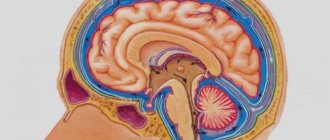
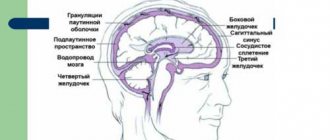
Hydrocephalus in adults can be an independent disease or a manifestation of pathology of other organs and systems. In patients with hydrocephalus, the process of excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid spaces, caused by disturbances in its production, circulation or absorption, is actively progressing. It is manifested by an enlargement of the ventricles of the brain, a decrease in the density of the brain matter due to its saturation with cerebrospinal fluid and a narrowing of the subarachnoid spaces. At the Yusupov Hospital, neurologists treat hydrocephalus with the most effective drugs that have a minimal range of side effects. Patients are examined using modern research methods performed by experienced specialists from the neurology clinic.
Symptoms
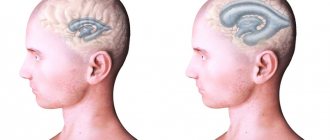
Mixed atrophic hydrocephalus of the brain is an acquired form of the disease. The pathology is characterized by enlargement of the cerebral ventricles and subarachnoid space in conditions of progressive brain atrophy.
Based on the rate of progression of the disease, the following are distinguished:
- acute hydrocephalus (no more than 3 days pass from the first symptoms of the disease to severe decompensation);
- subacute progressive hydrocephalus (develops within a month from the onset of the disease);
- chronic hydrocephalus (forms within 3 weeks to 6 months).
Based on the level of cerebrospinal fluid pressure, hypertensive, normotensive and hypotensive replacement hydrocephalus are distinguished. Mixed asymmetric hydrocephalus is characterized by an enlargement of one of the ventricles of the brain. Mixed hydrocephalus of a replacement nature occurs against the background of traumatic brain injury, arterial hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, instability of the cervical vertebrae, and alcoholism.
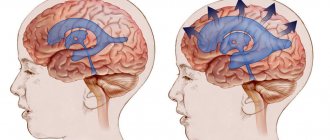
A distinctive feature of mixed hydrocephalus is the replacement of the vacated brain space with cerebrospinal fluid. Minor mixed hydrocephalus contributes to a decrease in cerebral blood flow. This leads to inhibition of neurological functions. If replacement hydrocephalus is accompanied by an increase in the volume of the cerebral ventricles, then a decrease in intracranial pressure is detected in patients, in other cases it will be increased.
Moderate mixed asymmetric hydrocephalus of the brain may be asymptomatic for a long period of time. Signs of ventricular asymmetry are determined during the examination of patients. Patients with replacement hydrocephalus complain of severe headache in the morning after waking up, caused by a long-lasting horizontal position of the body, nausea, and vomiting. They experience increased blood pressure, increased heart rate, and arrhythmia. The following signs of the disease are also determined:
- insomnia and sleep quality disturbances;
- drowsiness and lethargy;
- increased fatigue;
- irritability;
- decreased hearing and visual acuity;
- unsteadiness of gait, loss of coordination of movements.
In the later stages of the disease, symptoms of dementia appear: absent-mindedness, memory loss, impaired short-term memory, and inability to think logically. A severe complication of replacement hydrocephalus is epileptic syndrome. The patient develops dementia and may fall into a coma.
Hydrocephalus in children
This disease is detected in newborns and does not become a defect for life. Israeli doctors treat hydrocephalus in children, giving them the opportunity to live and develop without problems. Treatment of cerebral hydrocephalus in children should be identified in a timely manner by identifying symptoms and making a diagnosis.
Neurosurgeons treating hydrocephalus:
- Neurosurgeon, prof. Menashe Zaharur – Head of the Department of Neurosurgery, Medical
- Neurosurgeon, prof. Zvi Ram – Head of the Department of Neurosurgery, Medical
- Neurosurgeon, prof. Moshe Hadani – Head of the Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Hospital
- Pediatric neurosurgeon, prof. Shlomo Constantini - Head of the Department of Pediatric Neurosurgery, Medical.
Diagnostics
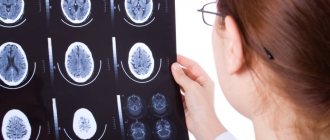
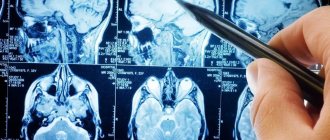
At the Yusupov Hospital, computer and magnetic resonance therapy are performed immediately after the patient’s admission to the neurology clinic. To assess the stage of hydrocephalus and determine indications for surgical intervention, doctors calculate ventriculo-cranial coefficients, which show the degree of expansion of the ventricular system. Computed tomography makes it possible to clarify the presence and extent of ischemic brain damage in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage.
To predict the outcome of surgical treatment of replacement hydrocephalus, all patients undergo a tap-test. Its essence is that by removing at least 40 ml of cerebrospinal fluid during lumbar puncture in patients suffering from chronic hydrocephalus, their health status improves for a short time. If the test is positive, it is more likely that the patient will recover after surgery.
At the Yusupov Hospital, neurologists conduct a comprehensive examination of patients with replacement hydrocephalus. It includes ultrasound examination of the brain, craniography (x-ray of the skull), and fundus ophthalmoscopy. Patients are consulted by an ophthalmologist, cardiologist, and neurosurgeon.
If mixed replacement hydrocephalus occurs in a moderate form with minimal symptoms, patients are examined every 6 months for timely detection of negative dynamics of the disease. If there are pronounced signs of increased intracranial pressure, treatment is started immediately. In the case of severe replacement hydrocephalus, at a meeting of the expert council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category, tactics for managing the patient with hydrocephalus are developed.
Treatment methods for hydrocephalus
The surgical method of treating hydrocephalus is used only in extreme cases (decompensated forms of internal hydrocephalus), excess fluid is drained from the cranial cavity into the abdominal cavity using a tube (shunt), this operation, like any other, is quite traumatic; in the future, several more surgical operations may be required interventions to replace and check the operation of the shunt.
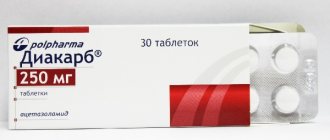
A medicinal method of treating hydrocephalus - the use of diuretics, such as Diacarb, is often used by neurologists in outpatient practice. Diakarb removes fluid not only from the cranial cavity, but also from the body as a whole, at the same time a loss of microelements occurs, the effect of this treatment method is temporary, after its cessation, the fluid begins to accumulate again and intracranial pressure increases.
Herbal medicine - the use of diuretic herbs (horsetail, fennel, lingonberry leaf), does not cause addiction and loss of microelements. It is used, as a rule, for preventive purposes: to avoid exacerbation of hydrocephalus during colds, when changing climatic zones, in the autumn-spring period with pronounced changes in weather conditions.
Massage is an effective method for children with motor impairments (increased muscle tone, delayed motor development), and is mainly aimed at relaxing tense muscles. It is advisable to use only in complex treatment, since massage does not affect the main cause of the disease - hydrocephalus and hypoxia of the cerebral cortex.
MICROCURRENT REFLEXOTHERAPY - the method is effective in children with various manifestations of hydrocephalus, it allows you to eliminate not only external manifestations (hysterics, developmental delays, etc.), but also treat hydrocephalus itself, that is, it has a complex therapeutic effect on the body. The effect of treatment is stable and does not stop after the end of treatment.
How to treat dropsy?
This brain pathology is practically incurable. Existing medications are designed only to slow down the process.
The most effective treatment method today is surgical, when the patient undergoes bypass surgery or endoscopic surgery.
Massage plays an important role in the treatment of hydrocephalus. Dropsy helps to increase muscle tone, and stroking and rubbing movements have a relaxing effect, helping to restore motor functions.
Another type of treatment, manual therapy, is used as an addition to the use of medications. Manual influence is aimed at activating the human body’s own reserves. The use of manual therapy for secondary dropsy is especially effective.
Recommendations for the use of treatment methods are given by a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
Drugs
Drug therapy is carried out using the following drugs:
- Diuretics. The diuretic effect of these drugs allows you to stop the production of cerebrospinal fluid. Most often the choice falls on Piracetam, Diacarb and Glyserol. All these drugs are administered by injection. Along with diuretics, the patient is prescribed vitamin complexes, since diuretics wash out magnesium, potassium and sodium from the body.
- Antibacterial drugs. Prescribed to eliminate infectious pathogens.
- Medicines that promote blood circulation in the brain.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes. The most commonly prescribed vitamins are C, B and E. They improve cellular metabolism throughout the body.
- Enzymes of animal origin. Pyrogenal and lidase help break down and remove excess cerebrospinal fluid.
- Glucocorticoids.
If drug therapy for mixed replacement hydrocephalus in adults does not show positive dynamics in the patient’s condition, surgical intervention is prescribed.
How does dropsy manifest itself?
With moderate development of the process, minor neurological disorders appear. You can't ignore:
- Nausea;
- Headache;
- Vomiting;
- Deterioration of vision;
- Changes in the appearance of the eyeballs;
- Problems with the vestibular system;
- Mental abnormalities.
The open external form has manifestations similar to mental disorders. If the diagnosis is made incorrectly, the patient will be treated in a psychiatric clinic, and the underlying disease will go unnoticed. To make a correct diagnosis, the neurologist prescribes additional tests:
- MRI of the brain is clear - the results of tomographic diagnostics will show the localization of the pathology and the catalyst for the disorders (infants may be prescribed neurosonography instead of MRI);
- puncture - children are tested using general anesthesia;
- fundus examination.
At the initial stages of the development of the process, an accurate diagnosis can only be made using instrumental methods.
Clinical picture
The characteristic clinical picture of mixed replacement hydrocephalus is the following:
- Constant pain in the head and a feeling of heaviness, intensifying during sleep and immediately after waking up. Inability to determine the source of pain. When a person is in a lying position, the symptom becomes more pronounced as the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid increases.
- Nausea and vomiting in the morning, regardless of food and time of consumption.
- Feeling of pressure on the eyes.
- Persistent hiccups.
- Constant weakness, increased fatigue, drowsiness.
- Difficulties with concentration and attentiveness; it is difficult for a person to perform basic actions.
- Apathy, nervousness, decreased intellectual abilities.
- A sharp drop in blood pressure, slowing or increasing heart rate.
- Permanent dark circles under the eyes. When the skin of the lower eyelids is stretched, blood-filled capillaries are clearly visible.
- Significant increase in sweat, tendency to faint.
These symptoms indicate intracranial increased pressure.
What is the danger of mixed hydrocephalus in adults?
- 7 minutes to read
Mixed hydrocephalus (hydrocephalus) is a very dangerous disease, the development of which primarily affects the brain. In most cases, this pathology is diagnosed in newborns, but it can also be observed in adults.
Content
What is needed for the initial diagnosis of hydrocephalus in Israel
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a primary diagnosis. To do this you need:
- Blood test – $280
- Computed tomography – $630
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – $1350
- Consultation with a neurosurgeon based on examination results – from $660
To get tested, you can sign up:
- Call us at: +972(77)4450-480.
- By leaving a request on the website.
We will contact you quickly.
What causes the disease?
There are many factors that influence the mechanism of cerebrospinal fluid circulation, and they are different for intrauterine development and for acquired forms of pathology.
The causes of congenital hydrocephalus include:
- deviations in the formation of the brain’s liquor system;
- structural defects of the subarachnoid space;
- anomalies of the craniovertebral region;
- influence of intrauterine infections;
- birth injuries.
In cases of acquired hydrocephalus, the causes of impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid differ sharply. This:
- infectious inflammation of the tissue and membranes of the brain;
- traumatic brain injury;
- pathological processes in the vessels of the brain (strokes, hemorrhages, hematomas);
- intracerebral tumors, ventricular cysts.
Sometimes there is an atrophic form of the disease, which develops as a result of age-related or traumatic atrophy of brain tissue due to cerebrovascular accidents.
Classification of the disease
There are three main forms of pathology:
- occlusive hydrocephalus, or internal, is a condition in which fluid does not flow from the ventricles, while the space around the brain is compressed;
- non-occlusive hydrocephalus, or external - fluid can enter from the ventricles into the space between the brain and its membranes, while they expand and compress the nervous tissue from the outside;
- mixed hydrocephalus is a combination of several blocks of cerebrospinal fluid outflow pathways.
External replacement hydrocephalus is a severe form in which the substance of the cerebral cortex atrophies, and excess fluid takes its place. A synonym for this condition is atrophic hydrocephalus.
The disease is also divided depending on its causes into post-traumatic, post-infectious and post-hemorrhagic forms. Hydrocephalus can be progressive (active) or chronic (compensated). It is accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure.
Prevention and consequences of hydrocephalus
The prognosis for this disease is difficult to determine. It largely depends on how early treatment is started and the extent of irreversible brain damage.
The consequences of hydrocephalus include delayed physical and mental development. However, with the right rehabilitation program, many children with this diagnosis can lead normal lives with minor limitations.
With a progressive form of pathology, the prognosis is unfavorable.
On the other hand, even bypass surgery is not always accompanied by complete recovery. The factors on which this depends have not been fully established.
Therefore, disease prevention is important:
- if necessary, genetic counseling for expectant mothers;
- protection against infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- prevention of traumatic brain and birth injuries;
- vaccination against pneumococcus, which protects against meningitis;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases causing hydrocephalus in adults.
Which doctor should I contact?
Hydrops is treated by neurosurgeons. When you contact the RAS clinic in Moscow, you will be provided with qualified, effective assistance: they will conduct an examination, prescribe tests, make a diagnosis, and determine an effective treatment strategy.
If any symptoms of neurological diseases appear, you must immediately make an appointment with a neurologist to prevent the situation from worsening. We invite you to a consultation with a neurologist in Moscow at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Registration can be made by phone or using the feedback form on the website.