Neurosis - what is it?
Neurosis is a collective term that refers to certain types of neurotic disorders. It can develop in both women and men. At risk are people who are in a certain phase of physiological changes: aging of the body or puberty. However, neurosis can occur at absolutely any age. In children, it usually goes away on its own, without treatment, and does not lead to any mental disorders. In adulthood, neurosis can greatly affect health - both physical and psychological. Often, neurotic disorders in adults cause pathologies of internal organs.
Negative stressful situations and acute psychological trauma can cause various painful manifestations in a person. The catalyst for neurosis can be an unresolved internal conflict or strong pressure from external factors that are uncomfortable for the patient. At the same time, not only severe injuries can provoke a neurotic disorder. Sometimes it becomes a consequence of mental fatigue or constant worry.
Neurotic disorders can manifest themselves in a variety of ways. Their most common signs are general malaise, obsessive thoughts, and fears. Neurosis often contributes to a decrease in mental activity and physical endurance. A person cannot fully perform his work, the quality of his work deteriorates. The patient becomes irritable, aggressive, and conflictual.
If this disorder is not treated promptly, severe mental illness may occur.
Atypical antipsychotics
Of all the atypical antipsychotics, the ophthalmic side effects of clozapine are the most studied. Clozapine is commonly used as an alternative to traditional phenothiazines due to the reduced risk of extrapyramidal side effects [8]. E. Ceylan et al. showed that taking clozapine leads to the development of dry eye syndrome (DES) and a decrease in corneal thickness. This prospective study involved 60 people: 30 patients diagnosed with schizophrenia took clozapine for 2–4 years (group 1), the remaining 30 people formed a control group (group 2). In the clozapine group, there was a statistically significant decrease in tear production (during the Schirmer test, the length of the area moistened with tears in group 1 was 3.33 ± 0.72 mm, in group 2 – 13.6 ± 1.59 mm) and a decrease in the central thickness of the cornea (495 –554 µm and 520–580 µm in groups 1 and 2, respectively), apex of the cornea (497–556 µm and 521–581 µm in groups 1 and 2, respectively), cornea at its thinnest point (492–551 µm and 518–578 µm in groups 1 and 2, respectively) [11]. This side effect is based on the anticholinergic effect of clozapine (action on M- (including M3-), N-receptors). This contributes to a decrease in the secretory activity of goblet cells and disruption of the formation of the water-mucin layer of the tear film [8], which leads to the development of dry eye syndrome [11]. In advanced cases of dry eye syndrome, a decrease in visual acuity is observed. In order to prevent the development of these visual impairments, the administration of cyclosporine is effective [12].
When taking clozapine, pigmentation of the eye structures is also noted: the skin of the eyelids, conjunctiva, cornea, retina, but this side effect is less common than when taking typical antipsychotics [8].
A prospective study involving 452 patients, which lasted for 6 years, also found that when taking atypical antipsychotics (risperidone, olanzapine, ziprasidone, quetiapine, clozapine, aripiprazole), oculogyric crisis (dystonia) developed in 1.8% of cases (8 patients). oculomotor muscles, characterized by fixation of gaze upward for several minutes or hours [13]. The etiology of this condition is complex and probably involves blockade of dopamine receptors [14].
Atypical antipsychotics may cause metabolic syndrome, which can potentially lead to early formation of diabetic cataracts [4]. However, a retrospective study of 4366 patients found no association between atypical antipsychotics and an increased risk of cataracts [15].
Benzodiazepine tranquilizers
When taking diazepam, there is a risk of developing allergic conjunctivitis [4]. The pathogenesis of this reaction is based on the formation of a metabolite of desmethyldiazepam, which acts as an antigen and promotes the development of a type 1 immune reaction. As a rule, allergic conjunctivitis occurs within 30 minutes after taking the drug, the maximum reaction occurs within 4 hours and resolves after 1–2 days. Symptoms include decreased vision, photophobia, burning, lacrimation and foreign body sensation [16]. If an allergic reaction occurs, switching to another benzodiazepine is preferable [5].
Anxiolytics can cause dose-dependent ocular movement disorders; Taking these drugs should be avoided whenever possible while driving [17], especially in combination with alcohol or other antidepressants [4]. According to U. Ettinger et al., lorazepam leads to a decrease in the amplitude of saccades and their peak speed, while it increases the duration of saccades and does not significantly affect their average speed [18].
Theoretically, taking benzodiazepine tranquilizers can provoke the development of an attack of angle-closure glaucoma (ACG), since they have mild anticholinergic properties. However, in earlier reviews, this group of drugs was not included in the list of drugs leading to the development of an attack of PAH [19]. Thus, in patients who do not have a predisposition (no history of PAOG and a narrow anterior chamber angle), the risk of developing an attack of PAOG is minimal [4].
Causes of neurosis
There are several theories, each of which suggests considering certain factors that provoke neurotic disorders. So, from the physiological point of view, neurosis is a pathology of the body, the cause of which is a malfunction in the nervous system. Excessive mental activity, accompanied by a large number of nervous processes, can contribute to the destabilization of the psychological state.
There is another theory, according to which the cause of neurosis is a combination of an irritant and personality characteristics. For example, there is a stressful situation. People may perceive it differently. Some may treat it indifferently or with great patience, others are not always able to adequately respond to various stimuli.
General health is also important. People who do not take care of their health, smoke, eat poorly, abuse alcohol, do not have a clear regime and daily routine, often get sick, are constantly overworked physically and mentally, and are more susceptible to neuroses. In the event of a stressful situation, they are especially vulnerable. At the same time, not only negative factors can provoke a disorder. Even positive emotions can lead to the development of neurosis. The sharp and constant alternation of positive and negative factors has an even worse effect on the psyche. Thus, in childhood, a neurotic disorder can be the result of a “carrot and stick” type of upbringing.
There is also a psychoanalytic theory. Neurosis, according to its postulates, is the result of an internal conflict that arose due to the dissatisfaction of a basic need.
Moreover, the foundations of conflict can be laid at any age. Subsequently, they manifest themselves in the form of an unstable psychological state.
In general, the causes of neurosis in certain cases are the following factors:
- isolation of a person from society;
- conflict between instinctual drives and moral standards;
- strong pressure and control from others;
- a person's strong need for protection or recognition;
- a thirst for power, glory that cannot be satisfied;
- striving for ideality, perfectionism;
- inability to rest, uncontrolled workaholism;
- lack of life experience and skills to adequately perceive stressful situations.
These are psychological reasons. Physiological diseases include diseases of infectious or inflammatory etiology, addictions, including alcoholism and smoking. These factors reduce immunity, and therefore the body’s resistance to the external environment. How does a neurotic disorder manifest itself? Is it possible for vision to deteriorate with neurosis?
Myopia can be mild to moderate or severe
| Degree of violations | Indicators in diopters | Change in eyeball length | Visibility |
| Weak | Up to 3 diopters | Above approximately 1.5 mm | Objects close up are clearly visible, but objects in the distance are a little blurry |
| Average | 3-6 diopters | Higher than 3 mm | Objects are clearly visible close up at a distance of up to 30 cm, but in the distance they are difficult to distinguish |
| High | 6-30 diopters | Changes are observed not only in the length of the eyeball but also in the retina of the fundus and choroid | Objects are visible at a distance of up to 10 cm |
Ophthalmologists also talk about true and false myopia.
In the first case, real changes in the length of the eyeball are observed. In the second, visual impairment is associated with a spasm of accommodation of the eye muscles, which occurs due to eye fatigue. However, it is possible for the false form to transform into the true one if no measures are taken, the vision continues to be strained too much, and the disease is not treated.
Symptoms of neurosis
There are two large groups of signs of neurosis: psychological and physical. The first include:
- emotional instability, frequent and causeless mood swings;
- lack of initiative, indecision;
- inadequate self-esteem: overestimation or underestimation of one’s own abilities;
- obsessive thoughts, uncontrollable fears;
- irritability, aggressiveness;
- constant feeling of anxiety, restlessness;
- a cynical attitude towards others, a desire to criticize everyone and for any reason;
- inconsistency of desires and needs;
- tearfulness, vulnerability, excessive impressionability, touchiness, suspiciousness.
A person in a state of neurosis concentrates heavily on traumatic events. In other words, this or that situation does not let the patient go; he constantly thinks about it, considers himself guilty, even if there is no reason for this. It’s almost impossible to focus on work or positive life moments. In this state, it is impossible to perform the amount of work that is normal for a healthy person. Labor productivity is falling. Because of this, a conflict situation at work may arise. This will worsen your mental state.
The most common symptom of neurosis is insomnia. It becomes increasingly difficult for a person to fall asleep at the usual time. If he does fall asleep, he has nightmares and wakes up in a cold sweat. In the morning you feel very tired, and drowsiness persists throughout the day.
Sometimes neurosis is accompanied by increased sensitivity to sounds. Loud voices and music irritate the patient. Photophobia and meteosensitivity develop. These factors are associated with the physical manifestations of neurosis. Among them:
- headache that hardly goes away, dizziness;
- discomfort in the heart area;
- digestive problems;
- increased blood pressure;
- weakness and trembling of hands;
- decreased appetite;
- excessive sweating;
- frequent need to urinate;
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- decreased sex drive;
- the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes, blurring of vision, and a decrease in its acuity.
These symptoms are quite common and characteristic of many diseases. It’s difficult to call them specific. Consequently, when they appear, the doctor does not always look for reasons in the psychological state of the patient. Because of this, neuroses are always very long lasting.
Types of myopia and features of their treatment
Modern medicine identifies three main forms of this visual impairment - congenital, hereditary and acquired.
- With congenital myopia
, you can notice a deformation of the eyeball as soon as the child is born. - Hereditary pathology is passed on from generation to generation in the family. This is due to the structural features of the connective tissue of the eyeball, which are determined genetically. In some people it may stretch more, in others less. The chance that a nearsighted father will have a child who will eventually experience the same problem is about 15%. For a mother with this visual impairment, the risk of having such a baby increases to 30%. If both parents are myopic, then it increases to 50%. However, even if mom and dad have one hundred percent vision, this does not guarantee the absence of pathology in the child.
Acquired myopia
is formed over time under the influence of various factors: excessive stress on the eyes, lack of necessary preventive measures.
Deterioration of vision due to neurosis
Neurosis and vision: can they be connected? As mentioned earlier, neurotic disorder occurs for various reasons, including as a result of infectious diseases. Moreover, the consequences of these disorders are also varied. Deterioration of vision due to neurosis is a fairly common picture observed by doctors.
Psychogenic manifestations of an unstable mental state include: narrowing of visual fields and a decrease in its acuity. Patients come to the ophthalmologist with complaints that they see poorly or see almost nothing. In this case, the patient is well oriented in space, does not bump into objects, and can even drive a car. Upon examination, it turns out that there are no visible reasons for the decrease in visual functions. This is due to the fact that the main factor leading to vision deterioration is a person’s reluctance to “see the problem.”
Narrowing of the visual fields is characteristic of hysterical neurosis. Usually it is also accompanied by increased photosensitivity and various signs of asthenopia - rapid eye fatigue.
The behavior of patients also changes. It can be partly called strange. On the one hand, a person complains of decreased visual function, and sometimes partial or complete blindness. On the other hand, such a condition does not cause him great anxiety, as it does in people who suddenly become blind. In other words, vision loss is not so painful if there are no pathological reasons behind it. They are not detected during examination. When the ophthalmologist has ruled out all hypothetical ailments that could explain the deterioration of vision, we are talking about psychological factors.
When a person is very frightened, he develops anxiety, a desire to hide, he instinctively closes his eyes so as not to physically see the problem. This is how a person protects himself with the help of various functions of his body. Psychological protection will manifest itself in the appearance of a veil before the eyes, narrowing of the visual fields and other ophthalmological symptoms.
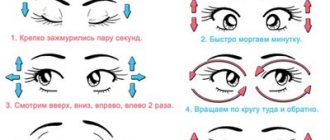
Gymnastics for the eyes
Ophthalmologists recommend setting aside a little time every day to do eye exercises. This will help relieve tension from the muscles and improve blood circulation in the blood vessels. Below are several exercise options:
- Opening/closing the eyes with force 5-6 times (2 repetitions, break 30 seconds).
- 3 times alternately look up and down, left and right with a fixed position of the head, with open and closed eyelids (3 repetitions, break 1 minute).
- Rotate your eyes in a circle in different directions with your eyelids open and closed (3 repetitions, break 1 minute).
- Close your eyes tightly for 5 seconds, then rest for 5 seconds (8 repetitions).
- Rapid blinking for 1 minute.
- Shift your gaze from the tip of your nose to any distant point (10-15 repetitions).
A sharp or gradual deterioration of vision always negatively affects a person’s quality of life. Taking care of eye health should concern people every day; this will significantly reduce their incidence. Good vision is the key to success and longevity!
New modern treatment methods
According to doctors, only surgery can restore vision to 100% in case of myopia. Modern medicine does not offer any other options for a radical solution to the issue.
The most effective correction method today is considered to be laser, using a femtosecond laser device.
- Laser correction is carried out on the basis of precise calculations performed by a computer.
- The correction accuracy is very high.
- Using a laser, a new surface of the cornea is formed: a thin layer is cut off to provide the required thickness for normal refraction.
- The patient does not feel pain during or after the operation.
- Vision is restored to 100% within a month.
If the degree of impairment is high (more than 16 diopters), patients over 18 years of age undergo abdominal surgery: the lens is corrected or replaced with an artificial one.
As the disease progresses, scleroplasty is performed. The posterior pole of the eyeball is strengthened, which prevents it from stretching in the future.
To prevent myopia
in adults, laser coagulation can be performed: the retina is welded near the thinned areas of the cornea.
Any surgical intervention requires a thorough preliminary examination of the patient. This is necessary to identify possible contraindications and exclude the occurrence of complications in the postoperative period.
Quotes
“Forecasts of world statistics indicate that by 2050, 50% of the population will be myopic, 10% will have a high degree of myopia, and about one billion people will be blind,” Tatyana Pavlova, Associate Professor of the Department of Ophthalmology, Pediatric Faculty, Pirogov Russian Medical University, leading expert of the interprofessional Alliance for Vision Care “Gate of the Sun”
“Children should undergo regular check-ups with doctors. The main goal of such examinations is the prevention of eye diseases. Eye hygiene is also important: walk outside more often, limit the use of gadgets. This is, of course, a matter of discipline, and parents must monitor this. The younger the child, the less time he should spend with computers and smartphones. Until the age of 3-4 years, such gadgets are generally not recommended for use,” said Brian Holden, director of education at the Brian Holden Vision Institute (Australia) to Luigi Bilotto.
Can it be cured?
Myopia
amenable to correction and treatment.
The best results are achieved if treatment begins as early as possible - with mild or moderate impairment. And provided that several methods are combined: eye exercises, physiotherapy,
wearing glasses or lenses.
It is important to follow all the recommendations of your ophthalmologist, carry out procedures, do exercises and wear glasses or lenses regularly. Only in this case is it possible to noticeably improve vision and stop the progression of the disease.
Radical treatment methods include surgery performed with a laser. Using this technology it is possible
vision restoration
completely in most cases.
In the true form of the pathology, cure myopia without surgery,
Doctors are sure it’s impossible.
If myopia
is false, then non-surgical methods can help restore normal vision, but only if the patient is sufficiently persistent and follows all the ophthalmologist’s recommendations.