Medical history
Stuttering has several related names. It can be found within the framework of such concepts as logoneurosis and laloneurosis, logoclonia, balbucio, as well as battarism named after King Batta, who also suffered from this defect.
On the planet, logoneurosis is observed in 1% of the adult population and 3% of children. Typically, the disease manifests itself in childhood, between 2 and 5 years, when speech begins to develop. Being, so to speak, in a raw, unripe form, it is quite vulnerable and is subject to distortion in the event of any malfunction in the functioning of the nervous system.
The disorder has been known since ancient times. The prophet Moses and the pharaohs of Egypt had such a defect. One of the most famous individuals with logoclonia was Demosthenes, who nevertheless became a famous orator in Ancient Greece. His story is interesting because of how he tried to cope with his shortcomings, what unique techniques the philosopher used to do this. The most popular is pronouncing phrases with stones in the mouth. Along with this, Demosthenes also resorted to reading against the background of the sound of sea waves, pronouncing words mentally, in his mind. Another unconventional method of combating the disease that Demosthenes used was to listen to silence while sitting in a cave. The methods invented by the philosopher to eliminate stuttering turned out to be truly effective, since they turned him into an outstanding speaker.
From ancient times until the 20th century, the disorder was surrounded by a shadow of mystery. Doctors of various specialties tried to unravel his secret, but everything turned out to be in vain. Stuttering was attributed the status of a mysterious illness and was considered the result of damage to the speech organs. They tried to fight it with the help of herbs, spells, assault and even bloody operations in the oral cavity, but this did not bring visible improvements.
At the end of the 19th century there was a revolutionary revolution in understanding the nature of logoneurosis. It was carried out by the Russian psychiatrist I.A. Sikorsky. He came up with the idea that logoclonia originates in childhood at the time of the formation of speech activity. Pathologies of the nervous system and hereditary factors contribute to its occurrence. Sikorsky connected the concept of stuttering with neurosis.
Tartakovsky I.I. made an invaluable contribution to the development of the theory of the disorder. He came up with the idea of treating the disease. In particular, he proved the effectiveness of individual and group psychotherapy in the treatment of illness.
A separate branch, speech therapy, was formed already in the 20th century, and to this day it deals with problems of speech activity.
Formation mechanism
The occurrence of laoneurosis is based on the appearance of muscle spasms of the organs responsible for speech formation. These bodies include:
- language;
- lips;
- lower jaw;
- soft sky;
- larynx.
The facial muscles are also involved in the process.
The cause of convulsive contractions of the muscles of the speech-motor apparatus are pathological processes occurring in the brain.
The normal functioning of higher nervous activity is ensured by the harmonious interaction of the processes of excitation and inhibition in the cortex and subcortex of the brain. For a number of reasons, this harmony can be disrupted, leading to hyperexcitation or predominance of inhibition in speech centers. Immature, vulnerable speech areas in children are the first to be affected, leading to stuttering. Such susceptibility is also associated with the absence of inhibitory conditioned reflexes in children, which leads to increased excitability and its spread.
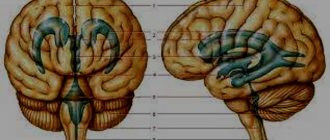
There are special nerve centers in the brain that are responsible for speech activity. The most significant of them:
- Broca's center is the vocal center, the largest speech authority in the brain. Activates the muscles and ligaments that form speech activity;
- Wernicke's center is auditory. Participates in recognizing one’s own and others’ speech;
- associative center - analyzes what was said and gives the command to the voice center to act.
It turns out that all three centers work in a circle. Under the influence of the voice center, we pronounce a phrase, and the auditory center is activated, forcing the associative center to analyze the information. After analysis, it allows you to re-engage the voice area.
This is a well-coordinated mechanism that operates strictly and clearly. The problem arises when the speed of the centers changes. Most often this occurs due to hyperexcitation of Broca's center. The speed of its action increases, which entails the opening of the circle. Excitation is transferred to nearby motor areas of the cerebral cortex. This leads to seizures. Then the vocal center relaxes, the circle closes again.
Another reason lies in the disruption of the activity of the striopallidal system. This system is responsible for the contraction and relaxation of muscles or for maintaining normal muscle tone and its restructuring. If a malfunction occurs in its operation, this leads to an imbalance in the tone of the articulatory, respiratory, and vocal muscles, causing them to spasm. They are under constant tension, which cannot but affect the quality of speech.
Another reason for stuttering is the struggle between the right and left hemispheres of the brain. The first is responsible for rhythmic, clear speech, while the second is responsible for arrhythmic speech. Normally, the right hemisphere should obey the left, but in stutterers they are simultaneously well developed, which is why they enter into competition. Violation of the pattern of their interaction entails confusion in speech class=”aligncenter” width=”700″ height=”482″[/img]
Classification and causes of the disorder
Stuttering can be classified according to different criteria. First of all, laloneurosis is divided into:
- clonic;
- tonic;
- mixed.
Clonic laloneurosis is based on clonic spasms of the muscles of the speech motor apparatus. They are characterized by small muscle twitches, as a result of which a person monotonously repeats the same sound or syllable or word. For example, o-k-k-k-kno.
Tonic convulsions are characterized by prolonged muscle spasms. In this case, the muscle freezes in one position and seems to become stiff. In this case, a manifestation of the disorder will be a long pause in a word or in speech: cow…..cow. The patient has great difficulty speaking.
The mixed form combines the characteristics of both previous forms.
According to localization, logoneurosis is divided into:
- articulatory – accompanied by spasms of the muscles of the face, lips, palate;
- vocal - spasm occurs during the pronunciation of vowel sounds. In this case, the patient may make indistinct sounds instead of a word or “sing” a vowel. In extreme cases, a person cannot say anything at all due to the closure of the vocal cords;
- respiratory – difficulty inhaling or exhaling prevents the patient from speaking freely, creating pauses in speech.
But the most significant classification divides the disorder into neurotic and neurosis-like.
Neurosis-like laloneurosis occurs in the presence of a specific physiological pathology. In such children, deviations in EEG indicators are observed, brain disorders, motor impairments, increased intracranial pressure, and spasmophilia are detected. Reasons for this form of stuttering:
- intrauterine, birth injuries;
- complicated pregnancy of the mother;
- infectious diseases.
Typically, neurosis-like stuttering appears at 3-4 years of age and increases gradually. His character has no situational dependence. Children begin to speak late. Nervous tics, ritual movements, and pronounced speech defects are characteristic.
Boy, 8 years old. The mother's pregnancy was difficult. During childbirth, the child experienced asphyxia. Subsequently, he was registered with a neurologist for perinatal damage to the nervous system. Received treatment. The boy was characterized by increased excitability and motor activity from birth. Stuttering appeared at the age of 3 spontaneously, for no reason, and worsened against the background of colds.
Neurotic laloneurosis occurs without physiological disorders of the nervous system. Initially, the child is characterized by normal and even early speech development. As a rule, it is possible to trace the specific cause that caused the disorder. It may be completely absent in a calm environment and worsen under the influence of stress factors. The following factors predispose to its occurrence:
- overload of the child’s nervous system due to excessive demands from parents;
- early learning of foreign languages;
- severe fear or stressful situation;
- imitating family members who stutter;
- tension in the family, quarrels, conflicts;
- incorrect parenting model: hyper- or hypo-custody;
- early speech development;
- learning costs, poor vocabulary.
Stuttering also exists in 3 stages of its development:
- mild – the defect manifests itself periodically, under the influence of a traumatic situation;
- medium – speech is impaired due to anxiety, emotional stress;
- severe – stuttering is present in the patient constantly.
Diagnosis of neurosis-like stuttering in children
The examination reveals brain damage and its consequences at an early age in the form of delayed psychomotor development. The child is examined by specialists:
- a neurologist can diagnose residual effects of perinatal damage to the central nervous system, increased irritability, fatigue, motor disorders, disorders of motor function and coordination;
- a speech therapist identifies stuttering and determines its type, diagnoses pathology of speech (oral, written), auditory-verbal memory;
- the psychologist determines the degree of disturbance of the emotional-volitional sphere.
Instrumental examination methods: skull radiography, echo-EG, electroencephalography, CT, MRI help to detect organic changes and their prevalence.
After diagnostic procedures, specialists draw up a correction plan.
Manifestations
There is no one specific symptom that can characterize the disorder. In the minds of most people, stuttering manifests itself as a rhythmic repetition of individual sounds or syllables. For example, mm-m-ma-ma. However, this is not the only symptom of the disease.
Manifestations of laoneurosis include excessive stretching of speech units, long pauses during a conversation, and swallowing of words. A person may experience hesitation in statements and difficulties in pronouncing words.
Often the face of a person who stutters is distorted by grimaces and tics. This is a kind of attempt to cope with a hated defect.
With spasms of the respiratory muscles, the patient experiences breathing problems. There is a feeling as if he is suffocating.
Inability to speak leads to mental imbalance. Such people are nervous and aggressive; children are withdrawn and avoid communication for fear of ridicule from their peers. The child refuses to go to kindergarten and does not want to play with other children. His sleep and appetite are disturbed.
Do not think that impaired speech does not entail any consequences. It's not like that at all. If you don’t deal with your baby’s problem in time, you may end up with:
- mental retardation;
- problems with learning and learning at school;
- enuresis;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- character accentuations, neuroses;
- As you grow older, you experience difficulties in obtaining a profession and further employment.
Often, stuttering provokes the formation of phobias and defensive ritual movements. Among the possible phobic options are logophobia - fear of talking, social phobia - fear of people leading to social isolation, glossophobia - fear of public speaking.
People with logoneurosis develop a system of protective rituals for themselves. Among students, touching their forehead with their palm is common - a sign of intense thinking, and squeezing the table top with their fingers. In adults, when communicating with superiors, the following is observed:
- trampling from foot to foot;
- touching the earlobe;
- patting your hand on your thigh.
In addition, patients form rituals similar to obsessive actions: knock on wood, turn around 3 times around its axis.
Boy, 11 years old. Diagnosis: “Stuttering, severe, mixed form. Ritual movements. Logophobia." He was raised by suspicious, overprotective parents. Despite the fact that his classmates treated him well, he was overly worried about his stuttering and feared that he would become an object of ridicule.
The child is characterized by increased pedantry in relation to everything related to school and anxiety. He is constantly worried about his and his parents’ health. Against the background of stuttering, he developed obsessive rituals that turned into the whole system. So, before leaving for school, he needs to pull the button on his clothes 3 times, then knock three times and finally shift from foot to foot. If the ritual was interrupted, the child begins the sequence again. The boy claims that this relieves tension and he worries less about his defect.
In the case of stuttering, you should know that the sooner therapy is started, the higher the chances of recovery. The insidiousness of the disorder is that it is prone to recurrence.
Thus, the young man claimed that he managed to get rid of logoneurosis in 1.5 months. Rejoicing, he stopped studying, and the disorder returned after a while. Then the guy realized that the disease was not so simple and required a careful, thoughtful approach. He subsequently created a website for people with stuttering, zaikanie . com , designed to help those in need overcome this unpleasant disease.
Treatment of neurosis-like stuttering in children
Correction of neurosis-like stuttering requires the participation of several doctors: a speech therapist, a neurologist, a psychologist. The treatment is complex and includes:
- drug therapy - metabolic drugs, nootropics, vitamins, absorbable drugs, diuretics, if necessary - antidepressants, sedatives;
- speech therapy correction - classes directly with a speech therapist or speech pathologist, massage, breathing exercises;
- Classes with a psychologist, psychotherapy, art therapy allow you to achieve emotional and volitional stability and adapt to society.
All treatment measures must be carried out strictly according to the plan. It is necessary to follow the recommendations of the speech therapist, including practicing at home independently. At the same time, you need to develop fine motor skills.