In this article, medical doctors will help you understand the symptoms of stroke and micro-stroke and tell you what to do if a person has an attack.
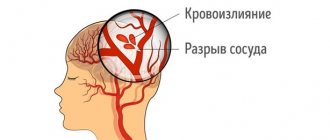
A stroke is a cerebrovascular accident that causes a blood vessel to become blocked or ruptured when a blood clot disrupts the flow of blood to the brain. Brain cells die from lack of nutrition and oxygen, which leads to impaired speech, cognitive and motor functions. If a person does not receive timely assistance, death occurs within 2–3 hours.
Symptoms of a stroke
- Sudden clouding of consciousness. Slurred thoughts, confusion and delirium of speech, difficulty understanding speech.
- Vision problems - blind spots, blurred vision.
- Impaired coordination and balance. The gait may look strange, as if the person has weakness in one or both legs, difficulty moving in space, lost, or dizzy.
- Facial asymmetry: one side of the face relaxes, a person cannot smile from both corners of the mouth.
- Weakness in arm and leg on one side. Ask the person to raise both arms straight in front of them and to the sides.
- A sharp, severe headache for no apparent reason.
A stroke develops quickly. A person himself can identify symptoms within a minute and call for help. If you see the above symptoms in a person near you, immediately call an ambulance and provide first aid.
Help without delay. Beware, spinal stroke!
Numbness of the skin, impaired movement in the leg... One of the diseases in which such manifestations occur is stroke. The connection is firmly established in the mind: if there is a stroke, it means the brain.
However, it can also be spinal, affecting the “main cable” of the body - the spinal cord. We are talking with Irina Vladimirovna Vlasova, a neurologist at the Expert Voronezh Clinic, about this pathology. Spinal stroke is the topic of our interview.
— Irina Vladimirovna, now in many cities of Russia there is a campaign aimed at informing people about the first signs of a stroke. But in addition to cerebral stroke, there is an equally dangerous disease - spinal stroke. Tell me what it is?
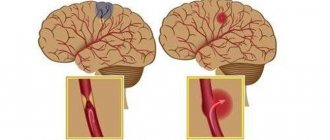
This is an acute disorder of spinal circulation, which can develop due to compression, blockage or rupture of the spinal artery. In this case, two scenarios are possible: ischemia or hemorrhage. Based on this, spinal stroke is divided into ischemic and hemorrhagic. The first form is more common.
Read material on the topic: Ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: what is the difference?
— Is spinal stroke reflected in ICD-10?
Yes, its code is G95.1
— How often does this pathology occur among Russians and who is at risk?
It is relatively rare: in the structure of neurological diseases it accounts for 1-1.5%. The risk of occurrence in women and men is generally the same. Most often, this diagnosis is made in the age range of 30-70 years.
IN THE STRUCTURE OF NEUROLOGICAL DISEASES, SPINAL STROKE IS 1-1.5%
What are the causes of spinal stroke? There are several groups, including:
- pathological changes in the vessels supplying blood to the spinal cord (can be congenital - for example, aneurysms, malformations, underdevelopment, and acquired - for example, atherosclerosis);
Read the material on the topic: Will traditional methods of treatment help in the treatment of atherosclerosis?
- processes leading to compression of blood vessels supplying the spinal cord from the outside (tumors, other space-occupying formations in the chest or abdominal cavity, enlarged lymph nodes, vertebral fragments due to injuries);
- complications that arise during operations on the spine or nearby vessels (in particular, on the aorta).
WHEN SYMPTOMS OF A SPINAL STROKE APPEAR, A PERSON NEEDS URGENT MEDICAL CARE AND EMERGENCY HOSPITALIZATION TO A VASCULAR CENTER. CALL AN AMBULANCE
Most often, this pathology develops due to a combination of several factors.
— What are the symptoms of a spinal stroke?
Signs appear quite quickly (from several minutes to several hours, less often - days). They are quite diverse, which is explained by the location of the lesion and its prevalence.
At the level and below the site of the lesion, disturbances in movement (paresis), sensitivity and functions of the pelvic organs are noted.
Ischemic stroke develops more often against the background of “precursors”. These can be various short-term sensitivity disorders (numbness, tingling, mainly in the lower extremities), transient motor disturbances in the form of paresis.
With a hemorrhagic spinal stroke, severe pain in the spine is noted, with radicular symptoms, as well as the motor and other disorders listed above.
— What should be done if there are signs of a spinal stroke? What is first aid?
If a person experiences any of the above symptoms, he needs urgent medical care and emergency hospitalization at a vascular center. Call an ambulance.
— In order to help a patient with a cerebral stroke, doctors have only four hours. How quickly should a patient with suspected spinal stroke be admitted to hospital?
We are talking about the so-called “therapeutic window”. It is up to 4-6 hours (the sooner the better). The sooner help is provided, the smaller the area and severity of the lesion will be.
After this time, the chances of reversing the changes that occur decrease.
— What is included in the “gold standard” for diagnosing spinal stroke?
A collection of complaints and medical history and a neurological examination are required.
Computed and magnetic resonance imaging, spinal angiography, lumbar puncture and electroneuromyography are used.
You can sign up for an MRI of the spine here
A general and biochemical blood test, coagulogram (study of the characteristics of the blood coagulation system), glucose and lipid levels are performed. Consultations with other specialists are carried out.
— What diseases are differentiated between spinal strokes?
The range of pathologies for differential diagnosis includes acute inflammation of the spinal cord, its tumors and space-occupying formations, epidural abscesses, and syringomyelia.
— How is spinal stroke treated? What are its principles?
Regardless of its type, nonspecific therapy is carried out aimed at reducing edema, maintaining metabolic processes in nerve cells, and preventing complications.
For ischemic spinal stroke, neuroprotective therapy is carried out, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents are prescribed.
If this is a hemorrhagic spinal stroke, drugs are used to stop the bleeding, and, if indicated, surgery is performed to eliminate its source.
— Irina Vladimirovna, what is the prognosis for patients with spinal stroke? Has modern medicine learned to successfully treat this disease and rehabilitate such patients?
This pathology has a mostly favorable outcome, but sometimes it can result in disability or death. This can be, in particular, in case of malignant tumors, a severe general somatic background (for example, the presence of diabetes), or the addition of an infection (for example, the development of pneumonia).
The outcome is also influenced by factors such as the cause that led to the development of the stroke, the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the “bypass” blood circulation. Early treatment improves the prognosis of the disease.
SPINAL STROKE MOSTLY HAS A FAVORABLE OUTCOME. EARLY TREATMENT IMPROVES THE DISEASE PROGNOSIS
Recovery after a spinal stroke is ensured by rehabilitation measures. Early rehabilitation includes the use of physical therapy, kinesiotherapy and physiotherapy, massage, and ergotherapy.
The success of rehabilitation also depends on the extent of damage to the spinal cord tissue and the timeliness of seeking help (within the “therapeutic window”).
— Our material will be incomplete if we do not talk about disease prevention. How to avoid spinal stroke?
Its prevention lies in timely diagnosis and treatment of vascular pathologies; detection and elimination of malformations, aneurysms; treatment of intervertebral hernias; prevention of spinal column injuries.
Read material on the topic: What are hernias and protrusions of the spine?
It is important to lead an active lifestyle, normalize weight, eat rationally, and get rid of bad habits.
Other materials on topics:
Let's pull and pull! Who can benefit from spinal traction?
What will an MRI of the spinal column show?
For reference:
Vlasova Irina Vladimirovna
Graduate of the Faculty of General Medicine of the Voronezh State Medical Academy in 2007.
From 2007 to 2009 she completed clinical residency in the specialty “Neurology”.
Currently holds the position of neurologist at Clinic Expert Voronezh. Receives at the address: st. Pushkinskaya, 11.
Symptoms of a microstroke
- Sharp and severe headache.
- Sudden memory loss, difficulty understanding and constructing speech.
- Loss of balance and coordination.
- Numbness in an arm or leg, numbness in one part of the face.
- Severe sound and photophobia.
In case of a micro-stroke, a person can be helped within 4 hours. It is necessary to seek help as soon as possible - either go to the vascular center or call an ambulance.
65% of patients subsequently develop a full-fledged stroke after a mini-stroke, so it is necessary to promptly treat and restore normal blood circulation in the brain.
Treatment of male microstroke
The very first measure in treatment is to restore normal blood flow to the brain. This is done with the help of special medications:
- Means for normalizing blood pressure;
- Cardiac glycosides that help normal heart function;
- Vasoactive drugs that help improve blood circulation in brain tissue;
- Drugs that help reduce blood clotting;
- Nootropics that allow you to stimulate brain function, thought processes, and nutrition of brain cells.
- In addition to medications, the patient undergoes additional rehabilitation measures:
- Massages;
- Special exercises for breathing;
- Physiotherapy;
- If necessary, meet with a psychologist or speech therapist.
What to do if a person has a stroke?
- First of all, call an ambulance. Sometimes the minutes count.
- Provide fresh air, open windows and doors, and free the person’s neck from constricting clothing.
- Leave the person where the attack occurred. The patient cannot be moved.
- Elevate the person's head and upper body 30 degrees by placing several pillows under the thoracic spine.
- If vomiting occurs, turn the person's head to the side and ensure that the vomit passes away so that the person does not suffocate.
- In the event of an epileptic attack, carefully hold the person, turn his head to the side and insert an object wrapped in cloth into his mouth - a stick, a comb, a spoon.
- In case of cardiac arrest, immediately begin compressions through the chest and perform artificial respiration.
- Wait for the ambulance.
First aid
If your arms and legs suddenly become weak and numb, your face is distorted, speech and vision are impaired, consciousness is upset, dizziness appears, there is reason to think that a cerebrovascular accident has occurred.
There is no need to wait until the next day to invite a local doctor or family doctor; you need to urgently call an ambulance. The best option is immediate hospitalization.
But even before the ambulance arrives, it is necessary to provide proper care for the patient at home and carry out the first treatment measures.
Create a calm, comfortable position for the patient, preferably lying on his back with a small pillow under his head. The head and shoulders should lie on a pillow to prevent flexion of the neck and deterioration of blood flow through the vertebral arteries. If a person falls as a result of an attack, when lifting and laying him down, try (this is very important) to avoid sudden movements of his head. You feel that you can’t cope alone, don’t rush - it’s better to stay on the floor until help arrives.
Pay attention to the patency of the upper respiratory tract, especially in cases of impaired consciousness. Be sure to remove removable dentures from the mouth. If there is excessive salivation or accumulation of mucus in the oropharynx and nasopharynx, carefully turn the patient’s head to the side. Be sure to open a window or window - fresh air is necessary.
Monitor your blood pressure. Every person, and especially those suffering from hypertension (himself or his close relatives), should know the blood pressure numbers at which he feels comfortable. Then, when neurological symptoms appear, it is not difficult to trace on what blood pressure indicators they developed. If there are elevated blood pressure numbers, it is recommended to give antihypertensive drugs that the patient usually uses (hypertensive patients always have them in their home medicine cabinet). After giving the medicine, measure your blood pressure - it should be 5-10 mm Hg. column higher than the numbers usual for the patient.
A sharp decrease in blood pressure below the patient’s “working” numbers is strictly contraindicated; this will lead to an increase in cerebral ischemia and an increase in the size of the pathological focus.
To reduce high blood pressure before the ambulance arrives, it is recommended to give clonidine under the tongue. Sometimes a hood can help.
In the acute period of a stroke, you should avoid taking so-called peripheral vasodilators - papaverine, nicotinic acid, no-shpa, nicoshpan. They contribute to the development of the “steal” syndrome in the ischemic zone - there is a predominant dilation of unaffected vessels and an increase in cerebral blood flow in non-ischemic areas. But if nothing else is at hand, it is still better to lower blood pressure with these drugs than to leave it high.
The latest clinical and experimental studies have shown that there is a “temporary therapeutic window” within which it is possible not only to influence the functional state of the brain, but even to prevent the formation of its infarction. However, this can be achieved completely only within 6-8 minutes after the appearance of the first clinical symptoms. However, even after 3-6 hours it is possible to ensure significant reversibility of functional changes in the brain. Most drugs that protect tissue from the harmful effects of ischemia (they are called metabolic) are prescribed only by a doctor! They are taken under the control of clinical and laboratory parameters.
However, there are metabolically active drugs that must be given to the patient as quickly as possible before the ambulance arrives. This is glycine, cerebrolysin or nootropil. They are safe, do not produce unwanted side effects, and will not cause harm even when the diagnosis has not been established and the stroke is, say, hemorrhagic in nature, that is, caused by bleeding in the brain.
Dangerous age and consequences of stroke
After age 55, the risk of stroke increases significantly. For men, the most dangerous age is considered to be from 45 to 55 years, since during this period they have a stroke 2 times more often than women.
If a person can be saved, the stroke still does not go away without leaving a trace. The person may be left partially paralyzed and lose control of urination and bowel movements. Cognitive functions decrease—problems with memory, speech, and information perception appear.
Recovery after a stroke is possible, but it often requires a lot of time and effort from both the patient and his loved ones. Therefore, it is better to prevent a stroke than to deal with its consequences later.
Micro-stroke “on your feet”
Since the symptoms of a mini-stroke can last for a fairly limited time, some resilient men can suffer them without even stopping their daily activities. It seems to them that nothing terrible is happening - just a slight malaise, which goes away after an hour. Accordingly, neither a visit to a doctor nor adequate treatment occurs here.
This is very dangerous, because an ignored attack often becomes the reason for its rapid recurrence or, in general, the main factor in the development of cerebral ischemia. If this happens, the consequences will be very serious, including disability, and treatment will take several months or even years.
How to avoid stroke and mini-stroke?
Stroke and its precursor, microstroke, are most often caused by features of a person’s lifestyle. The risk of developing an attack increases:
- Hypertension.
- High cholesterol.
- Diabetes.
- Overweight.
- Smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels.
This can be avoided if you undergo preventive examinations on time, treat chronic diseases and modify your lifestyle. Giving up bad habits, losing weight and maintaining normal blood pressure are the three main steps towards healthy blood vessels.
At the medical level, you can visit a general practitioner, cardiologist and neurologist, as well as undergo a Holter study and 24-hour blood pressure monitoring. If you are already worried about health problems, do not expect a miracle - consult a doctor to avoid serious consequences.
Call the number listed on the website and make an appointment with a doctor today!
Prevention
To prevent a micro-stroke, you need to follow these fairly simple recommendations from specialists:
- Give up bad habits: alcohol, smoking, and especially drugs;
- Avoid stress and overexcitement, do not quarrel whenever possible and do not succumb to depression;
- Play sports with moderate physical activity;
- Get enough sleep;
- Avoid obesity, eat properly and in moderation;
- Periodically undergo examination and preventive treatment.
It is enough to follow these simple rules, and the likelihood of a micro-stroke can be minimized.