Loss of speech during a stroke is a common complication of a dangerous disease that occurs in every third patient who has suffered an attack. This condition is called aphasia: the patient cannot express his thoughts, has difficulty speaking on simple topics, and cannot even name simple objects. You can often regain lost skills if you enroll in a rehabilitation center after a stroke and undergo recovery under the supervision of experienced doctors.
The prognosis largely depends on the severity of hemorrhage or ischemia, but even with a mild form of stroke, rehabilitation requires concentration on the part of the patient and supervision by a doctor. The doctor must identify aphasia and prescribe a rehabilitation program.
How to recognize aphasia?
Lack of speech after a stroke does not always mean a complete loss of speaking skills. A person may confuse words, letters, sounds, stutter, and try to use the simplest expressions. When a stroke occurs, the speech motor analyzer is affected, phonetics when speaking, as well as syntax, grammar and vocabulary when writing words may suffer. In severe cases, the patient completely loses writing skills.
Speech impairment during a stroke in a patient can be determined by the following signs:
- similar sounds or words are confused;
- there is a violation in the construction of even simple sentences;
- there is an inability to correctly construct a sentence (for example, instead of “I’ll take the bus to the dacha,” a person says “I’ll take the bus to the dacha”);
- stuttering and frequent repetition of the same words are noted;
- obscene language is used.
The last sign often causes anxiety among relatives - even well-mannered and intelligent people often begin to swear after an attack. Scientists explain this by the fact that obscene language is considered one of the most ancient and simplest pronunciations, and therefore settles in the subconscious of every person.
Sometimes dysarthria is observed - the quality of pronunciation of sounds suffers. The intonation changes, the voice may become dull or nasal. In severe cases, there is complete loss of speech during a stroke.
Neurology Center in Moscow
Aphasia refers to the partial or complete loss of speech function. This disorder is associated with organic brain damage. May result from acute cerebrovascular accident, brain tumor or traumatic brain injury. The development and degree of aphasia depends on the location of the brain lesion.
Aphasia ranges from mild to severe forms. Total aphasia implies a complete absence of speech and its understanding. Then the transition of total aphasia to a motor or sensory form is possible.
Motor aphasia
With motor aphasia, a person understands speech addressed to him. However, he can only communicate with others using one word or sound combination. So, motor aphasia is a condition in which a person cannot speak, but can understand speech addressed to him. Motor aphasia is associated with damage to the frontal lobes of the cerebral cortex.
Sometimes the patient can still pronounce words with great difficulty (he sometimes speaks words in syllables). A person tries to avoid complex words in words, limiting himself to simple ones. The patient's speech is quite difficult to distinguish. However, in most cases the speech is understandable. With motor aphasia, speech is always meaningful - this is different from sensory aphasia. Speech is accompanied by eloquent gestures, this is how the patient helps himself to express himself.
Every year, acute cerebrovascular accident affects a large number of people. Afferent motor aphasia develops if the pathological focus is located in the parietal lobe of the brain. A characteristic feature of this disorder is confusion of sounds that are similar in pronunciation. This type of motor aphasia is also characterized by reading impairment. Motor aphasia has a better prognosis than sensory aphasia. Treatment of these types of diseases in stroke patients is carried out by highly qualified speech therapists at the Yusupov Hospital.
Sensory aphasia
Aphasia is a language disorder that affects expressive and expressive language and the ability to read and write.
Aphasia can be so severe that communication with the patient is almost impossible, or the disorder can be very mild. This can affect the ability to select words, the ability to combine words in sentences, and the ability to read. Typically, several aspects of communication are disrupted while some channels remain available for limited information exchange.
With sensory aphasia, speech understanding is impaired. A person does not understand either his own speech or someone else’s, but the ability to speak is often preserved. The condition is associated with damage to the left temporal lobe of the brain. As is correct, the patient is talkative and talks a lot. However, he does not understand himself or those around him. The patient's speech is incomprehensible. There is no meaning in the patient’s words - due to the lack of understanding of one’s own and others’ speech, there is a loss of control over speech. The patient can invent new words, change words, rearrange letters and syllables, pronounce unrelated strings of sentences and words. Since the perception of sounds is impaired, the speech of others becomes incomprehensible to the patient.
Sensory aphasia is otherwise called acoustic-gnostic. The auditory zone of the cerebral cortex is affected. This is the so-called Wernicke's area lesion. Damage occurs to the auditory analyzer - the primary auditory field.
Aphasia refers to the destruction of already established speech. This usually occurs as a result of brain damage. A person can no longer speak normally, ceases to understand other people’s speech, read and write. Neurolinguistics deals with the problem of speech impairment after brain damage. Aphasiologists and neuropsychologists are involved in the study of this problem.
Causes of aphasia
Aphasia often develops due to brain injury or stroke, especially in older people. Aphasia can also be caused by brain tumors or infections.
The most common cause of aphasia is stroke. Sometimes seriously ill patients after a stroke experience aphasia, but this is a temporary phenomenon, and then speech is restored. Less common causes of aphasia are traumatic brain injury, neuroinfection, and neurosurgical intervention.
Aphasia is characterized by difficulty remembering words. Sometimes the fluency of speech is impaired. Such patients have a limited vocabulary and speak little. There are constant hesitations in speech. Speech is distorted and incorrect. Severe situations of aphasia are manifested by the use of just one word or syllable in any communication situations. Aphasia affects adults with already formed speech skills - this is its difference from alalia.
The consequence of aphasia is problems with the perception of the surrounding world. A sick person is unable to recognize sounds, voices, or objects. The sentences are distorted and short. The patient finds it difficult to perform simple language gestures: he cannot fold his tongue into a tube, click his tongue, or put his tongue between his teeth and upper lip.
Dynamic motor aphasia is characteristic of damage to the anterior and middle parts of the inferior frontal gyrus. This is an area located next to Broca's area. There is a decrease in speech initiative. The amount of spontaneous speech decreases. With aphasia, only “remnants” of speech may remain - truncated words and syllables. This disorder is effectively treated at the Yusupov Hospital. Corrective work is carried out by highly qualified speech therapists.
Aphasia after stroke
Aphasia after a stroke is a disease that requires the help of a highly qualified speech therapist. Aphasia is a condition where a person can no longer speak coherently. Speech disorders significantly affect self-confidence and social status.
Speech restoration specialists work at the Yusupov Hospital. The clinic uses special rehabilitation methods such as therapeutic massage, physiotherapy and electrical stimulation. Restoring speech after a stroke is not a passive process. The patient must be ready to study, he must believe in himself, and be patient. In aphasia, cells in one or more of the brain's language centers die. This is a consequence of a stroke. As a result, the patient's speech becomes slurred and severely truncated. Sometimes the patient speaks in syllables or uses one word. Daily therapy should be carried out to the extent feasible for the patient.
One of the treatments for aphasia is physical therapy. After a stroke, to treat aphasia, physiotherapeutic procedures are performed that improve cerebral circulation. What are the responsibilities of a doctor who treats speech disorders after a stroke? First of all, you need daily activity that affects the areas of the brain that are located next to the dead zone.
With medication, you should try to ensure sufficient blood supply to the brain, especially in the affected area. The brain must be provided with the necessary supply of oxygen. These are the principles of treating aphasia after stroke. Therapy should be started as early as possible, immediately after cerebral edema is relieved - it manifests itself as convulsions, hallucinations, depression of consciousness (up to coma). It is necessary to start therapy as early as possible. Treatment of aphasia after stroke is one of the very important tasks of early rehabilitation of stroke patients.
Sign up for the Neurology Center:
- by phone: +7 925 191 50 55
- fill out the form: APPLICATION FOR TREATMENT
- Get advice by email [email protected]
- Clinic address: Moscow, Nagornaya st., 17 to 6
+7 (495) 506 61 01 –
REQUEST TO THE CLINIC
What types of aphasia are there?
Speech impairment can be different; this condition depends on which centers were damaged during ischemia or hemorrhage. Each Broca's area is responsible for its activity; based on the presence of specific signs, doctors determine the severity of the attack.
Types of speech impairment in stroke:
- if the patient cannot name specific objects, optical-mnestic aphasia is diagnosed - the patient usually says “what they write with” instead of the word “pen”;
- if conversational perception is impaired with preserved hearing, sensory aphasia is diagnosed;
- when the patient cannot repeat a word or phrase that is spoken to him, he suffers from an acoustic-mnestic form;
- If a person cannot speak words, but understands everything and can pronounce syllables and letters, motor aphasia is diagnosed.
Forms of speech disorders after stroke
The most common disorders are aphasia and dysarthria. Aphasia
In aphasia, speech suffers due to damage to the speech centers in the brain. Aphasia can be complete (when there is no speech at all) or partial. In the first days after a stroke, there is often a complete lack of speech. The situation usually improves over time. There are several forms of aphasia:
- Dynamic. With dynamic aphasia, it is impossible to formulate a statement - not only external, but also internal speech is impaired.
- Motor. The patient is able to pronounce individual sounds and understand speech, but cannot pronounce words and sentences.
- Sensorna. With sensory aphasia, the situation is exactly the opposite - the ability to speak is combined with the inability to understand speech (in mild cases - only complex and long sentences).
- Amnestic. With amnestic aphasia, a person recognizes objects, knows why they are needed, but forgets their names.
- Semantic. Semantic aphasia is difficulty in perceiving complex grammatical and case structures. Simple sentences are perceived normally.
Dysarthria
Disorders with dysarthria are associated with impaired mobility of the organs of articulation - the tongue, palate, lips. With dysarthria, it is possible to distinguish speech by ear, but the patient’s speech itself is slurred, sluggish and dull, expressed in separate sounds or absent altogether.
Rehabilitation
As soon as a speech disorder after a stroke is diagnosed, doctors develop a rehabilitation program: how to restore it and return the patient’s social life skills. The speech therapist determines which skills are impaired and develops an individual program, conducts training and gives homework. Here, success largely depends not only on the quality of rehabilitation, but also on the efforts and determination of the patient himself.
The program may include:
- reading short sentences with the doctor;
- learning standard phrases with gradual expansion of the vocabulary;
- reasoning about the functional significance of objects;
- as recovery progresses, more complex word forms are used;
- at the end the patient retells the sentences in his own words.
Each speech therapist has his own peculiarities of treating speech impairment during a stroke - the doctor tries to use effective techniques that bring results. It is better to contact trusted and qualified doctors who will help you gain conversational and social skills.
Our rehabilitation center provides a comprehensive program for the recovery of patients with speech impairment after a stroke. We try to select an effective program and monitor the rehabilitation process.
There are four main types of post-stroke speech disorders
Damage to the language center in the dominant hemisphere - Broca's area - leads to the fact that patients lose the ability to convey their thoughts using coherent and grammatically correct language structures. Conversely, pathological changes in Wernicke's area (sensory center) lead to problems in receptivity to language. Such patients have difficulty understanding spoken or written language. They often use correct grammatical structures, but their statements may not make sense. The most severe form of aphasia (global or total) occurs in patients with extensive damage to several areas of the brain responsible for understanding and language. The mildest form of aphasia—amnestic—leads to difficulty working with vocabulary.
How do these types of aphasia manifest themselves in practice?
Damage to the language center in the dominant hemisphere - Broca's area - leads to the fact that patients lose the ability to convey their thoughts using coherent and grammatically correct language structures. Conversely, pathological changes in Wernicke's area (sensory center) lead to problems in receptivity to language. These patients have difficulty understanding spoken or written language. They often use correct grammatical structures, but their statements may not make sense. The most severe form of aphasia (global or total) occurs in patients with extensive damage to several areas of the brain responsible for understanding and language. The mildest form of aphasia—amnestic—leads to difficulty working with vocabulary.
How do these types of aphasia manifest themselves in practice?
- Motor aphasia. You know what you want to say, but you can’t find (remember, use and pronounce) the right words.
- Sensory aphasia. You hear someone speak or see printed text, but cannot understand the meaning of the words.
- Amnestic aphasia. You find it difficult to select and use the correct words to refer to certain people, objects, places or events.
- Global aphasia. You cannot speak, write, read and do not understand what is being said to you.
Causes
Aphasia is an organic brain lesion, which means that it is caused by serious disturbances in metabolic activity. There are many reasons that can have a pathological effect on brain neurons, the most common of which include:
- Acute cerebrovascular accident or stroke;
- Traumatic brain injury;
- Oncological damage to brain tissue;
- Infectious diseases such as encephalitis or meningitis;
- Alzheimer's or Pick's disease;
- Surgical interventions on the brain.
All of the above reasons can lead to damage to neurons involved in the formation of speech function.
It is also important to note predisposing factors that significantly increase the risk of developing the above diseases. These factors include:
- Dysmetabolic disorders;
- Dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Rheumatism.
Consequence of stroke
Most often, motor aphasia develops after a stroke. In this case, ischemic damage followed by necrosis occurs in Broca's area, which is responsible for the motor function of speech. Moreover, most often, damage to this zone occurs as a result of thrombosis of the branches of the middle cerebral artery. In second place after cerebrovascular accident is damage to Broca's area of an oncological nature.
Diagnostics
The plan for a diagnostic examination of a patient with motor aphasia is practically no different from the examination of a patient suffering from an acute disorder of cerebral blood supply or with brain damage. Mandatory studies are:
- Tomographic research methods, especially magnetic resonance imaging, which allows you to clearly display organic damage to soft tissues, especially the brain. Allows you to confirm the presence or absence of foci of decay of nervous tissue or a tumor process;
- Ultrasound Doppler examination of neck vessels to detect atherosclerotic vascular lesions;
- X-ray contrast examination of cerebral vessels or angiography is used in the topical diagnosis of ischemic brain damage.
It is mandatory to conduct standard laboratory tests, such as: general urine and blood analysis, biochemical blood test.
At the Clinical Institute of the Brain there is a highly functional advanced diagnostic department, as well as a clinical laboratory complex equipped with modern equipment. The clinic’s highly qualified staff allows for quick and accurate diagnosis to formulate a subsequent treatment regimen in the shortest possible time.
Differential and topical diagnostics
It is carried out to clarify the localization of brain lesions, as well as to clarify the form of aphasia. Carrying out differential diagnosis is necessary for the correct formation of further effective treatment tactics. When communicating with the patient, it is possible to find out which symptoms characteristic of a particular type of aphasia prevail, which allows us to determine a clinical diagnosis.
Basic methods of speech restoration
As a result of an acute circulatory disorder, a person learns to communicate again. This is a labor-intensive and long process. During the rehabilitation period, coordinated work between doctors and the patient’s family is important. In order for him to recover faster, his close relatives should be patient and follow the following rules:
- Do not forget to let your loved one know that he is dear and important.
- Support the person as much as possible, show full confidence in a speedy recovery, and celebrate his progress.
- Talk regularly, tell all the latest news.
During treatment, your support and participation is very important to the patient. You can listen to his favorite music, watch movies, read books with him.
Let's take a closer look at the main methods of restoring speech function.
Training with a speech therapist
A speech therapist plays a major role in the rehabilitation process. He conducts tests, assesses the patient's condition and performs appropriate exercises with him. A specialist is present at every session, helps the patient and monitors the correctness of the technique. In the future, constant supervision by a speech therapist is not required; the patient can train independently. It is important to adhere to the following rules:
- complete tasks gradually, starting with simple ones and moving on to more complex ones;
- be sure to avoid overwork (if the patient gets tired, the training will be over);
- maintain regularity of classes (the optimal frequency of classes is 5-7 times a week for half an hour).
The task of a speech therapist is to involve various areas of the brain in the process of speech control. Several complexes are used at once that are aimed at restoration:
- phonetic. They are required to improve facial control. During classes, individual sounds and words are repeated;
- visual. If sensory aphasia is diagnosed, then in classes they use cards with pictures and special aids that encourage finding sequences;
- semantic. They are required to stimulate active thinking. During classes, he is asked to continue the phrase he started or engage in an impromptu dialogue on a specific topic.
Massage
In addition to problems with speech, people who have experienced an acute circulatory disorder experience a number of other complications, in particular, sagging soft tissues (cheeks, corners of the mouth), impaired chewing function and excessive salivation.
Thanks to special massage sessions, it is possible to restore the tone of the facial muscles and significantly improve facial expressions. As a result, it will be much easier for the patient to pronounce words. Only a specialist can find the necessary points for massaging. He knows exactly which areas should be toned and which, on the contrary, should be relaxed.
In addition to facial massage, a person is prescribed a massage of the tongue, lips, cheeks, ears, scalp, and hands. Thanks to an integrated approach, it is possible to relieve muscle stiffness and improve speech.
Articulation exercises
Exercises that will be prescribed on an individual basis allow you to restore speech after a stroke. Their main task is to improve control over facial expressions, tongue and lips. Exercises to develop the muscles of the tongue may look like this:
- movement of the tongue in a circle;
- moving the tongue across the palate;
- tongue clicking;
- biting a relaxed tongue;
- sticking out the tongue, directing first to one corner of the mouth, then to the other;
- moving the tip of the tongue across the palate in different directions.
Lip exercises include smiling with your lips open, curling your lips, pulling them forward, puffing out your cheeks, and rolling air from one side to the other.
Exercises for correct and clear pronunciation include attempts to pronounce consonants alternately (first voiceless, then voiced), then vowels (with one sound flowing into another).
Exercises for facial expressions: include opening the mouth wide (hold for a few seconds and relax), raising, lowering and relaxing the eyebrows, folding the lips into a tube, stretching the tongue in different directions.
These exercises are not universal; the doctor develops a plan for each patient individually. There are many similar exercises. They should be performed in the presence of a speech therapist. To achieve positive results faster, it is recommended to perform the exercises regularly.
Abdominal breathing
Abdominal breathing (with the diaphragm) allows you to increase the volume of inhaled air and improve the saturation of cells with oxygen. As a result, heart function normalizes, blood pressure stabilizes, and anxiety goes away.
The breathing technique is carried out under the supervision of a specialist. There are many exercises, one of which could be this: in a comfortable horizontal position, take a deep breath through your nose, and then slowly exhale through your mouth. This exercise is repeated several times and then made a little more complicated. To do this, adding several sounds while exhaling:
- stretched [f];
- stretched [s];
- stretched [w];
- stretched [x].
The optimal number of repetitions is determined by a specialist.
Drug therapy
In addition to exercise, another important component of the rehabilitation period is drug therapy. Good cerebral circulation plays one of the key roles. A stroke significantly impairs the functioning of brain cells, so doctors prescribe medications that stimulate their functioning. Depending on the nature of the lesion, different groups of drugs are additionally prescribed to restore speech after a stroke. These include:
- Antihypertensive drugs (ACE inhibitors) to stop a strong jump in blood pressure.
- Antidepressants to combat chronic stress and bad mood.
- Nootropics to stimulate regeneration, improve memory, help restore the functioning of brain cells.
- Sedatives to relieve emotional stress and normalize sleep.
- Anticoagulants to reduce blood viscosity and prevent blood clots.
Medicines help to significantly reduce the severity of disorders, but they are not able to completely restore lost functions. A positive result will only come from an integrated approach to solving the problem (due to combination with other methods of therapy).
Ischemic stroke: symptoms, consequences, treatment - MEDSI
Table of contents
- Forms of ischemic stroke
- Causes of ischemic stroke
- Main symptoms
- Diagnosis of stroke
- Ischemic cerebral stroke - treatment
- Nutrition after stroke
- Rehabilitation measures after a stroke
- Prevention and prognosis of ischemic cerebral stroke
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
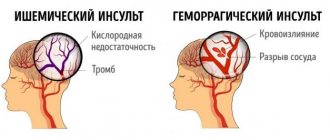
Ischemic stroke
is a condition that occurs against the background of damage to brain tissue due to impaired blood circulation in its vessels and is accompanied by various neurological signs. As a result of its appearance, the functioning of parts of the brain is disrupted (depending on the focus of the disease).
Of the three existing types of strokes, ischemic stroke is the most common, occurring in 80% of cases. The other 20% are subarachnoid hemorrhage and hemorrhagic stroke.
Stroke has especially dangerous consequences: impaired cognitive and neurological functions, paralysis, problems with oral and written speech, etc.
Forms of ischemic stroke
There are several classifications of stroke: by reason of occurrence, by the degree of damage to brain tissue and by severity.
- Reasons for appearance:
- Lacunar – the syndrome affects a tissue area up to 15 mm in size and is accompanied by a small number of neurological symptoms
- Thromboembolic - occurs due to blockage of a blood vessel by a thrombus
- Hemodynamic - in this case, vascular spasm is prolonged, and brain cells stop receiving the necessary nutrients
- Transient attack - the lesion is small, and neurological signs quickly disappear
- Small – brain functions are restored within 21 days
- Progressive - its neurological signs do not appear immediately and accumulate over time; after treatment, some of these symptoms may persist
- Extensive - signs of its appearance are recorded for a long time, including after treatment
- Mild – symptoms are mild and disappear within a few days
- Medium – signs appear, but are not accompanied by a disorder of consciousness
- Severe – in this case consciousness is depressed and brain tissue is severely damaged
Causes of ischemic stroke
The causes of stroke include diseases and dysfunctions of the body such as:
- Hypertension
- Cardiac ischemia
- Arrhythmia
- Bleeding disorder
- Various diseases of the vascular system
- Pathologies of blood vessels of the neck and head
- Migraine
- Kidney diseases
- Diabetes
- Atherosclerosis
- Obesity
- Thrombophlebitis
The following people are also at risk:
- Heavy and frequent smokers
- Experiencing constant psycho-emotional overload
- Those who have suffered blood loss
- Suffering from chronic headaches
- Excessive alcohol drinkers
- Regular overeaters
Given the above factors, men and women over 50 years of age are especially at risk of ischemic stroke.
Main symptoms
Signs of ischemic stroke consist of general signs characteristic of all types of stroke and symptoms that reflect the nature and location of damage to brain tissue.
- General symptoms:
- Fever
- Vomiting and nausea
- Loss of consciousness
- Headache
- Problems with orientation in space
- Inability to move limbs or move incorrectly
- Dizziness
- Speech difficulties - problems with reading, speaking, understanding what is said, writing, counting
- Visual dysfunction – sudden deterioration, double vision
- Swallowing dysfunction
- Inability to perform simple everyday activities (comb your hair, etc.)
- The occurrence of amnesia and other serious memory impairments
- If the left hemisphere is affected, paralysis may also occur
- With damage to the temporal lobe - depression, impairment of cognitive and logical functions
Diagnosis of stroke
A qualified neurologist can determine the presence of a stroke quite quickly. But in order to prescribe the most effective treatment, he needs to identify both the localization of the lesion and the causes of its appearance, concomitant diseases. For this, the following diagnostic procedures and equipment are used:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic resonance angiography
- Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Cerebral angiography using contrast agent
- Blood biochemistry for sugar and cholesterol
- ECHO-KG
- Electroencephalogram
- ECG
- Coagulogram (blood clotting test)
Ischemic cerebral stroke - treatment
Since this phenomenon disrupts brain function, ischemic stroke requires treatment that will be complex and long-term. Otherwise, swelling, thromboembolism and other negative consequences may occur.
- A patient in acute condition is sent to the ward or intensive care unit
- First of all, medical personnel restore the functioning of the respiratory and circulatory systems
- If necessary, surgery may be performed to remove the blood clot.
- Medicines can also be used to liquefy the clot.
- In general, in the process of treating a patient, the following types of drugs are used: anticoagulants, blood thinners, vasoactive drugs, antiplatelet agents, angioprotectors, neurotrophics, antioxidants
Remember, all medications must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous!
Nutrition after stroke
If the patient is diagnosed with ischemic stroke, treatment should not be limited to hospital stay. An important part of the fight against the consequences of a stroke is proper nutrition and rehabilitation measures.
It is necessary to include in the diet such products as:
- Porridge
- Lean fish, meat and seafood (boiled)
- Vegetables (cabbage, spinach, beets, etc.)
- Berries (blueberries, cranberries, etc.)
- Fruits
- Dairy
- Vegetable oil
The following should be strictly avoided:
- Fried
- Smoked
- Fat
- Dishes with a lot of spices
- Flour products
It is also necessary to reduce the amount of salt in food.
It is important to remember that after a stroke you need to get rid of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
Rehabilitation measures after a stroke
Since a stroke can lead to many negative consequences (impaired speech skills, memory, cognitive functions, paralysis), it is better to undergo rehabilitation procedures in a specialized institution (sanatorium). To restore a number of functions, you need to contact professionals:
- Speech therapist – for restoration of speech and graphic skills
- Physical therapy specialist – to improve coordination and motor function
- Specialist in physiotherapeutic procedures (electrical stimulation, reflexology, etc.) - to accelerate the regeneration of nerve tissue and improve blood supply
- Neurologists and psychologists – to eliminate cognitive and emotional disorders, restore memory
Prevention and prognosis of ischemic cerebral stroke
If concomitant diseases or other risk factors persist, ischemic stroke may recur. Therefore it is necessary:
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations of the circulatory system and heart
- Treat hypertension and other concomitant diseases in a timely manner
- Contact a doctor immediately if you feel unwell
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition
According to statistics, the occurrence of a stroke ends in death in the first weeks in 25% of cases, in 50% of cases the patient lives after a stroke for about 5 years, the remaining 25% can live at least 10 years.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- A full range of services for the management of patients with stroke: from stabilizing the patient to prescribing rehabilitation procedures and therapy
- MEDSI specialists are candidates of medical sciences, have high qualification categories and have extensive experience working with stroke patients
- Experienced surgeons of a specialized department perform precise operations on blood vessels through mini-accesses using the latest expert-level equipment
- All studies and procedures are in one place
- MEDSI doctors provide follow-up care for patients who have suffered a stroke, including at home
- At the first signs of a stroke in you or your relatives, call 8 (495) 7-800-500
Symptoms and signs
Broca's center is considered motor or speech motor, which, when damaged, causes the appearance of characteristic functional disturbances in speech production. Motor aphasia is manifested by a violation of the motor function of speech, and the affected person mentally does not experience problems in forming speech, but experiences extreme difficulty when speaking.
Motor aphasia is characterized by:
- The collapse of the grammatical structure of speech or, in other words, agremmatism. There is confusion in cases and tenses, and it is also difficult for the patient to pronounce articles and prepositions. Speech stereotypes are formed;
- Anomie is difficulty in selecting the right words, while speech slows down significantly as the patient tries to find synonyms for the previous word.
- Articulation disorder is a confusion of sounds, a violation of their order.
Already when communicating with the patient, one can confidently make a diagnosis of motor aphasia based on the presence of the symptoms described above.