Babies, as a rule, often fall in the first year of life, when they are learning to walk or due to the neglect of adults, falling out of bed is very common. If this occurs, it is important to calmly assess the situation and pay close attention to signs of injury.
Although it may look scary, falling out of bed usually does not cause serious harm. However, injuries can occur, so parents should know the signs that indicate their child needs medical evaluation after a fall.
Possible symptoms of a concussion
- Brief confusion or loss of consciousness. With a strong blow, the moment of injury disappears from memory.
- Dizziness even at rest, and when turning, bending or other changes in body position, the symptom intensifies.
- Severe headache, nausea and vomiting.
- Double vision, inability to concentrate on one point.
- Increased sensitivity to light and sounds.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Reaction inhibition - the victim gives an answer to the question after some time.
- Pale skin, weakness, sweating.
Important! A concussion is not always accompanied by visible head injuries, so the absence of wounds does not exclude brain injury.
Cyanosis (blueness of the skin)
Iron deficiency
22131 January 26
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Cyanosis: causes of appearance, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
In many cases, the condition and color of the skin are an important diagnostic criterion for the doctor. Blueness of the skin (the medical term is cyanosis) indicates a lack of oxygen in the blood. Unfortunately, with the gradual development of cyanosis, a person and the people around him often do not notice a progressive change in skin tone, while the doctor is especially wary of cyanotic skin, which may indicate diseases of the vital organs of a person.
Types of cyanosis
Cyanosis is classified according to several parameters, each of which is important for the diagnostic search.
Depending on the prevalence of cyanotic coloration of the skin, total
cyanosis, characterized by a change in color of the entire surface of the skin, and
local
, localized in certain areas of the skin.
Local cyanosis may be central
and
peripheral
. Central cyanosis includes cyanosis of the oral mucosa (perioral cyanosis), nasolabial triangle, and area around the eyes (periorbital cyanosis). In addition, peripheral cyanosis, or acrocyanosis, is distinguished, which is characterized by a bluish coloration of the parts of the body most distant from the heart, located on the periphery - cyanosis of the fingers and toes, cyanosis of the earlobes, etc.
Depending on the speed of development, acutely emerging
cyanosis (rapidly progressing) and
chronic
cyanosis, which develops gradually and is present in a person for a long time.
Possible reasons for the development of cyanosis
The color of the skin is formed by two main factors: the presence of coloring pigments (for example, melanin) and the condition of the superficial blood vessels (the degree of opening of their lumen and the color of the blood in them).
The bluish tint of the skin is determined primarily by the color of the blood.
It is known that one of the most important functions of blood is the transfer of oxygen by attaching it to the protein hemoglobin, which is part of red blood cells.
Blood enriched with oxygen in the lungs is called arterial and has a scarlet tint.
As the cells of organs and tissues become saturated with oxygen, there is less oxygen in the blood and it takes on a cherry hue. Blood poor in oxygen is called venous. It is the accumulation of venous blood in the tissues that determines the characteristic bluish tint of the skin.
There are two main reasons for the accumulation of venous blood in tissues. The first reason is a circulatory disorder, in which the outflow of venous blood from the cells is disrupted. This mechanism underlies the development of cyanosis of the skin in diseases of the heart and blood vessels. The second reason is a violation of the enrichment of blood with oxygen in the lungs, which occurs with diseases of the respiratory system, with damage to the respiratory center (the functional structure of the brain and spinal cord that regulates the functioning of the respiratory muscles) or with a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the air, for example at high altitudes.
What diseases cause cyanosis?
Cyanosis in most cases is a manifestation of pathology of the cardiovascular or respiratory systems.
Among heart diseases, it is worth noting a group of congenital heart defects, which are formed during the intrauterine development of the fetus and are manifested by cyanosis from infancy, and a group of acquired heart diseases, which includes a wide range of diseases leading to the development of heart failure. We list the main ones:
- Coronary heart disease, which includes, among others, angina pectoris and the consequences of myocardial infarction. The basis of this disease is insufficient oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
- Cardiomyopathies are primary lesions of cardiac muscle cells.
- Arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation.
- Infectious myocarditis is an inflammatory lesion of the heart muscle of infectious origin.
- Heart valve defects, such as aortic stenosis, mitral regurgitation, etc.
Among other diseases of the cardiovascular system, it is worth noting a violation of the patency of the peripheral veins, as a result of which there is a retention of venous blood in one or another segment of the body with the development of local cyanosis.
An example is chronic venous insufficiency of the lower extremities, in which varicose veins and a bluish discoloration of the skin of the feet and legs are observed.
Diseases of the respiratory system, often leading to the development of respiratory failure with the appearance of cyanosis, include:
- Pneumonia (pneumonia).
- Bronchiolitis (inflammation of the smallest bronchioles - the airways).
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Bronchial asthma, not controlled by taking special medications, and other rarer diseases.
It must be taken into account that the primary cause of circulatory and respiratory disorders can be explained by pathologies of other organs and systems, for example, endocrine glands, the central nervous system.
Which doctors should I contact if cyanosis develops?
Often, diseases of the circulatory and respiratory organs are treated jointly by several specialists. A therapist almost always appears among them. It is to him that you need to contact if a bluish tint of the skin appears. After the examination, the issue of referral to doctors of a narrow specialization is decided, for example, a cardiologist, pulmonologist (a doctor specializing in lung diseases), an allergist, an endocrinologist, a surgeon.
Diagnosis and examinations for cyanosis
The success of diagnosing the disease that led to the development of cyanosis largely depends on the conversation between the doctor and the patient and on the clinical examination. The patient needs to be told when cyanosis appeared, how intensively it developed, and on which parts of the body it manifested itself at first.
It is necessary to describe accompanying complaints, for example, cough, shortness of breath, interruptions in heart function, swelling, etc.
As a rule, acute cyanosis is accompanied by other significant manifestations, and it is these that serve as a reason to consult a doctor.
After the conversation, the doctor will examine the condition of the cardiovascular system, respiratory system and rule out damage to other organs. As a rule, already at this stage the doctor assumes one or another disease, the presence of which can be confirmed using laboratory and instrumental research methods:
- An exercise electrocardiogram can help diagnose heart disease and suggest lung disease.
First aid for concussion
- If one or more symptoms are present, immediately call an ambulance or take the victim to a doctor.
- Treat a wound on the head if it appears as a result of an impact.
- For an hour or until the doctor arrives, it is important not to fall asleep, but to remain at rest.
- If you lose consciousness, lay the person on his side, bend his knees, and put his hands under his head.
- If symptoms of a concussion do not immediately appear, it is recommended to rest and not begin vigorous activity.
Concussion in children - symptoms and treatment
When diagnosing SHM, it is necessary to take into account the nature of the injury and interviewing witnesses to the incident. In some cases, traces of trauma on the head and the psychological state of the child may indicate a concussion.
Since the signs of a concussion in a child are not very clear, changes in symptoms over time are important in diagnosis. Their disappearance after 3-7 days is a good reason to suspect SMG.
The difference between SHM and bruise and other forms of traumatic pathology:
- no skull fractures;
- the pressure and composition of the cerebrospinal fluid are unchanged;
- M-echo without offsets;
- CT and MRI without traumatic abnormalities in the parenchyma of the brain and in the cerebrospinal fluid-containing intracranial spaces.
To determine the severity of TBI, the following is assessed:
- duration of loss of consciousness in the acute phase of the injury (if it occurred);
- duration of post-traumatic amnesia (if present) and assessment of vital functions;
- degree of depression of consciousness at the time of examination (Children's Glasgow Coma Scale).
Electroencephalography and ophthalmoscopy can indirectly contribute to the objectification of concussion in the acute phase of TBI. Neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain) has become widespread in the diagnosis of TBI in children .
Ultrasound of the brain is performed on children from the first day of life until the period of closure of the large fontanelle, which is an acoustic window through which the state of all brain structures can be visualized. The study evaluates the cerebrospinal fluid system (lateral ventricles, choroid plexuses, III and IV ventricles, occipital cistern), thalamus, cerebellum, brain parenchyma, cerebral blood flow, the presence of free fluid between the brain parenchyma and the skull, as well as the skull bones.
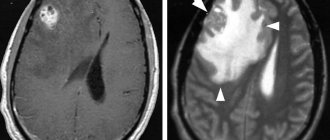
This study allows us to exclude changes in the brain after injury - swelling of the parenchyma, displacement of the midline structures, fractures of the skull bones, areas of brain contusion and intracranial hemorrhage.[5][13]
Ultrasound signs of brain injury that exclude BMS:
- with edema of the brain parenchyma - a decrease in the echogenicity of the brain parenchyma in the first hours after injury, its increase in dynamics and normalization on days 6-7.
- in case of brain contusions - the presence of hyperechoic inclusions in the brain parenchyma against the background of a general decrease in the echogenicity of parenchyma tissue (intracranial hematomas have a higher echogenicity).
- for severe brain contusions:
- areas of the brain parenchyma of an isoechoic nature, visible only due to their additional volume;
- areas of additional volume with a moderate increase in echogenicity and an unclear contour;
- areas of additional volume with a clearly demarcated contour and an intense increase in echogenicity.
- areas of additional volume with a sharp increase in echogenicity.
- with epidural hematomas - a clearly demarcated spindle-shaped area adjacent to the skull bone, with increased or slightly decreased echogenicity, displacing the structures of the brain;
- for subdural hematomas:
- local changes in density boundaries (usually spindle-shaped), covering the entire hemisphere;
- chronic subdural hematomas with reduced echogenicity;
- for intracerebral hematomas:
- hyperechogenicity stage - lasts up to 8-10 days;
- anisoechoic stage - characterized by the appearance in the center of the lesion of zones of reduced echogenicity with an increase in size over time (10-30 days after injury);
- anechoic stage - only indirect signs of a volumetric process are visualized (1-2 months);
- the stage of subsequent residual changes with the formation of cysts or areas of brain atrophy.
- with intraventricular hemorrhages caused by trauma - the presence of an intraventricular hyperechoic zone, expansion of the lumen of the lateral ventricles and changes in the shape of the choroid plexus (rare, usually occur in the presence of multiple hematomas).[5]
Neurosonography also makes it possible to identify rare variants of the location of hematomas - the posterior cranial fossa, the pole of the frontal lobe with displacement of the echo structures of the brain and the “plus tissue” effect, the presence of free fluid along the anterior surface of the brain parenchyma. If the hematoma is located in the posterior fossa of the skull, signs of hydrocephalus are observed - expansion of the lateral ventricles of the brain and the third ventricle of the brain.[5]
Recommendations for the treatment of concussions
If hospitalization is not required, with the permission of a doctor, a mild concussion can be treated at home:
- Bed rest and rest are required, no work. Long sleep is very important.
- You cannot read, watch TV, play computer games or use gadgets.
- Under no circumstances should you play sports.
- You are allowed to listen to music, but not through headphones.
- You can use herbal sedative drops or herbal infusions.
- In your diet, you should give preference to dairy and plant products, limit salt intake - to prevent increased pressure, including intracranial pressure.
If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner and all recommendations are followed, recovery will occur quickly and without complications.
First aid
Immediately after the impact, carefully place the child on the bed and carefully examine his head. At the same time, there is no need to rush and fuss so that the baby does not become even more frightened. After all, hysteria can increase intracranial pressure or increase bleeding from a wound.
When a lump forms, apply ice wrapped in a piece of cloth to it. A cold water bottle or a bag of frozen food wrapped in a towel will do. A cooling compress will help relieve swelling and prevent the development of a hematoma. But you need to hold it for no more than five minutes.
If you find a wound, treat its edges with hydrogen peroxide and apply a gauze or cloth swab to absorb the blood. If bleeding does not stop within 10 minutes, call a doctor.
If there is no damage at the site of impact, the child's condition should be closely monitored for at least a week. Moreover, in the first few hours it is better not to put the baby to bed, since the main symptoms of a concussion appear precisely at this time.
Children of the first year of life cannot talk about their health. Consult a doctor if you notice prolonged crying, refusal to eat, restless sleep, or vomiting.
An older child needs to be asked in detail how he fell and where the pain is felt. If the impact is muffled by the carpet, and the fall itself was not dangerous, medical attention is not required. But it doesn’t hurt to watch the baby for a few days to make sure there are no dangerous consequences.