Consultation with a neurologist – RUB 1,750.
- What is encephalopathy?
- Types of acquired encephalopathy
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of encephalopathy
- Popular questions
Encephalopathy
is a general term used to describe non-inflammatory diseases of the brain.
Characterized by a decrease in the volume of nervous tissue and impaired brain function. Encephalopathy of the brain can be congenital
or
acquired
. Congenital encephalopathy occurs due to genetic disorders or abnormal development of the brain during fetal development, or damage to the brain during childbirth.
Acquired encephalopathy is divided into several types.
Types of acquired encephalopathy
Depending on the cause of the disease, the following types of acquired encephalopathy are distinguished:
- Post-traumatic encephalopathy
- develops as a result of traumatic brain injury. It is often detected in athletes. It happens that signs of the disease appear long after the head injury. - Toxic encephalopathy
is caused by long-term negative effects on the brain of toxic substances, for example, alcohol, certain medications, heavy metals, and poisons. - Discirculatory encephalopathy
- occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the brain. - Residual encephalopathy
occurs due to the death of cells of the central nervous system. - Hepatic and uremic encephalopathy
- caused by severe diseases of the liver and kidneys. - Pancreatic encephalopathy
- occurs with diseases of the pancreas. - Hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic encephalopathy
- occurs in diabetes mellitus. - Radiation encephalopathy
– occurs due to radiation damage. - Vascular encephalopathies
- occur with chronic disruption of the blood supply to the brain. They develop as a result of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, hypertension, etc.
Symptoms
Dysarthria is a speech disorder that is expressed in difficult movement of the articular apparatus. Characteristic signs are noticeable even at an early age. The baby holds his head later than his peers (about 5-7 months); the skills of sitting and crawling are acquired at 8-11 months. The first walking skills appear after 1.5 years. In infancy, a weak sucking reflex leads to rapid fatigue. The nipple latching is incorrect due to weakness of the articulatory muscles.
The baby begins to pronounce sounds and words later than the established norm (they are monotonous, articulation is weak and unexpressed). There is no reaction to the actions of the parents (lack of smiling, walking, motor activity of the arms and legs, or manifestations of a feeling of joy). The later symptoms of dysarthria include the following:
- Slurred speech.
- Disturbance in the rhythm of speech and breathing, so words are pronounced with different intonation and volume.
- Nasality.
- Words are pronounced syllable by syllable, some syllables are swallowed.
Increased tone of the muscles of the speech apparatus, as a result of which the speaker quickly gets tired. Or hypotension occurs (flaccid tongue, lips, cheeks, increased salivation). In the future, such deviations in neurology manifest themselves in too strong or weak grip, uncoordinated actions. There are disturbances in the field of visual and spatial perception (the shape, size of objects, and their location are incorrectly determined).
Oral tasks, physical exercises, dance, and imitative movements are difficult to perform; modeling from plasticine or clay also fails. Grapho-motor skills are not fully developed (it is not possible to hold a writing object correctly, draw a straight line, or draw a figure).
Secondarily, with dysarthria, the following components of speech are disrupted: phonemics and phonetics, vocabulary, grammar. Increased tone of the facial muscles and speech apparatus leads to weak articulation, voluntary movements appear (tremor, myoclonus). There is a poor vocabulary, amicability, and sometimes a lack of emotions.
Children with dysarthria cannot independently overcome the difficulties encountered when pronouncing sounds. To choose the right treatment method, it is necessary to correctly diagnose the disease; possible symptoms with problems pronouncing sounds are associated with another disorder.
In terms of external manifestations, dysarthria may be similar to alalia. But the causes of speech disorders are different. If with alalia the mobility of the articulatory muscles is not affected, then in children with dysarthria, on the contrary, the speech apparatus is primarily affected.
Symptoms of erased dysarthria
Erased dysarthria is a consequence of brain damage. Pronunciation is slightly impaired, speech pathology is not immediately noticeable to the child’s loved ones. The following symptoms are identified in the erased form of dysarthria:
- Poor pronunciation of sounds in words and phrases.
- Speech is slurred, inexpressive, blurred, blurred.
- Sounds are replaced and distorted.
- No self-care skills.
- Gross motor skills are impaired.
- The mouth is always open because the jaw muscles are sluggish.
If parents have an assumption about the presence of such a disease, it is necessary to consult a neurologist. Erased dysarthria in preschool children is easily corrected.
Fine motor skills in children with dysarthria
Fine motor skills - precise, coordinated movements of the hands, feet, and fingers. There is a direct relationship between the development of fine motor skills and the formation of speech and mental perception. In children with dysarthria, general and fine motor skills of the body are constrained, and subtle actions are difficult.
The reason lies in the insufficiency of the motor part of the brain, the first signs of which make themselves felt from infancy. At an early age, the baby does not show interest in toys above the cradle, or in objects in the hands of parents. This interest is necessary for the transition to communication based on joint actions, for the development of a gestural form of communication.
In the subsequent period of development, an indicator of dysarthria is the absence of objective actions. Dysarthria is characterized by a lag behind peers in grasping and perceiving objects. Pincer grip with fingers does not appear or is very difficult. Manipulation with toys is either inadequate or typical for normally developing younger children.
Inappropriate actions with objects, inability to correlate shapes and sizes are a clear indicator of the diagnosis of dysarthria. The sequence of the baby’s actions is not educational: he tries to push a large ball through a small hole, does not understand how to string rings onto a pyramid, and tries to place inappropriate figures into a sorter toy.
Through the formation of finger movements, the development of children's speech is stimulated. General motor skills of the body may be normal, but if the development of fine and precise movements of the fingers lags behind, speech development is most often delayed. The easiest way to correct a delay in the development of fine motor skills is with an erased form of dysarthria. Minimal dysarthric disorders are very common in the practice of speech therapists and defectologists.
Note! Under the influence of correctional and educational work, deficiencies in fine motor skills in the erased form of dysarthria are successfully corrected and smoothed out, especially in the early and middle preschool years.
Methods for correcting fine motor skills in children with dysarthria
Children suffering from dysarthria are often called clumsy - they cannot clearly perform motor exercises, stand or jump on one leg. The development of fine motor skills should be carried out long before school age in order to solve the following tasks:
- classes have a beneficial effect on the overall intellectual development of the baby;
- Some school learning problems can be avoided by developing writing and visual skills.
At first, the classes are passive in nature - in the infant period of life, the hands are carefully stroked, the fingers are massaged, bent and unbent, and come into contact with each other. As the child grows, the exercises become more complex.
Development of fine motor skills with dysarthria
Starting from the first year of life, simple speech therapy rhythm classes are shown. At a later age, logorhythmic exercises become more complicated. From 2-3 years of age, manual skill gradually develops; finger gymnastics is performed from simple to more complex movements:
- Fingers clench into a fist. Perform circular movements from the wrist 5 times alternately in both directions.
- The fingers are clenched into a fist with force and unclenched 5 times.
- The palms open, the fingers straighten. The thumbs are moved to the sides, perform circular movements 5 times to the left and to the right.
- The first two phalanges of the fingers are bent and extended five times.
- Straighten your fingers, simultaneously bend and straighten the first two phalanges. 5 - 6 times.
- Each finger is bent and unbent separately, the remaining fingers should be clenched into a fist. The child sits with his elbows on the table. Start with a small number of repetitions, gradually increase to 15 times.
- Upon completion of the gymnastics, relax your hands, wave them and shake them vigorously several times.
In addition to special finger gymnastics, the scope of possible types of activities is unlimited, including weeding beds in the garden, picking berries, sorting cereals, peeling and cutting vegetables (does not require a sharp knife!). It is important to involve your child in any activity available to him. Systematic variety will allow you to gain arm strength and improve differentiation of movements.
Diagnosis of encephalography
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using a number of methods:
- Rheoencephalography (REG)
is a non-invasive examination method that allows you to obtain information about the condition of the walls of blood vessels in the brain. - Doppler ultrasound (USD)
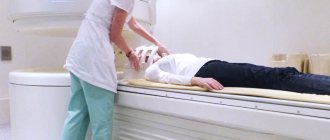
is a safe and highly informative method for diagnosing vascular disorders that lead to the development of encephalopathy. - MRI
- MRI of the vessels of the brain, head and neck, pituitary gland, and eyeball is performed.
For some types of encephalopathies (for example, dyscirculatory encephalopathy), the following are used as diagnostics: Source: Kadykov A.S. Dyscirculatory encephalopathy: algorithm for diagnosis and treatment in patients with arterial hypertension / A.S. Kadykov, N.V. Shakhparonova // Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics. - 2010. - pp. 12-17.
- neuropsychological research with special attention to the state of memory, attention and intelligence;
- ECG and dynamic blood pressure measurement, if necessary, echocardiography, Holter monitoring, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring;
- study of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
Danilova Olga Andreevna
neurologist
Encephalopathy is a group of diseases, the main manifestation of which is the gradual degeneration of brain tissue. To treat the disease, it is important to eliminate the main factor that is gradually destroying the brain. This may be insufficiency of liver or kidney function, atherosclerosis, previous traumatic brain injury, diabetes mellitus and many other reasons. At SM-Clinic we carry out a full diagnosis to determine the cause of encephalopathy, and only after that we begin treatment.
Perinatal form of the syndrome
A similar diagnosis is made to the patient if unspecified encephalopathy is present. This term only means that the damage to the “gray matter” developed in the perinatal age (from 28 weeks of pregnancy to 8 days of the child’s life).
The perinatal form of encephalopathy in babies can occur for various reasons:
- carrying a child into adulthood or early childhood,
- long-term infertility treatment, miscarriages and abortions,
- encephalopathy in a newborn often develops due to illnesses of the mother suffered during the period of bearing the child (diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, surgery, kidney diseases, some types of influenza),
- threat of miscarriage,
- harmful hobbies: drinking alcoholic cocktails, tobacco products,
- taking medications,
- toxicosis, influence of radiation.
A congenital form of encephalopathy can also be considered one that developed as a result of complications during labor: trauma, slow or rapid labor, placental abruption, narrow hips in the mother and a large head in the baby, abnormal positioning of the fetus.
Residual organic damage can appear in the very first days of a newborn’s life, due to purulent infections, hemolytic disease or complex surgical intervention. In all these situations, the risk of hypoxic encephalopathy is high.
Treatment of encephalopathy
Treatment methods for encephalopathy directly depend on the disease that caused the brain damage.
The most common treatment methods are:
Drug treatment
— a wide range of different groups of drugs are used, which are selected depending on the cause of the disease, possible concomitant diseases, and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Drugs that optimize cerebral circulation, neuroprotectors, vasodilators, diuretics, nootropics, amino acids and other drugs are prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
— for non-drug treatment of encephalopathy
magnetic therapy
, electromagnetic stimulation,
electrophoresis
,
ultraviolet irradiation of blood , ozone therapy
,
acupuncture
, and plasmapheresis are used.
Surgery
— most often, operations are performed on blood vessels necessary to normalize blood flow in the brain. Surgical treatment is used for brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, congenital anomalies of cerebral vessels
Lifestyle correction
— in order to increase the effectiveness of treatment, it is recommended to lose excess weight, eliminate saturated fats, salt, alcohol from the diet, move more, stop smoking and taking drugs.
If symptoms of encephalopathy occur, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. If you delay the start of treatment, there is a risk of depression of brain function and even disability.
Timely treatment, in turn, can not only slow down the development of the pathology, but also completely get rid of the negative consequences of the disease.
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price, rub.) | In installments* |
| Electrophoresis (1 field) | from 700 | — |
| UHF therapy (1 field) | from 700 | — |
| Magnetotherapy category I difficulty | from 550 | — |
| MRI of the brain | 4 200 | — |
* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments.