Home / Articles / Deterioration of vision due to nervous conditions
The importance of vision can hardly be overestimated; through it we receive the most information about the world around us. The human eye is a surprisingly balanced, but at the same time quite fragile structure. Therefore, when exposed to negative factors, the balance of this system can be disturbed, which often becomes the cause of the development of eye diseases. One of the reasons for the deterioration of vision is the ever-accelerating pace of life, constant tension, stress and worries that accompany modern people.
Why does vision deterioration occur due to nervousness?
If we consider the structure of the human eye, we can see that various muscles are responsible for its proper functioning, which constrict the pupil, change the curvature of the lens - the natural lens of the eye that ensures focusing of vision, etc. In addition, the good functioning of the visual organs depends on the normal circulation of intraocular fluid, as well as sufficient blood supply and tissue nutrition.
Mental experiences and stress lead to excitation of the nervous system, as a result of which excessive tension of the eye muscles occurs, the shape of the eyeball changes, vasoconstriction occurs, and the tissues begin to experience a lack of blood supply. The constant overstrain of the eye muscles that occurs due to nervous conditions causes their improper functioning, leading to the development of refractive errors - myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism. In this case, people usually resort to wearing glasses or contact lenses, but as a result, the eye muscles weaken even more and the problem gets worse. And insufficient blood supply to the retina and optic nerve leads to the emergence of pathological processes that threaten the development of glaucoma and other very serious diseases.
How does stress affect vision?
A moment of stress is marked by an increase in blood pressure and a simultaneous increase in the content of adrenaline in the blood, the excess of which is transformed into chemicals that have a narcotic effect on the body. This cannot but affect vision. At the moment of strong emotions, complete blindness may even occur as an extreme reaction to a stressful situation.
In psychology and physiology, two types of stress have been studied: “good” and “bad”. In the first case, positive stressors act, and the state caused by them is called eustress. An example is the feeling of falling in love, pleasant surprises, the birth of a child and many other joyful events. In the bad version, we are talking about distress, which is what leads to health problems, including with the eyes.
A stressful situation is reflected in the brain through the senses. It is negative factors that cause the fastest reaction. The body mobilizes to eliminate the threat and a “fight or flight” response to stress occurs. It was first described by the scientist psychophysiologist Walter Cannon. He noted that a sharp increase in adrenaline in the blood immediately causes increased breathing, dilated pupils and tunnel vision. Tunnel vision syndrome is expressed in a person’s loss of peripheral vision and the eye’s perception of only those images that fall on the central part of the retina. An association arises with a telescope. In the process of evolution, a simple logic of changes in the state of the eye has developed: danger causes the dilation of the pupil as the main opening for the entry of light - the wider, the better the person’s orientation in space and, accordingly, the greater the chance of salvation. This logic worked in times of lack of artificial lighting. Nowadays, under altered conditions, pupil dilation can cause visual disturbances in the form of blurring of the real picture or aberration. As a rule, these visual disturbances and features appear only under severe stress and are temporary.
Increased breathing and vision in a stressful situation are closely interrelated. The state of hyperventilation with frequent breathing leads to oversaturation of the human body with oxygen, generally by 40-50%, and a drop in the level of carbon dioxide. It is this imbalance that causes the appearance of “floaters” and “stars” before the eyes.
Stressful situations can have different durations. The described symptoms accompany short-term stress. Long-term problem situations can cause additional disorders in the form of dry mucous membranes, eye twitching, increased eye pressure, and, as a result, migraines. All these factors can lead to serious eye diseases and decreased visual acuity.
How to avoid vision deterioration
In order to maintain good vision, you need to try not to succumb to stress and relax more often. To relieve overstrain, especially if your professional activity involves working on a computer, special eye exercises are well suited, which are best performed on a regular basis.
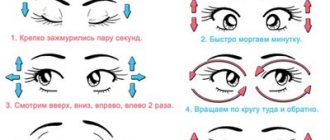
Eye exercises:
- Close your eyes and then open your eyes wide. Repeat the exercise 5-6 times.
- Look up, down, to the sides without moving your head. Repeat 3 times and then do the same with your eyes closed.
- Rotate your eyes clockwise and in the opposite direction. Repeat 3 times, then perform the exercise with your eyes closed.
- Blink rapidly for a minute.
- Stand near the window, look for some point or scratch on the glass. Look at it for 15 seconds, then for the same time, turn your gaze to some distant object outside the window. Borrow back to the point on the glass. Repeat 3-5 times.
- Rub your palms until they become hot. Then close your eyes for a few minutes, relax and imagine something pleasant, for example, the seashore or a forest landscape.
Proper nutrition is of great importance for eye health. The diet must include foods rich in vitamins A, C, D and E. Experts especially recommend eating fresh blueberries, which contain a substance that restores visual pigment. You can take special vitamin and mineral complexes for eye health, drink herbal teas that strengthen vision and have a calming effect on the nervous system.
The ARTOX Clinic offers diagnosis and treatment of any eye problems at affordable and affordable prices. Our experienced specialists will help you regain and maintain good vision.
View prices
Making an appointment with an ophthalmologist
Why do my eyes hurt with VSD?
If a patient with VSD has floaters in front of his eyes, this is a common visual disorder caused by a sudden narrowing of the blood vessels in the eye. Flashes of light, distorted images, pain in the eyes, a cloudy or dark background with partial vision or a complete lack of vision of objects may also be bothersome. Examination of the patient's systems and organs helps to identify diseases associated with neuroses; the doctor prescribes treatment for depression, neurosis, and prescribes medications to relieve panic attacks, pain, and anxiety.
Pain in the eyes with VSD is often accompanied by headache and pain in the heart area. Often, along with pain in the eyes, vision drops sharply, the image becomes blurred, the vision becomes dark, flashes and spots appear before the eyes. Visual disturbances can indicate not only VSD; if such symptoms appear, you should consult an ophthalmologist, who, if there are no ophthalmological problems, will refer the patient to a neurologist or oncologist.
Neurosis - what is it?
Neurosis is a collective term that refers to certain types of neurotic disorders. It can develop in both women and men. At risk are people who are in a certain phase of physiological changes: aging of the body or puberty. However, neurosis can occur at absolutely any age. In children, it usually goes away on its own, without treatment, and does not lead to any mental disorders. In adulthood, neurosis can greatly affect health - both physical and psychological. Often, neurotic disorders in adults cause pathologies of internal organs.
Negative stressful situations and acute psychological trauma can cause various painful manifestations in a person. The catalyst for neurosis can be an unresolved internal conflict or strong pressure from external factors that are uncomfortable for the patient. At the same time, not only severe injuries can provoke a neurotic disorder. Sometimes it becomes a consequence of mental fatigue or constant worry.
Neurotic disorders can manifest themselves in a variety of ways. Their most common signs are general malaise, obsessive thoughts, and fears. Neurosis often contributes to a decrease in mental activity and physical endurance. A person cannot fully perform his work, the quality of his work deteriorates. The patient becomes irritable, aggressive, and conflictual.
If this disorder is not treated promptly, severe mental illness may occur.
Diagnostics
Visual impairment in VSD is not associated with organic diseases. But in any case, a person experiencing any symptoms needs to undergo a diagnostic examination.
The initial examination of the visual organs includes:
- consultation and examination by an ophthalmologist.
- Consultation with a neurologist;
- checking visual reflexes;
- computer vision diagnostics;
- blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound and MRI if there is a suspicion of compression of nerves and vessels in the spine or other disorders.
Interesting facts about vision:
- Fact 1
- Fact 2
- Fact 3
The eyes process about 36,000 pieces of information every hour.
The eyes use about 65 percent of the brain's resources. This is more than any other part of the body.
The wriggling particles that appear in your eyes are called floaters. These are shadows cast on the retina by tiny filaments of protein inside the eye.
How it manifests itself
A person with vegetative vascular dystonia with visual impairment experiences the following symptoms:
- spots before the eyes;
- bright single flashes;
- pain syndrome in the eyes.
The appearance of outbreaks can be either episodic or constant. This happens when a person abruptly assumes a vertical position.
The pain syndrome may be aching in nature. It appears sporadically or is constantly present. The pain usually occurs in bright light. Also, discomfort can occur when a person touches the organs of vision through closed eyelids.
Darkening in the eyes
This is one of the main symptoms of VSD. When a person’s condition worsens, his blood pressure begins to “jump.”
At the same time, the person suffers from headaches and dizziness. Sometimes there is loss of consciousness. An overloaded central nervous system ceases to cope with its responsibilities.
Simultaneously with the increase in blood pressure, an increase in intracranial pressure is observed.
Darkening of the eyes is often a precursor to fainting.
Distortion of the picture of space
The disorder provokes a distortion of the picture of the surrounding space. It seems to a person that surrounding objects stick together or move apart.
The outlines of things are unclear. Objects that come into view are capable of:
- appear taller;
- appear wider;
- bend.
To a person standing or sitting in one place, it seems that stationary objects are approaching or moving away.
How to treat visual impairment with VSD
For VSD with visual impairment, complex therapy is used. It is useless to treat just one thing. Moreover, any symptom of dystonia is only the result of a complex disorder that has a cause. And as you know, in 90% of cases the cause of the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia is psychological problems or physical fatigue.
To eliminate vision problems with VSD, the following treatment methods are prescribed:
Drug therapy
To relieve symptoms and correct physical condition, the doctor may prescribe medications from the following groups:
- Tranquilizers to relieve anxiety.
- Sedatives, to suppress excitement of the nervous system.
- Nootropics – improve blood circulation, supply the brain with oxygen, and have a positive effect on cognitive functions.
- Vitamins to strengthen blood vessels, the nervous system and the body as a whole.
The dosage and duration of treatment are determined by the doctor. Self-administration of medications is prohibited. If the drug does not help, the doctor cancels it and replaces it with another.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy treatments provide more effective results, especially when combined with the other two.
These include:
- Massage.
- Manual therapy.
- Acupuncture.
- Hydrotherapy.
- Exercise therapy.
Any type of physical therapy should also be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the patient’s history and current condition.
Psychotherapy
Although psychotherapy is often put in last place or excluded altogether, it is the key in the treatment of VSD, visual impairment and imbalance of other organs. For successful recovery, the patient needs to balance his psycho-emotional background and learn to react differently to irritating factors.
There are often cases when internal problems, psychological trauma and conflicts become the cause of the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia and anxiety disorder.
For example, a person is tired of working at a certain job and everything there irritates him terribly. But he is afraid of being left without income or condemnation from his loved ones. A serious conflict occurs inside, which the unfortunate person tries to suppress. Even if you manage to drown out the suffering for a while, it doesn’t go away. Internal tension negatively affects the nervous system, gradually depleting it. At some point, the body cannot stand it and a crisis of VSD occurs.
The problem is that often such causes of illness are unconscious or strongly suppressed. A person begins to treat symptoms without understanding the true cause. Recovery is slow or there is no improvement at all.
Psychotherapy allows you to identify such psychological problems and resolve them. This significantly speeds up recovery and often the patient manages to improve his health even without medication.
Online appointment with a doctor in any city in Russia
Factors provoking visual impairment in VSD
There are three main factors that cause physiological disorders in the visual organs. Above, we looked at why vision at the physical level deteriorates with VSD. Now let’s figure out what exactly provokes disruptions in the body and leads to dysfunction of all processes.
- Distorted perception of reality (brain disorders ). People suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia are prone to increased anxiety, fears, hypochondria, and obsessive thoughts. When a sufferer is constantly fixated on his mental “horror stories,” negative thoughts become entrenched at the subconscious level. The lesions that process them spread throughout the cerebral hemisphere and affect the visual center. As a result, there is a violation of the transformation of information received from the eyes. The brain simply cannot compare what you see in your fantasies and what is outside (in reality). The pictures are too different and the brain, coming into a kind of stupor, cuts off vision for a while, because in its opinion, your internal pictures are more real.
- Anxiety and panic attacks. The cause of visual impairment in VSD is constant tension caused by fears and stress. When a person is nervous, worried, worried and experiences severe attacks of fear, his whole body becomes stiff. Muscles tense, blood vessels constrict, blood circulation slows down. It’s not for nothing that there is an expression “the blood in your veins froze with fear.” This leads to the consequences described in the chapter above - insufficient tissue nutrition and disruption of metabolic processes in the organs of vision.
- Lack of nutrients. With VSD, the entire body suffers . Nutrients begin to be absorbed worse. In a stressful state, it is impossible to produce some valuable elements that our body supplies itself with on its own. The eyes begin to lack essential substances. This is also one of the causes of visual impairment in vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Interesting to know!
The simplest visual acuity test. Look at the sky at night and find the Big Dipper. And if in the handle of the ladle, near the middle star, you clearly see a small star, then your eyes have normal sharpness. This method of testing vision was adopted by the ancient Arabs.
Mental symptoms
- Emotional stress, which often manifests itself in the form of obsessive thoughts and obsessive actions that arise for no apparent reason.
- Complexity about one’s role in society, sharply low or high self-esteem.
- Sharp mood swings depending on trivial reasons, severe irritability in response to weak stimuli.
- Sharply increased sensitivity to fluctuations in ambient temperature, loud sound and bright light.
- Acute reaction and unpreparedness for stress. At the same time, neuroses are characterized by isolation and fixation in response to stressful situations, and not aggression or tearfulness.
- Tendency to constant worries and anxieties for any, no matter how insignificant, reason. At the same time, the particular importance of early treatment of neuroses in the event of the appearance of these symptoms was noted.
- Symptoms of fatigue and chronic fatigue. Characteristic in this case is only a slight decrease in fatigue even after prolonged sleep and rest. This is what may indicate problems in the neuropsychic or immune spheres of the human body.
- Inconsistency and uncertainty in the priorities of a person’s life, incorrect emphasis on priorities and preferences are also symptoms of neuroses.
Contact a specialist
Sign up for a consultation tel. 242-82-65
Make an appointment
Dmitry Roaldovich Sosnovsky
Psychiatrist-narcologist
Total medical experience is 33 years, of which 18 years in the field of psychotherapy and narcology. Author of many articles on psychotherapeutic topics