Our clinic specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the nervous system, incl. non-surgical treatment of increased intracranial pressure and hydrocephalus. You will also find help in treating the consequences of intracranial hypertension: depression and nervous exhaustion, vegetative-vascular dystonia, headaches, visual disorders and others. We will be happy to help you!
- Increased intracranial pressure: treatment at the Echinacea clinic with and without medications
- Make a diagnosis
- Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure
- Causes and consequences of increased intracranial pressure
- What is intracranial pressure
- What is hydrocephalus of the brain
Increased intracranial pressure: treatment at the Echinacea clinic with and without medications
We actively use methods to normalize intracranial pressure, both classically and without drugs. Some simple measures may be enough to get you back to good health. The effect is usually noticeable already in the first week of treatment.
1. Unloading the venous bed of the head using special methods of soft manual therapy and osteopathy;
Normalization of intracranial pressure: for treatment, sometimes it is enough to eliminate the infringement of blood vessels by the vertebrae
2. Special gymnastics to reduce intracranial pressure (used by the patient independently, developed by the doctor after examining muscle tone); 3. Individual drinking/eating regimen.
Living with increased intracranial pressure is both unpleasant and harmful. The human brain cannot work normally under the influence of excess pressure ; moreover, slow atrophy of the brain substance , this leads to a decrease in intellectual abilities, disruption of the nervous regulation of internal organs (hormonal disorders, arterial hypertension, etc.). Therefore, we will take measures to normalize intracranial pressure as soon as possible.
In the treatment of increased intracranial pressure, it is important to reduce the release and increase the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. Traditionally, it is customary to prescribe for this purpose drugs that reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid and improve venous outflow (evacuation of venous blood from the cranial cavity). Often it is enough to take the medicine 1-2 times a week.
But still, we strive to free our patients from constant medication use. There are two ways to do this:
- If possible, eliminate the cause of increased intracranial pressure and hydrocephalus;
- Use more non-drug methods for treating cerebral hydrocephalus.
What to do in very severe cases
In very severe cases (for example, cerebrospinal fluid block after neurosurgical operations or congenital cerebrospinal fluid block), surgical treatment is used. For example, a technology has been developed to implant tubes (shunts) to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment
To improve the patient's well-being, it is necessary to achieve normalization of intracranial pressure. In modern practice, non-surgical and surgical treatment methods are used. Surgery is required if diagnosis reveals a tumor or cystic change. Some patients are diagnosed with a congenital abnormality of the brain structure. Such tumors must be removed. The operation will eliminate the compression and thereby normalize the pressure.
Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, the procedure is performed immediately, or the patient is given a date for surgery. Urgent surgical treatment is carried out in severe condition of the patient, when the degree of the disease threatens brain dislocation. With dislocation syndrome, compression causes a displacement of brain structures relative to each other. There are eight types of brain dislocation, each of which has its own characteristic manifestations.
In one of them, the cerebellar tonsils penetrate the foramen nagnum - a large oval hole in the occipital part of the skull; due to increasing hypertension, the brain stem, on which vital nerve centers are located, is compressed. They are responsible for the functions of the heart and respiratory system. When these areas are damaged, the disease is most severe. The patient's breathing becomes impaired, the pharyngeal reflex disappears, and the pressure drops. These conditions are directly life-threatening and require immediate surgery.
Make a diagnosis
Intracranial pressure can be directly measured only by inserting a special needle with a pressure gauge connected to it into the fluid cavities of the skull or spinal canal. Therefore, we do not use direct measurement of intracranial pressure.
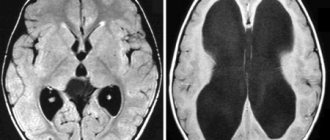
On the left is an MRI scan of a normal brain. The brain matter is shown in gray, the cerebrospinal fluid is in white. Normal size of the fluid spaces of the brain (they are slit-like). The ventricles are visible inside the brain. The subarachnoid spaces are the white border around the brain.
In the center there is internal hydrocephalus. Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid inside the brain in the form of a butterfly is visible. On the right is external hydrocephalus. External hydrocephalus is also an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid outside the brain in the form of a wide white border. The volume of the brain matter is reduced - brain atrophy from fluid pressure
We can confidently judge the increase in intracranial pressure based on the following data:
- Dilation and tortuosity of the fundus veins is an indirect but reliable sign of increased intracranial pressure;
- Expansion of the fluid cavities of the brain (internal hydrocephalus of the brain, external hydrocephalus) and external hydrocephalus (rarefaction of the medulla) along the edge of the ventricles of the brain, clearly visible on computed x-ray tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Violation of the outflow of venous blood from the cranial cavity, established using ultrasound vascular studies.
How much the brain suffers from increased intracranial pressure can be judged from EEG data. The gold standard for instrumental examination of patients in our clinic is an assessment of symptoms, brain tomography , fundus images and EEG .
Good optics helps us see the subtle nuances of the fundus vessels
Echoencephalography (Echo-EG) provides indirect and not always reliable data on increased intracranial pressure; it is less reliable than CT and MRI, so we do not use this method.
What to do if the above symptoms appear?
If there are signs of the disease, you should consult a neurologist. To treat a pathological condition, it is necessary to find out its exact cause. That is why the doctor prescribes a set of diagnostic procedures:
- Fundus examination. Allows you to identify swelling of the optic nerve - one of the main signs of intracranial hypertension.
- Echoencephalography is an ultrasound procedure for examining brain tissue. Such diagnostics will help confirm or refute the presence of a tumor, cyst, hemorrhage, or other pathological changes in tissue structure. This diagnostic method does not require preparation, changes in daily routine or nutrition.
- X-ray of the skull. Prescribed for suspected birth defects, fractures or bone displacement. This method also identifies possible tumors that are causing compression.
- CT or MRI of the head. The most accurate and informative diagnostic methods. They allow you to thoroughly assess the condition of bones, soft tissues, and blood vessels. As a rule, the doctor prescribes such a diagnosis after echoencephalography, if it shows the presence of a pathological process.
- Ultrasound of the vessels supplying the brain. It is necessary to identify possible anomalies, tortuosities, and thromboses.
- Angiography. Allows you to visualize large and small vessels and detect areas of affected arteries.
The purpose of the above procedures is to determine the cause of the malaise. Based on the examination results, the specialist prescribes additional diagnostics or decides on treatment.
Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure
Increased pressure on the brain substance can disrupt the functioning of the central nervous system. Hence the characteristic symptoms:
- Heaviness in the head or headaches that increase in the morning or in the second half of the night;
- In severe cases, nausea and/or vomiting in the morning may occur;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia (sweating, a drop or increase in blood pressure, palpitations, lightheadedness, etc.) is an almost obligatory symptom;
- Fatigue, “dullness”, easy exhaustion during work or study loads;
- Nervousness;
- “Bruises” under gases (if you stretch the skin under the eyes in the area of the “bruise”, dilated small veins are visible);
- Possible decrease in sexual desire and potency;
- If the human body is in a horizontal position, cerebrospinal fluid is released more actively and absorbed more slowly, so intracranial pressure and its symptoms tend to peak in the second half of the night or in the morning;
- The lower the atmospheric pressure, the higher the intracranial pressure, so the deterioration of the condition is associated with changes in weather.
Diagnostics (or how can you measure it)?
Spinal puncture gives us absolutely accurate numbers , but it can only be done in a hospital setting. This is a rather unsafe and traumatic procedure. And they do it only according to indications, when there is a threat to the patient’s life. In this regard, to clarify intracranial pressure, we recommend doing at least two studies.
This is Doppler ultrasound . The most informative study in this situation is that we see the blood supply - how the brain is nourished - this is arterial blood flow, and we also see the venous outflow - how waste food from brain cells is disposed of. And this is already a serious step in finding the cause of intracranial pressure.
Echoencephalography - we look to see if our brain is symmetrical, if the third ventricle is dilated (a sign of intracranial pressure - ICP).
Examination of the fundus by an ophthalmologist , where there may be congestion.
Well, let’s say things like: computed tomography , nuclear magnetic resonance , that is, layer-by-layer scanning of the brain. But even there it is impossible to directly touch and see the intracranial in numbers. There we already see its consequences. I will say figuratively, just as a tractor or bulldozer passes and we see its mark on the ground, so in these studies, on the very substance of the brain, a rough imprint of intracranial pressure is noticeable, which, alas, it leaves there.
Express laboratory . This is a blood draw without blood, that is, the skin is not broken during the study. The information is read by microsensors using the infrared spectrum. On average, this study takes 30-40 minutes. We see 131 blood indicators. And, in particular, the width of the 3rd ventricle and the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid, and by these signs one can also judge whether there is intracranial pressure or not.
Causes and consequences of increased intracranial pressure
The reasons we find most often:
- disruption of the outflow of venous blood from the cranial cavity
- hypoxia (oxygen starvation)
- suffered a traumatic brain injury (even a very old one, up to birth trauma)
- meningitis or encephalitis
- congenital structural features of the central nervous system (Arnold-Chiari anomaly, congenital intracranial hypertension, etc.);
- poisoning with brain damage.
Consequences As a result of the disease, brain cells are gradually destroyed, and their place is filled with fluid. The functions of systems controlled by the brain become disordered, and complete or partial loss of vision, hearing, memory, potency, miscarriage, depression, nervous exhaustion and other health problems may occur.
On the left is a normal brain, the liquid (cerebrospinal fluid) is indicated in white. On the right is untreated internal hydrocephalus: brain atrophy, almost the entire cranial cavity is occupied by fluid.
What is intracranial pressure
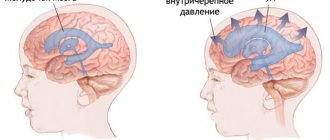
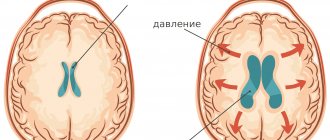
Wise nature placed the human brain in a protective liquid environment ( subarachnoid fluid spaces ) and provided it with internal fluid cavities ( ventricles ). Thus, the brain is actually suspended in a special fluid - cerebrospinal fluid (also known as cerebrospinal fluid or CSF ). The cerebrospinal fluid is in the cranial cavity under a certain pressure. It is the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid on the brain that is called intracranial pressure .
A normal level of intracranial pressure is very important for the proper functioning of the brain and all processes subordinate to it. We often see a total improvement in the well-being of our patients as intracranial pressure normalizes.
What is increased intracranial pressure? All fluid spaces and ventricles are interconnected by ducts. The liquor is constantly circulating. In some parts of the brain it is released, and then flows through the cerebrospinal fluid ducts to other parts of the brain, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream. Complete renewal of the cerebrospinal fluid occurs on average 7 times a day. Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid causes an increase in its pressure on the brain substance. This is called increased intracranial pressure (intracranial hypertension).
Three common causes of chronic increased intracranial pressure:
- too much cerebrospinal fluid is released;
- the cerebrospinal fluid is not absorbed fully enough;
- the patency of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation pathways is impaired.
Pressure measuring instruments
A home blood pressure monitor is a necessary medical device in every home. There are two options for tonometers:
- Mechanical devices are durable, but require an understanding of the operation of the device and experience in its use.
- Electronic tonometers - automatic or semi-automatic. They are easy to use, as they are equipped with a special display that instantly displays data after measurement, but their price exceeds the cost of mechanical ones.
The starting point for determining blood pressure is a consultation with a doctor. A specialist will determine the normal pressure for your body, show you how to measure it correctly and give the necessary recommendations for stabilization. It is important to understand that the normal pressure is determined individually for each patient.
What is hydrocephalus of the brain, external hydrocephalus
If intracranial pressure is increased significantly and for a long enough time, the fluid cavities of the brain may expand; this expansion is called internal or external hydrocephalus. Since the cranial cavity is a closed space, the expansion of the fluid cavities of the brain occurs due to a decrease in the mass of the brain matter itself. To protect you from the death of working brain tissue, we will offer you a course of medications, in combination with a set of exercises to reduce intracranial pressure and, if necessary, osteopathic correction.
External hydrocephalus (brain) - expansion of the external cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain (subarachnoid spaces).
Internal hydrocephalus (brain) - expansion of the internal liquor cavities of the brain (ventricles).
Our clinic pays great attention to finding the root causes of such a condition as increased intracranial pressure. In this case, treatment can be kept to a minimum, and our assistance to patients will be reliable.
Causes of increased ICP
It is worth mentioning what causes intracranial pressure:
- skull injuries;
- the presence of a hematoma, a specific foreign body or a space-occupying tumor;
- inflammation of the brain (meningitis, ventriculitis, encephalitis);
- intoxication of the body;
- obesity;
- circulatory disorders in the brain;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- abnormal brain development;
- liver pathologies;
- excess cerebrospinal fluid;
- abscess;
- stroke;
- helminthiasis
High pressure inside the skull can also be triggered by: otitis media, severe migraines, bronchitis, excess amounts of vitamin A, malaria and mastoiditis. An important reason is long-term use of antibiotics, corticosteroids and hormonal contraceptives. All of the above reasons can increase the generation of cerebrospinal fluid, disrupt its circulation, and also interfere with normal absorption. Next, you should determine the signs of pathology and how to measure intracranial pressure at home.