Vomiting is a forced, uncontrolled expulsion of stomach contents
or intestines through the mouth with the participation of the abdominal muscles and diaphragm. Vomiting is also accompanied by weakness, drooling, watery eyes and dizziness. Both the feeling of nausea and vomiting are triggered by a special nerve center located in the brain stem. The signals come from sensitive receptors in the digestive tract, so irritation of these receptors triggers the gag reflex. Irritation of the sensitive receptors of the gag reflex occurs, for example, with strong stretching of the walls of the stomach, with eating foods with an irritating effect, with inflammation of the walls of the stomach and intestines (gastritis, gastroenteritis). Direct irritation of the “vomiting center” can also cause vomiting, even if there is no irritation from the digestive tract. This phenomenon is observed in various diseases of the nervous system.
What causes headaches
The central nervous system is designed in such a way that it perceives pain signals from all parts of the body, including certain areas of the head. Along the nerve endings, information about the problem that has arisen passes to the deep parts of the brain, causing irritation in the receptors, and then pain. Such signals can come from the periosteum, nasal sinuses, subcutaneous tissue layers, mucous membranes, eyes, large nerve canals, vascular network, and muscular apparatus. Some areas are completely insensitive to external stimuli due to the lack of receptors, therefore they are not capable of causing pain: bones, the neural network of the brain, vascular plexuses.
Description of attacks
When a patient wants to understand the cause of a pathological condition and consults a doctor, he must describe his feelings in as much detail as possible. Soreness with nausea is not an independent disease, but only a common symptom of a huge number of diseases that need to be distinguished from each other.
When a patient describes his feelings, he should talk about the following nuances:
- How often do attacks occur?
- The predominant time of day for the onset of discomfort.
- Approximate location of the lesion, intensity.
- What provokes it?
- Feelings after a long rest/sleep.
- Does vomiting provide relief from nausea?
- Are there other symptoms?
You need to prepare such a story for the doctor in advance so as not to forget the details during the consultation. This will help the specialist understand the situation as efficiently as possible.
Causes of nausea and vomiting
Vomiting does not always indicate a disease of the digestive tract, but most often the cause of vomiting and nausea is found in the digestive system.
- Gastroenteritis, or inflammation of the stomach and intestines, due to ingestion of poor-quality food, contaminated water, leading to the development of food poisoning.
- Long-term (chronic) diseases of the stomach (chronic gastritis, gastric ulcer, gastroparesis - complete lack of mobility and contractions of the stomach), stomach spasm (persistent tension of the stomach muscles, with the impossibility of passing food further), duodenal ulcer, duodenitis.
- Diseases of the gallbladder and liver, cholelithiasis, dyskinesia of the gallbladder, cholecystitis, blockage of the bile ducts, hepatitis.
- Emergency conditions: acute appendicitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, intestinal obstruction, perforation of a gastric or duodenal ulcer, gastric bleeding, etc.
- Anomalies in the development of the digestive system: diverticulum (blind appendage) of the esophagus, intestines usually lead to periodic nausea and vomiting.
- Stenosis (narrowing of the lumen) of the esophagus or pylorus.
- Tumors of the stomach and intestines.
Sudden nausea and vomiting, accompanied by rumbling in the stomach, diarrhea, mild fever, and weakness are most often a sign of food poisoning
. If food poisoning is suspected, the stomach should be rinsed with plenty of liquid. You can also drink activated carbon.
Nausea and vomiting accompanied by severe diarrhea (possibly mixed with blood), a significant increase in temperature, and severe weakness may be a sign of an intestinal infection. Severe nausea and vomiting, accompanied by discoloration of stool, dark urine and jaundice, are a clear sign of viral hepatitis. If you suspect hepatitis or acute intestinal infection, you should urgently show the patient to a doctor.
Nausea and vomiting that occur periodically (often) accompanied by symptoms such as abdominal pain, stomach pain, sour belching, bitterness in the mouth, stool discoloration, chronic diarrhea, constipation, are usually a symptom of gastritis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, cholecystitis, chronic hepatitis, chronic pancreatitis. In these cases, treatment of nausea and vomiting
possible only after eliminating the underlying disease.
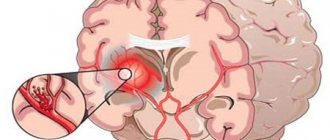
Since the initiation and process of vomiting itself is controlled by the “vomiting center” of the brain, some diseases of the nervous system can cause vomiting and nausea. Increased intracranial pressure is characterized by a persistent increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure and compression of the brain. A slow increase in intracranial pressure is observed, for example, with brain tumors. In such cases, nausea and vomiting occur either in the morning, or mild nausea is observed throughout the day. Along with nausea, the patient may complain of headache, balance disorder, blurred vision, disturbances in gait or sensitivity, or weakness in any part of the body.
A sharp increase in intracranial pressure (cerebral edema, traumatic brain injury, concussion, bruise) is accompanied by severe vomiting and impaired consciousness.
Attention!
Persistent headaches accompanied by nausea or periodic “unreasonable” vomiting may be a sign of brain tumors or other diseases characterized by a slow increase in intracranial pressure! If you notice this symptom, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Infectious diseases of the nervous system (meningitis, borelliosis), damage to the nervous system due to syphilis or AIDS are also accompanied by vomiting. Of the conditions described, meningitis is most often observed. Nausea and vomiting may be among the first symptoms of meningitis. Attention!
In addition to nausea and vomiting, meningitis causes high fever, severe headache, and severe tension in the neck muscles. If these signs are detected, you should immediately call a doctor! Lesions of the vestibular apparatus (vertigo, motion sickness, motion sickness) are often accompanied by nausea and vomiting in combination with severe dizziness and loss of balance. With benign vertigo, nausea and dizziness occur suddenly at the moment when the patient abruptly changes the position of the body and head (for example, turning on the other side in bed). With seasickness or motion sickness, nausea and vomiting occur during travel by sea or land. If such symptoms are detected, you should contact a neurologist or otoneurologist!
Migraine is a special type of headache that occurs in 15-20% of the population. With migraine, nausea and vomiting occur against the background of a severe (sometimes throbbing) headache. In addition to nausea and vomiting, during a migraine attack there is photophobia (the patient cannot tolerate bright light) and noise intolerance. Migraine attacks recur periodically and can be triggered by foods such as wine, chocolate, cheese, and strong odors. If you suspect a migraine, you should consult a neurologist!
Possible reasons
There are a large number of factors that can cause an unpleasant sensation in the head and gastrointestinal tract at the same time. Among them there are both safe conditions and serious pathologies that can lead to serious consequences. The most common causes of pain are the following clinical or life situations:
- overwork; lack of sleep; food poisoning;
- sensitivity to weather; overheat; stressful situations;
- thermoneurosis (vasoconstriction as a result of emotional shock);
- vegetative-vascular dystonia; hormonal disorders in the body;
- migraine; transferable cold, ARVI; osteochondrosis;
- dental problems; pinched nerve canal;
- tumors in the skull; high pressure;
- previous injuries; hypothyroidism; Lyme disease;
- vision problems; gastroenteritis; meningitis, encephalitis.
Many of the listed conditions require external intervention: a review of diet, sleep, work/rest, and getting out of the stressful rhythm of life. But in serious clinical cases this may not be enough. To determine whether there are serious illnesses in the initial stages of their development, you cannot ignore a headache with nausea; it is better to get checked and undergo an examination.
Diagnostic methods
The Clinical Brain Institute has all the conditions for examining patients with complaints of headache, nausea and vomiting. The first stage is an examination by a neurologist - he will collect all the necessary data, check reflexes and prescribe additional diagnostic methods. These may include instrumental and laboratory techniques, including:
- blood tests will indicate the presence of a source of inflammation in the body, bacteria and antibodies to a viral infection, and blood composition disorders;
- diagnostics of the condition of the vessels of the head using the ultrasound method - for a more complete picture, the use of a contrast agent may be required;
- MRI, CT are the most informative and modern techniques, thanks to which you can obtain a three-dimensional image of any part of the brain, especially if a stroke, neoplasm, or aneurysm is suspected;
- Ultrasound of internal organs is prescribed as an additional examination method if systemic diseases are suspected.
Our center prescribes individual diagnostic regimens. This approach allows you to avoid carrying out costly, uninformative procedures and focus on the main problem. Specialists will be able to determine the cause of headache, nausea and vomiting in a short time in order to quickly begin treatment of the underlying disease.
How to find the reason?
Depending on the description of the main manifestations, the therapist may involve other specialists in the work: an endocrinologist, a neurologist, a dentist, an oncologist. After making the first assumption about the disease, laboratory procedures are carried out designed to give a comprehensive picture of the person’s condition. The most common research methods are:
- Laboratory analysis of urine/blood.
- CT scan.
- Angiography.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Blood pressure measurement.
Through tests, an inflammatory process can be detected in the body, but it does not always occur with headaches and nausea. Tomographic technologies are considered the best ways to detect even microscopic changes in the body. Only through MRI and CT can one find hidden, complex diseases, find out the causes of previously diagnosed disorders, plan treatment and safely monitor the course of the pathology.
Migraine phases
Migraine is characterized by enormous clinical diversity. But in its course there is usually a staged pattern that distinguishes this disease from other causes of headache.
1. Prodromal period . Lasts from several hours to 2 days. Irritability and increased physical and mental activity appear. Frequent urination, increased intestinal motility (flatulence, frequent bowel movements), thirst are possible. Sometimes concentration is impaired, yawning, slurred speech, weakness and poor appetite appear.
2. Aura . A short period lasting from 5 minutes to 1 hour. There is no pain yet, but dizziness, nausea, and blurred vision appear. Sometimes neurological disorders occur: movement disorders, hallucinations, speech impairment. In such cases, doctors have to differentiate migraine aura from transient ischemic attack or stroke.
3. Headache . Pain appears in the eye or temple. Usually the symptom is one-sided, but the side can change even within the same attack. At first, the pain is dull and intermittent. Then it becomes pulsating and constant. The aura period lasts from several hours to 3 days.
4. Pain resolution . Symptoms gradually regress.
5. Postdromal period . After the headache is eliminated, some symptoms may remain. These are difficulties with concentration, weakness, depressed emotional state, drowsiness. The period lasts from several hours to 2 days.
Aura is observed in 80% of patients. Usually, if it is present, it appears with every attack. In only 10% of migraine patients, aura may be present only occasionally.
Diagnostic features
Laboratory tests and physical examinations can be done at any local clinic, but CT scans require special equipment. Not all clinics have it. To find your nearest imaging centers, please visit our appointment portal. Here we collect data on all diagnostic centers, divided according to various parameters: ratings, reviews, prices, characteristics of tomographs, discounts, etc. Select the studies you need, call the site operators for consultation, sign up for any type of scanning under special conditions from the service.
Nausea and vomiting during pregnancy
Nausea and vomiting are possible signs of pregnancy. In pregnant women, nausea usually occurs in the morning and is accompanied by slight dizziness, weakness, and drowsiness. Nausea and vomiting in pregnant women are symptoms of early gestosis (toxicosis). The occurrence of nausea and vomiting in a pregnant woman may be a sign of worsened pancreatitis, gastritis, gastric ulcer, treatment with iron supplements, therefore, in all cases of nausea and vomiting in pregnant women, this problem should be discussed with doctor.
Treatment
As first aid, it is necessary to exclude all possible external irritants, including unpleasant odors, loud sounds, and bright lights.
Take your usual painkiller, lie down and massage your head. You need to try to relax, before that open the window to freshen the air, drink a cup of weak tea. You cannot prescribe medications for yourself; this can only be done by a specialist. After consultation with him, a specialized examination and diagnosis, further treatment is planned.
The doctor can prescribe analgesics and adsorbents only for frequently recurring or unbearable attacks. The basis of therapy is the fight against the root cause; special drugs are prescribed, depending on the source of the disease. In particularly difficult cases, the issue of surgical intervention is decided. During the rehabilitation period, medications are also continued and physiotherapy is prescribed: massages, magnetic effects, gymnastics, cool compresses.
Other causes of vomiting
- Myocardial infarction, arterial hypertension. With high blood pressure, vomiting is combined with a severe headache. During a heart attack, vomiting occurs simultaneously with severe chest pain.
- Diabetes mellitus in case of non-compliance with treatment regimens and diet. In this case, vomiting is combined with severe thirst and frequent urination. Severe vomiting in diabetes may be a sign of impending ketoacidosis.
- Kidney disease in the final stages (renal failure).
- Some medications may have the side effect of vomiting. If vomiting occurs during treatment with any drug, you should consult the doctor who prescribed the drug.
- Mental factors: stress, fear, anorexia, excitement, severe pain, individual unpleasant associations with any food, smell, taste, situation can also provoke nausea and vomiting. Recurrent vomiting may be a symptom of hysteria.