Causes of the disease
Arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis (often a combination of both) are one of the main provocateurs of the pathological process. Pathologies such as:
- heart and vascular diseases - accompanied by heart failure, arrhythmia;
- vascular anomalies of the aortic arch, cervical and brachial regions, and head brain;
- venous diseases - extra- and intracranial, with compression of veins, vessels, arteries and tissue compression (tumors, aneurysms);
- cerebral amyloidosis - applies to elderly patients.
The etiology of cerebral ischemia is mainly mixed. This is a dominant factor (hypertension or atherosclerosis) and many other causes, interpreted as additional provocateurs that significantly aggravate the course of the disease.
According to pathogenetics, encephalopathy is divided, according to morphological characteristics, into 2 types:
- Discirculatory - bilateral foci of diffusion.
- Lacunar - multiple lesions of the white matter.
It is not uncommon to diagnose a mixed version of ischemic lesions.
Degrees of cerebral ischemia
Cerebral ischemia grade 1
At this stage, the symptoms of the disease are mild. The patient suffers from headaches, heaviness in the head, gets tired quickly and experiences general weakness. Sleep is disturbed, problems with hearing, vision and memory are possible. The disorders are stable, but the formation of syndromes has not yet occurred. This allows you to reduce the symptoms or eliminate them completely, as well as the disease as a whole. The changes concern the patient’s psychological state: emotional lability is possible, that is, a rapid change of mood for no reason.
Cerebral ischemia grade 2
Asthenic symptoms are less common. Stage 2 of cerebral ischemia is characterized by loss of memory and ability to work. The patient experiences constant weakness, dizziness, and may have difficulty performing the simplest movements, for example, walking. Vision problems appear, oral automatism reflexes are disrupted, and convulsions occur. The duration of the periods during which disturbances appear increases.
Pathological reflexes are reflected in intellectual-mnestic disorders. This means that mental work becomes impossible for the patient. As with grade 1 cerebral ischemia, the patient experiences psychological difficulties and emotional lability progresses.
Cerebral ischemia grade 3
At this stage, organic brain damage is observed. Patients often faint and are unable to perform simple actions on their own, so they need help. Circulatory disorders manifest themselves in the form of “small strokes” or a progressive “complete stroke”. At stage 3 of cerebral ischemia, dementia, that is, dementia, is possible.
Patients' cognitive ability decreases, they can no longer carry out full intellectual activity. In addition, patients experience memory problems. This causes a sharp decline in their quality of life and social adaptation. Violation of gnosis and praxis, which are one of the main functions of the brain, leads to the inability to navigate in space, recognize familiar objects and perform complex motor acts.
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia
Cerebrovascular insufficiency has clinical features in which there is an inverse relationship between the disease and the patient’s complaints - the more pronounced the encephalopathy, the fewer complaints.
The main symptoms of ischemic damage:
- memory disorders;
- motor dysfunctions;
- decreased learning ability;
- disturbance of emotional state;
- inert attitude towards everything.
Cognitive dysfunctions detected at the 1st stage and progressing to the third are recognized as the core of the overall picture of cerebral ischemia.
The disease is divided into three stages:
- Stage 1 - active complaints of mild emotional disorders, cognitive impairment. The patient performs neuropsychology tests and has no limitations in life activities;
- Stage 2 - the neurological syndrome dominates, complaints decrease, adaptation in society and profession worsens. Cognitive impairments are complemented by neurodynamic ones;
- 3rd degree - pronounced neurological disorders with loss of balance, urinary incontinence, personality and behavioral disorders. The development of dementia and maladaptation in the everyday, social, and labor spheres are possible.
As the disease progresses, the basic ability to care for oneself is lost.
Cerebral ischemia in newborns
Congenital cerebral ischemia in children develops due to hypoxia during childbirth or pregnancy. The risk of oxygen deficiency increases with the age of the mother. In young girls, the risk of cerebral ischemia in children is slightly lower than in women after 30.
However, this factor is not decisive. An important role is played by the presence of various diseases in the mother, for example, diabetes mellitus, and taking various medications during pregnancy. The development of cerebral ischemia can be prevented by the competent work of doctors during childbirth, when there is a danger of lack of oxygen.
Depending on the degree of the disease, various symptoms are distinguished. In the early stages, cerebral ischemia manifests itself in the form of increased depression or excitation of the child. Grade 1, which is considered the mildest, is diagnosed most often. As a rule, the disease goes away some time after birth. Cerebral ischemia grade 2 is characterized by more serious brain damage.
Loss of appetite and frequent mood swings may also be a reason to contact a neurologist. The child has dystonia, impaired psychomotor and speech development, and motor activity. For example, he may stand on his toes when walking. At stage 3 of cerebral ischemia, hospitalization of a small patient is necessary.
Diagnostic examination
A history of cerebral ischemia usually includes pathologies such as myocardial infarction, cardiac ischemia, arterial hypertension, diabetes, etc. At the stage of physical examination, possible causes of CVS pathology that trigger the process of cerebrovascular insufficiency are identified. The following manipulations are carried out:
- blood pressure measurements in all extremities;
- determination of heart rate using auscultation;
- checking pulsation for integrity and symmetry in the head and limbs.
Laboratory diagnostics are aimed at identifying the factors that caused and triggered ischemic processes in the brain. The patient is prescribed:
- blood test (general, sugar, lipids);
- instrumental examination (ECG, ECHO, duplex/triplex scanning, etc.).
For correct diagnosis, it is important to distinguish encephalopathy from other neurodegenerative conditions that are characterized by cognitive and neurological disorders.
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia
The first signals indicating cerebral ischemia are rapid fatigue during mental work and forgetfulness. Older people often do not consider this a sign of a serious illness, given their age. But if your memory suddenly deteriorates, you should consult a doctor. Patients with cerebral ischemia suffer from constant headaches.
As the disease progresses, falls, fainting, and dizziness are possible. There is a sharp increase in blood pressure, nausea, turning into vomiting. In the later stages of cerebral ischemia, vision and hearing are impaired. The patient is not capable of work, mental activity, or self-care. He loses sleep, cannot make complex movements, and suffers from unsteadiness when walking.
An acute form of cerebral ischemia is a stroke. It is focal in nature and occurs when a plaque inside a vessel ruptures and blocks the lumen. As a result of thrombosis, blood stops flowing to the brain, which is why tissue necrosis, that is, ischemic stroke, is inevitable. After it, deep neurological disorders occur: sensitivity and the ability to move independently may disappear.
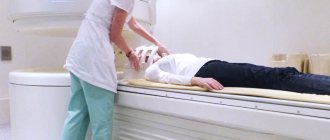
Diagnosis of cerebral ischemia is carried out by visible symptoms, as well as on the basis of studies of cerebral and sensory function. A survey is conducted of the patient and his relatives, since patients in the later stages of the disease often suffer from dementia and memory loss. Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are necessary to examine the cerebral cortex. The results of the procedures allow the doctor to see the changes that have occurred in her.
Treatment of chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency
The meaning of therapeutic measures is to stabilize/stop the destruction of brain cells, stop/slow down the rate of progress and prevent stroke. The latter is an indication for urgent hospitalization, as is the development of complex somatic disorders. In other cases, cerebral ischemia is treated on an outpatient basis, under the supervision of a neurologist. On the contrary, depriving the patient of a familiar environment during treatment can cause a worsening of the condition. Patronage is assigned to patients at the 3rd stage of encephalopathy.
Treatment includes several areas:
- medication - to normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system and optimize the blood supply to the intracranial brain;
- hypotensive - to normalize and maintain blood pressure, regulate the mechanism of blood flow, which can cause damage to target organs;
- hypolipidemic - for patients with dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis (diet without animal fats and lipid-lowering drugs);
- antiplatelet - to activate hemostasis processes;
- combo drugs - to normalize blood functions and improve venous outflow.
Chronic cerebral ischemia may be an indication for surgery if the main blood arteries are affected.
Diagnostics
The disease is usually diagnosed within the first few hours.
The presence of pathology is indicated by deviations in checking reflexes and a general blood test . Typically, the analysis shows an increased level of carbon dioxide in the body.
If obvious symptoms of a serious illness are detected magnetic resonance imaging , as well as electroencephalography , which reveals hidden convulsions and other abnormalities in the functioning of the brain.
Forecast and preventive measures
With early diagnosis and adequate therapy, the prognosis for slowing down pathological processes is relatively favorable. If cerebral ischemia is aggravated by serious concomitant disorders (vascular, endocrine, etc.), then the consequences are quite disappointing, including disability.
Prevention of the disease consists of preventing and eliminating risk factors: obesity, prolonged stress, smoking, alcohol. At the first symptoms of the disease, you need to eliminate all bad habits, limit physical activity and exposure to direct UV radiation.
Make an appointment with a neurologist at the Integra Med CDC (formerly NDC) on Gakkelevskaya. Get diagnosed using our modern equipment. Find health and longevity!
Causes
In the vast majority of cases, the causes of cerebral ischemia in newborns are various disorders of gestation in recent weeks, as well as non-standard situations during childbirth.
- Detachment of the placenta or disruption of blood flow in it.
- Compression of the umbilical cord, suffocation of the fetus.
- Congenital heart defects.
- Circulatory problems.
- Intrauterine hypoxia.
- Infection during childbirth.
- Openness of the ductus arteriosus.
- Acute placental insufficiency.
Treatment
Unfortunately, medicine cannot give an accurate and definite answer to the question of how to treat cerebral ischemia in newborns.
Pharmacology has not created a cure for oxygen starvation, and there are no effective methods for restoring dead central neurons. With mild to moderate ischemia, all hope lies in the compensatory capabilities of the child’s body. In the third degree, by the way, too. Healthy neurons can take on the responsibilities of dead “comrades.” For minor ischemic brain damage, this works great. The more severe the defeat, the more difficult it is to compensate.
This does not mean that the child does not receive treatment. The task of doctors after detecting ischemia in a newborn is to quickly determine the extent of the damage and begin to promote natural compensatory mechanisms in every possible way. For this, symptomatic treatment is prescribed. If the baby is excited, he is given sedatives; if he has seizures, he is given anticonvulsants.
Commonly accepted treatment regimens include drugs to improve blood circulation to the brain. For this, vascular and nootropic drugs are recommended. The effectiveness of these groups of funds is currently in question, but they have been approved by the Ministry of Health.
In the third degree of ischemia, the child is provided with a full range of resuscitation measures. This includes artificial ventilation, tube feeding, and heating of the incubator. The medications used are basically the same. The task at the resuscitation stage is to stop the death of neurons and prevent the death of areas of the cerebral cortex adjacent to the affected areas. After the child is transferred to the general department, he is prescribed a long course of treatment and rehabilitation, depending on the severity of the consequences of ischemia.
After discharge home, a child with a history of ischemia is prescribed massage. Walking in the fresh air, following a daily routine, water procedures, swimming in the bathtub with a cervical orthopedic circle (from 1 month) are recommended.
Hypoxia results
A lack of oxygen to the brain can have the following results:
- Severe cerebral ischemia
This condition is fatal in a quarter to half of cases. The babies do not survive even a few days. Another scenario is pneumonia or another infection that kills the child a little later. Most of those who do not die are diagnosed with autism, cerebral palsy or dementia. And only 10% of survivors experience no consequences.
- Moderate ischemia
According to statistics, severe long-term consequences occur in 30 to 50% of children.
- Mild ischemia
The outcome in most cases is favorable, no disability is noted.
Degrees
- light
With mild ischemia, muscle tone increases, but not too much. Deep tendon reflexes in such children are enhanced. They suckle poorly, cry constantly, or, conversely, sleep constantly. During the first 3 days of life, manifestations of pathology are eliminated. Children who have not spent 9 months in their mother’s belly may have decreased rather than increased reflexes and muscle tone.
- average
- frequent apneas
- decreased grasping and sucking reflex
- sluggish Moro reflex
- decreased tendon reflexes
- weak muscle tone
Symptoms of moderate ischemia in newborns appear in the first 24 hours after birth. Doctors talk about a favorable prognosis if the symptoms of ischemia disappear within 14 days.
- heavy
- uncoordinated eye movements
- strabismus, nystagmus
- lack of reflexes that a newborn should normally have
- irregular breathing, such children have to be connected to a ventilator
- stupor or coma
- convulsions
- surges in blood pressure (BP)
- heart rhythm disturbances
Read also
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, which manifests itself in the form of various clinical symptoms.
This disease is diagnosed at different times… Read more
Swelling of the legs
Causes of Swelling in the Legs The legs are common sites for swelling due to the effect of gravity on the fluids in the human body. However, fluid retention is not the only cause of leg swelling. Injuries...
More details
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
What it is? Why is this happening? Is this condition dangerous? What to do if doctors make such a diagnosis? These questions are always asked by patients who come to see a neurologist. According to classification...
More details
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is a type of acute cerebrovascular accident, which is characterized by the effusion of blood into the brain substance with the development of neurological deficit, often leading...
More details
Alzheimer's disease
47,000,000 people suffer from dementia in the world. Doctors call Alzheimer's disease the most common cause of dementia. Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease accompanied by...
More details
Main goals of ischemia therapy
If the diagnosis is confirmed after all the studies, then measures begin to maintain normal temperature, humidity, and protection from external irritants.
Therapy in newborns should be as less aggressive as possible. It pursues the following goals:
- Provide adequate ventilation.
- Support hemodynamics.
- Constantly monitor the biochemical parameters of the tests.
- Prevent seizures.
Prevention of ischemia
It is necessary to talk about pregnancy in advance. Preparations begin half a year, or at most 3 months before conception. And not only the expectant mother, but also the father of the child must prepare. During gestation, a woman should undergo all examinations on time, especially in the first trimester. Tests are taken and ultrasound diagnostics are performed.
Before and during pregnancy, a woman is examined for infections. As is known, after conception, latent infections can worsen and manifest themselves. Mom needs to give up smoking, alcohol, drugs and other habits that are harmful to her and the baby. Smoking has a particularly negative effect on the process of oxygen supply to the fetus. If the doctor discovers pregnancy complications, it is important for the woman to go to the hospital on time.