Conclusion
To prevent the development of cerebral hemorrhage in a newborn, you should follow some rules:
- Register as early as possible ;
- Do not insist on natural childbirth if there are indications for cesarean section;
- Closely monitor the condition of the newborn, his appetite and sleep;
- Avoid sudden movements and pressure on the baby’s body;
- Strictly follow medical recommendations;
- Do not ignore the baby's crying.
If a birth injury occurs, parents should call a doctor as soon as possible and hospitalize the child.
In premature babies
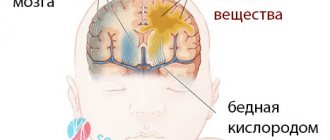
Cerebral hemorrhage in prematurity is an acute birth injury in children born before 28 weeks. The high probability of hemorrhage at this stage is associated with underdevelopment and pliability of the skull bones, softness and weakness of blood vessels, tenderness and friability of the meninges. Features: respiratory and cardiac dysfunction, lethargy, poor mobility predominate.
IMPORTANT! Hemorrhage is often asymptomatic, which leads to delayed diagnosis.
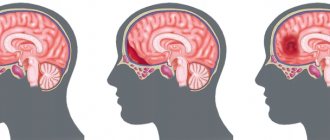
The injury is divided into 4 degrees depending on the depth of damage to the ventricles of the brain:
- 1st degree: Hematoma under the inner lining of the ventricle, not penetrating into its cavity;
- Grade 2: Filling of less than half of the ventricular cavity with blood;
- Grade 3: Damage to more than half of the ventricle;
- 4th degree: Penetration of blood into the brain matter.
Forecast for recovery
The recovery process takes from 1 month to 2 years. The prognosis for life is determined by the severity of the hemorrhage, body weight and condition of the newborn. With small hematomas, long-term consequences may not be observed - the child will grow and develop without complications.
If the hematoma was voluminous, the prognosis becomes less favorable: after treatment, such children need frequent examinations by doctors, regular courses of treatment by a neurologist, gymnastic exercises, classes with a speech therapist, and correction of brain disorders.
Surgery
Treatment of minor hemorrhages is carried out using puncture, which not only has a diagnostic effect, but also helps reduce pressure in the brain. Fluid removal is carried out slowly, since rapid removal of the hematoma and excess cerebrospinal fluid can lead to brain displacement and serious complications.
There are several types of puncture - lumbar (removal of cerebrospinal fluid), ventricular (removal of blood from the ventricle) and hematoma puncture . After the procedure, the child's condition often improves due to restoration of intracranial pressure and reduction of cerebral edema.
If the puncture is ineffective, shunting is indicated (artificially creating an outflow of excess fluid from the cranial cavity).
For a subdural hematoma, a puncture of the skull is performed to remove the accumulated blood. The lack of results from the procedure is an indication for trepanation.
IMPORTANT! In case of breathing problems, resuscitation and connection to an artificial respiration apparatus are carried out immediately.
Rehabilitation: massage, breathing exercises, oxygen therapy.