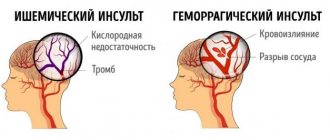
Strokes are severe lesions of brain tissue caused by acute disorders of cerebral circulation. Against the background of prolonged spasm of the great vessels or their blockage, the ischemic form develops, and with rupture of the vascular wall and subsequent hemorrhage, the hemorrhagic form develops. In the first case, the symptoms may increase gradually, but in the second they always appear abruptly. At the same time, cerebrovascular insufficiency gives quite serious complications, one of them is paralysis and impaired fine motor skills after a stroke.
The recovery of such patients takes a very long time, but rehabilitation measures are needed as early as possible. And they need to be done under the supervision of experienced doctors. The specialists of the Verimed clinic will help the patient return to a full life.
What are fine motor skills?
Fine motor skills are clear, purposeful movements of the hands and fingers, controlled by the central nervous system. They are possible only with impeccably coordinated work of the brain, organs of vision and impulse-conducting nerves. There is an inextricable connection between motor activity and cognitive functions. Therefore, to fully restore fine motor skills after a stroke, not only the development of muscles and joints is required, but also exercises aimed at activating mental processes.
Exercises for the torso
To restore good coordination of movements, it is necessary to use special physical exercises after a stroke, which should be performed every day. A set of the most effective exercises for the torso:
- Extend and connect your arms together, then perform forward inclined movements with your body. In the first few days, it is recommended to perform this exercise while sitting, after which - standing. They must be repeated 15 to 20 times.
- Pull your knees towards your chest while lying on the floor. Then lower one leg to the floor, holding the other with your hands. The exercise significantly works the abdominal muscle tissue.
- From a sitting position, place your hands on your belt, and then perform inclined movements of the body in different directions. When you feel better, it is recommended to perform the exercise while standing.
To normalize the muscle fibers in the neck, the patient needs to make short movements of the head to the right and left. To restore the fingers, they should be bent and unbent 15-20 times.
Symptoms of impaired hand motor skills after a stroke
Clinical signs of motor activity disorders are:
- a sharp decrease in muscle strength (until complete disappearance);
- rapid muscle fatigue;
- severe impairment of joint mobility due to contractures;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- reduction or loss of local sensitivity.
Mobility and coordination may be further affected by pain and tissue swelling.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
- Diseases of the nervous system of an infectious nature in the acute period of the disease.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (pronounced clinical signs).
- Diseases of the nervous system with a progressive course, with mental, pelvic disorders and dementia.
- Cachexia; tuberculosis, severe dysfunction of internal organs; drug addiction.
- Consequences of brain diseases with significant impairment of motor functions, episyndrome with the development of seizures more than twice a month, dementia with impairment of self-care, independent movement and speech.
- Diseases of the nervous system, accompanied by severe mental disorders (severe hypochondriacal psychoses, depressive disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorders).
What interferes with the recovery of motor skills after a stroke?
Improving the motor activity of the hands and restoring fine motor skills after acute cerebrovascular accidents is a rather complex process. It can be accelerated by the use of effective treatments, or it can be slowed down. The reasons for the slowdown (and sometimes impossibility) of rehabilitation may be:
- incorrect diagnosis;
- late treatment;
- serious disturbances in the nutrition of local tissues (circulatory disorders);
- injuries or chronic pathologies of nearby areas;
- depressive and apathetic states of the patient;
- other mental disorders.
How is post-stroke rehabilitation carried out?
- Recovery after a stroke begins with an examination by a Neurologist.
The neurologist assesses the patient’s condition, the degree of neurological impairment, determines the composition of the rehabilitation team and treatment strategy, and prescribes drug therapy. - Next, the patient is examined by a physical therapy doctor.
The tasks of this specialist include identifying movement disorders, planning physical rehabilitation activities, setting goals and objectives in this section and determining the methods that will be used in the treatment process. Thus, the exercise therapy doctor, together with the patient, develops a program for restoring motor skills after a stroke. The exercise therapy doctor also determines the degree of impairment of everyday skills and plans measures to restore them. During the first visit, we always teach relatives how to properly insure the patient and help him when moving, tell him how to make the home environment safe and comfortable for the patient, and select the necessary devices and equipment. - The third mandatory member of the interdisciplinary team is the Neuropsychologist.
Its tasks include diagnosing disorders of higher nervous functions, as well as planning and implementing measures for their restoration, and helping the patient adapt to changed capabilities. A neuropsychologist will help you find a common language with the patient in cases where memory, attention, and thinking have been affected as a result of a stroke. - If speech or swallowing is impaired after a stroke, a speech therapist-aphasiologist is included in the rehabilitation team.
In case of speech disorders, this specialist will determine the type of disorder, the severity of the defect and will deal with restoration. If swallowing is impaired, the speech therapist’s tasks include assessing the swallow, determining the possibility of feeding through the mouth, selecting the consistency and quantity of food for safe feeding. It is the speech therapist who can help relatives protect the patient from such an unpleasant complication as aspiration—food getting into the respiratory tract. - If necessary, the interdisciplinary team may include a therapist, orthopedist, physiotherapist and other specialists
. The composition of the rehabilitation team is determined by the needs of the patient.
Get advice from a rehabilitation specialist or make an appointment
+8
Record
How is motor skills restored?
Combating hand motor dysfunction after a stroke requires an integrated approach. It is important to start treatment as early as possible. Timely therapy gives a much greater chance of quickly achieving positive results.
Please note: It is important to remember that every day without training contributes to the formation of a stereotype of lack of movement in the central nervous system. The direct consequence is tissue trophic disorders; Muscle atrophy and bone decalcification develop.
The main methods for developing hand motor skills in the recovery period after a stroke are massage and gymnastic exercises. Hands and fingers contain a huge number of nerve endings. If there is not an adequate signal for movement from the central nervous system, it is important to direct it from the fingers to the brain. Local massage prescribed to patients helps restore the transmission of nerve impulses - the so-called. reflex arc. In addition, the physical effect on tissue helps to improve local blood flow (microcirculation) and, accordingly, improve tissue trophism. Thanks to professional massage, used in combination with other techniques, you can quickly restore the ability to make active, precise movements, as well as tactile sensitivity.
Another important point when restoring fine motor skills after a stroke is regular exercise. Such exercises serve to prevent further decline in motor activity, prevent the development of muscle and joint contractures and promote functional restoration. Regular classes under the guidance of doctors help patients after a stroke quickly adapt to living conditions. The possibility of complete self-care is one of the most important tasks of rehabilitation techniques.
All exercises must be performed with both hands synchronously. Usually the mobility of one of them is impaired, and symmetrical actions will significantly speed up recovery. The duration of gymnastics should be no more than 8-10 minutes per hour, so as not to develop significant fatigue. It is important to repeat the set of movements regularly in order to re-form the muscle reflex and motor stereotype.
Examples of exercises:
- Clench your fingers into a fist, increasing your efforts in the final phase of the movement. Slowly unclench them, trying to imagine the action of each muscle.
- Place your hands on a horizontal surface with your palms facing up. Spread your fingers a little. Raise your little fingers while trying to keep the other fingers still. Lock them in this position for 3-5 seconds and relax. Perform a similar exercise sequentially for all other fingers.
- Place your palms on the table in the same way as in the previous exercise. Alternately make circles (clockwise and counterclockwise) with raised fingers, starting with the little finger.
To develop fine motor skills when recovering from a stroke, it is useful to use available materials. An excellent effect can be achieved by such actions as sorting through cereals, modeling from plasticine, fastening buttons and tying knots in a rope.
Methods of rehabilitation after stroke, injuries, operations. "Unscientific" description
Voight method
It is also known as Vojta therapy, reflex comotion, Vojta therapy. The method is aimed at restoring balance and coordination of movements. Just like in Bobath therapy, fixed poses are used on the side, back, and stomach. In these poses, the patient is subjected to reflex stimulation by using his hands on the affected area, achieving a response characteristic of normal motor skills.
The complex of stimuli made it possible to activate reflective models in the form in which they should manifest themselves during the normal physiological development of motor skills. The muscles of the whole body are activated, including skeletal muscles, and reflexes are evoked to correctly move the body in space and maintain balance. During this therapy, the muscles of the entire body are activated, and the nervous system sends impulses to all its parts.
The method is used both in the therapy of infants and in the rehabilitation of adults with disorders of the nervous and musculoskeletal systems.
Filkendreise method
The method focuses on awareness of movements. The movements used are calm, allowing the patient to concentrate and comprehend his sensations, and thereby perform them more efficiently and under control. During classes, both practical everyday movements and more complex ones aimed at development can be performed.
Depending on the patient’s condition and the structure of the exercises, the patient’s movements can be passive (the specialist controls the patient’s limbs and postures), or the patient himself performs the exercises.
By influencing the nervous system as a whole and its desire for self-regulation, exercises help restore motor functions, reduce pain, and develop mobility. In rehabilitation, methods are used for strokes (restoration of the damaged side, activation of neuroplasticity of the brain) and other neurological diseases, diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system.
Applied kinesiology
The methods of applied kinesiology are based on the concept of the connection between the tone of a particular muscle and the state of the organs and systems of the body: dysfunction that occurs is accompanied by a weakening of the corresponding muscle. Based on muscle testing, therapeutic correction is made, which involves influencing spinal reflexes, neurolymphatic massage points, neurovascular points, meridians, and muscle attachment points.
Applied kinesiology is based on the integrity of the human structure, the relationship of physical, biochemical, neurophysiological, and emotional processes. Therefore, a component of the adjustment is specific manual-verbal-nonverbal communication between the patient and the specialist.
The goal of the intervention in applied kinesiology is to restore balance through strengthening a weakened muscle, which, in turn, helps to normalize a muscle that is in hypertonicity due to the increased load that it has to bear. The method is used as an additional method in the rehabilitation of patients with neurological diseases, diseases of the musculoskeletal system, as well as for general health improvement.
Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy links the restoration of motor and other functions impaired by illness or injury with the goals of returning to a normal lifestyle to the maximum extent possible. The level of achievement in this case is individual: from small elements of self-care to a complete return to normal activities.
The method is used in the rehabilitation of patients with neurological diseases, diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system, and patients after long-term bed rest.
Therapy goals are set jointly with the patient, taking into account his interests and motivation. Occupational therapy involves the proper arrangement of the patient’s life, the participation of his family members, and a focus on achieving the maximum possible independence and quality of life.
Speech therapy
In the context of rehabilitation, we mean classes with a speech therapist after a stroke, traumatic brain injury, or neurological diseases. Speech is restored more slowly than motor and other functions, but recovery requires the same early and intense efforts.
Speech impairment as a result of a certain lesion of the cerebral cortex can manifest itself in different ways: aphasia can be motor, sensory, semantic and total - the differences are manifested in how much the patient is able to speak, understand, and remember.
For this reason, effective speech restoration requires the participation of a neurologist. Regular classes are required, which are conducted and corrected by a specialist (involving the patient’s relatives in their implementation so that they can work with the patient additionally). A neurologist may prescribe medications.
Mechanotherapy
Mechanotherapy is the use of special simulators and devices for the physical rehabilitation of the patient. Exercises on machines help restore muscle tone and range of motion. As a rule, simulators allow you to dose the load (strength, amplitude, etc.). Most often, exercises in mechanotherapy involve repeated performance of individual voluntary movements.
Currently, the amount of robotic equipment that almost completely shapes the patient’s movements is growing. The most popular simulators are automated mechanical devices that operate thanks to an electric drive. And of course, there are always simple mechanisms that require the patient to exert physical effort in its entirety.
Mechanotherapy is most effective in the treatment of diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system and joints. It is also used in the rehabilitation of stroke patients and neurological diseases.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a targeted and controlled influence of certain physical factors on the human body. Produced using special equipment and devices.
The most commonly used physical factors are ultrasound, laser, electrical impulses, thermal radiation or cold. Physiotherapy methods such as magnetic therapy, aromatherapy, ozone therapy, salt and sun baths, hyperbaric chamber therapy, contrast showers, and shock wave therapy are widely used.
The full text of the article is posted on the website lamadirekt.ru
The influence of psychological attitude in the development of hand motor skills
A stroke often becomes a real tragedy for both the patient and his family. Brain damage provokes a decrease in mental activity and emotional lability. The patient can, as it were, “give up” on himself; he develops indifference, periodically replaced by outbursts of irritability and even anger. Apathy can be so great that a person does not want to do any exercises, try to get up, or move in any way.
To the objective reasons for the decrease in psychological activity are added internal experiences caused by a change in the usual lifestyle, the inability to look after oneself, and make some kind of global decisions. Immobility, isolation, fear of becoming a burden, fear of the future turn an active and freedom-loving person just yesterday into a completely weak-willed and apathetic one. He loses faith in his own strength, the possibility of developing hand motor skills and returning to his former life. Against this background, depression may appear, which will only worsen the situation. Such a person definitely needs not only the moral support of family and friends, but also the help of a doctor.
The experience of psychologists and psychiatrists allows us to quickly and accurately determine the root of the existing problem and find the “key” to both the patient himself and his relatives. Specialists will select the correct treatment regimen that will help motivate the patient to perform the necessary exercises, eliminating the main manifestations of apathy, depression and other mental disorders. And with faith in a speedy recovery, the restoration of fine motor skills of the hands after a stroke will go much faster.
Don't let a decadent mood ruin your future life - just call us now!
How to help yourself
Contrary to popular belief, it is strictly forbidden to independently engage in exercise therapy after a stroke at home, even if the illness experienced is characterized by the absence of negative symptoms. At the first stage, the patient in any case requires outside help - from medical workers or relatives.
At this time, loved ones need to make sure that the patient does not get hung up on negative thoughts and focuses on correctly performing exercise therapy after a stroke. In addition to physical therapy, you must remember to take prescribed medications, physiotherapy and massage in a timely manner.
What happens after the patient is examined by specialists?
After the patient is examined by all specialists, a rehabilitation program is formed and procedures are planned to restore the body.
Our managers will select a convenient time for specialist visits for you.
A physical therapy instructor, occupational therapist, massage therapist and other specialists will come to you and carry out doctor’s orders.
During the rehabilitation program, doctors will monitor the patient’s condition and, if necessary, adjust the program.