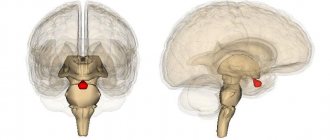
Hydrocephalus of the brain (dropsy) is a local increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid spaces, occurring due to excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular system against the background of its impaired secretion, circulation or absorption. According to WHO, the prevalence of the pathology around the world is as follows: about 700 thousand patients, including children, are diagnosed with hydrocephalus.
Visual model of the disease.
Causes of hydrocephalus
Such a lesion can be either acquired or congenital. According to statistics, for every 500-1000 newborns, there is 1 case of birth of a child with hydrocephalus of the brain. The clinical debut of the congenital form occurs, as a rule, in early childhood (0-6 months). A key role in the etiology of the development of a birth defect is played by:
- intrauterine infections (the main cause) and hemorrhages;
- consequences of birth trauma;
- fetal asphyxia;
- abnormal formation of the cerebral vessels of the fetus (malformations);
- congenital neoplasms;
- genetic factor.
If we talk about the acquired form, the formation of cerebral hydrocele is most often facilitated by:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- cerebrospinal fluid infections;
- meningitis;
- tumor process in the brain;
- intracranial hemorrhages.
Hydrocephalus
Olga
Dad has cardioesophageal cancer; his last course of chemotherapy took place in December 2021. Stabilization of the process, last appointment with the oncologist in May 2021. At the end of June-July, problems with vision and coordination began, which dad hid. When I started getting up on July 10, I was paralyzed on the right side. This all passed in 10-12 minutes. The ambulance arrived, I explained what happened, they suggested ischemic brain disease. On 12 the therapist came and prescribed Mexidol, Actovigin, and nicotinic acid. After a few days there was improvement. Dad ate himself and went outside. On August 3rd we are credited with Sermion. In response to my requests from NATO for a referral to an MRI and a neurologist, the therapist said that she did not see any reason yet. She was diagnosed with vertebral artery syndrome. In August, nighttime incontinence and problems with walking began. He took a few steps, and then began to walk half-bent. He said that it felt like cottony legs. I called the doctor, she suggested putting B12. As a result, not seeing any improvement, I contacted the Ministry of Health. They sent a neurologist on September 2. By that time, his neurological problems had already worsened. Started in front of the right hand. He diagnosed a stroke, gave a referral for an MRI and prescribed Mildronate, Gliatilin, Cortexin. Before the neurologist, he took care of himself, but after treatment everything worsened. 13 were supposed to undergo an MRI, but could not because dad was unable to lie with his head still. The radiologist called me and explained that this is not a stroke or MTS, but there is a formation that creates high intracranial pressure. She suggested that we undergo at least MSCT as quickly as possible, since the treatment tactics are fundamentally different from the one that was prescribed to us. 15 underwent MSCT. The conclusion states: signs of space-occupying formation of the quadrigeminal area, with occlusion of the aqueduct. Internal occlusive hydrocephalus. Signs of chronic cerebrovascular accident. I had a consultation with a neurosurgeon, having learned that he had a history of cancer and was 67 years old, they suggested just watching the person die. That shunting would prolong his life by 3 months. Now dad was hospitalized for a brain drying procedure. I don’t understand what this is, but I understand that all this is a temporary measure. I beg you, you are the last hope. Miracles happen in life, maybe this is our case. It may be possible to improve Dad's condition with the help of herbal medicine. He says little, his arms and legs move, but when I try to stand him, he stands with his arms around my neck or leaning on the table. I slowly massage his arms and legs with laurel oil, after which he can walk a few steps with my help. I also noticed that when it’s clear and sunny outside, he communicates as he did before his illness. Good mood. When the weather is bad, 20 words per day. And then you ask the question 8 times before he answers. You are our last hope.
Classification of pathology by form
Hydrocephalic syndrome is classified according to localization, pathogenesis, fluid pressure level, and flow rate.
The localization of the outbreak comes in three varieties:
- internal - cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in excess in the lateral ventricles;
- external - overconcentration of cerebrospinal fluid is determined in the subarachnoid space;
- mixed - simultaneous accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles and subarachnoid space.
Based on the pathogenesis, GM hydrocephalus can be:
- occlusive (closed) – the most dangerous form, resulting from blockage (occlusion) of the cerebrospinal fluid passages by a tumor, hematoma, or post-inflammatory adhesions;
- communicating (open) - with this pathogenesis, there is a disruption of resorption processes due to damage to the structures involved in the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the venous system.
Based on the CBF pressure indicator, they are distinguished:
- hypertensive hydrocephalus – the level of intracranial pressure is increased;
- normotensive – ICP remains within normal limits;
- hypotensive – the pressure inside the skull is reduced.
Hydrocephalus is diagnosed based on the rate of progression:
- acute - from the appearance of the first signs to the phase of severe clinical decompensation it takes no more than 72 hours;
- subacute – develops within 30 days;
- chronic - formation occurs at a slow pace, over months and even years (more common in open forms).
In ICD-10, hydrocephalus is assigned a general code of G91. Each form has its own alphanumeric symbol: communicating - G91.0; occlusal – G91.1; normotensive – G91.2; post-traumatic unspecified – G91.3; another type – G91.8; hydrocephalus of unspecified origin – G91.9.
Signs of the disease
The symptoms of the disease are dictated mainly by reduced perfusion of brain tissue, overstretching of groups of nerve fibers (conducting pathways) due to increased ICP.
- In acute pathogenesis, weak microcirculation (hypoperfusion) leads mainly only to functional disorders of intracranial metabolism. This is
a change in energy metabolism, a reduction in the level of creatine phosphate and ATP, an increase in the concentration of lactic acid and inorganic salts of phosphoric acids. The acute clinical picture is reversible. - The long-term existence of hypoperfusion causes irreversible transformations at the structural level. These are
defects in the vascular endothelium and disruption of the BBB, axonal damage (destruction of axons, up to their complete disappearance). Dropsy of prolonged duration ultimately causes brain atrophy. - The morphology of signs in hydrocephalus in combination with high intracranial pressure is characterized, first of all, by atrophy of the substance of the brain and periventricular edema. There is also damage to the vascular mesenchyme, disruption of brain homeostasis, axonal lesions, and in rare cases, neuronal death. These signs are combined with the clinical picture of the primary pathology that provoked hydrocephalic syndrome.
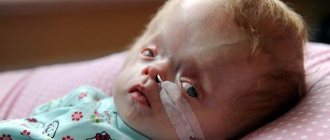
The symptomatic complex characteristic of hydrocephalus in early childhood includes such distinctive features as:
- increased head size;
- frequent regurgitation;
- restless behavior of the child;
- bulging of a large fontanel;
- divergence of cranial sutures;
- the severity of the venous pattern on the scalp;
- delayed psychomotor development, less often physical;
- throwing the head back;
- “setting sun” syndrome (Graefe);
- congestive optic disc;
- paraplegia of the lower extremities (in severe, advanced conditions).
In adults and older children, the clinical picture depends on the rate of progression of hydrocephalus. In the acute form of the disease, combined with high ICP, the following are observed:
- a bursting and pressing headache that spreads to the orbits of the eyes (one of the features is the peak of pain in the morning after a night's sleep, and then, during the day, the severity of the pain syndrome decreases);
- nausea, which usually accompanies morning headaches (vomiting often occurs in the morning, after which a person notices an improvement in the condition);
- visual disturbances usually include blurred vision, blurred vision, double vision and a burning sensation in the eyes;
- fatigue, drowsiness, lethargy;
- convulsive phenomena (like an epileptic seizure);
- when the brain stem is compressed due to dislocation of brain structures - oculomotor disorders, forced head position syndrome, clouding of consciousness (up to a coma), respiratory failure.
Hydrocele of the brain in the chronic stage manifests itself:
- signs of dementia (dementia), emotional instability;
- apraxia of walking, more often it manifests itself with a shaky and uncertain gait, disproportionately large steps (being in a lying position, patients often do not experience difficulties in imitating walking and twisting a “bicycle” with their legs);
- decreased muscle strength, sometimes patients complain of pain in the neck;
- severe imbalance (in the final stages), which is expressed by a person’s inability to move and sit independently;
- partial or complete loss of sensitivity (not always!):
- urinary and/or fecal incontinence (with a massive lesion).
The pathology is dangerous due to its life-threatening complications! In no case should you ignore an urgent visit to the doctor if one or more symptoms from the lists provided are identified. Timely visit to the hospital for the purpose of diagnosis and receiving adequate medical care increases the chances of a favorable prognosis, including complete recovery.
On average, out of 10 patients who do not receive treatment at the right time, 6-7 people die soon (this also applies to children). Those who did not undergo therapy but survived are doomed to disability with neurological disorders, mental and physical disabilities with a tendency to progress.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus
Symptoms of hydrocephalus appear as the disease progresses and the pressure of the accumulated cerebrospinal fluid increases. The first symptoms include severe headaches, especially in the morning after waking up, accompanied by attacks of nausea and vomiting. There is also a feeling of pressure from the inside on the eyeballs, a burning sensation in the eyes.
As hydrocephalus develops, the patient develops a state of constant drowsiness. This serves as a bad signal and indicates the progression of the disease. In the absence of treatment, the patient experiences rapid depression of consciousness. In some cases, the person may fall into a coma.
The most important thing if your health worsens is to seek medical help in a timely manner. At the Yusupov Hospital, anyone can undergo an examination. All procedures are performed using modern medical equipment. This allows you to obtain the most informative and reliable results.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital, based on the results of their research, develop an individual treatment program for each patient. If necessary, the patient is treated in a hospital setting; if the situation is not so severe, then therapy can be carried out at home, strictly following all the doctor’s recommendations.
The wards of the Yusupov Hospital are well equipped with modern equipment and furniture. The atmosphere here is not reminiscent of a hospital, which makes the patient’s stay during treatment as comfortable as possible.
If the patient does not consult a doctor in a timely manner, the disease begins to progress. A person experiences a change in voice and problems with swallowing. Normal sleep is also disrupted: the patient either suffers from insomnia or constantly wants to sleep.
Also, the development of the disease can lead to a constant feeling of fatigue. Then the patient develops disturbances in motor coordination. He has difficulty maintaining balance when walking and then just when standing.
There is a frequent urge to urinate, especially at night. Then the body demands immediate immediate emptying of the bladder. In the most advanced cases, a person completely loses the ability to control the process of urination; it becomes spontaneous.
Diagnosis of dropsy of the brain
Clinical manifestations are so specific that they allow a neurology specialist to suspect hydrocephalus already during the initial examination of the patient. Despite this, the diagnosis of pathology always involves differentiating hydrocephalic syndrome from other possible diseases that have similar symptoms.
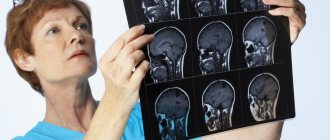
To differentiate, as well as establish the localization, degree and form of hydrocephalus, the etiological factor of its development, according to the doctor’s decision, the leading visual diagnostic tools are prescribed in a certain combination:
- magnetic resonance imaging (the most informative);
- conventional or multislice CT;
- echoencephalography (shows the level of ICP);
- neurosonography (done on infants through an open large fontanel to determine ICP);
- radiography (more of a backup method, sometimes recommended for assessing the condition of the skull bones).
If cerebral vascular pathology is suspected, the patient is examined using MR angiography. Dropsy of infectious origin additionally involves performing a PCR analysis to identify the type of infection. All patients are prescribed ophthalmological examinations, including examination of the fundus with an ophthalmoscope, eye perimetry, and visometry.
Hydrocephalus of the brain - treatment at different stages
Treatment of hydrocephalus in the early stages can be carried out with medication. The clinically advanced form of the disease requires surgical intervention.
At the Yusupov Hospital, acute hydrocephalus that threatens the patient’s life is treated by craniotomy and external drainage to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid. For chronic hydrocephalus, a liquor shunt operation is performed. We are talking about removing excess fluid through a complex system of catheters and valves into other natural cavities of the body.
At the Yusupov Hospital, such operations are performed by highly qualified neurosurgeons. It is possible to achieve the patient’s recovery and return to normal social life.
Treatment of hydrocephalus in children and adults
Treatment tactics are determined by a specialist based on the severity of hydrocephalus and the disease that gave rise to excessive accumulation of CBF. In the most isolated cases, for example, with a mild form, a conservative approach can be used (based on the use of diuretics to reduce ICP), but it does not lead to a complete cure. Conservative therapy can also be used as a preparatory step for surgery.
For patients of all ages with this diagnosis, surgical intervention is recommended, and on an emergency basis. The danger of the pathology is that even from a mild form it can quickly reach a critical stage at any time with a disappointing prognosis for the patient.
Today, depending on the indications, various neurosurgery techniques are successfully used to eliminate hydrocephalus. They are united by a common goal - creating the necessary conditions to ensure the removal of excess cerebrospinal fluid and maintaining normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Thus, brain functionality is restored, ICP is stabilized, neurological and cognitive symptoms disappear or are noticeably reduced. Let's consider what operations can achieve this goal.
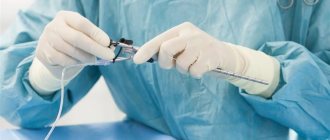
Liquor shunt interventions
CSF shunting is the installation of elastic silicone implant systems to remove cerebrospinal fluid outside the central nervous system. The systems are equipped with catheters in the form of flexible hollow tubes, as well as valves with an anti-siphon (reverse) mechanism and with fixed or adjustable opening pressure.
The operation can be performed in various ways. But surgeons consider ventriculoperitoneal (the most commonly used method) or ventriculoatrial shunting to be the most successful in terms of safety. Interventions are performed under endotracheal anesthesia, manipulations are controlled by intraoperative fluoroscopy, CT, and ECG.
- Ventriculo-peritoneal shunt. The principle of the procedure is based on the implantation of silicone catheters, through which an excess of CBF goes into the intra-abdominal cavity, where it is resorbed between the intestinal loops.
- The procedure begins by making an incision on the scalp, after which a small burr hole is created in the skull. The dura mater is opened sparingly.
- A ventricular catheter is introduced through the created access, its end is placed in the lateral ventricle of the brain.
- The valve element is implanted in the area of the auricle (at the back or slightly above). The ventricular (ventricular) and distal catheter (DC) are fixed to it.
- Next, the neurosurgeon places a distal catheter into the abdominal cavity through a specially formed subcutaneous channel.
- Upon reaching the desired abdominal area, the specialist makes a small incision (no more than 10 mm) and inserts the end of the DC into the abdominal cavity.
- The procedure ends with thorough disinfection of the surgical field, followed by closing the wound areas with antiseptic dressings (sutures are applied if necessary).
- Ventriculoatrial shunting. The essence of this operation is to divert cerebrospinal fluid through installed shunts from the ventricle of the brain into the right atrium.
- Dissection of tissue in the neck along the anterior sternocleidomastoid muscle is performed to open the common facial or internal jugular vein.
- The atrial catheter is removed into one of the indicated veins, fixing it with specially designed ligatures.
- The shunt is directed through the catheterized vein to the right atrium. The end of the atrial shunt is generally located in the superior vena cava.
- For the installation area of the distal end of the vascular catheter, yes, the superior vena cava is often preferred. Here the blood flow is turbulent, and this reduces the likelihood of thrombosis of the drainage system by blood clots.
- The cranial part of the intervention, when the ventricular element of the system is implanted, a valve and two catheters are connected to it, is identical to VP shunting.
For adults, shunts are permanently implanted. In childhood, they are periodically replaced with elongated models. We emphasize that patients after surgery with shunt implantation are shunt-dependent people.
Endoscopic operations
Endoscopic surgical techniques are used in the treatment of occlusive hydrocephalus, among them:
- ventriculocisternostomy;
- ventricular cystocisternostomy;
- ventriculoplasty of the aqueduct of Sylvius;
- septostomy;
- etiotropic endoscopy (getting rid of the causative factor - removal of a tumor, cyst, hematoma, etc.).
In 90% of cases, the method of endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy is used. The purpose of this operation is perforation of the bottom of the third ventricle of the brain under endoscopic control through a miniature trepanation window. The anastomosis created during the endoscopic procedure allows you to restore the natural path of outflow of cerebrospinal fluid between the third ventricle and the basal cisterns of the brain.
Endoscopy of any kind is a more gentle tactic of neurosurgery; it does not require the implantation of foreign bodies into the body and is less likely to cause postoperative consequences. Despite the promising characteristics of endoscopic methods, in some cases it is impossible to do without shunting or the use of open microsurgery.
Modern neurosurgery technologies have been honed to perfection in the Czech Republic; brain surgery in this country is a leading field of medicine. Neurosurgical care in clinics in the Czech Republic is no worse than in Germany and Israel, but the price is much lower (about 2 times). People with this diagnosis are operated on here at the most exemplary level, and upon completion of the full course of rehabilitation they are discharged with excellent and good results.
Drugs for hydrocephalus in adults
Drug treatment of hydrocephalus in adults is carried out using the following drugs:
- reducing intracranial pressure and promoting the removal of excess fluid. Such drugs include Diacarb, Mannitol and Mannitol in combination with Lasix and Furosemide. In this case, the patient must be prescribed the drug “Asparkam”, which corrects the level of potassium in the body.
- improving nutrition of brain tissue. This group includes Cavinton, Gliatilin, Cortexin, Choline, Actovegin, Semax, etc.
The earlier the disease is diagnosed, the easier it will be to cope with it. At the early stage of hydrocephalus, treatment can be limited to a course of medications. If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, surgery may be necessary.
Be attentive to your health and do not be afraid to seek advice from doctors. You can make an appointment for an examination at the Yusupov Hospital by calling the clinic.