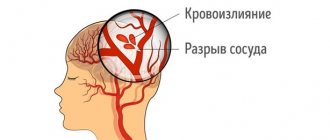
A microstroke is a pinpoint injury to the structure of the brain. They mean a tiny cerebral hemorrhage. Unfortunately, due to the fact that it is not large in scale and is practically invisible, patients rarely give it due importance and do not go to the hospital.
Symptoms rarely make themselves felt longer than 24 hours. After this, it goes away on its own, and it is very easy to attribute it to fatigue, weather dependence or similar phenomena. Moreover, at subsequent scheduled visits to a neurologist, if you do not report the incident, it is impossible to identify signs of a microstroke in women.
The Yusupov Hospital welcomes specialists of the highest category, doctors and candidates of medical sciences, whose specialization is pathology of the nervous system. They resort to innovative methods, including neuroimaging. This method combines several techniques, thanks to which it is possible to assess the functions, structure and biochemical characteristics of the brain. Thus, it is possible to use equipment to record which areas are already damaged and which are at risk of necrosis in the future.
About microstroke
“Micro-stroke, symptoms, first signs in women” is the topic of our article today.
Minor stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA) , transient cerebrovascular accident - different names for the same vascular process - micro-stroke.
A microstroke is a local lesion of the blood vessels of the brain , has a number of similar symptoms to a large stroke, but its manifestations are not so pronounced, and the attack is characterized by “transience”, lasting from several minutes to a day.
Men and women can be equally exposed to transient ischemic attack , but due to the natural differences between male and female bodies, the course of the process will differ in the clinic.
Differences between a microstroke and a stroke
A microstroke is a transient circulatory disorder in the cerebral vessels . It occurs against the background of constantly elevated blood pressure, its sharp rise, or atherosclerosis, when cholesterol plaques are deposited on the inner walls of blood vessels.
Important! Regularly measure your blood pressure with a tonometer, if you don’t have a tonometer, be sure to buy one, it’s not expensive, but every family should have it, here (on Aliexpress) you can always choose an inexpensive option.
The mechanisms of development of TIA and stroke are the same, they are similar in manifestations and symptoms:
- Bursting pain appears in the back of the head.
- You can clearly feel the blood pulsating in your temples.
- The sense of orientation disappears even in a familiar, familiar space.
- Limbs become numb and swollen. Swelling begins in the toes and feet, then swells in the fingers and forearms.
- Hyperhidrosis begins - increased sweat production throughout the body.
- The heart rhythm is lost.
- Both with a micro-stroke and with a large stroke, dizziness, fainting, and loss of consciousness are noted.
- In both the first and second cases, a change in vision is noted: “spots” or colored spots or circles appear before the eyes. At the very beginning of attacks, objects may look unnatural
- bright and clear, after a few minutes the colors fade, the surroundings are seen as if through a veil or fog.
- Loud sounds and bright colors begin to irritate.
- Paresis develops.
- Dysphagia develops - a violation of the swallowing reflex.
- Facial facial muscles are affected. And as a result, facial distortion occurs. A crooked, lopsided smile appears on the face, and the corners of the mouth droop.
Both during a stroke and during a transient ischemic attack, the whites of the eyes may turn red. In both cases, confusion and speech disturbances may occur, when it becomes slurred and difficult to understand.
Polysorb or activated carbon, which is better?
With all this, the processes differ in clinical picture:
- The symptoms of a microstroke are less pronounced.
- All manifestations of TIA disappear in a short period of time, the maximum duration of an attack is 24 hours, but usually it lasts no more than a few minutes.
- With a microstroke, a rapid heartbeat is observed, the skin of the face turns red; With a major stroke, the heart rate slows and the face turns pale. Facial pallor during a stroke is an alarming sign indicating a serious condition of the patient.
- With a microstroke, paresis develops - partial loss of motor activity; with a stroke, complete paralysis of the upper or lower extremities is possible.
- With a major stroke, large vessels supplying a given area of the brain are blocked or ruptured and, as a result, necrosis of the affected area and death of its nerve cells occurs. With a microstroke, small vessels are affected - capillaries and arterioles, the recovery of which occurs faster.
- In case of a microstroke, examination for the Babinski reflex will always give a negative result.
- With TIA, there is no enuresis; with a stroke, urinary incontinence is one of the constant symptoms.
- With a microstroke, gaze paresis does not develop, when friendly eye movement becomes impossible.
- With a microstroke, the pupils are the same size. With a stroke, anisocoria develops when one pupil is enlarged and the second is reduced in size.
This is the danger of a micro-stroke - in most cases it is endured “on your feet” , once, twice, three times, until an acute vascular catastrophe occurs, a major stroke. In case of a stroke, doctors have negligible time left to save the patient - only four and a half hours.
Prognosis and possible complications
Stroke in old age often has severe complications and consequences. The most favorable prognosis is partial restoration of functions affected by damage to parts of the brain.
Most often, older people who have suffered from this disease have problems with disorientation, speech and coordination of movements. However, this is only possible if medical care was provided in a timely manner.
If medical assistance is not provided within 2-3 hours after the onset of the first symptoms, then the person is susceptible to complications such as:
- Paralysis, paresis.
- Serious speech defects (up to its complete absence).
- Strabismus and other vision pathologies.
- Urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Poor circulation of the inner ear, often hearing loss.
- Parkinson's disease.
In most cases, people who have had a stroke are unable to lead a normal life and require constant care.
Distinctive features of female and male microstroke
Despite the similarity of symptoms and clinical picture, there are a number of specific differences between a “female” microstroke and a “male” one :
| Microstroke in women | Microstroke in men |
| The changes affect the vessels located in the occipital part of the head. This disrupts blood flow to the occipital and temporal lobes, cerebellum, and brain stem. | The vessels located in the front of the head are affected |
| Emotions are not controlled; the transition from tears to aggression can take several minutes. Mental disorders are one of the signs of a “female” microstroke | Changes in mental state occur rarely; a man is able to control his psycho-emotional state. |
| The risk of developing cerebrovascular accident is higher if a woman: · had an abortion or miscarriage; · had complications during pregnancy | The risk of developing TIA in men has nothing to do with reproductive function |
| The recovery period takes longer, there is a high risk of relapse with more severe symptoms | Recovery is faster, consequences are less obvious |
Early subtle signs of microstroke in women
Early neurological symptoms depend on which part of the brain is affected by the ischemic attack.
Phosphogliv or Karsil, which is better? Doctors' opinion
So, if the blood vessels of the parietal lobe are affected, there is a decrease or complete loss of tactile sensitivity . It is impossible to determine the characteristics of an object with closed eyes, it is impossible to determine whether it is cold or warm, what kind of surface it has, smooth or rough; What shape is it - square, round, triangular.
When the occipital lobe is damaged, ophthalmological problems : vision decreases, it is impossible to visually identify even well-known objects.
The manifestations of a microstroke are surprising when the temporal lobe is affected. There are lapses in memory and a feeling of “déjà vu” - “recognition of the past,” a mental state when a person “remembers” a place, situation or event.
The following are considered as common and earliest manifestations of microstroke in women:
- Semi-fainting conditions, accompanied by constant dizziness and severe headaches.
- Nausea, retching, or vomiting directly.
- Redness of the face and whites of the eyes.
- Characteristic tingling in the limbs.
Noticeable signs of the disease
As the process develops, the symptoms and first signs of a microstroke in women become brighter. This is exactly the moment when a microstroke can be differentiated from other diseases:
- Facial expressions are disrupted. When trying to smile, one corner of the mouth remains motionless, the smile turns out to be “crooked.”
- The sense of orientation in space disappears.
- Memory lapses begin.
- Numbness in fingers or toes.
- Vision is partially lost. An object or image is not completely visually perceived; only its right or left side is visible. With a microstroke, one of the symptoms is photopsia. a phenomenon where “floaters”, colored spots, zigzags or circles appear before the eyes.
- Muscle tone sharply decreases, the body is subjected to a drop attack, when a person suddenly loses consciousness for no apparent reason.
- In some cases, Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome is observed - loss of coordination on one side of the body, unsteadiness of gait, dragging of the legs, inability to maintain balance.
Symptoms of a stroke
- Sudden clouding of consciousness. Slurred thoughts, confusion and delirium of speech, difficulty understanding speech.
- Vision problems - blind spots, blurred vision.
- Impaired coordination and balance. The gait may look strange, as if the person has weakness in one or both legs, difficulty moving in space, lost, or dizzy.
- Facial asymmetry: one side of the face relaxes, a person cannot smile from both corners of the mouth.
- Weakness in arm and leg on one side. Ask the person to raise both arms straight in front of them and to the sides.
- A sharp, severe headache for no apparent reason.
A stroke develops quickly. A person himself can identify symptoms within a minute and call for help. If you see the above symptoms in a person near you, immediately call an ambulance and provide first aid.
Symptoms and warning signs that should prompt you to see a doctor
Symptoms of microstroke in women quickly disappear; often the disease can be diagnosed only in a medical institution.
There are several “ifs”, the combination of which makes it necessary to see a doctor:
- If severe and persistent headaches begin.
- If you see black or colored circles, spots, lightning before your eyes.
- If your heart rate and pulse rate are abnormal.
- If the limbs lose sensation.
- If control over facial expressions is lost.
- If one eye is in normal condition, and the other is half-closed.
- If speech is impaired and it is impossible to pronounce a logically completed phrase.
- If coordination is impaired and movements become uncoordinated.
Recovery
To restore impaired brain functions after an attack, doctors select nootropic drugs. Their goal is to make the affected areas of the brain work and protect those parts that are in close proximity to the focus of necrosis. Taking nootropics has a positive effect on the condition of people who have suffered from certain neurological diseases.
Psychotherapists are involved in the recovery process of a woman after a mini-stroke. Working with them restores a deteriorated psychological state and strengthens the body's resistance to stress factors and nervous overload.
Providing first aid for a microstroke
If it is impossible to quickly call a doctor, follow this algorithm:
- The patient is placed in bed, providing unhindered access to fresh air.
- They give you a tablet of Aspirin, Agrenox or, if they are intolerant, Clopidogrel.
- To improve blood flow and protect brain neurons, give Piracetam or Vinpocetine.
- Blood pressure is measured, and if its first number exceeds 200, it is slowly lowered. Furosemide or Captopril are used.
- In diabetes mellitus, glucose levels are reduced.
For micro-strokes, do not take popular painkillers containing caffeine (Citramon), as they increase blood pressure even more.
Check out the list of the best blood pressure pills.
What to do if a person has a stroke?
- First of all, call an ambulance. Sometimes the minutes count.
- Provide fresh air, open windows and doors, and free the person’s neck from constricting clothing.
- Leave the person where the attack occurred. The patient cannot be moved.
- Elevate the person's head and upper body 30 degrees by placing several pillows under the thoracic spine.
- If vomiting occurs, turn the person's head to the side and ensure that the vomit passes away so that the person does not suffocate.
- In the event of an epileptic attack, carefully hold the person, turn his head to the side and insert an object wrapped in cloth into his mouth - a stick, a comb, a spoon.
- In case of cardiac arrest, immediately begin compressions through the chest and perform artificial respiration.
- Wait for the ambulance.
Treatment (therapy) of microstroke
When treating a microstroke, the following is prescribed:
- Thrombolytics : drugs that kill blood clots, restore blood flow, dissolve blood clots. Indicated for micro-strokes and ischemic strokes. But their use in hemorrhagic stroke leads to the death of the patient.
- Anticoagulants : reduce blood clotting and prevent blood clots.
- Disaggregants : prevent blood cells from joining into a single clot.
- Diuretics : relieve swelling in brain tissue.
- Neuroprotectors : restorative therapy drugs that support brain cells and reduce the risk of relapse.
Treatment includes physical therapy classes, water treatments, massages, breathing exercises, and diet. An important factor in eliminating relapses and maintaining vascular activity is giving up alcohol and smoking and controlling weight.
Prevention
To prevent a micro-stroke, it is necessary to constantly monitor your health. If a woman suffers from arterial hypertension or other pathologies of the cardiovascular system, then she needs to measure her pulse and blood pressure twice a day. It wouldn’t hurt to get into the habit of keeping a diary with your morning and evening readings.
Those with diabetes are advised to regularly check their blood sugar levels. If this indicator is normal, it is enough to do a similar analysis a couple of times a year: it takes a little time, but warns of incipient health problems.
In addition, it is important to adhere to general recommendations for a healthy lifestyle: give up bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol, pay attention to physical education or gymnastics, and include walks in your life. It is better to reduce the amount of fatty foods on the menu and give preference to natural products.
Consequences of a mini-stroke
TIA does not go away without a trace. The symptoms will disappear, but the attack will happen again and again. In 300 people out of a thousand, TIA will lead to the development of a stroke - its most severe and most dangerous consequence.
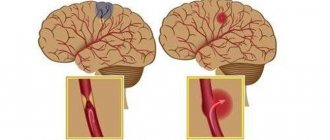
There are two types of stroke development:
- Ischemic (the most common consequence of a microstroke), when blood flow to a certain area of the brain stops. It is the result of either a blood clot that has closed the vessel or prolonged vascular spasm.
- Hemorrhagic (rarely develops after TIA, considered only as a special case) - a severe brain catastrophe, the result of a breakthrough of large vessels and hemorrhage in the brain.
During a stroke, cells in large areas of the brain die, the patient develops paresis and plegia with complete or partial loss of sensitivity, the person ceases to adequately assess the situation, memory loss occurs, and in some cases, swallowing dysfunction occurs.
In addition to the risk of stroke, recurrent TIAs threaten:
- decline in intelligence;
- memory impairment;
- changes in mental state, lack of control over emotions and their frequent changes, when from tears to aggression, from irritability to apathy and depression - one step.
Today TIA is “getting younger.” Micro-strokes are diagnosed in women who have barely crossed the 30-year mark. Neither self-medication nor letting the disease “go on its own” is permissible, because the consequences can lead to irreversible changes.
Risk factors for microstroke:
Oddly enough, factors that are quite ordinary for most of us can provoke a mini-stroke.
- Not following a healthy diet; excess animal fats in the daily diet; overeating leading to obesity.
- Unhealthy lifestyle (drinking alcohol, smoking).
- Insufficient physical activity (exacerbated by sedentary work).
- Low stress resistance and constant experience of stress factors.
- Poor ecology (high percentage of exhaust gases, low oxygen content indoors and outdoors).
- Cold climatic conditions (they contribute to increased blood pressure) or a sharp change in the usual climate to the opposite.
- The age factor, and previously people over 60 years of age were at risk; today, prevention of micro-strokes is necessary even for 35-year-olds.