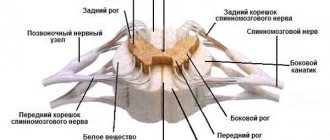
Neurology is a branch of medicine that studies the nervous system: structure, function, norms and pathologies, influence on other organs and systems, as well as its treatment. This industry is closely related to such medical disciplines as: anatomy, physiology, neurogenetics, angiology, psychiatry.
The Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital provides diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the nervous system, as well as rehabilitation of patients with neurological ailments. Modern medical equipment and the latest treatment methods allow neurologists to establish an accurate diagnosis and select treatment tactics individually.
Neurological diseases
Diseases of the brain and spinal cord for which people come to our center:
- Neurodevelopmental disorders. Neuroses and psychopathy.
- Movement diseases: pyramidal and extrapyramidal disorders.
- Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system.
- Systemic atrophies of the central nervous system, neuromuscular diseases.
- Conformational diseases. Demyelinating diseases – pathies and neuropathies.
- Epilepsy.
- Cerebrovascular diseases.
- Migraine.
- Lesions of the peripheral nervous system: radiculopathy, plexitis.
- Nervous system injuries.
- Neurotic somatoform disorders, disorders associated with physiological disorders.
- Comorbid conditions.
Types of Nervous System Disorders
In medicine, neurological problems are usually divided into two fundamental blocks: pyramidal and extrapyramidal. The extrapyramidal system is a brain structure that is responsible for balance, emotions, posture, movement and muscle tension. Failures in the operation of this system lead to the development of hypokinesia or hyperkinesia.
Hyperkinesia is a pathological condition in which an increased number of involuntary movements is observed. This occurs when neurons are damaged. The disease can spread to all human organs. The disease has no age restrictions.
Hypokinesia – has the opposite effect, as a result of which motor activity becomes inhibited. Develops against the background of an inactive lifestyle and psychological disorders.
The pyramidal system is responsible for coordination and reflexes. If the system malfunctions, the integrity of the cortico-muscular pathway is disrupted. In other words, nerve impulses do not reach the target, as a result of which the body does not react. The most common diseases of this group are paralysis and paresis (a group of ailments characterized by loss of movements).
Symptoms and signs of neurological disease in adults
How neurology manifests itself in adults - in the form of symptoms familiar to many. Here are the most common:
- Headache.
- Migraine.
- Dizziness.
- Painful sensations of varying intensity in any part of the body (pain in the head, back and lower back, pain in the legs, arms, joints).
- Speech impairment.
- Decreased memory and attention.
- Decreased visual acuity, drooping eyelid (ptosis), double vision.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Decreased performance.
- Sleep disorders.
- Tendency to depression.
- Tendency to faint.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Noise in the head.
- The appearance of convulsions, epileptic seizures.
- Numbness of the limbs, coldness, loss of sensitivity in the fingers.
- Tremor (shaking) of the limbs.
- Difficulty in swallowing.
- A nervous tic in the form of frequent blinking in adults is also a cause of neurological disorders.
- Etc.
What diseases of the nervous system does a neurologist treat?
Neurology is a field of medicine that deals with the treatment of diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system of humans. Neurological problems are associated with genetic inheritance, congenital pathologies and previously acquired diseases. Analysis of symptoms and accurate diagnosis of the disease make it possible to determine in which part of the nervous system the disorder has occurred.
Frequent symptoms indicating a dysfunction of the central nervous system include: headaches, dizziness, disturbances in the functioning of the organs of hearing, vision and speech. Muscle atrophy, numbness and decreased sensitivity in the extremities indicate disturbances in the functioning of the peripheral nervous system. In any case, only an experienced specialist will be able to accurately determine the cause of the disease.
Most diseases are associated with disruption of the nervous system, as it interacts with all functional structures of the body. Therefore, specialists from other medical categories refer patients to a neurologist. Neurologists investigate the causes of diseases, analyze the symptoms of the disease, and determine methods for diagnosing the problems that have arisen. Based on the identified diagnosis, the doctor prescribes effective treatment for the patient.
Symptoms of neurological diseases:
- dizziness, tinnitus, increased fatigue;
- insomnia, memory disorder;
- convulsions, tremors, tics;
- numbness, tingling in the limbs;
- pain in the head and other parts of the body;
- loss of consciousness, impaired coordination of movements and balance;
- speech impairment, sharp deterioration of vision.
How does a consultation with a neurologist proceed?
A consultation with a neurologist takes place in several stages. First of all, the patient describes the symptoms that bother him and the possible causes of their occurrence. After analyzing the complaints, the doctor begins an examination: studies the general neurological condition of the patient, analyzes motor activity, examines the patient for hand tremors, asymmetry of the face and body. Then, using auxiliary objects such as a “hammer”, the neurologist determines the functional state of the nerves of the cranial region, analyzes the patient’s reflexes and checks the patient’s sensitivity to tactile, pain and temperature stimuli. After the initial examination, it is not always possible to accurately determine the diagnosis. Therefore, a neurologist uses modern methods for diagnosing the disease.
Diagnostic methods in neurology
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- a magnetic resonance imaging scanner allows you to obtain visualized information about the state of the brain matter, soft tissue structures of the body, spinal ligaments, detailed images of nerve fibers and intervertebral discs without the use of x-rays; - Computed tomography (CT)
is a radiation diagnostic method that allows you to analyze the examined human organs and tissues for the presence of pathologies. It is possible to obtain precise layer-by-layer images of “slices” of the spine, skull, brain and spinal cord; - Electroneuromyography (ENMG)
is a unique study of the functional state of muscles and peripheral nerves, which allows us to determine the causes of muscle spasms, pain and shooting in the spinal region, the cause of muscle weakness; - radiography
is a method of radiation diagnostics that allows you to examine the condition of the bones of the skull and musculoskeletal system; - Ultrasound examination (ECG)
- Using ultrasound diagnostics, you can obtain real-time information about the functional state of blood vessels, including the main vessels of the brain (main arteries, vertebral arteries, posterior cerebral arteries, carotid arteries and their branches); - laboratory tests
- In neurology, laboratory methods are used to obtain a complete picture of the disease, clarify or exclude the disease, and check the effectiveness of treatment.
What diseases does a neurologist treat?
- diseases of an inflammatory nature
(epidemic, tick-borne and influenza encephalitis, meningitis, poliomyelitis, neuritis, radiculitis); - degenerative diseases of the nervous system
(Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, osteochondrosis, herniated discs); - vascular disorders of the nervous system
(migraine, vegetative-vascular dystonia, hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke, hypertension, atherosclerosis, traumatic damage to cerebral vessels, arterial aneurysms); - autoimmune diseases
(multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, Guillain-Baré syndrome, myasthenia gravis); - neuralgia
(cranial, vertebral, intercostal and clavicular-costal neuralgia); - convulsive disorders
(epileptic seizures, febrile seizures). - problems with the spine and joints
(intervertebral disc herniation, spinal osteochondrosis, arthritis).
Vegetovascular dystonia
A condition that develops against the background of disruption of the autonomic nervous system.
Pinched sciatic nerve
A set of symptoms associated with nerve compression.
Intercostal neuralgia
A disease that occurs due to damage to the nerves passing between the ribs.
Migraine
A chronic disease characterized by periodic attacks of severe headaches.
Panic attacks
Attacks of severe anxiety.
Cervical osteochondrosis
A chronic disease that causes thinning of the discs between the vertebrae.
Encephalopathy
A term that includes similar types of brain lesions.
Multiple sclerosis
A chronic autoimmune disease of the nervous system that can lead to severe disability.
Trigeminal neuralgia
A disease that manifests itself in severe pain, as well as concomitant dysfunction of the facial and masticatory muscles.
You can learn about other diseases in the “Diseases” section.
Non-drug methods of treating neurological diseases at the Health Energy clinic
The Health Energy Clinic actively uses non-drug therapy methods to treat neurological patients.
The main areas of non-pharmaceutical treatment are: physical therapy (physical therapy), physiotherapy, reflexology, manual therapy, therapeutic and hardware massage, osteopathy, auxiliary support devices that facilitate the patient’s movement (canes, wheelchairs, prostheses, walkers, orthopedic products - braces and orthopedic insoles). Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy)
— a method of medical rehabilitation based on complex functional therapy. A set of exercises allows you to increase muscle tone, increase blood circulation, and restore conductive impulses along damaged nerves. Exercise therapy is most often prescribed to patients with the following diseases: osteochondrosis, protrusions, vegetative-vascular dystonia, neuritis, cerebral palsy, consequences after injuries and fractures, Parkinson's disease, strokes, herniated intervertebral discs.
Manual therapy
is the treatment of patients using hands. Unlike therapeutic massage, which stimulates soft tissues, manual therapy uses a set of therapeutic techniques that affects the anatomical structures of the human body in order to free them from functional blocks, as well as to restore the circulation of fluids and improve the patient’s motor condition. In neurology, manual therapy is actively used to treat diseases such as osteochondrosis, scoliosis, arthritis, arthrosis, radiculitis, intervertebral hernias, headaches, and neuroses.
Therapeutic massage
is a set of techniques with which the massage therapist exerts mechanical effects on the patient’s tissues and organs. The use of massage in conjunction with other non-drug methods (physical therapy and physiotherapy) is most effective in the rehabilitation of patients with neurological diseases. A course of therapeutic massage can normalize blood circulation and normalize blood pressure. A gentle effect on nerve fiber receptors has a positive effect on the recovery processes of the nervous system - muscles become toned and mood improves. Therapeutic massage is effective in the treatment of scoliosis, osteochondrosis and osteoarthrosis, disorders of the cerebral blood supply, intercostal neuralgia, herniated discs, radiculitis and joint pain.
Osteopathy
is an alternative medicine method based on the treatment of diseases using special manual techniques. Osteopathy considers structural and anatomical disorders between various organs and parts of the body as the primary cause of disease. Acting gently and painlessly with the help of palpation, the osteopathic doctor assesses the density, shape and size of certain organs, thereby determining the slightest changes in their structure and location. In neurology, osteopathy is given special attention, since it can help cope with problems such as: increased intracranial pressure, headaches, spinal diseases, encephalopathy of various etiologies, asthenovegetative syndrome, problems with speech and hyperexcitability in children.
Reflexology
is a set of diagnostic methods, the essence of which is to influence active biological points of the body (acupuncture). There are more than 800 such points on the human body. Treatment is based on the idea that the body is an integral interconnected system - an imbalance in one part of the body affects all other interconnected structures of the body. Recovery occurs not only on a physical level, but also on an emotional one. Reflexotherapy is actively used in the treatment of radiculitis and osteochondrosis, pain in the spine of various origins, for convulsions and consequences after injuries.
Kinesio taping
is a simple and effective method of treating sprains, muscle pain and other injuries, hematomas and swelling by gluing a special elastic adhesive tape - tape. Indications for use: injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system (MFPS, postural disorders, initial forms of scoliosis, infantile torticollis, periarthritis, epicondylitis, arthrosis, spinal osteochondrosis); hematomas and edema of various origins; cicatricial skin changes; tension headache.
Make an appointment with a neurologist in St. Petersburg
You can make an appointment with a neurologist in St. Petersburg by calling: 8 (812) - 701-03-03
.
Clinic "Health Energy" is located at :
Engels Ave. 33 to 1., 4th floor. Author: Elena Minaeva
Rate this article:
| 3.18 out of 5 (based on 8 reviews) |
Share to:
Diagnostics
Since such signs of a neurological disease in adults are also observed in other somatic diseases, a differential diagnosis is required, on the basis of which the specialist makes a conclusion about damage to the nervous system.
All studies in our center are carried out on our own diagnostic base using equipment from leading world companies in the field of neurophysiology:
- Electroencephalography of all types.
- EEG video monitoring (day, night, multi-day).
- Polysomnography (PSG), polysomnography with MSLT test (multiple sleep latency test).
- Electroneuromyography (cutaneous EMG, needle EMG, stimulation EMG).
- Transcranial Dopplerography.
- Duplex scanning of the vessels of the brain and neck.
- Evoked potentials: auditory, visual, somatosensory.
- Fundus examination.
- All types of laboratory diagnostics, including drug monitoring.
- Evoked potentials: auditory, visual, somatosensory.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
To understand complex situations, specialists of other profiles are brought in: otoneurologists, neurosurgeons, neuroorthopedists, geneticists, psychiatrists, endocrinologists, gastroenterologists.
Who is a neurologist and when should you contact him?
Neurology is a science that deals with a wide variety of diseases, from headaches to infectious diseases. The main diseases are divided into blocks.
Brain problems: attention disorders, manic psychosis, neuroses, epilepsy, restless legs syndrome, brain injuries.
Problems with cerebral vessels: fainting, ischemic cerebral disease, consequences of strokes, dizziness.
Problems of the autonomic system: Raynaud's disease, mountain sickness, migraine, vegetative-vascular dystonia, Parkinson's disease, cerebral palsy, enuresis, muscular rheumatism, increased sweating, Alzheimer's disease.
Problems with the spine: scoliosis, back pain, radiculitis, osteochondrosis, radicular syndrome, neuralgia, intervertebral hernia.
In order to receive a referral to a neurologist, you first need to undergo a consultation with a local therapist, who will determine whether the patient needs to be examined by a specialist doctor or not.
An appointment with a neurologist begins with an analysis of the patient’s complaints and subsequent diagnosis, which can take the following forms:
- X-ray;
- functional diagnostics;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- laboratory diagnostics;
- ultrasound.
Preventive measures
Prevention allows you to prevent the development of neurological diseases, and also helps to maintain the achieved results in their treatment. Basic recommendations for all groups of patients (with congenital and acquired pathologies of the nervous system):
- consult a doctor promptly if alarming symptoms appear;
- undergo regular medical examinations (especially for previously diagnosed diseases of the nervous system, including those in remission);
- follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle (eat rationally, give up bad habits, regularly take walks in the fresh air);
- devote time to moderate physical activity (in the absence of contraindications);
- maintain a sleep-wake schedule;
- exclude or limit the effect of provoking factors (stress, high psycho-emotional stress);
- practice autogenic training to restore mental balance during stress and relieve emotional tension.
If you have symptoms of neurological disorders, as well as to get an alternative opinion on the treatment of such diseases, contact the neurologists of the Consultative and Diagnostic Center (formerly the National Diagnostic Center).