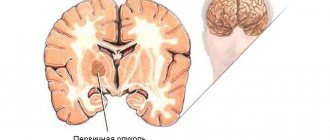
Cerebral edema occurs against the background of blood circulation disorders caused by various diseases or functional abnormalities.
- Cerebral edema: prediction and symptoms
- Symptoms of swelling from hemorrhagic stroke
- Symptoms of swelling from ischemic stroke
- Cerebral edema from stroke and its features
- Reasons for development
- Care and rehabilitation
- Boarding houses for post-stroke patients "Olympia House"
The pathological condition has its consequences and can even lead to death; depending on the symptoms, it helps to determine the type of stroke suffered.
If even minor signs are detected and there is a suspicion of the formation of edema, it is necessary to arrange a visit to the doctor. An emergency call will help diagnose the condition of an elderly patient and promptly provide the necessary assistance, provide decent care and concern.
Cerebral edema: prediction and symptoms
Stroke is defined by medicine as a circulatory disorder and this condition leads to oxygen starvation of a certain area of the brain. Cortical cells die, and the patient's condition worsens due to the accumulation of watery secretions that put pressure on certain brain centers.
Watery accumulations are not capable of causing physical harm to soft tissues, but they accumulate in areas of nerve cells. This effect provokes an increase in intracranial pressure, which affects intracranial hypertension, the consequences of which (without providing the necessary assistance) become fatal.
With cerebral edema, a high degree of severity of the consequences of a stroke is determined, because this can cause unstable brain activity. The irreversibility of the impact is determined by real indicators of the extent of the spread and localization of edematous activity.
Without certain knowledge and understanding of the clinical picture, it is impossible to identify the symptoms of a pathological condition. The most difficult cases are considered to be attacks of hemorrhagic stroke, in which cerebral edema develops rapidly, putting the life of an elderly person in serious danger.
How does the postoperative period proceed?
In the postoperative period, you will be taken to the intensive care unit, where you will spend time until your condition stabilizes and possible complications are monitored. A drain (tube) will be placed in the wound area and removed the next morning.
You will be able to drink and eat in the next few hours after surgery if there are no contraindications. Pain in the wound area will be eliminated with the help of analgesics.
You will be prescribed treatment to reduce blood clotting.
After transfer from intensive care, the patient is in 1-2-bed wards, more reminiscent of the rooms of an excellent hotel, but with medical specifics (call button, functional beds, round-the-clock observation, wards for patients with disabilities).
When I will be at home?
After removal of the drainage and transfer to the ward, you will persistently return to your normal lifestyle. After monitoring the necessary tests and monitoring the result of the operation using ultrasound, you will be discharged with detailed recommendations in writing.
Symptoms of swelling from hemorrhagic stroke
There are many risk factors on the basis of which one or another type of pathological condition develops.
Hemorrhagic stroke is often characterized by the release of internal fluid with characteristic hemorrhage and health complications, with pronounced symptoms:
- disturbance of speech functions and functioning of muscle tissue;
- decreased limb control and facial paralysis;
- temporary loss or weakening of vision and hearing, extraneous noise;
- manifestations of swelling of the limbs and fainting, memory loss.
With a hemorrhagic stroke, there is a rapid impact on the brain and its tissues, nerve cells. The consequences of such exposure may be irreversible, therefore, if these symptoms are recorded, it is necessary to seek help as quickly as possible, providing the person with professional care and rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after a stroke lasts 1.5 – 2 months. In severe cases, the recovery period can take a year. To help the animal, you must follow all the recommendations of your doctor and take prescribed medications.
During the rehabilitation period it is important:
- Buy hard, warm and dry bedding for your pet. It must be changed when it gets dirty.
- Turn the dog over to prevent the formation of bedsores.
- Treat the animal's skin with special gels, ointments or creams (prescribed by the attending physician).
- Avoid drafts in the room where the animal is located. Cold draft air can cause pneumonia. This is one of the most common complications after a stroke.
- Take prescribed medications regularly.
- If necessary, attend physiotherapeutic procedures. Your veterinarian may prescribe magnetic therapy or electrical muscle stimulation for your dog. If the animal is paralyzed, it is necessary to massage the limbs. Massage is also recommended as a preventive measure (excluding complications from the musculoskeletal system).
- Watch your diet. It is important that your pet’s food is light and has a semi-liquid or liquid consistency. The diet should include lean chicken meat, oatmeal, beef puree, chicken broth, and pureed vegetables. It is better not to change the usual menu: it is important to exclude the consumption of fatty foods. You should also avoid rice and buckwheat cereals. Up to 4–6 meals (small portions) are recommended per day.
Symptoms of swelling from ischemic stroke
An acute ischemic condition leads to a functional disruption of the normal reproduction of metabolic processes in neuronal cells.
Their intermediate area is filled with intracellular fluid, which leads to an increase in pressure and the formation of swelling, which has its own symptoms:
- acute headache that cannot be relieved even with strong medications;
- the appearance of vomiting and increased feeling of nausea with frequent convulsions;
- temporary disturbance of spatial orientation and feeling of loss;
- severe shortness of breath without any exertion or physical activity in patients;
- fainting and fainting, a visually determined disturbance of blood circulation.
In ischemic stroke, cerebral edema develops gradually and there is a high probability of prompt provision of the necessary assistance. At a certain level of diagnostic complications, it is important to organize constant monitoring of older people at risk.
Prevention
Knowing your risk factors for stroke, following the advice of highly trained professionals, an annual comprehensive body check-up and a healthy lifestyle are the best steps you can take to prevent stroke. If you have had a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), these steps may help prevent another stroke.
The help you receive in the clinic plays a significant role in stopping the acute period of a cerebral infarction.
The risk factors for possible complications after an attack will depend on how qualified and prompt assistance a team of neurologists, cardiologists, neurosurgeons, rehabilitation therapists and physiotherapists will provide you.
Many stroke prevention protocols are the same as cardiovascular disease prevention protocols. Basic recommendations for a healthy lifestyle include:
- Constant blood pressure monitoring. This is one of the most important things you can do to reduce your risk of stroke. If a patient has already had a stroke, lowering blood pressure may help prevent a subsequent TIA or stroke.
- Exercise, manage stress, maintain a healthy weight, and limit sodium, alcohol, and tobacco. In addition to recommending lifestyle changes, our doctor may prescribe medications to treat high blood pressure, as well as a vitamin and mineral supplement and fish oil.
- Reduce the amount of cholesterol and saturated fat in your diet. Eating less cholesterol and fat, especially saturated fat and trans fat, can reduce plaque in the arteries.
- Quitting tobacco use. Smoking increases the risk of stroke for smokers and nonsmokers exposed to secondhand smoke. Quitting tobacco use reduces the risk of stroke.
- Diabetes control.
- Maintaining a healthy weight. Excess weight contributes to the development of other risk factors for stroke, such as high blood pressure, heart disease and diabetes.
- A diet rich in fruits and vegetables. A diet containing five or more daily servings of fruits or vegetables may reduce the risk of stroke.
- Exercise can lower blood pressure. It will also help you lose weight, control diabetes and reduce stress.
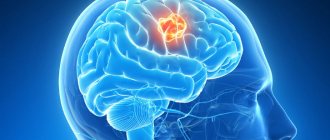
Cerebral edema from stroke and its features
The edematous condition is associated with quite serious consequences that may not appear immediately after a stroke. Depending on the location of the lesion, the degree of consequences and dysfunction of internal organs, the central nervous system, and the brain is determined.
Without rapid remission, which occurs thanks to good health and comprehensive rehabilitation, this condition can provoke irreversible consequences.
A severe intracranial complication associated with disruption of the central nervous system provokes the following consequences:
- distorted facial expressions;
- chronic headaches;
- limited movement;
- weakening of the sensory organs;
- deterioration of mental abilities.
After a stroke and cerebral edema, older people need to be re-taught to live and perform the usual activities for each person. To do this, it is necessary to provide him with complete rehabilitation, surround him with attention and care, and guarantee targeted medical care.
Reasons for development
Disruption of blood microcirculation in brain tissue stimulates the formation of a state of oxygen starvation.
This leads to cell necrosis, and intracellular fluid enters the cavity of the free space of the skull; brain edema can be caused by a number of reasons:
- stroke and fluid accumulation in the localization of nerve tissue;
- surgery with edema provoking coma;
- alcohol dependence and accumulation of toxic substances in tissues;
- a specific reaction of the body to a specific allergen.
Cerebral edema occurs in people of different ages, but those at risk are those whose age has exceeded 60-65 years. That is why it is important to organize constant supervision for an elderly relative with poor health, conduct regular medical examinations and strictly monitor his well-being.
Care and rehabilitation
To create optimal conditions for recovery after a stroke, it is better to choose a private boarding house for the elderly in the Moscow region. Specialized institutions provide recovery after timely identified cerebral edema, which helps minimize health consequences. Targeted and specific care ensures that negative impacts are reduced and conditions are created to restore the elderly person’s well-being.
Recovery at home
The doctor prescribes medications in the form of tablets or injections. Rehabilitation therapy is carried out using the same medications that were used for emergency treatment. Most often these are blood thinners, diuretics, and nootropics. The duration of the appointment is determined by the doctor.
Many animals are prescribed the drug Cerebrolysin. It accumulates in body tissues, acts slowly, and helps avoid complications after a stroke. Nicotinic acid restores blood circulation. Prozerin is recommended for paralysis. If an animal has lost its appetite due to a stroke, intravenous infusions are given to prevent dehydration.
Boarding houses for post-stroke patients "Olympia House"
Providing professional and qualified care for the elderly in Moscow, our network of boarding houses offers excellent living conditions.
Thanks to an integrated approach, each ward receives maximum attention to their health, medical care and constant supervision:
- conducting regular inspections;
- medical service;
- good nutrition and walks;
- development of a rehabilitation plan;
- psychological support.
The expanded network of private boarding houses for the elderly Olympia House includes a complex of nursing homes located in different regions. Using the services offered, you can choose the best conditions for elderly relatives and select a complex for rehabilitation and recovery.
Bedsores
Late consequences of acute cerebrovascular accident include bedsores, which are areas of necrosis (death) of soft tissue. The main reason for their appearance is constant pressure on soft tissues and the development of local circulatory disorders. This condition occurs during prolonged immobility against the background of complete or partial paralysis. The depth of necrosis can be very great - in the most advanced cases, the skin and muscles are affected to their full depth, exposing the tendons of the bones.
To prevent bedsores, a bedridden patient must be regularly examined, turned over, provided with hygienic care, and massaged problem areas. It is also recommended to place special inflatable rings, or use a special bed.
The skin should be wiped with camphor alcohol twice a day (only if there is no damage to the skin). It is important for the patient to provide adequate nutrition, since one of the factors contributing to the appearance of foci of necrosis is insufficient protein intake into the body.
Treatment methods depend on the stage of the process and are determined by the attending physician.
Pneumonia
Long-term consequences of cerebral infarction or ischemia include pneumonia. It can be hypostatic and aspirational. In this case, the patient experiences cough, respiratory failure and hyperthermia (fever). Hypostatic pneumonia develops due to stagnation in the pulmonary circulation. Aspiration is possible when food enters the respiratory tract due to dysphagia (swallowing disorders).
The immediate cause of the inflammatory process is a bacterial infection. To combat it, a course of antibiotic therapy is necessary. Treatment in this case takes place only in a hospital. With correctly selected medications, the first signs of improvement appear within 1-2 days. If a patient in the post-stroke period cannot swallow on his own, he needs to be fed through a tube.
Stroke is a disease that requires immediate attention. Timely initiation of treatment measures helps reduce the likelihood of early complications. But good care of the victim minimizes the risk of developing late consequences. That is why, at the first signs of a stroke, immediately call an ambulance, and then strictly follow all medical recommendations.
Sensory impairment
Impaired sensitivity of the limbs and facial area almost always develops after a stroke. The severity and nature of the disorders depend on the location and size of the lesion. An increase or decrease in pain and tactile sensitivity is more often recorded with damage to the right hemisphere.
The recovery process may take many months. The patient needs to do exercises regularly to improve fine motor skills. Cryotherapy, balneotherapy, heat treatment and other physiotherapeutic techniques give good results.