- Home /
- Branches /
- Therapy /
- Neurological diseases
According to statistics, approximately 50% of cases of childhood disability are associated with disorders of the nervous system.
But at the same time, the majority of pathologies, approximately 70%, arose during the period of intrauterine development of the child or in the first time after birth. Thus, timely diagnosis and correctly prescribed treatment are of great importance for young patients and can help avoid serious consequences. Specialists at the pediatric department of the Yauza Clinical Hospital have ample opportunities for early diagnosis of neurological disorders and their effective treatment. An individual therapy option is selected for each patient, which increases the effectiveness of treatment.
Causes of neurological diseases in children
The development of neurological diseases in children under one year of age is usually associated with the peculiarities of the intrauterine development process. Experts name the most common reasons:
- the child receiving a mechanical injury to the spine or brain during childbirth;
- oxygen starvation (hypoxia) of the fetus, which occurs for various reasons, for example, due to repeated entanglement of the umbilical cord around the neck;
- the complex process of childbirth and labor, which leads to infection of the birth canal, an increase in the anhydrous gap, the development of inflammatory complications, bleeding during or after childbirth;
- acute toxicosis of pregnant women throughout the entire period;
- genetic inheritance.
As for children over 1 year old, the root of neurological pathologies should be looked for in:
- low immunity and persistent infectious diseases of the child;
- frequent stress, depression;
- misuse of certain medications, such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids;
- excessive stress on the body – physical and mental;
- being in constant fear and depression caused by the behavior of parents and peers at home, in kindergarten, school, clubs and sections;
- excessive emotionality of the child;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- diseases of the brain, internal organs, injuries.
Whatever the causes of neurological diseases in children, it is important to promptly detect disorders and begin treatment. The sooner this happens, the less likely it is to develop serious complications and the better the prognosis for recovery.
Schedule of mandatory visits to a neurologist
A pediatric neurologist should examine a newborn every 3 months in the first year of life. The specialist assesses the pace of the child’s development and adjusts the vaccination schedule if necessary. Subsequent techniques take place at important stages in the formation of the child’s psyche:
- 4-5 years;
- 7 years;
- 13-14 years old.
It is recommended to examine a neurologist at least once a year throughout the child’s life. During the examination, the doctor checks the child’s emotional and motor functions, and also monitors the mother’s psycho-emotional state. Often problems of the nervous system of children are associated with the restless behavior of parents.
The age of three is considered important and dangerous in the development of the nervous system. During this period, the first neurotic states appear in children:
- obsessive fears;
- sleep disorders
- obsessive movements (unusual blinking, sobbing, sighing, etc.).
Such problems are often associated with improper communication between parents and child; a neurologist can identify and correct this problem in time.
At the Serdolik clinic in Novosibirsk, you can choose an experienced pediatric neurologist who can exclude pathology or prevent its development.
Symptoms of neurological diseases in children
The first signs of neurological disorders can be noticed in a child at a very early age. You should consult a doctor for help if you experience the following symptoms:
- twitching of the chin and arms at rest;
- throwing your head back while crying;
- lack of reaction to bright light and the sound of a rattle;
- inability to hold a rattle 30 days after birth;
- inability to hold the head 30 days after birth;
- excessive salivation after feeding;
- hyperexcitability (frequent crying) or passive behavior (does not cry at all);
- increased anxiety, sleep disturbances (difficulty falling asleep, sleeping more than 20 hours a day);
- frequent regurgitation in a fountain;
- the occurrence of seizures with a slight increase in temperature;
- hypertonicity (constant tension) of the leg muscles, arching of the body or tilting of the head to the side, which makes it difficult to change the child’s clothes;
- difficulty swallowing food;
- temporary loss of consciousness;
- A 3-month-old baby does not imitate the speech of adults;
- sunken fontanelle;
- the child does not want to sleep on his stomach;
- When leaning on his legs, the child bends his fingers.
As for an older child, the symptoms of neurological diseases in children will be somewhat different:
- forgetfulness, absent-mindedness;
- fainting;
- urinary incontinence;
- delayed speech development;
- excessive nervousness;
- panic attacks;
- the child has difficulty making contact with other children;
- insomnia;
- poor appetite;
- constant despondency and melancholy attitude towards life;
- constant headache.
If parents detect even some of these signs, it is necessary to urgently consult a specialist.
Diagnosis and principles of treatment of diseases of the nervous system
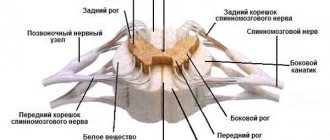
To make a diagnosis, a neurologist examines and interviews the patient and collects anamnesis. The doctor checks reflexes using special neurological tests. To obtain an objective picture of the disease, the patient undergoes laboratory tests (blood, lumbar fluid) and undergoes instrumental diagnostics, including:
- encephalography;
- angiography;
- electrocardiography;
- computed tomography;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- electroneuromyography;
- neurosonography;
- Doppler ultrasound;
- polysomnography.
Depending on the patient’s condition, treatment measures can be:
- urgent (aimed at restoring human life);
- medications that serve to maintain vital functions (for example, for patients in a coma);
- medications, which are aimed at accelerating the restoration of nerve connections, improving nerve conduction, as well as courses of neuroprotectors, muscle relaxants, antidepressants, vitamins, specific drugs for infections, tumors;
- surgical (surgical interventions to remove tumors, restore vascular patency, treat malformations and consequences of injuries);
- physiotherapeutic (massage, exercise therapy, manual therapy, acupuncture, ultrasound and magnetic therapy, electrical stimulation, UHF);
- rehabilitation (after brain and spinal injuries, after a stroke, with multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease).
Different neurological diseases require different approaches to therapy. Neuralgia and VSD can be treated at home. In case of acute cerebrovascular accidents (stroke), immediate hospitalization in a neurological hospital is required. Recovery from concussions and injuries is carried out in specialized rehabilitation centers.
List of neurological diseases in children
The list of neurological diseases in children is quite impressive, so we will limit ourselves to listing the most common ones.
- Epilepsy. The disease manifests itself by sudden, recurring convulsive attacks.
- Cerebral palsy . The disease is characterized by limited motor capabilities of the child, difficulties in maintaining an upright posture and walking. Often accompanied by reduced intelligence, delayed speech development and epilepsy.
- Neurosis (psychoneurosis, neurotic disorder) . This name unites a group of reversible disorders, which are characterized by obsessive, asthenic or hysterical manifestations, weakening of both mental and physical performance.
- Hyperactivity . The disease manifests itself in the child’s excessive energy and mobility, impaired attention and sleep, lack of appetite, anxiety and some bad habits, for example, the habit of biting nails.
- Asthenic syndrome . Often occurs as a consequence of traumatic brain injury. It manifests itself as rapid fatigue, irritability, isolation and self-doubt, or a complete loss of the ability to perform physical activity for a long time.
Treatment of neurological diseases in children
Treatment of neurological disorders in children includes taking medications that restore the functioning of the nervous system, physical and psychological correction. The child may be prescribed courses of therapeutic massage, special physical education, and exercises in water. Physiotherapeutic methods are often used - stimulation with a high-intensity magnetic field or electric current, laser therapy, ultraphonophoresis of enzyme preparations, electrophoresis and others.
What treatment the doctor will prescribe depends on the child’s age, concomitant diseases, the totality of all the features of the development of neurological pathology from beginning to end, as well as on the effectiveness of correction at the previous stage.
In the city of Penza, you can be examined by a pediatric neurologist and receive qualified assistance at the medical ]"Stoletnik"[/anchor], located at the address: st. Chaadaeva, 95 on the first floor of a five-story residential building. On Wednesdays from 9.00 to 12.00 and on Fridays from 13.00 to 15.00, consultations are conducted by a doctor of the highest qualification category.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
Treatment of pathologies
Depending on the cause of the neurological disorder, treatment is prescribed, which is selected individually. The treatment uses: medication, nutraceuticals, physiotherapy methods, classes with teachers (neuropsychologist, speech therapist), special diets, adherence to the regime. Medications, if necessary, are selected taking into account the diagnosis and are very specific. There is no single treatment regimen that would be effective in all of these cases.
For example, if a child has epilepsy, they may be prescribed anticonvulsants. If disorders of the peripheral nervous system are observed, treatment is carried out with anti-inflammatory drugs, antivirals, drugs that relieve spasms, and so on.
A doctor must monitor the child’s condition; medications are prescribed taking into account the child’s characteristics. As the condition improves, the dosage of medications is reduced or completely discontinued. Many neurological disorders can be treated at the initial stage of the disease, if you consult a neurologist in time.
Literature:
- Belyaeva I. A., Bombardirova E. P., Tokovaya E. I., Kharitonova N. A., Lazurenko S. B., Turti T. V., Illarionova M. S. Non-drug habilitation of children with perinatal lesions of the nervous system / / Issues of modern pediatrics. – 2021. – No. 16 (5). – pp. 383–391.
- Bombardirova E. P., Yatsyk G. V., Stepanov A. A. Treatment and rehabilitation of perinatal lesions of the nervous system in children in the first months of life // Attending physician. – 2005. – 2. – P.67–69.
- Petrukhin A. S., Pylaeva O. A. Current problems of pediatric neurology // General Medicine. – 2005. – No. 2. – P. 3–11.
Prices
Dear patients! Check the cost of seeing a specific doctor at the reception desk.
- Diagnostics
- Procedures
- Analyzes
- Ultrasound
| Name | Price, children | Price, adults |
| EEG video monitoring (electroencephalographic video monitoring during sleep) (3 hours) | 6 135 | 6 500 |
| EEG (electroencephalogram) | 1 985 | 2 080 |
| Evoked potentials: auditory, visual, somatosensory (each) | 2 300 | 2 300 |
| REG (rheoencephalogram) | 800 | 915 |
| ECHO (ECHO-EG, echoencephalogram of the head) | 730 | 830 |
Show all prices...