A description is given of the forms of hydrocephalus that can be incidental findings on MRI/CT of the brain - primary hydrocephalus and conditions with which a differential diagnosis must be made. Information about benign intracranial hypertension (BIH), normotensive and replacement hydrocephalus is presented to the extent that is necessary for a neurologist in outpatient practice to make decisions and explain to the patient the essence of his condition. The structure of the document reflects the tasks facing it. You can get acquainted with the question in more detail using the links in the relevant sections of the text. The clinical picture of intracranial hypertension consists of general cerebral and focal symptoms. Intracranial hypertension is characterized by the absence of pathognomonic disorders. In a typical clinical picture, a triad stands out: headache, vomiting, congestion in the fundus. Increased intracranial pressure is often associated with hydrocephalus, a disorder involving the accumulation of excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the cerebral ventricles and/or subarachnoid spaces, due to an imbalance between secretion and absorption, which is accompanied by dilation of the ventricles and/or subarachnoid spaces. The set of disorders in patients may be similar to the clinical picture of other lesions of the nervous system: - disseminated demyelinating focal lesions of the brain substance and cranial nerves, - focal lesions of the brain stem with involvement of the medial longitudinal fasciculus and the development of disorders of consciousness - space-occupying formations of the brain with general cerebral changes, focal symptoms and symptoms of damage to the cranial nerves, - conditions with diffuse brain damage - encephalopathy. — neuroinfections (congenital syphilis, cytomegalovirus infection, mumps, etc.) — thrombosis of the sinuses and veins of the brain. Asymptomatic cases of intracranial hypertension (ICH) are accompanied by nonspecific complaints - dizziness, fatigue. The variety of variants of the clinical picture, both in severity and in the set of symptoms, is the reason for the overdiagnosis of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, both in adult and pediatric neurological practice. An additional harmful effect is the high rate of false-positive data on dilation of the ventricular system when using echoencephaloscopy. Doctors can claim that a patient has ICH if rheoencephalography, duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries, or transcranial Doppler sonography reveals venous drainage from the cranial cavity.
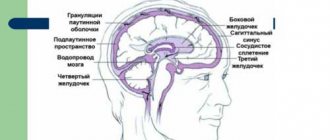
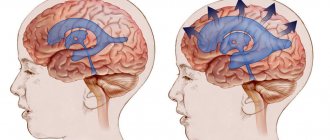
Imaging signs of hydrocephalus with increased ICP include: An increase in the size of the inferior horns of the lateral ventricles by more than 2 cm with the absence of visualization of the subarachnoid spaces of the convexital areas, interhemispheric and lateral fissures of the brain; Balloon-shaped dilatation of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles (Mickey Mouse symptom) and the third ventricle; Periventricular decrease in tissue density seen on CT or increased T2 signal seen on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a result of transependymal infiltration or migration of cerebrospinal fluid. In addition to structural changes, the clinical manifestations of hydrocephalus are taken into account. The last clarification is necessary, since taking into account only structural changes does not allow us to classify disorders of liquorodynamics without changing the configuration of the ventricles as hydrocephalus, for example, benign intracranial hypertension (BIH).
What types of external hydrocephalus of the brain are there?
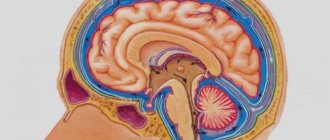
External hydrocephalus of the brain refers to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal or cerebrospinal fluid) outside the cerebral hemispheres - in the subarachnoid space. Due to the large accumulation of fluid, the subarachnoid fissures widen, which causes increased pressure on the cerebral cortex and the resulting negative consequences.
The nature and level of complexity of the disease directly depend on the specific type of dropsy. Several criteria are used for classification. The most common ones are:
- intensity of manifestation (pronounced - accumulation of a large amount of cerebrospinal fluid, causing neurological symptoms; moderate - minimal amount of fluid, no signs);
- degree of impact on brain structures (compensated - cerebrospinal fluid does not affect the brain; decompensated - there is a deterioration in the functioning of the nervous system and brain);
- causes of occurrence (replacement - more often diagnosed in older people and is accompanied by the death of brain cells; acquired - occurs due to the spread of infections and mechanical traumatic brain injuries);
- nature of the course (chronic form - a gradual increase in neurological disorders; acute form - a sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being).
Employees of the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev will first determine the type of external hydrocephalus and only then begin treatment. Particular attention is paid to diagnostic data and a thorough study of the symptoms of the identified disease.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The human brain consists of soft tissues located in the skull. To protect against damage, cerebrospinal fluid circulates in the cavity - the liquid fills the internal ventricles and grooves. When a person is healthy, the inflow and outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is balanced. The performance of its functions does not affect the patient’s health. If disturbances occur due to the development of tumors, injuries and infections, intracranial pressure increases and the process of cerebrospinal fluid movement is disrupted, causing changes in brain function and neurological manifestations.
Hydrocephalus can develop due to a stroke or tumor development.
Symptoms of external hydrocephalus
The clinical picture in each specific case will be different, and the nature of the manifestation of the disease depends on the severity of the pathological process and the state of the central nervous system. Common symptoms are frequent headaches, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, and weakness. By the way, pain is more localized in the frontoparietal region and in the area of the eyeballs. A person with dropsy experiences pain in the first half of the day, with sudden movements, coughing, sneezing, or severe physical exertion.
Symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the disease. Scientists distinguish 3 stages, and each has its own characteristics:
Mild external hydrocephalus. With a minimal amount of dropsy, the human body will try on its own to cope with such a problem as impaired circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid. In this case, you will feel a slight malaise, periodic dizziness, short-term darkening in the eyes, and a tolerable headache.
The middle stage of development of the disease. At this stage of the spread of the disease, symptoms appear intensely and are more pronounced. Due to an increase in intracranial pressure, severe headaches occur during physical activity, swelling of the optic nerve and facial tissues, increased fatigue, nervousness, depression, and surges in blood pressure.
Severe form of the disease. Signs of pathology in severe forms of external hydrocephalus are reduced to convulsive seizures, frequent fainting, a state of apathy, loss of intellectual abilities, memory loss and inability to care for oneself. Progressive dropsy can even lead to death, so there is no need to delay going to the doctor. It is better to do this at the first suspicion and a slight deterioration in health.
With chronic accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid, symptoms such as unsteady gait, paralysis of the upper and lower extremities, urinary incontinence, nighttime insomnia and daytime sleepiness, depressed mood, and a complex of psychoneurological disorders can be observed.
Why does dropsy of the brain occur?
In adult patients, acquired hydrocephalus is often encountered, which develops either due to any mechanical damage to the head, or as a result of the development of pathological processes. Why does cerebrospinal fluid accumulate outside the cerebral hemispheres? The explanation is simple: brain structures are disrupted, adhesions appear in the veins, arachnoid villi are destroyed, and as a result, the cerebrospinal fluid does not circulate as it should.
If we delve deeper into the question of the causes of such a disease as external dropsy of the brain, we can identify some factors:
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis, meningitis, encephalitis);
- post-stroke condition, development of sepsis, extensive hemorrhage;
- concussion, head or cervical spine injury;
- malignant tumors that develop in the stem region.
Frequent intoxication of the body leads to the appearance of external hydrocephalus. For example, alcohol abuse, which damages neurons and leads to tissue death. Those patients who suffer from metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, encephalopathy, and atherosclerosis are also at risk. Another reason that deserves due attention is irreversible age-related changes that cause aging of blood vessels and brain tissue.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
What is the danger of the disease?
The consequences of dropsy largely depend on the age at which the disorders occurred and the development of complications:
- Infants experience high excitability, sleep disturbances, and increased muscle tone. The most severe manifestation is developmental delay and mental deviations.
- Preschoolers show aggression, stutter, develop strabismus, and experience developmental delays.
- School-age children experience memory loss and headaches. The learning process is difficult.
- In adults, epilepsy, increased excitability, and hallucinations appear.
The danger of the disease in adulthood is the development of mental disorders, motor functions and motor skills. If urgent measures are not taken, the patient becomes disabled.
Diagnosis of external hydrocephalus in adult patients
Studying the symptoms and visual examination of the patient is not a sufficient condition for determining external hydrocephalus of the brain. Indirect signs, of course, are important, but you can’t do this without professional diagnostics. Today, 6 methods for detecting dropsy are used:
- Ultrasound examination (US) of the neck and head to assess the condition of blood vessels;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) helps to identify changes in soft tissues and most accurately determine the type of hydrocephalus and the stage of development of the pathology;
- computed tomography (CT) is intended to determine the degree of damage to brain tissue, the size of subarachnoid fissures, and the presence of neoplasms;
- X-rays with the introduction of a contrast agent are aimed at identifying disturbances in the outflow of venous blood and damage to the vascular bed;
- a spinal puncture is prescribed if there is a suspicion of the development of dropsy after encephalitis or meningitis and you need to find out what level of cerebrospinal fluid pressure;
- ophthalmological examination - an opportunity to determine whether the patient has swelling of the optic nerve and atrophy of the tissues of the ocular apparatus.
IMPORTANT! If the diagnosis of “chronic external hydrocephalus of the brain” is confirmed, it is advisable to carry out an additional diagnostic examination after 6 months. The intensity of further visits to the doctor depends on the data obtained and is determined individually.
Diet
The patient's nutrition should be aimed at improving the water-salt balance. Foods that cause fluid accumulation should be excluded from the diet. Instead, vegetables and fruits, steamed meat, and cereals are introduced into the menu.
It is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, exercise with moderate exercise, and walk a lot. Following these recommendations will help maintain the patient's mental and mental fitness.
Dropsy is a serious disease that does not go away on its own. The patient requires qualified specialist assistance for life. The disease is in an advanced stage and cannot be treated.
Treatment of external hydrocele in adults
Treatment methods are selected at a consultation with a neurosurgeon or neurologist after diagnosing the disease. Intervention must be timely, otherwise the risk of various neurological complications increases. It is important to take into account both the type of pathology and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
In the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev practice only effective methods of treating external hydrocele of the brain. Methods are divided into two large groups: conservative (medicinal) and surgical (operative), each of which has its own characteristics and advantages.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT
Drug treatment is only relevant at a mild stage of the disease. Special medications accelerate the outflow of fluid from the brain, increase urination, relieve inflammation and swelling, strengthen blood vessels, and normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system. To combat severe headaches, your doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Common groups of medications are vascular, neurotropic, venotonics, diuretics. But in acute illness they will be ineffective. Mixed hydrocephalus is poorly corrected. In this case, conservative treatment will not get rid of the disease, but will only restore or improve the functioning of individual systems and functions of the human body. Often surgical intervention is not possible.
SURGERY
If acute external dropsy is diagnosed, in most cases drainage of the cerebral ventricles is prescribed. The main technologies are endoscopy and open surgery.
In the first case, we are talking about manipulations that are characterized by minimal trauma, a very low risk of complications, and fairly rapid postoperative recovery. Endoscopy methods allow, with minor intervention, not only to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid, but also to eliminate vein defects, hematomas, and blood clots.
Currently, open surgery is chosen only in exceptional cases. Why? It is difficult to imagine performing open surgery without craniotomy. And trepanation always means increased risks and a long postoperative recovery period.
Another way to get rid of external dropsy is bypass surgery. Doctors use a system of valves and silicone tubes to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid from the skull. The fluid is redirected to other cavities of the body, in particular to the abdominal cavity, right atrium, and superior vena cava. According to statistics, the effectiveness of this technique is 85%.
Is it possible to protect against the occurrence of external hydrocephalus of the brain? This is a very difficult question. But, if you completely give up bad habits and avoid traumatic brain injuries, there is a high probability that trouble will bypass you. Another important point is the timely and professional treatment of such serious diseases as encephalitis, polio, meningitis, as well as other infectious diseases.