External hydrocephalus of the brain is considered a disease of newborns, but the disease also occurs in adult patients. The development of hydrocephalus is caused by impaired absorption or outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. At the Yusupov Hospital, neurologists use modern diagnostic methods that make it possible to establish the causes, form of the disease and severity.
For mild hydrocephalus, conservative therapy is carried out aimed at reducing intracranial pressure and improving the function of nerve cells in the brain. Neurosurgeons at partner clinics perform surgical interventions that eliminate the cause of the disease. After surgery, patients’ quality of life improves and impaired nerve functions are restored.
Reasons for development
Acquired hydrocephalus can develop due to pathological processes that result in adhesions in the vessels of the brain and destruction of arachnoid villi. The disease is provoked by the following factors:
- Infectious diseases of the brain (encephalitis, meningitis, tuberculosis);
- Sepsis;
- Previous hemorrhagic stroke;
- Head, neck injury;
- Traumatic brain injuries;
- Traumatic spinal injuries;
- Malignant neoplasms of the brain stem.
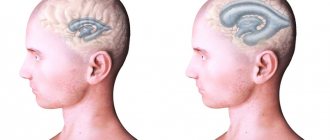
Atrophic hydrocephalus occurs due to age-related changes in cerebral vessels, metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, and arterial hypertension. With external hydrocephalus, zones with reduced density of brain matter are formed. They atrophy, and the vacated space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. The cause of the development of external hydrocephalus can be constant alcohol intoxication.
Symptoms of external hydrocephalus
The human body has impressive compensatory abilities. A mild form of external hydrocephalus can go almost unnoticed for the patient - the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is restored independently. The prognosis for such a disease is the most optimistic, and its consequences are minimal.
An increase in intracranial pressure leads to the following symptoms:
- Headache that gets worse after a long stay in a horizontal position;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Drowsiness;
- Visual impairment (double vision);
- Increased fatigue;
- Weakness.
All these manifestations are a consequence of a decrease in the density of brain structures due to the fact that they are saturated with cerebrospinal fluid, narrowing of the subarachnoid and subdural space, and improper resorption of cerebrospinal fluid. When the brain parenchyma is replaced by cerebrospinal fluid, the symptoms of the disease worsen.
Symptoms of replacement external hydrocephalus:
- Violation of gross and fine motor skills;
- Uncertain shaky gait;
- Involuntary urination and fecal incontinence;
- Violations of intellectual activity, memory, attention;
- Signs of dementia.
If external hydrocephalus is diagnosed in an infant, the following symptoms occur:
- Dehiscence of sutures between the bones of the skull;
- Swelling of the fontanelles;
- Enlargement of the frontal part of the skull;
- Lack of appetite;
- Swelling of the veins on the skull, clearly visible under thin, stretched skin in the form of a venous network;
- Excessive increase in the circumference of the child's head.
Development mechanism
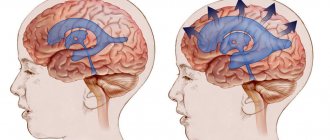
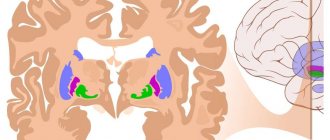
With external hydrocephalus, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates outside the cerebral hemispheres, in the subarachnoid spaces. Excessive amounts of cerebrospinal fluid compress the cerebral cortex. External non-occlusive hydrocephalus of the brain occurs as a result of hypersecretion or malabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid. Closed (occlusive) hydrocephalus is a form of the disease in which the exit of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles is blocked by a tumor or adhesions.
Internal hydrocephalus can be congenital or acquired. Congenital hydrocephalus develops during intrauterine exposure to the fetus, acquired hydrocephalus develops during life. Mixed hydrocephalus is a separate form of the disease in which cerebrospinal fluid accumulates both in the ventricles and under the meninges.
Make an appointment
The main types of hydrocephalus
At the initial consultation, the neurosurgeon will listen to the patient’s complaints, but will be able to make an accurate diagnosis only as a result of a comprehensive diagnosis. Special studies make it possible to determine what stage of the disease we are talking about - advanced or mild hydrocephalus.
There are quite a large number of varieties of dropsy:
- by origin, acquired and congenital diseases are distinguished;
- according to the characteristics of the course, hydrocephalus can be closed (occlusive), open (non-occlusive) and mixed;
- by location - internal and external hydrocephalus;
- according to clinical signs - acute, subacute, chronic degrees of hydrocephalus.
The dynamics of pathology development is also important. The most dangerous is considered progressive hydrocephalus, in which the number of symptoms constantly increases. The mild type is considered a regressive disease. With stable hydrocephalus, significant changes in the human body, as a rule, do not occur.
Symptoms and severity
According to clinical manifestations, external hydrocephalus in an adult is divided into 3 degrees: mild, moderate and severe. With mild hydrocephalus, the body can independently restore the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. The patient complains of slight malaise, headache, dizziness, and short-term darkening of the eyes. The average degree of hydrocephalus is manifested by intense signs of brain damage. Patients experience the following symptoms:
- Severe pain in the head, aggravated by physical activity;
- Pressing pain in the eyeballs, the appearance of colored circles of flashes when closing the eyes;
- Feeling of heaviness in the skull;
- Nausea independent of food intake;
- Vomiting without relief.
Sweating occurs periodically. An ophthalmological examination reveals swelling of the optic nerve head. Patients note swelling of the face, weakness, lethargy, and increased fatigue. They are worried about feeling tired in the morning, aggressiveness, increased nervousness, and tearfulness. A depressive state develops. Blood pressure is unstable. Unpleasant sensations intensify when coughing, sneezing, turning or tilting the head.
External hydrocephalus of the brain in an adult is accompanied by neurological symptoms:
- Decreased visual acuity;
- Strabismus;
- Impaired visual perception: double vision, blurred images;
- Paralysis or paresis of the limbs;
- Numbness of the face;
- Decreased sensitivity;
- Impaired coordination.
Patients have speech impairment, difficulty pronouncing sounds and perceiving spoken speech. With severe external hydrocephalus, epileptic and convulsive seizures, frequent fainting, and coma occur. The patient loses memory, intellectual abilities, and his self-care skills decrease.
Patients with occlusive hydrocephalus experience severe headache, nausea and vomiting in the morning. Congestion of the optic discs and signs of axial dislocation of the brain develop. An unfavorable prognostic sign is drowsiness. It intensifies on the eve of a sharp disruption of neurological symptoms. When brain structures are dislocated, cardiac activity and breathing are disrupted.
The clinical picture of chronic hydrocephalus consists of three pathognomonic symptoms: dementia, gait disturbance and urinary incontinence. Dementia is manifested by a decrease in the level of wakefulness, rapid exhaustion of the patient, disorientation in time, the development of severe intellectual disorders, and decreased criticism. Patients become unsure when walking and develop paresis of both lower extremities. The most recent symptom of hydrocephalus is urinary incontinence. This symptom of the disease is more common in men after 50-60 years of age.
Based on the intensity of the manifestation of hydrocephalus, a distinction is made between a moderate form of the disease, which occurs with minor symptoms, and a severe form - the accumulation of a large volume of cerebrospinal fluid provokes the manifestation of acute neurological symptoms.
Depending on the degree of impact on brain structures, external hydrocephalus can be compensated or decompensated. In the presence of compensated hydrocephalus, excessive secretion of cerebrospinal fluid does not affect the brain, but in the decompensated form of the pathological process, regardless of the amount of cerebrospinal fluid, brain function is disrupted and the functional activity of the central nervous system is reduced.
External non-occlusive hydrocephalus occurs when the process of cerebrospinal fluid absorption is disrupted. Atrophic (replacement) hydrocephalus develops most often in older people and is accompanied by the death of brain cells.
How does hydrocephalus of the brain manifest?
The main signs of hydrocephalus are directly related to the deterioration of the patient’s general health. Symptoms can be pronounced or unexpressed. Common consequences of cerebral hydrocephalus are headaches, nausea, and vision problems. Secondary symptoms: the occurrence of convulsive syndrome, tinnitus, impaired coordination of movement and fear of light.
Even moderately severe hydrocephalus, located in the cerebral ventricles, can lead to impaired sensitivity of the limbs and even paralysis. Convulsive seizures also appear, which in turn can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. Ventricular hydrocephalus is a rather dangerous disease. In newborns, the consequences of hydrocephalus are retardation in physical and mental development.
Diagnostics
When a patient enters the neurology clinic, the doctor conducts an examination, checks motor reflexes, muscle and joint reactions. To clarify the diagnosis, additional examinations are carried out:
- Ultrasound examination of the head and neck for a preliminary assessment of the condition of the vascular bed;
- Computed tomography, which helps to establish the degree of damage to brain tissue, assess the degree of expansion of the subarachnoid fissures, determine the presence of neoplasms in the skull that impede the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid;
- Magnetic resonance imaging, which allows you to see changes in brain tissue with maximum accuracy;
- X-ray of the skull to determine changes characteristic of liquor hypertension and space-occupying formations;
- An ophthalmological examination to determine the presence of congestion, swelling of the optic nerve, and atrophy of eye tissue.
Patients undergo a lumbar puncture, which is used to determine the level of cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Improvement in the condition of a patient with hydrocephalus after removal of 40 ml of cerebrospinal fluid indicates a good prognosis after surgery.
Make an appointment
Second opinion for hydrocephalus in children
Despite the fact that it is possible to recognize hydrocephalus using MRI scan data quite accurately, in practice, errors in identifying this disease often occur. They are mostly associated with insufficient experience of doctors, associated either with the fact that they have been working relatively recently and simply have gained enough experience, or with the fact that the doctor rarely had to deal with dropsy and he may not notice signs that are obvious to other MRI specialists .
It is for these reasons that it is very important, after conducting an MRI and obtaining an opinion, to obtain a second medical opinion, preferably from specialists with extensive experience. This will allow you to either be completely confident in the primary diagnosis or cast doubt on it and contact a specialist to prescribe additional examinations. This will help the child avoid unnecessary or ineffective treatment.
Today, getting a second opinion on hydrocephalus with the help of the National Teleradiology Network (NTRS) is easier than ever before. To do this, just upload the scan results to our server and within a day you will receive an authoritative opinion given by leading specialists working in the best medical institutions and institutes. And most importantly, it doesn’t matter where you live or how far from Moscow you are. All you need to get a second opinion is access to the Internet and MRI results in electronic form.