Every two seconds, someone in the world suffers a stroke. A stroke is a disruption of blood circulation in the brain due to blockage of a blood vessel in the brain by a blood clot. Just a few years ago, only elderly and senile people were susceptible to apoclexia. Today, young and seemingly healthy people are increasingly suffering from acute circulatory disorders. Stroke is making us younger and can affect each of us, but the stroke has already brought someone to their knees. Close relatives of such people should know that proper rehabilitation care for a bedridden patient after a stroke in the first three months after the stroke can help him restore up to 50% of lost functions !
The main thing is to seek help from the patronage service “Good Help 57” , so that a caring and qualified nurse for a bedridden patient can help him get back on his feet as soon as possible.
| Prices | |
| Schedule | Cost, ruble |
| Live-in caregiver for a stroke patient: | |
| for 10 days | 12500 |
| for 15 days | 17500 |
| from 30 days and it is possible to leave home for another order during the daytime for 4-5 hours | 20000/month |
| from 30 days always close only to your patient | 24000/month |
| only for 1 month | 28500 |
| Visiting nurse for rehabilitation after a stroke: | |
| 2 hours | 450 |
| 3 hours | 550 |
| 4 hours | 700 |
| 8 ocloc'k | 1000 |
| 10 hours | 1200 |
| 12 hours | 1400 |
| night shift 12 hours | 1300 |
| to the hospital 24 hours | 1600 |
| Morning-evening 3 (1.5 hours in the morning + 1.5 hours in the evening) | 800 |
| Morning-evening 4 (2 hours in the morning + 2 hours in the evening) | 1000 |
What is a stroke
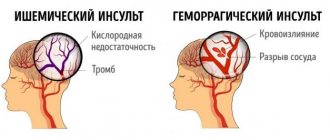
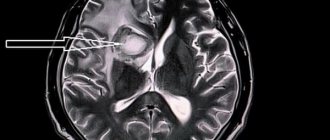
During a stroke, normal blood circulation in the brain is disrupted. Often the pathology develops without any noticeable preconditions, quite suddenly. The patient’s general condition worsens, cell damage occurs in the brain, which often leads to irreversible processes in the body or even death.
What are the causes of stroke? Doctors mainly highlight changes in blood composition (the appearance of blood clots, embolism) and atherosclerosis.
In sources, a description of the disease is first found in the works of Hippocrates. Later, the Greek surgeon Galen (200s AD) called this pathological condition apoplexy.
During an attack, control over areas of the brain that are responsible for certain body functions is lost.
We recommend
“Diapers for adults: sizes, absorbency and other characteristics” More details
It is extremely difficult to completely neutralize the consequences of a stroke; it depends on many factors. It is important to monitor your health and body signals.
Who is at risk? As a rule, these are men over 50, people suffering from obesity, diabetes, diseases of the cardiovascular system, alcohol abusers, smokers, drug addicts.
Stroke is associated with damage to the blood vessels of the brain and narrowing of the lumen in them. What are the causes of this pathology?
- Atherosclerosis or cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels.
- Diabetes mellitus types I and II, hormonal changes.
- Use of nicotine, drugs and improper use of medications.
- Sedentary lifestyle, lack of mobility, stress.
- Taking antibiotics and oral contraceptives in combination with alcohol.
- Old age and the associated wear and tear of the tissues of the heart and blood vessels, their fragility, spasms.
One of the main and most common causes of stroke is high blood pressure. Typically, people with high blood pressure are more at risk; 70% of strokes occur in people with high blood pressure (more than 140 over 90). Problems in the functioning of the heart provoke the formation of blood clots, which, in turn, lead to strokes.
Recommended articles on this topic:
- Features of older people: psychological and physiological
- The main problems of older people and ways to solve them
- Boarding home for the elderly: features and rules of choice
How to help sick people get dressed
Stroke often affects the motor system and limits the use of one side of the body. This can make it difficult for a stroke patient to get dressed. There are several things you can do to make dressing the patient easier, and you can help, too.
First, put clothing on the affected arm or leg
Advise the patient to assume a comfortable sitting position before dressing.
Prepare the clothes in the order in which they will be worn, with the items he will wear first on top.
When helping a person put on clothes, make sure they put the clothes on the affected arm or leg first and then on the unaffected arm or leg.
When undressing, the patient should do the opposite, first free the unaffected arm or leg, then quickly remove the clothing from the affected arm or leg.
Invite the patient to wear clothes with simple fittings. For example, clothes with Velcro instead of buttons, elastic waistbands instead of belts or suspenders, and slip-on shoes.
Simple devices can help patients dress themselves
Make sure that the patient does not wear clothes with tight-fitting sleeves, armholes, or tight-waisted pants.
Also make sure that patients do not wear clothing that needs to be pulled over their head.
Helping patients choose clothes that fasten in the front will be helpful.
Simple devices can help stroke patients dress themselves, such as a hook, ring or string attached to a zipper to pull, or a shoe horn.
Make sure you handle the affected side carefully to avoid further damage.
How to recognize a stroke and provide first aid
In order not to miss precious time during an attack, you need to know the main signs of a stroke:
- loss of consciousness or state of “stupefaction”;
- drowsiness or sudden agitation;
- rapid heartbeat and dizziness;
- increased sweating, nausea, and in some cases vomiting;
- possible disturbance of orientation in space;
- visual disturbances, loss of sensitivity, articulation disorders.
We recommend
“How to care for a bedridden elderly person” More
You should know how to confirm a possible stroke, even without being a doctor. To do this, you need to carry out a number of tests:
- Ask the person suspected of having a stroke to raise their hands, palms up. If it's really a punch, one arm will go up correctly and the other will swing out to the side or stay down.
- Invite the person to raise both arms up at the same time. During an attack, your arms will rise at different speeds and to different heights.
- Let the patient stick out his tongue. In the event of a stroke, it will be bent or twisted to the side.
- Ask them to say a phrase. During a stroke, a person will speak as if drunk, and articulation may be impaired.
- Ask the patient to smile and show his teeth. An asymmetrical, crooked smile is a sign of a stroke.
If you see any of the above signs, immediately call an ambulance or take the person to the doctor. The correct sequence of actions and quick reaction in the event of a stroke will help reduce the sad consequences of the attack and increase the chances of the most positive outcome. How should you behave in such a situation?
- Try to remain calm and do everything so that the patient does not get nervous; do not rush around and wring your hands: this will not bring any results.
- If you can, measure the pressure, check the patient’s pulse, his breathing.
- Identify the signs of a stroke: facial asymmetry, curved tongue, speech problems, lack of coordination.
- Call an ambulance.
- Lay the patient on his back or side, slightly raising his head and torso, or horizontally. If signs of nausea occur, turn your head to the side.
- Provide first aid if necessary; if there is no breathing, the heartbeat is weak, the pupils are dilated, perform simple resuscitation measures (artificial respiration, chest compressions).
- Open the windows, unbutton your shirt, unbutton your belt - let nothing interfere with the access of oxygen.
- Observe what happens to the patient, what changes in his condition.
We recommend
“Gymnastics for the elderly: the best exercises for various diseases” More
According to statistics, if you bring a patient with signs of a stroke in the first three hours after their appearance to a medical institution, where he will receive proper care, then:
- in 50–60% of cases, patients with severe forms of stroke survive;
- in 75–90% of cases, patients who have suffered a mild form of it recover completely;
- in 60–70% of cases, the abilities of brain cells are completely restored.
Time is the most valuable resource in a stroke situation. To prevent serious brain damage, it is important to act quickly and not panic. If help is provided to the patient in a timely manner, then there is every chance of his recovery and normal life in the future.
Helping sick people eat and drink
A stroke patient often has difficulty swallowing after a stroke. They may not be able to feel food or liquid on one side of the mouth or the other. They may have difficulty chewing or producing saliva. There are many ways to make chewing and swallowing food easier.
Choose foods or make them easy to chew, taste, and swallow. Food should not be too hot or cold.
Avoid giving sticky foods that are difficult to swallow
Prepare food so that it smells delicious. This stimulates the production of saliva, which helps swallow food
Avoid giving viscous foods that are difficult to swallow - foods such as milk and dairy products, syrup and viscous fruits such as bananas.
Do not give too dry, hard foods, such as rice, toasted bread, dry biscuits (crackers).
Cooked rice may be sticky or tough. Soften the rice by adding liquid such as soup.
Prepare soft foods or finely chopped hard foods. Soups or juices may be added to solid foods.
Let's drink juice if it is difficult to swallow water.
Thicken liquids with skim milk powder. Diluted liquids may cause suffocation because... they are more difficult to feel.
Give more time for food - 30 or 40 minutes
Give more time for food - 30 or 40 minutes. Ensure that the patient remains seated for 45 to 60 minutes after finishing a meal.
Encourage the stroke patient to eat on the unaffected side of the mouth. Make sure your mouth and throat are clean after every bite of food.
Food remaining in the affected side of the mouth should be removed carefully with a finger if the patient cannot do this himself with the tongue or finger.
Hold the cup or plate level if the patient is eating by himself. If possible, give him cutlery with a wide or elongated handle (fork, spoon).
Care for bedridden patients after a stroke in a hospital
In a medical institution, nurses provide care for bedridden patients after a stroke. They ensure that IVs are placed and patients take medications, carry out special procedures, feed, change linen, and change clothes.
In addition, care includes the prevention of bedsores, thromboembolic complications, pulmonary congestion, and contractures. Rehabilitation measures must be started as early as possible (of course, taking into account the severity of the person’s condition), even if the patient is bedridden. Early activation can help the rapid formation of compensatory mechanisms and even the disappearance of manifestations of the disease.
We recommend
“Boarding home for the elderly: how to place an elderly relative there” More details
A bedridden patient is unable to take care of himself. Such patients need help with the simplest things: feeding, changing clothes, combing. Daily hygiene procedures even more require assistance. Washing your face, brushing your teeth, wiping your body, and washing your face are done daily, and your hair is washed once a week. It is important to dry your head well and wipe all areas of the body dry with a towel, paying special attention to the folds of the skin. In addition, to prevent diaper rash, special creams are used.
To avoid constipation in the patient, it is necessary to monitor the quality of the intestines: a large amount of fluid and fiber consumed, as well as exercise, will help prevent the negative consequences of paralysis. If a bedridden patient is unable to urinate on his own, a catheter is placed; in addition, adult diapers may be used in the hospital.
Increased attention should be paid to the prevention of complications: bedsores, venous thrombosis, muscle contractures, congestive pneumonia.
Features of care
Stroke is a complex neurological disease. After damage to the blood vessels of the brain, a person’s quality of life always decreases. Some of his actions may be limited, and sometimes there is a complete loss of performance.
If stroke prevention is neglected, various complications may develop. To protect the patient from their appearance, it is necessary to organize patronage for the elderly person. Particular attention should be paid to the following points:
- preventing bedsores;
- prevention of the development of pneumonia and other congestive phenomena;
- fight against thromboembolism;
- digestive control;
- prevention of recurrent stroke;
- organization of leisure and psychological support.
How to care for a bedridden patient after a stroke at home
It is ideal if a bedridden patient after a stroke undergoes rehabilitation in a hospital under the supervision of professionals. But such care is available to only a few, because it costs a lot. Therefore, most victims of the disease have to recover at home, where they are looked after by relatives or special caregivers.
The vast majority of people who have suffered a stroke have problems with motor activity. This may be paralysis of one half of the body. But, unfortunately, often victims remain completely incapacitated and helpless. Caring for a bedridden patient after a stroke at home requires time, attention and effort.
Such patients are slow, and it is quite difficult for them to perform any actions. Therefore, relatives must be patient and understanding. It is very important to carry out all rehabilitation measures carefully and efficiently; the overall outcome of the disease depends on this. Manipulations included in caring for a bedridden patient:
1. Regularly change the patient’s position.
A bedridden patient should not be in one position for more than 2–3 hours; it is necessary to change his position, even if he is paralyzed. This is part of the treatment procedures.
How to position a patient:
- On the back. In this case, the paralyzed arm and leg should be placed on pillows so that the hand and foot do not hang down. It is important to place the shoulders and hip joints at the same level. The head should not bend at the cervical spine.
- On the healthy side. Paralyzed limbs are also placed on pillows in front. The leg is bent at the knee and hip joint.
- On the sore side. You should not allow yourself to fall on your stomach. The affected arm should be slightly brought forward, the healthy arm should be slightly to the side or behind the back. The paralyzed leg should be straightened at the hip joint, but can be bent at the knee. The healthy leg, bent at both joints, is brought forward and laid out on a pillow.
You need to make sure that your feet do not rest against the headboard of the bed, and that the postures are not unnatural and uncomfortable. In addition, there are now devices that can alleviate the condition of a paralyzed person and at the same time have a therapeutic effect.
2. Proper organization of feeding.
A bedridden patient after a severe stroke often cannot eat on his own. But, as you know, without nutrients, nutrients, minerals, vitamins, the body will not be able to fully recover and function normally. If you are caring for a patient yourself, you should know how to properly organize feeding.
We recommend
“Centers for pensioners: what they are and how to get there” More
For such patients, six meals a day in small portions is considered optimal. After each feeding procedure, it is important to clean the oral cavity to prevent asphyxia from food debris. If the patient has no appetite, he should not be forced to eat.
3. Control of the patient's stool.
Lack of movement and constant bed rest lead to disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, because it is physical activity that affects normal peristalsis. Constipation, bloating, discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract - these are the problems faced by both the patient himself and the relative caring for a bedridden patient after a stroke.
To prevent such complications, you need to monitor the amount of fluid consumed (it allows the intestinal contents to move), perform passive and active exercises, and turn the person over. In addition, you can use special medications that help the intestines work, as well as cleansing enemas with the permission of your doctor.
4. Change of bed linen.
It is recommended to change your underwear every day, and even more often if they get wet. There are several techniques for changing bed linen for a bedridden patient, which make the process easier and faster. It is important that the sheet and oilcloth lie flat. Folds on their surface can lead to the formation of bedsores in the patient. Take your time when performing the procedure, as haste can lead to injury.
5. Regular hygiene procedures.
Hygiene procedures are carried out daily, and if possible, twice a day. It is necessary to wipe the body of a bedridden patient with a damp sponge, brush teeth, and treat mucous membranes.
Ears are cleaned 1-2 times a week. The hair is washed once a week and then dried. If you don't dry your hair, it can lead to hypothermia and a cold. A bedridden patient is more susceptible to negative external influences than others.
6. Prevention of pneumonia.
Unfortunately, a lack of mobility and a lying lifestyle can lead to disruptions in the drainage functions of the respiratory system: blood stagnates in the lungs, and pneumonia can develop. This disease is extremely difficult to treat, especially in people who have had a stroke. You have to take strong antibiotics, which do not always help, so it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- conduct vibration massage sessions treating the chest;
- take special medications to remove mucus from the lungs, these drugs are prescribed by the doctor before sending the patient home;
- systematically do breathing exercises (for example, blowing into a glass of water through a straw, inflating balloons, etc.).
7. Prevention of bedsores.
To prevent the occurrence of bedsores, care for a bedridden patient after a stroke should include regular turning of the patient and massage. It is also important to monitor the condition of your skin. Special mattresses, massagers, and pads can help.
In addition, to prevent bedsores at home, it is recommended from time to time to use a special solution consisting of 1 liter of warm water, a glass of shampoo and a glass of vodka. All components are mixed without shaking, and problem areas are wiped. Alternatively, you can purchase a ready-made product at the pharmacy.
We recommend
“Interests of older people: how to improve the life of a pensioner” Read more
Preventing constipation
People after a stroke often have problems with bowel movements. Drinking plenty of fluids, abdominal massage, medicinal and natural laxatives (beets, dried apricots, prunes, bran, bananas, and other foods) help combat constipation. Abdominal massage is performed with light circular movements. The intestinal area can be massaged with gentle pressing touches.
You can help improve the bowel movement process by developing a bowel movement routine: daily enemas/suppositories should be done until the natural process is restored. Developing a reflex to have a bowel movement at the same time helps avoid constipation.
You can improve natural intestinal motility with proper nutrition. The patient's diet should include vegetables and fruits, cereals, and dairy products. You should not eat spicy or fatty foods, baked goods, alcohol, or sugar. It is better to steam or bake food.
What a nurse should be able to do when caring for a bedridden patient after a stroke
It happens that loved ones cannot constantly be at home next to a relative affected by the disease, because someone has to work. In this case, you can hire a nurse. A nurse will provide more professional care for a bedridden patient after a stroke at home. Such a specialist has a range of knowledge that will not only make life easier for you and your loved one, but will also improve their well-being and health. The nurse understands the mechanisms of the disease and knows how to cope with its consequences.
So, what are the responsibilities of a nurse:
- Carrying out basic care procedures. Despite their relative simplicity, they are included in the list of medical procedures. A nurse can have any work experience, the main thing is to know the theoretical foundations and be able to apply them in practice.
- Setting up IVs and injections. These procedures are performed only by people with specialized education, and if the nurse has one, she can independently ensure that the patient takes medications without inviting a nurse.
- Carrying out preventive measures regardless of the severity of the person’s condition. Often this part of the nurse’s work is the most difficult, since after a stroke a bedridden patient cannot move independently. Therefore, when hiring a nurse, it is necessary to take into account the weight and other parameters of the patient and look for a specialist who will be able to cope with this.
- Dressing bedsores or other wounds. These manipulations also require special skills and education.
- Ensuring that patients take medications. Patients after a stroke are prescribed a large number of medications. These medications ensure the restoration of all body systems after an attack. Therefore, it is very important to drink them on time and not skip them.
Thus, as in any other field, work experience and medical education are a big plus for a caregiver.
In addition, it is important to understand whether a bedridden patient needs constant supervision. In the case of a major stroke, an assistant must always be with the patient, because even at night he needs care, for example, constant change of body position to prevent bedsores.
If you yourself are periodically ready to sit with the patient, then the nurse will work according to a special schedule. If not, then you will have to hire two caregivers who will change each other. Everything is discussed individually and depends on the severity of the stroke and the patient’s condition.
Where can they help?
Caring for a patient on your own every day is not an easy task. Employees of the Good Help 57 patronage service, where experienced specialists work, will help you survive the blow. Each home nurse and caregiver for a bedridden patient after a stroke with the necessary level of knowledge in care and first aid and rehabilitation.
The services of the company’s specialists will be especially useful for relatives who are forced to work to provide for their family or for people who urgently need to go somewhere and there is simply no one to look after their husband, wife, or parent.
Contact the patronage service “Good Help 57” and rest assured for your relative, because caring for the elderly after a stroke should be carried out only by people who know how to help.
Advantages of private boarding houses that provide comprehensive care for bedridden patients after a stroke
Today, a bedridden patient can be treated in special boarding houses for the elderly. Such institutions provide rehabilitation after a stroke. This is an excellent opportunity to provide the patient with proper care, especially when the person cannot move or speak.
We recommend
“Clothing for the elderly: subtleties of choice” Read more Still,
it is difficult to equip an ordinary apartment with everything a bedridden patient needs, especially if we are talking about an old building where there is not even an elevator. The nursing home that cares for such people has special beds, conveniently organized space, ramps, etc.
Private boarding houses provide:
- convenience in registration, collection of documents and placement;
- transfer using the necessary vehicles and equipment;
- adequate nutrition necessary for a person who has suffered a stroke;
- medical services of qualified specialists;
- constant care and hygiene;
- leisure according to interests.
In a special institution, each bedridden patient has an individual rehabilitation program, which depends on the severity of the stroke and the degree of damage to the body. Such a program includes the following elements:
- Activities aimed at improving brain function. This organ is the first to suffer after a stroke, losing its functionality. To eliminate problems, specialists select a course of special medications.
- Physical training. Caring for a bedridden patient after a stroke involves, first of all, restoration of the musculoskeletal system. All exercises are selected individually and depend on the patient’s well-being. A medical worker monitors the performance of gymnastics, monitors the main health indicators, and measures pulse and blood pressure.
- Exercises to restore speech. A bedridden patient has great difficulty with articulation, and sometimes cannot pronounce words at all. During rehabilitation, doctors conduct motor skills and rhetoric exercises with the patient.
- Restoring self-care skills. Patients learn to take care of themselves again. A nurse is always with bedridden patients.
- Psychotherapeutic support. Of course, it is impossible to maintain a positive attitude when you have lost the ability not only to do your usual activities, but even to move and speak. Care for such people includes support from a psychotherapist. These specialists help get out of depression and set the patient up to work on themselves.
- Medication support. Health care workers ensure that medications are taken in full, according to the schedule and in compliance with all necessary rules and regulations.
In addition, when implementing a rehabilitation program, boarding house staff can evaluate the patient’s progress and make changes to it. This makes it possible to improve the dynamics of recovery of all indicators of the patient’s health.
As a result of a stroke, a person's life is turned upside down. The body stops listening, performing the most primitive actions causes enormous difficulties, and sometimes becomes simply impossible. The patient loses faith in himself, in life, and becomes depressed. This also becomes a blow for loved ones. Someone quits their job and becomes a nurse, someone starts working twice as hard to hire a medical worker and provide full care to the patient. We don’t even need to talk about the fact that the loss of a loved one’s legal capacity is, in principle, a tragedy.
But it is important to remember that competent care for a bedridden patient after a stroke, hard work to overcome the consequences of the disease, work on one’s psychological state, and faith in the success of rehabilitation can work wonders. Properly organized events will definitely bear fruit. Yes, it also happens that a person will never be able to restore all body functions 100 percent. However, it is possible to significantly improve the patient's condition and return him to the joys of life. It is important not to lose fortitude, be patient and work in the right direction.
Rules of care for severe stroke
The most severe is a hemorrhagic stroke - a violation of the integrity of the vessel with subsequent hemorrhage in the brain. In most cases, rehabilitation after a hemorrhagic stroke is longer and more complex, since the nature of the lesions is more severe. A moderate or severe stroke cannot be missed. A person may lose vision, hearing, and feel severe weakness. Symptoms may also include numbness in an arm, leg, or even half of the body. Sometimes facial asymmetry and disturbances of consciousness occur. With a severe stroke, unfortunately, only about 20% of patients survive. And here there is no need to talk about the chances of recovery. Patients who have suffered a severe stroke most often remain bedridden forever, suffer from speech problems, and require constant care. They remain disabled for the rest of their lives. If, as a result of a disruption in blood supply, serious damage to brain cells occurs, the consequences for the body will be terrible: Complete paralysis of the body; Loss of speech skill; Memory loss, decreased intellectual activity. Caring for a paralyzed person is not an easy task. Not every family is ready for such a turn of events. Especially considering that paralysis can occur suddenly and a once quite strong, smart pensioner suddenly loses all his abilities. Turns into a bedridden patient. This situation cannot be taken lightly. Care should be regular and professional. The list of mandatory procedures includes taking medications to prevent a recurrent stroke. Massage and physiotherapy, sessions with a psychologist, rehabilitation therapist, and speech therapist are required. Features of female stroke. Women are more likely to have strokes for a number of reasons that are not typical for men: removal of 1-2 ovaries at an early age increases the risk of stroke; disturbances in the synthesis of sex hormones contribute to ischemic stroke; Pathologies of the gonads increase the likelihood of stroke. The consequences of a stroke are the same for women and men, it all depends on the degree of brain damage. Rehabilitation therapy is carried out over a long period of time and at all stages of treatment, but it is especially important after the acute period of a stroke. Physiotherapy exercises are combined with physiotherapy, acupressure and classical massage, acupuncture, electrical stimulation, and magnetotherapy. Occupational therapy is required - training in self-care skills, work on training stands and work simulators. Psychotherapy is effective: individual, group, family; Autogenic, adaptive training, etc. are recommended. Speech therapy classes are required for persons with speech impairments. The patient needs treatment for a total of at least three to four months. This period for severe strokes is much longer, and can exceed a year. Patients must be registered at the dispensary. With a prolonged period of restoration of functions, patients are transferred to disability.
Depression
Depression is very common in stroke patients, and a patient is more likely to be depressed than not. Sometimes depression arises from the experience of loss of some functions. Moreover, if the patient becomes dependent on others, the likelihood of depression increases. Depression can also be caused by disturbances in brain biochemistry due to a stroke, even if there are no significant neurological deficits. Therefore, the very fact of a stroke, even with minor disturbances, can lead to the development of depression due to disturbances in brain biochemistry.
Early detection of signs of depression is necessary to allow the condition to be effectively treated. Sadness that lasts more than two weeks or fear that does not go away may be signs of developing depression.
The same signs of incipient depression are hopelessness and desperation of one’s situation. Patients may also not comply with medical advice and express thoughts about the futility of life and a desire to die, which are already signs of serious depression. Fortunately, depression is very successfully treated with medication thanks to modern advances in pharmacology. In addition to antidepressants, communication with the patient and discussion of the consequences of the stroke that have affected the patient's life can be beneficial. The presence of depression is not a sign of weakness in the patient, but only an integral part of the consequences of a stroke, and this condition can be successfully treated.
Physical Security
The first priority for a patient after a stroke is physical safety. If the patient is in a nursing home, there must be sufficient care staff and the floor must be level to minimize the risk of the patient falling. Falling after a stroke is a huge problem and can lead to further complications such as hip fracture and significantly worsen the prognosis of both recovery and even life.
Many nursing homes have special policies to prevent falls and equip the premises with the necessary equipment. In the same way, it is necessary to ensure safety at home, although this is a big problem.
You need to make sure your loved one can safely perform daily activities after a stroke. This includes cooking, toileting and bathing—three problematic activities that tend to cause falls.
If the neurological consequences of a stroke are insignificant, then the patient can take care of himself and it is only necessary to slightly improve living conditions in terms of safety of falls. If the neurological deficit is significant, then mandatory monitoring of the patient is necessary because even passing through the room of a patient with hemiparesis can be dangerous and lead to a fall. Therefore, there should be no barriers in the room that the patient could trip over.
Consequences of stroke in older people
Stroke can affect people of all ages, but the elderly are most susceptible to it. Starting at age 60, the risk of developing the disease increases sharply, and then doubles every decade. The diagnosis of stroke is made in 75% of recorded cases to patients over 65 years of age.
Since young and elderly bodies react differently to disturbances, the consequences after a stroke may vary:
- Course of the disease. In an old person, damage to brain tissue occurs in a very short time, and therefore the disease is severe. For patients after seventy, the prognosis for the development of events is extremely unfavorable. A fatal outcome from an attack is possible in 85%, and after 90 years - in almost everyone.
- It is much more difficult for an elderly person to rehabilitate after a stroke, so the prognosis for a full recovery does not inspire much optimism.
- Patients over 70 years of age are much more likely to fall into a coma after a stroke.
A large number of elderly people already have a history of a bunch of concomitant diseases, which not only complicate their general condition, but also become risk factors:
- high blood pressure or hypertension. It affects about 70% of elderly patients. The effect of treatment for this disease decreases with age;
- heart rhythm disturbance (atrial fibrillation);
- increased cholesterol levels in the blood due to an imbalance in lipid metabolism;
- heart failure due to myocardial infarction;
- vascular aneurysm;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- insulin deficiency (diabetes mellitus);
- disorders of the kidneys;
- development of rheumatism.
In addition to the above, there are additional provoking factors:
- excess body weight, which is accompanied by metabolic syndrome, as a result, increased load on the heart muscle;
- bad habits: alcohol and tobacco addiction;
- self-prescribing medications that affect the activity of the heart and blood circulation in general;
- constant stressful conditions and unnatural stress on the psyche, leading to nervous exhaustion;
- lack of physical activity. Approximately 1/3 of strokes occur in older people who lead a sedentary lifestyle.
If a person has two or more risk factors at the same time, the likelihood of an attack and then death increases significantly.
We recommend
“Rehabilitation of an elderly person after a stroke: main directions of recovery” Read more
Additional Information
Impact on relationships
A stroke patient may be dependent on a caregiver, at least initially and perhaps permanently. Caregivers may perform activities previously performed by those who are ill, such as keeping track of finances, driving, or shopping and preparing meals.
It is important that family and friends help cope with the burden of worries. The caregiver must select and determine their assistance in carrying out exercises/activities with the patient or being with the patient while the caregiver is absent.
Practical aids
Home appliances make life easier for the patient to continue leading a normal life. These include special equipment such as ladders to get up and down, installing a shower instead of using a bathtub, or attaching handles to the bathtub to make it easier to get in and out of the bathtub.
Mobility assistance such as a wheelchair may be needed.
Specially equipped devices for one-handed use can make daily tasks possible - peeling vegetables, dentures or nails, opening cans or a stick with a hook to help with dressing. A floating bath thermometer will prevent accidental scalding.
Sometimes a new way of performing a familiar task may be needed to overcome a physical disability. For example, cooking vegetables in a pan of water may require careful rethinking, step by step, as it can be done while sitting or with one hand.
How to help a sick person wash
As a caregiver, you can make washing easier by preparing the bathroom in advance. Make sure there is enough hot water and that towels, shampoo, soap and dental supplies are easily accessible.
Make sure that the place where the washing procedure will take place is warm and there is no draft. Place a non-slip mat in your bath or shower; Make sure the floor around your bathtub or shower is not slippery.
Make sure the path to the bathroom is clear of any obstacles.
Railings or handrails fixed to the walls can help the patient get in and out of the bath.
Always add hot water to cold water, never the other way around. Check the temperature with your elbow.
First, wash the patient's face and hands. The genital area should be washed last.
Make sure that the shampoo and soap are rinsed off well and that the washed area is well dried.
The patient can sit in a chair while he or she washes in the bath or shower; The chair should have rubber tips on the legs or be placed on a towel to prevent slipping.
A portable shower is most convenient for washing your hair and partial bathing. A shower with a long hose is easier to use.
Use as little shampoo as possible for minimal rinsing.
Please note that washing a patient in a lying position is more convenient and safer than moving him in the bathtub. If you decide this is the best option, make sure you wash and dry each body part in turn; keep only the part of the body being washed uncovered.
Assisting patients in brushing their teeth should be careful every morning, evening and after meals. Never force a patient to open their mouth. Use a toothbrush and very little toothpaste to avoid choking.
When helping a patient shave, it should be noted that an electric razor is safer than a regular razor and is recommended to be used.