Neonatal asphyxia is a clinical symptom in which a child immediately after birth does not have spontaneous breathing and oxygen does not reach the brain. Normally, a newborn should take his first breath and cry almost immediately as he is born, but sometimes this does not happen for various reasons. Severe asphyxia can cause permanent damage to a baby's brain, so it is extremely important to prevent it and treat it as quickly as possible.
Asphyxia is closely related to birth trauma in the infant. A large number of children with such consequences of asphyxia, such as delayed psychomotor development, stunted growth, poor academic performance, low or high tone, hearing and vision impairment, pass through our center every month. Although many of these children can be helped by osteopathy, it is much better if asphyxia could be avoided altogether.
The happiness of an osteopathic doctor, as well as of parents, would be if all children were born absolutely healthy. Simple rules of prevention during pregnancy and before childbirth can dramatically reduce the likelihood of complications in the child and prevent such undesirable phenomena as asphyxia and its consequences. It is much easier and more pleasant to prevent a disease than to treat its complications.
Varieties, reasons
Brain edema occurs:
- vasogenic;
- cytotoxic;
- interstitial;
- osmotic.
The signs of cerebral edema depend on the type of developing pathology.
Causes of disease progression:
- Vasogenic edema occurs due to increased cerebral vascular permeability.
- Cytotoxic is the “swelling” of brain cells due to an increase in the amount of fluid inside them.
- Interstitial edema develops when there is increased pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain.
- Osmotic edema - with an increase in the osmolarity of brain tissue.
The most common reasons that cause brain swelling are: brain injury and disruption of its tissues in various pathologies.
Brain edema most often occurs in the following pathological conditions of a traumatic nature:
- brain contusion;
- fracture of the base of the skull;
- intracerebral hematoma;
- subdural hematoma. The prognosis of surgery for cerebral edema depends on its size.
The described pathology develops against the background of such organic brain lesions:
- ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke;
- hemorrhage under the arachnoid membrane;
- tumors;
- infectious diseases - encephalitis (inflammation of brain tissue) and meningitis (inflammation of the meninges).
Extracranial causes of cerebral edema can result from:
- Quincke's edema is a severe allergic reaction of the body;
- infectious diseases - scarlet fever, measles, mumps;
- diabetes;
- liver failure;
- alcoholism.
On our website Dobrobut.com you will find more information about the causes of cerebral edema in a newborn child, the development of pathology in the elderly and other facts.
Treatment and prevention of asphyxia in newborns
Treatment of severe asphyxia should begin immediately after birth. To do this, the child is sucked out of the mucus from the respiratory tract, stimulated breathing with special techniques, and given oxygen. In the most severe cases, resuscitation incubators for newborns are used.
Asphyxia can be prevented by careful preparation for childbirth during pregnancy, and osteopathy is very helpful in this. Osteopathic techniques for working with pregnant women are aimed at improving the condition of the uterus and pelvic organs, improving blood circulation, reducing tone, and optimizing the position of the baby in the uterus before childbirth. If a woman’s body is balanced, then no unforeseen circumstances arise during childbirth, the baby is born unhindered and is not threatened by severe asphyxia. Read more about the work of an osteopath with pregnant women in the article Preparing for childbirth and the correct position of the child before it.
Our doctors have extensive experience working with expectant mothers, constantly improve their skills through advanced training courses, and attend scientific symposia on the problems of osteopathic care for pregnant women and infants. From experience, we can say for sure that careful preparation for childbirth, including osteopathy, significantly reduces the risk of complications and asphyxia during childbirth, guaranteeing the safe birth of your baby and good development in the future.
Signs of cerebral edema
Symptoms depend on how quickly brain swelling develops.
Signs of acute cerebral edema:
- disturbance of consciousness - from slight stupor to a state of coma with cerebral edema;
- convulsions – occur as swelling progresses;
- muscle atony – develops after seizures;
- membrane symptoms.
Gradual increase in edema – additional symptoms of cerebral edema in adults:
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief;
- movement disorders;
- visual and speech disorders;
- hallucinatory syndrome.
Signs indicating critical development of the condition:
- paradoxical breathing (deep breaths with long gaps between them);
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- unstable pulse;
- increase in body temperature above 40 degrees Celsius.
The appearance of such signs indicates compression of the brain stem, which leads to death.
Brain swelling
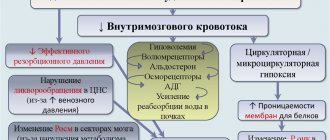
To date, researchers have clearly identified the main mechanisms of brain dysfunction during brain swelling. The brain becomes larger in volume, but the intracranial space cannot increase, which causes a mass effect. Secondary damage occurs—compression of the brain. Accordingly, an increase in intracranial pressure, a decrease in cerebral perfusion pressure is recorded, and blood circulation in the brain is disrupted. This means that cerebral ischemia has occurred. The metabolism of its tissue switches to the anaerobic type.
The following factors play a role in the pathogenesis of the disease in question::
- vascular
- circulatory
- tissue
Vascular factor means a violation of vascular permeability, which causes the penetration of blood plasma components and proteins into the brain tissue. As a result, the osmolarity of the intercellular fluid increases and cell membranes are damaged.
Researchers divide the circulatory factor An increase in blood pressure and dilation of the arteries of the brain cause a significant increase in pressure in its capillaries. Water is filtered from them into the intercellular space, resulting in tissue damage. The second link is damage to tissue elements; there is a tendency to accumulate water due to insufficient blood supply to the brain.
The concept of the pathogenesis of cerebral edema was presented in the form of a progression model according to the fundamental concept of Monroe-Kelly, which states that there is a connection between the components of the rigid skull (blood, brain, cerebrospinal fluid). That is, if one of the components increases, then the others decrease in the same proportion, this allows the body to maintain normal pressure inside the skull.
In an adult man or woman, the pressure inside the skull in the supine position ranges from 3 to 15 mmHg. It can reach 50–60 mmHg if there are the following factors:
- sneezing
- cough
- sharp rise in intra-abdominal pressure
Such fluctuations do not last long, and therefore do not cause disturbances in the human central nervous system.
Intracranial pressure refers to the uniformly distributed pressure in the cranial cavity. In an adult, the brain and the tissues surrounding it have a certain constant volume, which is limited by the rigid bones of the skull. The contents of the cranial cavity are conventionally divided into 3 parts:
- brain parenchyma,
- liquor,
- intravascular volume of arterial and venous blood
Of 100% of the intracranial volume, 80–85% is brain matter. Liquor takes up 5–15%, and blood accounts for 3–6%.
Degrees of intracranial hypertension:
- I – pressure inside the skull is increased from 15 to 20 mm Hg;
- II – 20-40 mmHg;
- III – from 40 mm Hg.
At each stage of progression of intracranial hypertension there is a corresponding mechanism of the cerebral protection system. The complex of compensation mechanisms is determined by the ability to adapt to an increase in the volume of the craniospinal system.
Cerebral edema in adults and children is divided according to the pathogenetic mechanism into the following types::
- cytotoxic
- vasogenic
- interstitial
- osmotic
The most common is the vasogenic type , which appears when the function of the blood-brain barrier is impaired. The pathogenesis is dominated by the release of plasma into the extracellular space and an increase in the volume of the white matter of the brain. When a person has suffered a traumatic brain injury, swelling can form within 24 hours. It develops around abscesses, tumors, surgical sites, areas of inflammation, and ischemic areas. This swelling is perifocal. It can lead to compression of the brain.
The cytotoxic form results from hypoxia, ischemia and intoxication. It occurs inside cells due to disturbances in astroglial metabolism. A disorder of osmoregulation of brain cell membranes, which depends on the sodium-potassium pump, is recorded. Edema is mainly observed in the gray matter of the brain. It can result from toxic-hypoxic encephalopathy, viral infections, carbon monoxide poisoning, ischemic stroke, poisoning of the body with hemoglobin breakdown products or cyanide.
The osmotic appearance results from hyperosmolarity of brain tissue when the functionality of the blood-brain barrier is not impaired. This happens when:
- drowning in fresh water,
- metabolic encephalopathies,
- improper hemodialysis,
- polydipsia,
- hypervolemia.
Interstitial OGM becomes a consequence of water permeating through the walls of the lateral ventricles into the brain tissue and develops around them.
Factors for the development of cerebral edema , isolated in 1979 by WF Ganong and team:
- increase in filtration pressure
- positive water balance
- increasing capillary permeability
- decrease in the osmotic pressure gradient between the blood and the intercellular environment
- disturbance of the nervous and humoral regulation of water and electrolyte metabolism
- violation of lymph outflow
Damage to the vascular endothelium is important in the pathogenesis of AGM. The endothelium has a high level of metabolism; it plays an important role in the system of homeostasis processes. Cerebral edema is divided into local or generalized according to its prevalence. In the local form, processes occur in a small area of the brain, and in the generalized form, even 2 hemispheres can be completely covered.
Pathological picture of cerebral edema
Brain specimens from AGM have characteristic pathological changes. Macroscopically, the following changes are observed: brain moisture, clouding of the surface of the hemispheres, unclear boundaries between the gray and white matter on the section.
With severe edema, the volume of the brain increases, which leads to a displacement of its areas under the falciform process of the dura mater, the tentorium of the cerebellum, or into the foramen magnum; strangulation impressions appear in the corresponding zones. There is flabbiness of the brain tissue; on the section it is too moist; swelling of the pia mater and local plethora are recorded. A clear liquid drains from the surface of the meninges. When swelling occurs, the density of the brain substance increases and it becomes dry.
Diagnostics
Cerebral edema should be suspected if impairment of consciousness increases, meningeal symptoms are observed, and the patient's condition worsens.
Instrumental methods that are used to confirm the diagnosis of cerebral edema:
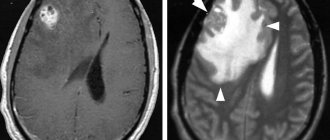
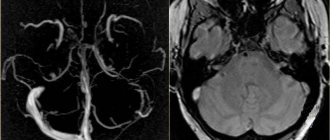
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This is an important diagnostic method - you can detect swelling of the spinal cord on MRI, and not just the brain.
Of the laboratory research methods, general and biochemical blood tests are important.
It is dangerous to perform a lumbar puncture for diagnostic purposes - displacement of brain structures and jamming of the brain stem in the occipital foramen of the skull may occur.
Symptoms of asphyxia in a newborn
Depending on the severity of asphyxia, it is customary to distinguish three degrees: mild, moderate and severe. The assessment of the condition is expressed in Apgar scores.
- Mild asphyxia (Apgar score 6-7) – the baby takes his first breath within a minute after birth. Breathing is weak, lips, arms and legs may be blue, muscles and tone are flaccid.
- Moderate severity (4-5 Apgar points) - about a minute passes from birth to the first breath. Breathing is weak, irregular, the cry is quiet and sluggish, the pulse is rare. The muscle tone is low, the limbs and face are blue, but the umbilical cord retains its pulsation.
- Severe asphyxia (1-3 points) – there is no breathing, or the child breathes irregularly and weakly, does not cry. The heart rate is very slow, the umbilical cord does not pulsate. The skin is pale.
Treatment of cerebral edema
The main principles of treatment for cerebral edema are:
- dehydration;
- improvement of metabolic processes in the brain;
- etiotropic treatment;
- symptomatic therapy.
What consequences of cerebral edema during stroke and other pathologies will accompany the patient depends on the timeliness and competence of the therapy.
Dehydration therapy
Its purpose is to remove excess fluid from brain tissue. Based on the appointments:
- osmotic diuretics (diuretics);
- magnesium sulfate and glucose solution - they enhance the effect of diuretics and also improve brain nutrition;
- L-lysine escinate - the drug is not a diuretic, but removes fluid.
Improving brain processes
For this purpose the following are appointed:
- metabolic drugs;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- oxygen therapy.
Etiotropic therapy
When treating cerebral edema, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of the development of the pathology and “destroy” the mechanism of edema formation. Destination:
- antibiotics;
- removal of tumors and hematomas;
- shunt operations, after which cerebral blood supply improves
This treatment is carried out after the patient’s condition has stabilized.
Symptomatic therapy
It is aimed at eliminating cramps, vomiting, pain, and so on. In addition to conservative therapy, surgical treatment can be used:
- decompression craniotomy;
- Ventricular drainage.
Consequences of a dangerous disease
When treatment for edema is started in time, it can be eliminated. But for this it is necessary to carry out high-quality and timely diagnostics . Even after treatment, it will be necessary to carry out constant examination throughout life. The child may have psychiatric disorders:
- Development is delayed.
- Absent speech with other mental disorders.
The disease caused the newborn an irreparable loss of some cells in the brain . Impaired blood circulation led some functions to an irreversible state and death. When normal physiological abilities are absent due to pathology, this is a natural phenomenon for edema. The child as a result:
- Starts to hold his head up at the wrong time.
- Lags behind in the accumulation of habits.
- Becomes too active or, on the contrary, indifferent to everything that surrounds him.
As a result of edema, the baby may develop:
- Cerebral palsy.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Epilepsy.
- Improper formation of organs.
Disturbances in the brain, swelling in this part of the body are dangerous for newborns, with a sudden onset and acute clinical symptoms that the baby can only express by crying.