Causes
Cerebrovascular diseases appear for the following reasons. Not enough physical activity on the body . Muscle tissue sag and lose shape. A similar process occurs with blood vessels. If the heart muscle does not tense sufficiently, its tone is lost and the movement of blood throughout the body becomes difficult.
Nutrition problems . Regularly increasing calories has a difficult impact on your health. Veins and arteries filled with cholesterol have problems performing their functions. Each new kilogram in the body requires the formation of several meters of blood vessels. For this reason, blood pressure often decreases.
Bad habits . The fibers of veins and arteries atrophy under the influence of alcoholic beverages; under the influence of alcohol, blood clots are created, due to which the cavities are stretched. Long-term abuse of strong alcohol causes individual personality degradation, in addition to addiction.
Regular stress . In modern society, stressful situations are as harmful as cigarettes. Not everyone’s blood vessels can withstand such a load, so many people with increased nervousness experience numbness in their arms and legs, feel dizzy, and lose consciousness.
Problems with sleep and rest have become more frequent recently . People have more and more working hours. Poor sleep does not allow you to restore vital energy. This negatively affects the condition of the veins and arteries, and there are no clear symptoms indicating serious problems.
These are the main reasons, but pathologies of the blood vessels of the head may be due to poor heredity.
Diagnostics
A neurologist deals with cerebral atherosclerosis. His task is to collect anamnesis, as well as conduct a series of tests. Doctor:
- will ask you to look up (a sick person will not be able to fulfill the request);
- will check the reflexes (they will be either excessively high or low, and asymmetrically);
- will ask you to stretch your arms forward and look to see if there is any tremors in the fingers, or if the patient is losing balance;
- will ask you to touch your nose with the tip of your finger with your eyes closed (the patient will not be able to cope with this task).
This is only a small component for assessing the patient’s health. Therefore, more detailed examinations are required next:
- consultation with an ENT doctor, ophthalmologist and other specialists depending on the identified disorders;
- biochemical blood test for triglycerides and cholesterol (lipid spectrum);
- According to indications, instrumental examinations are carried out.
To assess the condition of cerebral vessels, the following is carried out:
- Ultrasound of the brain and neck using two-dimensional and transcranial duplex scanning technology;
- angiography of cerebral vessels;
- Doppler ultrasound;
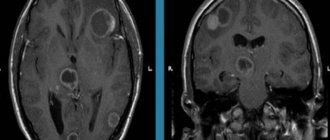
- MRI of the brain in vascular mode;
- REG (radioencephalogram);
- CT computed tomography of the brain and blood vessels;
- EEG – electroencephalogram.
The diagnostic capabilities of our multifunctional center of the FMBA of Russia allow us to carry out not only these, but also any other examinations necessary for the patient using the most modern and accurate equipment. You will be able to get advice from related specialists on any clinical case, including suspected cerebral atherosclerosis.
Signs of vascular diseases
The symptoms of the disorder depend on its location. When you constantly have a headache and feel worse in stuffy rooms, it means the person has problems with the blood vessels in the head. Symptoms are divided into two subcategories.
Are common:
- Accelerated fatigue
- Long-term depressive states.
- Memory deteriorates.
- Poor tolerance to dry or extremely hot conditions.
- Blood pressure fluctuates, tachycardia appears with little physical exertion.
Local:
- Migraine, feeling of pulsation in the head, confusion of consciousness.
- In the arms and legs, the blood vessels dilate, a tingling sensation, numbness appears, sweating increases, pain appears during physical activity, and swelling appears.
- Painful sensations and tingling in the chest area.
- Capillaries in the ENT area burst and bleed.
Regardless of the indicated symptoms, the reasons for the worsening health condition may vary. For this reason, you should not neglect going to the doctor for diagnosis. This will help avoid the following diseases: atherosclerosis, VSD, stroke, migraine. This is only part of the diseases that are caused by problems with the functioning of blood vessels.
Diseases of the cerebral vessels in the first stages are asymptomatic, so patients turn to doctors with advanced disorders. All difficulties lie in blockage and narrowing of blood vessels:
- Stage 1 . Increased fatigue, noticeable dizziness, drowsiness, problems with concentration.
- Stage 2 . Memory noticeably deteriorates, the patient cannot concentrate on anything, migraines appear regularly, the gait is uncertain, the person constantly staggers.
- Stage 3 . Dementia begins, the patient cannot control his actions and reflexes.
When the disease is too advanced, it will not be possible to get rid of it. After prolonged oxygen deprivation, neurons die and are excreted from the body in urine. Therefore, this process is irreversible.
Headache - migraine and more: why your head hurts and what to do about it
Headache - migraine and more: why your head hurts and what to do about it
Headache is probably one of the most common pain sensations in humans, both in childhood and in adults.
And it’s not for nothing that a person with a headache is called a “medical orphan.”
“He goes from an ophthalmologist to an otolaryngologist, a neurologist, a dentist, an orthopedist, a chiropractor. He is prescribed a lot of tests and
a huge number of medications, and in the end he is left alone with his headache..."
Headache (cephalgia)
- This is the most common complaint that a patient presents when visiting a doctor. And, unfortunately, he cannot always receive adequate medical care that will completely relieve him of these painful sensations.
The complexity of the problem of headache treatment
lies primarily in its pronounced etiopathogenetic heterogeneity.
In other words,
many reasons can lead to the formation of a pain syndrome
Changes in various structures
(bones, blood vessels, brain, spine, teeth, nerves, etc.) are accompanied by the same type of sensation called
headache.
The sensations may vary in intensity, localization, and frequency, but in general they significantly worsen the quality of life and in most cases require medication correction.
Relatively rarely, the causes of headaches are organic brain lesions (tumors, cysts, abscesses, inflammatory lesions of the meninges, etc.) ,
for which it is necessary to use invasive treatment methods.
In all other situations, relief (cessation) of headaches or a significant reduction in the frequency of attacks and (or) their intensity can be achieved in a conservative way using a complex of medications and additional treatment methods (physiotherapeutic, exercise therapy, massage, psychotherapeutic correction, etc.) .
But in order for the treatment to be successful
, first of all
, you need to understand what causes your headache specifically. These are not general words, since it is on this understanding that the approach to therapy is built .
Ignoring this means continuing to suffer and scolding everyone around.
The fact
that
you are
still
experiencing this pain is also your fault!
Naturally, the arguments
some,
boiling down to
the fact that
“everyone hurts”
,
“age, what do you want”
and
“this can’t be cured at all” do not stand up to any criticism
and cannot be perceived as serious.
ANY HEADACHE CAN AND SHOULD BE CURED
Causes of headache development
can be divided into several groups:
1. Inflammatory , not related to damage to the central and peripheral nervous systems
-
referred headaches
(with inflammatory processes of the paranasal sinuses and forehead - sinusitis, frontal sinuses, inflammation of the teeth, gums, bone structures of the upper and lower jaw, inflammation of the ear structures - otitis, inflammation of the salivary, lacrimal, thyroid glands, structures of the eyeball).
With all these processes, headache
is a complication of the main process and is completely relieved when it is cured
.
Painful sensations in the head are always accompanied by similar sensations in an inflammatory organ or tissue. When the acute inflammatory process passes into the chronic stage, only cephalgic syndrome (i.e. headache) often remains.
2. Inflammatory , associated with damage to the structures of the central and peripheral nervous systems
(acute lesions of the nerve trunks - neuritis, neuralgia, chronic degenerative-inflammatory changes in the nerve trunks - neuropathy, lesions of the membranes of the brain - meningitis, arachnoiditis, damage to the substance of the brain - encephalitis, meningoencephalitis, abscesses).
In these processes, headache
is one of the syndromes of a serious illness and is accompanied by a complex of objective neurological symptoms.
The mechanism of headache formation in these cases is multifactorial and includes: irritation of the meninges against the background of increased intracranial pressure, tension or dilation of cerebral vessels, pressure on pain-sensitive structures, hyperpulsation in the affected nerve trunks, etc. In all cases, along with other pathogenetic mechanisms of headache formation, a psychogenic one .
At the same time, psychogenic headaches exist both at the acute stage of the disease and at the stage of residual changes, taking into account the psychotraumatic effect of any infectious disease of the nervous system.
3. Tension headaches.
This type of headache is the most common and is associated with prolonged static load on the cervical spine. The headache is realized through irritation of the structures of the sympathetic nerve plexus of the vertebral artery at the level of the C5-C7 vertebrae, as well as irritation of the C2-C3 spinal cord roots. Involutional, degenerative, post-traumatic changes in the cervical spine contribute to such reactions. In these situations, headaches have a rather characteristic localization in the occipital region, “encompassing”, squeezing the head like a “helmet”. Often there is palpation pain in the cervical spine, a feeling of stiffness in the neck muscles, subjective limitation of neck mobility, possible sensations of tingling, “crawling goosebumps”, and burning in the occipital region.
4. Psychogenic headaches
. This type of headache is provoked by psycho-emotional stress of various origins, both as part of physiological reactions (to various everyday situations, changes in health, etc.), and as one of the manifestations of a mental disorder (schizophrenia, manic-depressive psychosis, obsessional neurosis and etc.). The nature of psychogenic headaches can vary significantly - from local, spastic, pulsating to diffuse, diffuse.
5. Headaches associated with cerebral vascular reactions.
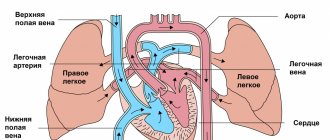
The causes of arterial vascular headaches can be various conditions accompanied by dilation of the lumens of the carotid and vertebral arteries at the extracranial level, as well as large arteries of the base of the brain (middle, anterior, posterior cerebral arteries). The main ones are: lowering blood pressure, administration of medications that cause polysegmental vasodilator reactions (nitroglycerin, papaverine, etc.), acute thrombosis or thromboembolism in large arterial trunks, increased intracranial pressure, accompanied by stretching of the walls of the deep veins of the brain, irritation of the brain shells. Headaches of this origin are constant, varying in intensity, and are often described by patients as a feeling of heaviness in the head with a predominance in the forehead and brow ridges. “Venous” headaches predominate in the morning and are accompanied by pastiness (swelling) of the upper half of the head and forehead.
6. Migraine
-
a special type of headache
, the development of which is based on a complex of pathological changes in various parts of the human body, including hormonal disorders of various origins (associated with pathology of the pelvic organs, thyroid gland, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, taking hormonal drugs, including contraceptives, etc.). d.), disorders of neurogenic regulation of vascular tone, the presence of pathological activity of brain neurons.
Migraine
- painful, usually long-term, systematically recurring attacks of headache -
is a paroxysmal condition .
In this regard, it can be classified as so-called “minor” epilepsy. A migraine attack in different people is provoked by different factors, but its clinical course is usually quite the same.
The main provoking factors include:
-increased blood pressure
-psycho-emotional load
-fluctuations in hormone levels in the second phase of the menstrual cycle
- drinking alcohol (especially red wine)
- fluctuations in atmospheric pressure.
Moreover, each of these factors in one way or another provokes the development of a spastic reaction of the cerebral arteries and subsequently initiates the first phase of a migraine attack.
In its development, a migraine attack goes through four phases:
1st phase
spastic (cerebral arteries narrow), not accompanied by headache;
2nd and 3rd phases
- dilator (cerebral arteries paralytically dilate), underlying a painful attack of headache
4th phase
- stage of residual (residual) changes (the tone of the cerebral arteries gradually returns to its original state).
In the first phase
During an attack, a variety of symptoms may appear (visual, coordination, motor, etc.), which are short-term in nature and completely reversible. This type of migraine is called migraine with aura.
In the second and third phases
attack, intense headaches develop, often of the hemicrania type (pain in half of the head), behind the eye, while it is painful to touch the scalp, photophobia, nausea, vomiting may be observed, and loud sounds are irritating.
After the attack ends
migraine develops weakness and drowsiness. During the interictal period, there are no objective clinical signs of the disease.
The process of examining and identifying the causes of headaches is even more complicated.
in every patient with cephalgia. This is explained by the fact that in the vast majority of patients, the causes of headaches are functional in nature and do not lead to visible structural changes either in the brain itself and its vascular system, or in the structures and tissues adjacent to them.
obvious
only when the patient has identified, according to imaging techniques, volumetric brain lesions, post-traumatic changes, signs of damage to the meninges, signs of inflammatory lesions of the paranasal sinuses and other organic processes of cerebral and precerebral localization.
In other situations
, in which
tension headaches and psychogenic headaches
, as well as
migraines
, there are no visible changes in the substance of the brain. The signs of damage to the vascular system and spinal column revealed are most often of a nonspecific nature.
Certain diagnostic information
can provide
a study of vessels and blood flow indicators in their lumens
at extra- and intracranial levels, as well as an assessment of flows in the deep veins of the brain.
In this case, not only background studies are important, but also reactions to stress testing
, which make it possible to assess the presence of regulatory tonic states caused by both fluctuations in systemic blood pressure and secondary extravasal effects, for example, from bone structures.
The optimal diagnostic method for these purposes is ultrasound, namely duplex scanning of extra- and intracranial segments of the brachiocephalic arteries with functional stress tests of myogenic and metabolic orientation.
To identify structural changes in the brain and bone formations
etc.
The optimal diagnostic method is magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
(if necessary, with contrast enhancement).
Verification of changes in the cervical spine, which often provoke headache syndrome, is carried out using magnetic resonance imaging
or
computed tomography.
To prescribe adequate treatment
patients with migraine sometimes require
electroencephalography
, which makes it possible to objectify disturbances in the bioelectrical activity of the brain that contribute to the occurrence of paroxysmal conditions.
At the same time, everyone seeking help for a headache should know that any instrumental and laboratory examination that is proposed to be carried out is absolutely useless if its results are not assessed by a competent clinician (neurologist) who is able to fully analyze the existing disorders and prescribe an individualized ( course of treatment that is right for you.
At the Multidisciplinary Professorial Medical Center, we offer only similar approaches to patients with headaches.
The diagnostic search is aimed at excluding organic causes of its occurrence and establishing the mechanism of development.
Treatment is selected individually; “template” schemes are not used. Therapy is prescribed only taking into account general pathological changes - the presence (absence) of arterial hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and other pathological processes.
What does MPMC "Vascular Clinic on Patriarch's" offer for headaches?
At the Vascular Clinic on Patriarch's Medical Center, we offer a full examination for people with headaches, including:
ultrasound examinations of the heart,
any vessels (aorta, neck and brain vessels, lower extremities, renal arteries, etc.),
vascular reactivity,
functions of the vascular endothelium,
properties of the vascular wall,
a set of laboratory tests, including hormonal status;
electrocardiography,
Holter monitoring ECG,
daily monitoring of blood pressure levels.
If necessary, in the conditions of an agent clinic, any computed tomography and magnetic resonance procedures can be performed for clients of our center.
We also offer an absolutely unique method, used only in large scientific centers -
transcranial Doppler monitoring with microembolodetection (the only method for intravital verification of embolism in cerebral vessels).
Our leading specialists - professors and doctors with extensive scientific and practical experience - will select the optimal therapy for your child.
We offer you consultations from the best specialists:
Lelyuk Svetlana Eduardovna
– neurologist, angiologist – teenagers from 15 years old
Malmberg Sergei Alexandrovich
– pediatric neurologist, neurophysiologist – children of any age
Ramazanov Ganipa Ramazanovich
– neurologist – adults
For in-depth examinations, our clinic has special patient examination programs for the prevention of stroke and acute coronary syndrome.
If you or your child has headaches, contact us.
We will conduct an examination and prescribe treatment.
We have every opportunity for early detection of signs of various vascular diseases.
We are ready to select effective therapy for both prevention and treatment of complications.
At your service are modern medications at reasonable prices in our pharmacy.
You can find out all the details by going to the relevant sections of the site or by calling or.
We will be glad to see you in our clinic.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis
Memory problems often indicate poor circulation in the head. When the lumen of blood vessels becomes narrow, blood flow to different parts of the brain is significantly reduced. This causes numerous violations. In addition to memory deterioration, patients experience hearing problems, increased fatigue, and poor coordination of movements.
Insomnia or waking up abruptly at night occurs when blood vessels in the neck and head become blocked. Fatigue in the morning, irritability and sudden changes in mood also require attention . Sugar addiction occurs when a large amount of glucose accumulates in the circulatory system. The brain regards this condition as a lack of micronutrients, carbohydrates and sweet foods.
Atherosclerosis occurs due to problems with hormones that affect the functioning of the sweat glands, the discharge becomes sticky and smells unpleasant. If you experience excessive sweating for no particular reason, you need to check the condition of the blood vessels.
A doctor should be consulted when gray hair appears in people under 40 years of age. When blood circulation deteriorates, problems arise with the synthesis of the protein responsible for coloring the skin and hair. Lack of nutrients causes early gray hair and pale skin . Cold hands, a feeling of heaviness in the limbs when they are lowered down, sometimes cramps appear, itching on the skin - all these are signs of circulatory problems.
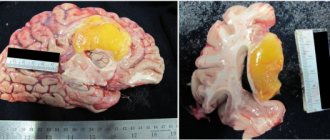
Aneurysms of cerebral vessels of various locations
The hemorrhagic period is characterized by rupture of pathologically thinned vessels and is clinically manifested by the syndrome of subarachnoid, intracerebral or mixed hemorrhage. It should be noted that with arteriovenous malformation, hemorrhages occur earlier (at the age of 20-30 years) than with saccular aneurysms (at 35-50 years), and repeated bleeding in the early stages after the first rupture of the aneurysm is much less common.
The posthemorrhagic period proceeds relatively favorably. Quite often, after the first hemorrhage, clinical recovery occurs; relapses of hemorrhage are observed after a long time and have a more benign course; Deaths due to relapses are relatively rare. Sometimes patients complain of pulsating noise in the head, exophthalmos, pulsation of the jugular veins, expansion of the saphenous veins of the head are possible, and the level of intelligence often decreases.
Diagnostic procedures
Vascular diseases of the brain are dangerous and require diagnostics in medical institutions. The procedures help to identify emerging pathology at the primary stages. After a detailed study of the etiological picture, the patient is referred to a specific doctor.
The specialist determines the feasibility of carrying out specific types of diagnostics and may prescribe one or a set of tests: MRI, duplex examination, administration of a contrast agent for tomography, blood tests and other biological materials.
Such examinations make it possible to identify the cause of spasms and problems with the functioning of cerebral vessels, and determine the course of treatment for a particular patient. In everyday conditions, such diagnostics are difficult to carry out. Therefore, going to the hospital should not be ignored if suspicious signs appear.
How to get rid of the problem?
To alleviate your condition, the patient needs to:
- Leave the patient alone, give him some motherwort.
- To eliminate headaches, you will have to use analgesics.
- If problems with the blood vessels in the brain continue, you will have to take a warm bath or give your feet a cold one.
- When the above methods do not stop the attack, you will have to consult a doctor for professional support.
- You need to wash your face with cold water.
- Lie down for a while and lay your head on the pillow.
- Massage the back of your head and temples.
- Drink some warm water and honey.
When problems with cerebral vessels appear systematically, it is necessary to determine the real cause that caused the disease. Once it is determined, it is easier to prescribe the correct treatment. The following methods are used: medications, surgery, traditional medicine.
You need to understand that treatment for spasms of blood vessels and other diseases are prescribed taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
The following are used in the form of safe medicinal methods for the treatment of mild disorders in domestic conditions: Amitripline, Anaprilin, Afabazole.
Problems with blood vessels imply a loss of elasticity. Therefore, medical procedures are carried out in 3 main directions : the use of drugs that strengthen the walls of blood vessels, thin the blood, surgery, and traditional medicine.
Medicines: drugs that improve lipid metabolism, sedatives, drugs that improve the dilation of blood vessels, drugs that eliminate spasms, anticoagulants, tranquilizers. Among the folk remedies we can mention herbal tinctures and medicinal tea. Gymnastics is one of the auxiliary measures suitable for treatment.
Vascular spasms
Let's list the symptoms: often headaches and dizziness, performance deteriorates, fatigue appears, white spots flash before the eyes, tinnitus, nausea, vomiting. Severe symptoms: problems with speech, poor memory, coordination of movements worsens, the patient has poor spatial orientation, faints.
With the rapid development of vasospasm, the symptoms manifest themselves sharply. The signs will be a little milder with chronic spasms, but there may be complications afterwards. Ischemic stroke is a serious problem resulting from blockage of the lumen of blood vessels. The consequences of this disease are serious because too many neurons in the brain die.
Cerebral vasospasm appears in children, ischemia appears. As a result, mental retardation can be observed. If the violations are too serious, blindness, paresis, and neurological diseases appear. Headache becomes a more persistent symptom as you get older.
Diagnosis of vascular diseases of the brain
To “take care of your health and get examined,” you don’t need to wait until you reach pre-retirement or retirement age - many vascular disorders begin to develop in young people. What do we have to do? It is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations, even if “nothing bothers you,” and do not be embarrassed to “bother” the doctor with complaints about a change in condition.
Diagnosis of cerebral vascular pathology includes:
- Analysis of patient complaints. You should tell your doctor even such “minor” symptoms as: fluctuations in blood pressure, headaches, dizziness, forgetfulness, and weather sensitivity.
- Anamnestic information: age, presence of risk factors, rate of development of symptoms, concomitant diseases (hypertension, diabetes, systemic and rheumatic lesions).
- Examination of the patient with analysis of neurological symptoms, examination of the fundus. Body mass index assessment.
- Laboratory data: blood sugar, blood lipid profile, coagulogram, platelet count assessment. CSF analysis to detect hemorrhagic stroke.
- Instrumental diagnostic methods: CT or MRI of the head, scanning of the vessels of the head and neck, ECG.
Treatment of cerebral vasospasm
Therapeutic techniques:
- Give up alcohol, tobacco and other bad habits.
- Stick to the established diet.
- Sanitation of infectious foci taking into account dental treatment.
- Elimination of spasms using calcium.
- Accelerated relief of painful symptoms through injections of Eufillin, Papazol.
- Use of nootropic drugs.
- Means that allow you to correct the functioning of the blood vessels of the head.
- Use of adaptogens.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- You need to massage the collar area.
- Go to sanatoriums.
When treating cerebral vasospasms, it is necessary to follow the system established by the doctor; in order to achieve a sustainable result, you will have to take 2 or more courses.
Prevention
You need to eat right and watch your own weight. In the morning, doctors advise eating whole grain porridge, seafood is suitable for lunch, and vegetables are a must. It is advisable to limit the intake of fatty and dairy products, and reduce the amount of sweets to a minimum .
Doctors often advise giving up fatty foods, fried, canned foods. As for drinks, it is better to give preference to herbal tinctures that can strengthen blood vessels. You need to drink at least 2 liters per day. This makes it possible to avoid stagnation in blood vessels and the accumulation of harmful microelements.
Some traditional medicines help improve blood circulation and have a beneficial effect on the walls of blood vessels. Garlic has a positive effect on the tissue of veins and arteries. The cloves are crushed into a paste, mixed with vegetable oil, and a little lemon juice is added every other day. Use the product in the morning, 1 tea. lie within 3 months.
Physical activity helps strengthen blood vessels and helps maintain their tone. Problems with the veins and arteries of the brain are treated in the primary stages. Often, therapeutic methods involve lifestyle changes, giving up bad habits, regular exercise, and light medications.
Diet
Changing your diet is also a way to improve your well-being and is a great help for other treatment methods. Atherosclerosis very often progresses precisely against the background of poor nutrition and lifestyle, so it is necessary
- follow a certain diet:
- reduce consumption of red and fatty meats and meat in general;
- limit the consumption of confectionery products and baked goods;
- eat as few egg yolks as possible;
- limit solid vegetable fats – margarine – in the diet;
- completely eliminate alcohol, sausages, fast food, and canned food.
Recommended products include vegetables (fresh, pickled, dried), cereals (rice, buckwheat, barley, millet, oats, flax, etc.), dried, fresh and dried fruits, turkey and chicken fillets, river and sea fish.
You need to eat at least 5 times a day at the same time in small portions. It is necessary to avoid fried foods and prepare food using the methods of boiling, steaming, stewing, and baking.