in tone, diffuse organic processes and damage to the subcortical-stem sections, all types of mnestic processes worsen: fixation, retention and reproduction. The localization of the focus in the frontal zones affects the selectivity and purposefulness of memorization. Pathology of the hippocampus is manifested by a decrease in long-term memory, impaired processing and storage of spatial information (disorientation).
Types of memory disorders
Memory diseases occur from a blow to the head, old age, stroke and alcohol. Amnesia can be fleeting and smoothly flowing. A person may forget his name, but remember his professional skills. Only parts of the events that take place can disappear from memory, or your whole life, along with your biography and surname, can disappear.
Such cases are told in movies. Too frequent memory loss in able-bodied, healthy men suggests that special drugs have been developed to eliminate memory. A person who does not remember himself can become an obedient doll in the unkind hands of others.
Korsakov's syndrome
Disorientation in time, the inability to remember present events with a complete memory of the past, is called Korsakoff's syndrome. Patients begin to believe in fictitious events that they themselves invented, and concentration is impaired.
These symptoms are the result of endless drinking, malnutrition, and sometimes head bruises. Young people who give up alcohol can recover by taking medications that improve brain function.
For those who continue to drink after 65, the prognosis is not so positive. Fatalities that result from regular drinking bouts are not uncommon.
The choice is yours! Vodka or life!
Dementia (dementia, senile insanity)
It's no one's fault that we grow old. The natural process of withering of brain cells leads to the fact that over the years, all older people experience absent-mindedness and poor memory.
Many people experience dementia after age 65. But those who learn poetry do not become isolated in their problems, know how to communicate on social networks, walk in the park, do exercises, read about the news in the newspaper every day, and do not fall into senile insanity. Active longevity is possible if you fight adversity.
Pick's disease
Sometimes insidious diseases await a person in old age. Why they attack one subject and bypass the other is unknown. Very transient atrophy of the cortex of the frontal and temporal parts of the brain leads to the destruction of personality.
The inattention of relatives in these cases can lead to unpredictable events. Treatment does not give quick results
Sincere attention, kind words, medicine, walks, fresh air and care slow down the development of the negative process
Alzheimer's disease
Many elderly people aged over 70-80 years suffer from this disease. What to do with bad memory during these years? Train her! Learn to use a computer. Do crossword puzzles. Go visit, support forgetful friends.
Read prayers in foreign languages. Breathe fresh air. Do exercises without getting out of bed in the morning. Go to the ballet with your grandchildren.
Age-related diseases take away memories, but if you struggle, these processes slow down. Life becomes rich, interesting and long. Children should definitely support their elderly parents during these difficult years.
Cerebral atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels
Cerebral atherosclerosis is a lesion of the vascular system of the brain. If in Pick's disease pathological proteins are deposited in the cell bodies of the cerebral cortex, in atherosclerosis cholesterol plaques are deposited on the walls of the arteries of the head, gradually impeding blood circulation.
Consequences of poor oxygen supply to the brain:
- memory deteriorates gradually;
- concentration decreases;
- characterized by absent-mindedness, sleep disturbance;
- headaches, blurred vision;
- other signs of deterioration in brain function.
How to treat atherosclerosis? Fight obesity, stick to a diet without fatty, fried, smoked and sweet “snacks”. Drugs that lower the percentage of cholesterol and blood sugar, vasodilators, anti-inflammatory drugs, and vitamins will help. Walking, daily physical activity, and a balanced diet will improve the condition of blood vessels and the brain.