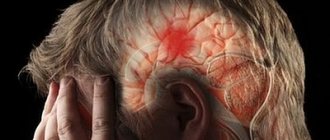
Stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation that causes focal damage to brain cells. The disease has typical neurological symptoms that persist for a long time: painful headaches, paresis or paralysis of the facial muscles or limbs (often one-sided), impaired memory, speech, vision, and coordination of movements.
In the elderly, and especially in old age, strokes are much more severe and pose a direct threat to a person’s life. Whether a patient will be able to return to a full life after suffering a stroke or at least partially restore lost skills depends on a number of factors. In any case, this is a long process, taking months and sometimes years.
Factors influencing recovery time after stroke
Stroke is one of the main causes of disability in old age, most often occurring as a result of untimely medical care or lack of competent rehabilitation. In 80% of cases, the success of recovery after a stroke is determined by the prompt action of medical staff. It is especially important to provide assistance in the first 3-4 hours after the onset of an attack. Rehabilitation must begin as early as possible, because the quality and duration of a person’s future life depend on it.
Other factors also influence the timing of rehabilitation after a stroke:
- The mechanism of stroke. There are 2 main types of strokes – ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic occurs in 80% of cases and is caused by a lack of blood supply to any part of the brain. With this type of stroke, if treatment is prescribed correctly and on time, the body has a good chance of recovery. Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by bleeding into the deep parts of the brain. The life prognosis is unfavorable, the probability of death reaches 50-70%.
- The degree of damage to brain tissue. The most serious violations of the basic functions of the body are observed with an extensive stroke affecting large areas of the cerebral cortex. In this case, if the person managed to survive, rehabilitation may take several years, and full recovery may never occur.
- Age and presence of concomitant diseases. The older a person is, the more difficult it is for him to cope with a blow, and in the presence of chronic diseases, especially the cardiovascular system, this often becomes impossible.
- What a seizure. Repeated strokes always increase the risk of death. While it takes an average of 8 months for an elderly person to recover from the first blow, it can take a year or more to recover from the second.
- Psycho-emotional state of the patient. In order to cope with such a serious illness, enormous willpower and desire to live are required, which not every patient has.
Ischemic stroke critical days. stroke stroke
stroke stroke
Statistics show that among working people aged 25-60 years, the incidence of stroke is 1 per 1000 inhabitants per year. In the most developed countries, this disease takes second place - right after cardiovascular pathology - in the sad line on the cover of the medical history, which states the cause of death.
Two reasons and many consequences...
.
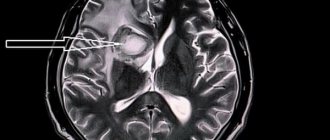
From the perspective of a modern doctor, a stroke is a severe and extremely dangerous vascular lesion of the central nervous system caused by a violation of cerebral circulation. There are two main reasons for this catastrophe: hemorrhage in the brain as a result of a rupture of the vessel wall (hemorrhagic stroke) and blockage of the lumen of the vessel by a blood clot or atherosclerotic plaque (ischemic stroke).
The word “stroke” itself is translated from Latin as “jump”, “jump”. The phrase “My blood pressure is jumping” will not surprise anyone. Unfortunately, hypertension is becoming one of the most common causes of hemorrhagic stroke. It develops rapidly: objects appear in red light, a feeling of nausea appears, vomiting, and the headache intensifies. Then a catastrophe occurs: the patient falls, he loses speech, and a state of stupefaction occurs, accompanied by loss of consciousness, up to coma. The skin of the face is moist with sweat, hot to the touch, purplish-red in color, with a cyanotic tint. Body temperature is initially low, after 20-24 hours it rises to 37.5-38°.
The appearance of a patient who has suffered a stroke involuntarily suggests a strong blow: a person, as a rule, lies on his back, his head and eyes are turned to one side, his mouth is half open. The muscles of the body and limbs are relaxed; if you try to raise the patient’s arms, they immediately fall sluggishly down like whips. Skin sensitivity is completely absent, the patient does not respond to injections.
In young people, the cause of a hemorrhagic stroke can be the rupture of a congenital aneurysm - a sac-shaped protrusion of a thinned vessel wall. It was an aneurysm of a cerebral vessel that caused the sudden death of the wonderful artist Andrei Mironov, who died during a performance on stage.
Ischemic stroke occurs due to a violation of the oxygen supply to nerve cells caused by blockage of a cerebral vessel. It can be considered as an acute cerebral infarction, which differs from myocardial infarction by an even more severe course and serious complications.
Blockage of a cerebral vessel can occur due to the penetration of a bubble (embolus) of fat into the lumen, which enters the bloodstream as a result of a fracture of long tubular bones or during abdominal operations in obese people. Most often, such emboli enter the left hemisphere of the brain. Constant stress, overwork, alcohol and smoking, excess weight, fluctuations in blood sugar - all these unfavorable factors can cause prolonged cerebral vascular spasm, which is also a harbinger of ischemic stroke.
The development of ischemic stroke does not occur as rapidly as with hemorrhagic stroke. The patient gradually begins to develop characteristic neurological symptoms: headaches, dizziness, transient gait disturbances, changes in skin and pain sensitivity - numbness or tingling of the extremities. Such ailments may last for several days.
Most often, ischemic stroke is a disease of older people. The blow hits them at night or in the morning. If ischemia is not caused by an embolus or thrombus carried by the bloodstream, then the disease proceeds relatively mildly: the patient may not only not lose consciousness, but also be quite critical of his condition and, noticing a deterioration in his health, manages to seek help from a doctor or relatives.
During the “strike” itself, the patient’s face is usually pale, the pulse is soft, moderately rapid. Soon, paralysis of the limbs occurs on the right or left side, depending on the area of brain damage.
Despite the apparent “decency” of ischemic stroke, its consequences are also very severe.
The drained part of the brain dies and can no longer perform its functions, which inevitably entails paralysis, disturbances in speech, memory, recognition, and coordination of movements.
If a circulatory disorder occurs in the right hemisphere of the brain, then paralysis and sensory disturbances occur in the left half of the body. In case of a catastrophe in the left hemisphere, the same phenomena are observed on the right. But the most severe consequences are observed when the stroke is localized in the brain stem, where vital centers are located, the defeat of which leads to the death of the patient.
Most often, a stroke affects only a small area of the brain. However, the consequences in any case turn out to be irreparable, because between all the cells of the brain there are complex communication connections, thanks to which all higher nervous activity is carried out.
When the pathological focus is localized in the center of motor speech (Broca's center), oral speech is disrupted: the patient either becomes completely mute or pronounces only individual words and simple phrases. At the same time, understanding of someone else's speech is preserved. If Broca's center is partially damaged, the patient begins to speak in a terse style of postal telegrams, completely forgetting about verbs and connectives.
Based on the symptoms observed in each individual patient, an experienced doctor can accurately say which part of the brain was affected by a stroke. To a large extent, this knowledge allows us to predict the further course of the disease. Clinicians give three prognoses: favorable, average and unfavorable. In the first case, the patient gradually recovers lost functions and abilities. In the second option, the course is complicated by additional diseases - pneumonia, diabetes, gastrointestinal disorders. At the same time, the patient’s condition periodically worsens, then recovers somewhat, the course of treatment is delayed indefinitely, and doctors only shrug their shoulders when asked by relatives.
The third option is even worse, when the lesion occupies a large area or the patient experiences repeated strokes. As a rule, in such cases nothing good can be expected. The likelihood of a recurrent stroke is very high, and in 70 percent it ends in the death of the patient. The third, seventh and tenth days after the first impact are considered critical. However, the possibility of relapse cannot be completely ruled out for at least another year.
Treat or care
Stroke is a disease that requires urgent hospitalization in a specialized neurological department. At the first stage, the patient is administered drugs that improve cerebral circulation and stimulate metabolic processes in the brain (aminophylline, nimotop, nimodipine, cerebrolysin, nootropil). In addition, therapy is carried out aimed at stabilizing blood pressure and cardiac activity.
Treatment options vary significantly depending on the type of stroke. In case of hemorrhagic, first of all, they strive to reduce blood pressure and reduce the phenomena of cerebral edema. For this purpose, antihypertensive drugs, diuretics, aminophylline, and no-shpu are administered.
When treating ischemic stroke, doctors use anticoagulants - substances that can dissolve the formed blood clot or, at least, prevent its further growth, always under the control of blood clotting.
In no case should one lose attention to issues related to the general care of the patient: carrying out thorough sanitary and hygienic measures, body toilet, and doing therapeutic and restorative gymnastics.
The patient should be placed in bed on his side, completely undressed. Dentures must be removed immediately and the upper half of the body should be slightly elevated. Due to involuntary urination, it is advisable to place an oilcloth covered with a double folded sheet or special diapers under the lower part of the body. To cleanse the intestines, an enema is given every other day. The room in which a stroke patient is lying should be regularly ventilated.
One of the most common complications is bedsores resulting from violations
microcirculation of blood in places in contact with the mattress, pillow, etc. Typically, bedsores form on the buttocks, sacrum, elbows, and ankles. At first these are bluish-red spots; then foci of necrosis are formed in them, capable of capturing not only large superficial ones, but also going deep into the muscle tissue. Intoxication caused by bedsores causes the death of many patients who managed to survive the first blow of the disease.
The patient's body must be wiped with camphor alcohol or a mixture of shampoo and hydrogen peroxide at least three times a day. If suspicious reddish spots appear on the skin, they should be treated with cotton wool moistened with a solution of potassium permanganate. This procedure must be carried out until the threat of a bedsore has passed.
Some patients who have had a stroke experience choking when swallowing and difficulty eating. Such patients may be asked to drink through a thin flexible tube placed in a cup or glass. Ice cream and baby food are well absorbed and can maintain the energy balance of patients who refuse normal food for a long time.
Another common complication of cerebrovascular accidents is pneumonia. Pneumonia is a constant companion to stroke. This is due to several reasons: the patient’s prolonged immobile position, impaired cough reflex, and the inability to cough up accumulated mucus.
To avoid this formidable complication, it is necessary to regularly massage the patient’s chest, allow children’s rubber toys to inflate, which stimulates the lungs, and apply mustard plasters or cupping massage once every two or three days.
And one more indispensable requirement for people surrounding a patient with impaired cerebral circulation - be patient! You will need a lot of it, but remember: a person close to you is suffering, and it is in your power to make his life at least a little more bearable; his future fate is in your hands. Without your participation, the best doctors will be powerless and the most effective medications will not help. Therefore, get ready for a long and difficult struggle for human health and well-being. After all, as they have said in Rus' from time immemorial, mercy is love in practice.
Alexander KRYLOV,
Candidate of Medical Sciences
Periods of rehabilitation after a stroke
Modern medicine recommends starting rehabilitation of a patient who has suffered a stroke in the first hours after the attack, as soon as hemodynamic parameters (heart rate, blood pressure) return to normal. This allows not only to restore lost functions as much as possible, but also to avoid various complications that can aggravate the patient’s condition.
The recovery period can be divided into several main stages:
- acute (first 3-4 weeks after the attack);
- early recovery (first 6 months after an attack);
- late recovery (from 6 months to a year);
- remote (more than a year).
The danger of a recurrent attack and how to behave
After primary ischemia has occurred, the risk of a second brain stroke increases significantly. In almost 70% of cases, relapses lead to death. And no matter how much time passes from the moment of the attack, it will not be possible to definitely get rid of the risk of relapse. The most dangerous in terms of the risk of relapse is the 1st year after the attack.
To reduce the risks during critical days and reduce the likelihood of relapse, it is necessary to develop the right behavior strategy. A brain stroke in any form always requires immediate hospitalization in a medical institution that has the necessary diagnostic and treatment equipment. Often, after an attack, it may be necessary to carry out competent resuscitation measures.
Acute stage of the disease
Rehabilitation in the acute period takes place in a medical institution under the guidance of doctors. It is advisable to begin rehabilitation treatment as soon as the patient’s condition stabilizes, optimally 3-4 days after the stroke. The main tasks at this stage are: restoration of simple motor and speech functions, prevention of complications and relapses, assessment of the degree of damage to the body and development of a rehabilitation program.
To restore the motor system, passive gymnastics, massage and treatment by changing body position are used, when the patient’s limbs are placed in various positions to prevent the development of muscle hypertonicity. The return of lost speech skills begins with simple articulation exercises, gymnastics of the tongue, cheeks, and lips. Speech is more actively restored 3-6 months after a stroke, but full recovery requires 2-3 years of work with the patient.
An important condition that accelerates rehabilitation in the acute period is the use of medications and physiotherapeutic pain-relieving procedures - magnetic, electro- and laser therapy.
The development of ischemic pathology and critical days in this case
In a situation with ischemic stroke, critical moments often begin to occur less abruptly than with hemorrhages. The onset of the acute period can be characterized by the fact that symptoms increase gradually:
- Harbingers appear;
- Precursors turn into general disruptions in brain function;
- Disorders begin in the musculoskeletal system.
Such ailments can last quite a long time - from a couple of days to several weeks. With a stroke of this type, the critical periods of time will also differ, although the first day for the victim is still always the most dangerous.
Doctors consider the 3rd day, as well as the 7th and 10th days after the primary manifestations of the pathology to appear critical for ischemic stroke. According to statistics, ischemic stroke most affects older people and occurs most often at night or in the early morning.
Rehabilitation after stroke in the early recovery period
The early recovery stage is crucial for the patient and should ideally take place in a sanatorium or rehabilitation center. When deciding to leave the victim at home, you should remember that successful recovery after a stroke is impossible without the active participation of specialized specialists who will have to be invited to the home.
The first three months after the onset of the disease are especially productive and favorable for rehabilitation. At this stage, they move from the simplest exercises to more complex ones - they teach a person to roll over, rise, sit down, and stand up independently. Next, elements of active physical therapy are gradually introduced, physiotherapy, massage, speech work are continued, and complexes are performed to restore vision and eye movements, cognitive functions (memory, thinking, attention).
A common consequence of a stroke is complete or partial loss of vision, dysfunction of the eyelid, presbyopia, when a person cannot distinguish small print or small objects at close range. All these disorders require qualified assistance from an ophthalmologist, who will prescribe either medication or surgical treatment. In mild cases, they can do with therapeutic exercises for the eyes.
To restore attention, memory, and intellectual abilities, there are many exercises: memorization tasks, memorizing poetry, solving riddles, rebuses, putting together puzzles, chess, checkers. However, for complete rehabilitation of cognitive functions, psychological and correctional classes are necessary individually or in groups. Additional stimulation is provided by medications that should be prescribed by a doctor.
Signs and symptoms of stroke
A stroke manifests unexpectedly for a person, although sometimes it is preceded by certain symptoms. If you interpret them correctly, you can avoid a terrible vascular catastrophe.
Warning signs of an impending stroke include:
- Prolonged headaches. They do not have a clear localization. It is not possible to cope with them with the help of analgesics.
- Dizziness. It occurs at rest and can intensify when performing any actions.
- Ringing in the ears.
- Sudden attack of atrial fibrillation.
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Memory impairment.
- Numbness of arms and legs.
- Loss of coordination.
- Insomnia.
- Increased fatigue.
- Decreased overall performance.
- Rapid heartbeat and constant thirst.
The listed signs may have varying intensities. You should not ignore them; you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke increase slowly. With hemorrhagic brain damage, the clinical picture unfolds rapidly.
You can suspect a brain catastrophe based on the following symptoms::
- General cerebral symptoms . The patient experiences unbearable headaches. Nausea ends with vomiting. Consciousness is impaired, and both stupefaction and coma may occur.
- Focal symptoms . They directly depend on where exactly the lesion is localized. The patient may have decreased or completely lost muscle strength on one side of the body. Half of the face is paralyzed, causing it to become distorted. The corner of the mouth lowers, the nasolabial fold smoothes out. On the same side, the sensitivity of the arms and legs decreases. The victim’s speech deteriorates and he has difficulty oriented in space.
- Epileptiform symptoms . Sometimes a stroke provokes an epileptic attack. The patient loses consciousness, has convulsions, and foam appears at the mouth. The pupil does not react to the light beam; on the side of the lesion it is dilated. The eyes move right and left.
- Other symptoms . The patient's breathing quickens and the depth of inspiration decreases. A significant decrease in blood pressure and increased heart rate are possible. Often a stroke is accompanied by uncontrolled urination and defecation.
When the first signs of a stroke appear, you should not hesitate to call an ambulance.
Late and remote periods
At a later stage, the body’s potential for rehabilitation after a stroke gradually decreases, but the patient must continue to study and train self-care skills. This period already passes at home, so responsibility for the health and mental state of the patient falls entirely on his loved ones.
You can change your usual exercise therapy complex by adding new exercises and classes with simple exercise equipment, for example, an expander. It is recommended to talk with the patient as often as possible, ask questions, thereby encouraging him to be vocal.
A year after the stroke, the exercises no longer have a pronounced effect, so in the long-term recovery period, the main attention should be paid to consolidating skills and periodic visits to the doctor for follow-up examinations.
Conditions for successful rehabilitation after a stroke
A stroke is a difficult ordeal, especially for older people, who can suffer from it with unpredictable consequences. How long it will take to recover - even doctors cannot answer this question for sure. But in order to shorten the rehabilitation period after a stroke, the patient must provide a number of conditions:
- rehabilitation should take place under the strict guidance of a qualified doctor according to an individually developed program;
- the rehabilitation process must be continuous and comprehensive. This means that it is necessary to work on restoring all body functions simultaneously and sequentially;
- in the home environment, it is necessary to create all the conditions for the successful rehabilitation of the patient: equip the sleeping place with an anti-decubitus mattress, allocate a place for doing therapeutic exercises and purchase the necessary exercise equipment, as well as additional equipment - walkers, wheelchairs, canes, special personal hygiene products;
- provide a balanced diet throughout the entire period of rehabilitation;
- take care to create a favorable home atmosphere, sensitive and caring attitude towards the sick person.
Treatment and rehabilitation
The patient receives treatment in a hospital. All patients with suspected stroke are hospitalized on an emergency basis. The optimal period for providing medical care is the first 3 hours after a brain accident has occurred. The person is placed in the intensive care unit of a neurological hospital. After the acute period has been overcome, he is transferred to the early rehabilitation unit.
Until the diagnosis is established, basic therapy is carried out. The patient’s blood pressure is adjusted, the heart rate is normalized, and the required blood pH level is maintained. To reduce cerebral edema, diuretics and corticosteroids are prescribed. Craniotomy is possible to reduce the degree of compression. If necessary, the patient is connected to an artificial respiration apparatus.
Be sure to direct efforts to eliminate the symptoms of stroke and alleviate the patient’s condition. He is prescribed medications to lower body temperature, anticonvulsants, and antiemetics. Medicines that have a neuroprotective effect are used.
Pathogenetic therapy is based on the type of stroke. In case of ischemic brain damage, it is necessary to restore nutrition to the affected area as quickly as possible. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that resolve blood clots. It is possible to remove them mechanically. When thrombolysis fails, the patient is prescribed Acetylsalicylic acid and vasoactive drugs.
In case of a stroke, it is extremely important to provide timely treatment to the damaged areas of the brain. A course of use of the drug accelerates the process of recovery of brain cells after a stroke, even in cases of impaired blood circulation or hypoxia. This allows for rapid restoration of memory, thinking, speech, swallowing reflex and restoration of other functions of daily activities. Gliatilin has a positive effect on the transmission of nerve impulses, protects brain cells from repeated damage, which prevents the risk of recurrent stroke.
The drug is well tolerated by patients; it is contraindicated for use by pregnant, lactating women and people with hypersensitivity to choline alfoscerate.
Courses will need to be taken regularly. You definitely need to do physical therapy, undergo physical therapy, and visit a massage therapist. After a stroke, many patients have to restore motor skills over a long period of time and learn to care for themselves independently.
Relatives and friends should provide support to the patient and not leave him alone with the problem. Psychologists are involved in the work. Sessions with a speech therapist are often required.
Where to go for help?
It is impossible to provide complete rehabilitation after a stroke in the home environment. Therefore, the most reasonable option for the family of an elderly person who has suffered an attack would be to enter into an agreement with a specialized institution, where he can receive help from highly qualified specialists and undergo a comprehensive rehabilitation program developed taking into account his diagnosis and characteristics of the body.
The Trust boarding house network has been providing care and rehabilitation to stroke victims for the past 5 years. The staff consists of highly qualified doctors and nurses with medical education. The boarding houses have all the conditions for a comfortable stay and full recovery after a stroke:
- Individual rehabilitation programs aimed at adaptation after a stroke and prevention of a recurrent attack.
- Regular medical examination of the patient.
- A full range of rehabilitation procedures: exercise therapy classes, exercises for the rehabilitation of speech and cognitive functions.
- Drug therapy.
- Social and psychological assistance, warm and attentive attitude towards each ward.
- Cozy rooms equipped with functional beds, wheelchairs, orthopedic mattresses.
- Prevention of bedsores and daily hygiene.
- Specialized 6 meals a day, rich in vitamins and microelements.
- Organization of leisure and communication.
By entrusting us with the care of your loved ones, you create decent conditions for life and restoration of their health, thereby reducing the recovery time after a stroke. To find out more details about our programs, leave a request on the website, and we will call you back at a time convenient for you.
Treatment and rehabilitation
The patient receives treatment in a hospital. All patients with suspected stroke are hospitalized on an emergency basis. The optimal period for providing medical care is the first 3 hours after a brain accident has occurred. The person is placed in the intensive care unit of a neurological hospital. After the acute period has been overcome, he is transferred to the early rehabilitation unit.
Until the diagnosis is established, basic therapy is carried out. The patient’s blood pressure is adjusted, the heart rate is normalized, and the required blood pH level is maintained. To reduce cerebral edema, diuretics and corticosteroids are prescribed. Craniotomy is possible to reduce the degree of compression. If necessary, the patient is connected to an artificial respiration apparatus.
Be sure to direct efforts to eliminate the symptoms of stroke and alleviate the patient’s condition. He is prescribed medications to lower body temperature, anticonvulsants, and antiemetics. Medicines that have a neuroprotective effect are used.
Pathogenetic therapy is based on the type of stroke. In case of ischemic brain damage, it is necessary to restore nutrition to the affected area as quickly as possible. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that resolve blood clots. It is possible to remove them mechanically. When thrombolysis fails, the patient is prescribed Acetylsalicylic acid and vasoactive drugs.
If a patient develops a hemorrhagic stroke, it is important to stop the bleeding. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that thicken the blood, for example, Vikasol. It is possible to perform an operation to remove the resulting hematoma. It is aspirated using special equipment, or through open access by performing craniotomy.
Relatives and friends should provide support to the patient and not leave him alone with the problem. Psychologists are involved in the work. Sessions with a speech therapist are often required.
When assessing the effectiveness of ongoing activities, the following are taken into account:
- volume of brain tissue damage;
- severity of residual effects;
- start time of treatment.
Due to ischemia in the affected area, nerve cells of the brain or compression by a hematoma cause their irreversible death. Between healthy and dead cells there is a border zone - a group of cells that are restored during drug therapy.
The duration of rehabilitation varies and depends on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the person who has suffered a stroke from several months to 3 years.
Initial period
The duration of the initial period is 6 months. During this period, basic drug therapy is supplemented with nootropic drugs, vitamin complexes and sedatives. From the moment consciousness is restored, in addition to rubbing with camphor alcohol and frequent turning over, massage of the chest and passive movements of the limbs are carried out. On the third day, breathing exercises are started.
By the end of the first week, the patient is recommended to sit and make active movements of the limbs. The selected exercises must be performed several times a day, the duration of the exercises depends on the patient’s capabilities. You shouldn't do them forcefully. After a few more days, the doctor may allow you to move around.
After 2 weeks, doctors allow you to attend physical therapy classes in the gym. The selected set of exercises is performed slowly and smoothly, while the patient is assisted in this by a trainer. He shows the correct technique for doing the exercises so that you can do them yourself in the future.