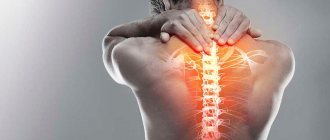
Disorientation is the inability to identify one’s own personality, the place of its physical location, the period in which it resides or its social affiliation. Personal disorientation often occurs as a result of damage to the structural elements of the brain. In addition, the deviation in question often arises as a result of excessive consumption of alcohol-containing liquids, the use of narcotic substances or potent pharmacopoeial psychotropic drugs. In other words, disorientation is a disorder of consciousness. In the described state, it is difficult for the subject to think quickly, perform actions, and there are difficulties with self-definition and orientation.
Medical classification
Disorientation is classified into radiation, occupational, spatial and social symptoms. Psychiatry identifies the term “autopsychic disorientation” - the lack of perception of personal factors (the inability to reproduce the last name, first name, patronymic, date of birth, that is, identification data). With this phenomenon, the individual’s surrounding world changes, and orientation in it is completely absent. A double perception of the world is noted, a real and imaginary environment is created, alternately visited by the psychological inner world. The full picture emerges after a proper examination by a doctor.
Pathogenesis
Successful navigation in space requires sufficient development and preservation of cognitive activity, including perception, recognition of spatial landmarks, discrimination between the left and right sides of the body, mental representation of space, and spatial memory. Visual information is processed in the primary projection zones of the occipital cortex, then goes to the posterior convexital parietal regions, the lateral surface of the temporal lobe, which ensures the recognition of objects and determination of their location.
The prefrontal cortex is responsible for short-term spatial memory and regulatory functions that implement human movement in space. Thus, the pathogenesis of disorientation is based on a violation of the cognitive component, a pathological change in the activity of brain structures that provide visual-spatial gnosis, mental representation of space, and topographic memory.
General information
Disorientation in space has several synonymous names: topographic disorientation, topographic orientation disorder, topographic agnosia, topographagnosia. Spatial orientation is a complex multicomponent function, thanks to which a person can determine his location and trajectory of movement relative to other objects. The state of temporary disorientation is familiar to anyone who has found themselves in an unfamiliar area. Pathological disorientation is most often diagnosed in elderly people with local organic brain lesions and neurodegenerative diseases.
Diagnostics
If you have such a symptom, you should consult a neurologist or psychotherapist. First of all, the doctor conducts a physical examination of the patient to determine complaints, life history and illness. To make an accurate diagnosis, the following laboratory diagnostic methods can be used:
- blood sampling for general and biochemical studies;
- test for the presence of narcotic substances in the body;
- CT and MRI of the brain;
- psychotherapeutic tests.
The exact diagnostic program will depend on the current clinical picture and general condition of the patient.
Basic therapy will depend on the diagnosis. In general, treatment interventions may include the following:
- providing rest to the patient;
- elimination of stress, excessive emotional stress;
- care.
As for drug therapy, it may include taking the following drugs:
- tranquilizers;
- antidepressants;
- sedatives;
- hypnotic;
- neuroleptics;
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
The dosage, regimen and duration of taking medications should be prescribed only by the attending physician. You cannot take such drugs without permission.
Let's sum it up
Disorientation causes a change in mental state. Some symptoms may also accompany this condition.
Disorientation does not have to be life-threatening. But some illnesses that cause confusion can be serious, so it's important that you seek medical help and get a proper diagnosis.
Sources:
Impulse follows strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, research institutions and medical associations. We avoid using insufficiently expert links.
- Berry B. (2014). Minimizing confusion and disorientation: Cognitive support work in informal dementia caregiving. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaging.2014.05.001
- Brown G.P. (nd).Assessment, intervention and disposition of patients with psychiatric symptoms. jucm.com/assessment-intervention-disposition-patients-psychiatric-symptoms/
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (2018). Delirium. mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/delirium/basics/symptoms/con-20033982
- Mental health in emergencies [Factsheet]. (2019). who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs383/en/
- When patients suddenly become confused. (2018). health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/when-patients-suddenly-become-confused
Identity structure according to E. Erikson
The psychoanalyst identifies four components of identity, which in symbiosis form the overall structure:
- Uniqueness of personality. The ability to recognize one's individuality and experiences, which distinguish a person as a separate social unit.
- Integrity. A person’s feeling of meaningfulness, identity and coherence with his existence. Integrity provides a connection to past experiences that carry over into the present and shape the future. Thus, a person understands what he was and what he wants to become.
- Unity. Internal harmony of the personality, which is formed from childhood images transferred into adulthood.
- Social solidarity. A person’s support for the ideas of a particular community. Expectation of approval and support from the referent group.
If all these elements in the personality structure develop harmoniously, overcoming crises occurs with relative ease and productively.
4) Somatogravic Illusion, another version of “somatogravitational illusion”)
0
Rapid straight-line acceleration creates the feeling that you are rising, forcing you to lower the nose of the plane. During rapid acceleration, the otolithic organs of the inner ear “think” that you are rising. This creates a desire to lower the nose of the plane and you put the car into a descent. The opposite is also true - during deceleration, you get the feeling that you are going down and there is a desire to raise the nose of the plane. How to prevent: Avoid rapid acceleration and deceleration in clouds.
Benefits of diagnostics
Timely detection of disorders contributes to rapid recovery, absence of consequences and progress towards a complete change in the condition for the better. Due to the fact that the signs of this disorder very often accompany similar disorders, sensible people will not put off visiting a psychotherapist in order to alleviate the fate of their loved ones who find themselves in a difficult situation.
The examination is performed by a psychiatrist or neurologist. Identifying disorientation and establishing its causes is important for objectifying the severity of functional limitations of activity in brain pathologies, determining the nature of confusion in psychotic states, alcohol or drug intoxication. Such an analysis of the symptoms of disorientation is necessary for the differential diagnosis of focal organic pathologies and neurodegenerative diseases, psychoses of various etiologies. The main research methods are:
- Clinical survey. At the first diagnostic stage, the doctor clarifies the symptoms, specifies their severity, duration, the presence of neurological diseases, mental disorders in the patient and his relatives. When disorientated, patients report that they cannot independently get to their usual places (hospital, store), and are unable to find their way back to home. They do not use landmarks and do not know how to use routes.
- Neurological examination. The clinical and neurological status of the patient is assessed, the presence of focal and cerebral symptoms is determined. Neurological tests reveal the ability to determine the left and right sides, the position of objects, and one’s body in space. Patients with disorientation perform tasks with errors and answer questions after a pause.
- Neuropsychological examination. The use of special tests makes it possible to analyze the structure of the deficit that forms the basis of disorientation. Topographic memory, perception of spatial relationships between objects, and preservation of the egocentric representation of space are studied. The type of disorientation and its severity are determined by the nature and frequency of errors.
What causes disorientation?
Disorientation can be a symptom of various diseases
It's important to look for other symptoms that accompany confusion
Delirium and dementia
Two common causes of confusion are delirium and dementia.
Delirium is caused by a sudden disruption of brain function. It only lasts for a short period. It can be caused by medications, infections, and injuries.
Something as simple as a change in environment can also cause delusions. For example, some adults may experience hospital delirium after surgery or after intensive care.
Three types of delirium:
- hyperactive
- hypoactive
- mixed
Hyperactive delirium can cause hallucinations and agitated behavior. Hypoactive delirium can cause drowsiness and withdrawn behavior. Mixed delirium can cause both types of behavior.
Delirium is characterized by:
decreased thinking skills, poor attention, hallucinations, abnormal speech behavior or content
Delirium often comes on quickly, resolves within days or weeks, and is variable in nature.
On the other hand, dementia develops more slowly than delirium. It is usually persistent and causes ongoing symptoms. Confusion and short-term memory loss may be some of the early signs of dementia.
Family members can play an important role in helping your doctor diagnose delirium and dementia.
Substances
Confusion can be a side effect of certain substances, including:
- alcohol
- marijuana
- prescription drugs
Withdrawal from certain medications can also cause confusion.
Other reasons
The following physical disorders may cause confusion:
- amnesia
- carbon monoxide poisoning
- cerebral arteritis, or inflammation of the arteries in the brain
- liver cirrhosis and liver failure
- central nervous system infections such as encephalitis or meningitis
- complex partial seizures
- shake
- dehydration
- drug overdose
- abnormalities in the electrolyte
- epilepsy
- fever
- heat-related illnesses
- hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia
- hypothermia when the temperature drops below 35°C
- hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
- hypoxia or decreased oxygen supply
- mass brain lesion such as a tumor or hematoma
- mitochondrial disease
- orthostatic hypotension
- renal failure
- Reye's syndrome
- sepsis
- stroke
- vitamin deficiency
- vestibular disorders that affect the inner ear
An emergency may also cause stress or mental distress and confusion.
What to do if someone is disoriented?
You should seek medical attention for someone who is disoriented.
If someone is trying to cope with confusion, including delirium, the following may be helpful:
- Keep track of his medical history. Make sure you have a list of all medications your loved one has taken. Your knowledge of his habits, medical history and symptoms can help the doctor make a diagnosis.
- Try to make the environment familiar. Changing the usual state of affairs can cause disorientation. Objects that remind your loved one of who they are can help restore direction.
- Stay nearby. Your presence can provide reassurance and comfort. Getting to know the person will also help the doctor determine what their normal behavior is.
You should encourage those who are disoriented to seek medical help. Call 911 if they are at risk of harming themselves or others.
5) Inversion Illusion
0
Moving the nose down too quickly can make you feel like you're falling backwards. If you move the plane too quickly from climb to level flight, you can feel like you're falling backwards. The real danger here is that it may encourage you to lower the nose of the plane further, which will put the aircraft into a descent position. What's much worse is that the more you give up the steering wheel, the more intense the illusion can become. How to prevent it: Control the controls slowly and smoothly when moving the airplane from climb to level flight.
Treatment
Before prescribing therapy, it is necessary to undergo a full examination. Therefore, first of all, you should visit a neurologist who will examine the individual, get acquainted with the complaints, find out the anamnesis and history of the disease.
In order to diagnose the presence of the described disorder, a biochemical blood test, an analysis to determine alcohol-containing substances or identify narcotic substances in the body, computed tomography, various psychotherapeutic tests, electrocardiographic studies, and determination of metabolic failures can be carried out.
Basic therapeutic tactics are determined by the diagnosis, since the methods of treating disorientation are directly determined by the etiological factor. If a sudden feeling of loss of orientation appears, it is recommended to try to relax, streamline the flow of your own thoughts, sometimes you even need to write them down. It is necessary to become aware of the perceived manifestations and understand what gave rise to this state.
So, for example, a decreased concentration of sugar can provoke disorientation if the last meal was taken several hours ago. To correct the situation, you should have a snack or drink a drink containing caffeine. If the described disorder is caused by dehydration of the body, it is necessary to drink water accordingly or drink a liquid containing electrolytes.
In general, the therapeutic strategy contains the following measures: ensuring peace, proper care, eliminating the effects of stressors, excessive emotional stress.
Drug therapy is based on the prescription of such categories of drugs as antipsychotics, tranquilizers, antidepressants, vitamins, sedatives, hypnotics, and mineral complexes. The selection of the required dose, duration and regimen of administration is determined by the doctor. Unauthorized prescription and use of pharmacopoeial drugs is not permitted.
Among the preventive measures, the following are distinguished:
– restriction in the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
– balancing the balance of healthy sleep and periods of wakefulness;
– balancing the diet, the foods consumed must contain the required concentration of minerals, vitamins, fiber, while foods containing “bad” cholesterol should be avoided;
– maintaining control over sugar levels in the presence of diabetes;
– getting rid of tobacco smoking.
In addition to the methods listed above, it is also important to devote time to mental exercise every day. The brain, as well as other organs, also needs training to maintain its performance.
Memorizing poems is considered a useful exercise. Daily walks also help to normalize the condition and minimize the occurrence of mental fog with manifestations of disorientation.
Psychoneurologist Hartman N.N.
Doctor of Medical and Psychological
The information presented in this article is intended for informational purposes only and cannot replace professional advice and qualified medical care. At the slightest suspicion of disorientation, be sure to consult a doctor!
Disorientation is a disorder of consciousness, as a result of which a person is unable to identify his social affiliation, personality, or navigate in time and space.
This condition is dangerous due to the loss of the ability to make decisions independently. The person does not remember people or places, times and dates.
disorientate this:
mislead , to fool, to fool one's brains, to fool one's head, to turn an ox, to refuel one's brains, to compost one's brains, to fool one's head, to twist one's head, to twist one's head, to confuse, to muddy the waters, to confuse one's mind, to fool one's brains, to confuse one's minds, to twist one's head, to twist one's brains , confuse, fool the brains, confuse, confuse
Dictionary of Russian synonyms.
disorient see confuse 2 (confuse 2)
Dictionary of synonyms of the Russian language. Practical guide. — M.: Russian language. Z. E. Alexandrova. 2011.
.
dic.academic.ru
Symptoms of spatial disorientation
The following types of personal disorientation are distinguished: radiation, spatial, professional and social disorientation.
Psychology offers the following classification of orientation disorders:
– autopsychic (which is a false recognition of oneself as a person or an absolute loss of self-identification);
– allopsychic (loss of orientation in the environment);
– double (the patient simultaneously or alternately resides in reality and imaginary reality);
– mixed or total disorientation.
A doctor can determine the state of disorientation only after conducting an examination.
Common clinical signs include symptoms such as sudden mood changes, dizziness, dream disturbance, and memory impairment.
Disorientation in space is often observed along with an inability to determine time. In addition, the disease in question may be accompanied by such manifestations as the subject’s inability to recognize himself as an individual, name the month, current year, country of residence or place of residence, and passport details.
A feeling of fear and anxiety also arises without an obvious reason. Apathy can suddenly give way to an attack of aggression. Therefore, it should be taken into account that the described state of the subject is often unsafe both for the person suffering from disorientation and for those around him. That is why, if the listed signs occur, a person should be immediately transported to a medical facility.
Social disorientation, as a rule, is not characterized by the presence of pronounced manifestations of a mental disorder. However, the following specific symptoms may occur. So, for example, the subject cannot tell his exact age. He also does not know his own social identity. In an unfamiliar environment, a feeling of uneasiness arises.
In the presence of VSD, spatiotemporal disorientation may be accompanied by: dizziness, ringing in the ears, nausea, partial hearing loss, headaches, and fluctuations in blood pressure. This condition poses a threat to the life of the individual. Self-medication or ignoring the described symptoms can lead to serious consequences and can also be fatal, since pressure surges can cause a stroke or provoke a heart attack.
Disorientation in space is a frequent accompaniment of twilight clouding of consciousness. Characterized by a sudden appearance and an equally sudden disappearance. The subject retains the ability to reproduce mechanical actions.
First aid for disorientation
If the reason lies in a decrease in blood sugar levels, then you will feel better within a few minutes. If the condition does not change for the better, it is best to call a doctor. If the reason lies in the medications, the doctor is more likely to cancel the one that causes the disorders. The doctor will advise you on how to properly control your weight if disorientation is the result of uncontrolled dieting. You should see a doctor immediately if the cause is a head injury. Any injury of this kind can be very serious.
How to get rid of disorientation and confusion?
If the diagnosis is established, comprehensive treatment of the underlying disease is carried out
It is important to stop all medications and ensure that there are no factors that could trigger confusion.
It is important to remember that loss of orientation in space can lead to the patient simply getting lost. It is also necessary to ensure maximum patient safety
If necessary, mechanical aids can be used. A person who has senile dementia - a disease of loss of orientation in time and space - should be in the most calm and friendly environment possible.
If the patient has only temporary loss of orientation, it is advisable to always keep a calendar and watch next to him. If possible, the patient should be constantly looked after by a nurse or one of the relatives. Depending on the patient’s condition, the doctor allows him to sit, walk, or go outside.
Sometimes patients with confusion are prescribed antidepressants.
It is important to constantly monitor blood pressure, pulse, and prevent dehydration.
If a person becomes confused suddenly, they should immediately consult a doctor. For example, disturbances of consciousness can suddenly appear in diabetes mellitus if the blood sugar level drops sharply.
As measures to prevent disturbances of consciousness and orientation, it is advisable to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition, not abuse alcohol, and regularly get enough sleep. Patients with diabetes need to constantly monitor their blood sugar levels. Elderly people should take the medications prescribed by the doctor
To prevent senile dementia, it is important to lead an active life whenever possible and be sure to train your memory and brain
Dizziness
The first thing you need to do is answer all the doctor’s questions as honestly as possible: is this the first time you’ve had this, have you had any injuries, are you on any strict diet, have you previously been diagnosed with any neurological disorders. The doctor will prescribe a series of tests and studies, such as MRI or ultrasound, to most accurately diagnose the cause of loss of orientation in space. And this will be the basis for prescribing treatment.
If the symptoms are neurological, then treatment usually begins with ensuring complete rest for the patient. It is necessary to isolate it from surrounding stress and nervous stimuli and provide it with proper care. Next, prescribe medications: antidepressants, sedatives, antipsychotics, vitamins. Let us remind you that all this is taken strictly in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations; you absolutely cannot calculate the dosage and frequency of administration on your own! Otherwise, the situation may only get worse.
If confusion is caused by external factors, such as a head injury, it is necessary to check whether it is a symptom of, for example, a concussion. If the problem is the wrong diet, you need to eat something high in calories and high in glucose. If this is due to taking medications, change the drug to an analogue or just something else and be sure to monitor the body’s reaction to taking it.
If this is the body’s reaction to alcohol, then it is better to refrain from drinking it completely, otherwise next time the consequences could be much worse. And take vitamins that strengthen the walls of the blood vessels in the brain. Which ones exactly - check with your doctor or pharmacist at the pharmacy. If there is an infection, confusion may be caused by a high fever.
In any case, so as not to cause loss of orientation in space, remember: a doctor and only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment for you. Self-medication not only may not help, but can also be extremely destructive for your body.
What diseases does it occur in?
- poisoning;
- manic-depressive disorders;
- senile dementia;
- metabolic disorders;
- injuries or surgical interventions;
- taking alcohol or drugs.
Sources
- https://psixsovet.ru/stati/dezorientatsiya-v-prostranstve-prichiny-simptomy-lechenie.html
- https://zna4enie.ru/opredelenie/chto-znachit-dezorientirovan-chelovek.html
- https://mir-tourista.ru/statyi/vyzhivanie-v-dikoi-prirode/medicinskaya-pomoshh/poterya-orientatsii.html
- https://SimptomyInfo.ru/simptomy/175-dezorientaciya.html
- https://FoodandHealth.ru/simptomy/dezorientaciya-i-sputannost-soznaniya/
- https://SimptoMer.ru/simptom/dezorientacija
- https://kartaslov.ru/%D0%B7%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5-%D1%81%D0%BB% D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0/%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%B7%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%82%D0 %B8%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D1%82%D1%8C
- https://medportal.org/symptoms/dezorientaciya-i-sputannost-soznaniya.html
Causes
The following reasons for the occurrence of the phenomenon of confused consciousness are identified:
- traumatic (consequences of penetrating traumatic brain injury);
- in case of brain injury (organ tissues are highly sensitive);
- the occurrence of an aneurysm (an enlarged blood vessel affects neighboring tissues);
- mercury poisoning;
- increased dose of alcohol in the blood;
- drug intoxication;
- effects of neurotropic gas on the respiratory system;
- entry of organophosphorus compounds into the digestive system;
- poisoning with neurotoxic substances – puffer fish, mushrooms, carambola;
- hyperthermia resulting from infectious diseases;
- pain shock during a fracture, dislocation, significant blood loss;
- severe diseases - tuberculosis, encephalitis, diabetes mellitus, all types of hepatitis, acquired human immunodeficiency syndrome at the final stage of development;
- progression of tumor growth at the last cancer stage (intoxication occurs during the process);
- ischemic disease, all types of strokes, occurring both unnoticed and obvious;
- myocardial infarction, with pronounced pain and impaired blood flow;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia – vasodilation occurs in areas of the body’s autonomic system;
- age-related diseases: senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease, marasmus of all types;
- bright emotional outburst;
- hypothermia;
- a period without sleep for a long time;
- oxygen starvation;
- 1st and 2nd degree stunning.
Loss of the ability to navigate the surrounding space can be caused by temporary pathological factors, such as intoxication or a drop in blood sugar, as well as neurological diseases, mental disorders that occur with psychotic episodes. The duration of disorientation, the ability to ask for help, and the use of compensatory functions (for example, memory) depend on the cause. Spatial disorientation is provoked by the following conditions:
- Focal lesions of the central nervous system. Local damage to brain structures is one of the most common causes of spatial orientation disorders. The symptom is found in traumatic brain injuries, brain tumors, and strokes.
- Neurodegenerative diseases. Violation of topographic orientation is observed in old, elderly people with Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, and other neurodegenerative pathologies. The inability to recognize the area and navigate a route occurs with the development of dementia, in a psychotic state.
- Psychotic disorders. Patients with mental illness in a state of psychosis lose the ability to correctly assess themselves and the environment. They find themselves disoriented in space, time, and their own personality.
- Use of drugs, alcohol. The state of alcohol or drug intoxication is often accompanied by a loss of the ability to determine one’s own location. The ability to act purposefully decreases, and planning a route becomes impossible.
- Action of drugs. Disorientation may be a consequence of taking certain medications. As a side effect, it occurs when using antihistamines, muscle relaxants, tranquilizers, psychostimulants, some painkillers, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Provoking diseases and provoking factors
Disorientation is just a sign of various diseases and disorders. Diseases accompanied by confusion:
- Alzheimer's disease;
- meningitis;
- renal failure;
- hypothyroidism;
- schizophrenia;
- hydrocephalus;
- epilepsy;
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease;
- manic-depressive disorders;
- encephalitis;
- hypoglycemia;
- brain tumors and cysts.
Disorientation appears not only as a consequence of neurological diseases and psychiatric disorders; negative changes in the perception of reality in adult patients also occur due to:
- alcohol abuse;
- taking drugs or certain medications (tranquilizers, antiallergic drugs, painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants);
- hypovitaminosis;
- dehydration;
- hypothermia;
- heat stroke;
- traumatic brain injury;
- infections;
- metabolic disorders;
- post-traumatic psychosis.
In older people, disorientation is often a consequence of senile dementia.
What are the symptoms of disorientation?
️The earliest symptoms of disorientation and confusion look like a deterioration in attention and ability to concentrate on something. As the disease develops, communication with the outside world is destroyed, gaps appear in memories, and logic is distorted. The person cannot understand what happened, ceases to recognize people and objects, and loses the ability to pronounce words.
️Because of this, he experiences stress, feels depressed, withdraws into himself and loses mobility. One skill or several at once may be affected. Sudden disorientation can be paroxysmal and go away over a period of time. Temporary disorientation is different from permanent disorientation. In the second case, signs such as delirium, dementia, hallucinations, limited mobility, and silence are visible.
️In the described condition, mental activity is disrupted, perception is distorted, and memories are lost. The perception of oneself as a person, one’s physical body, and other people changes. Memory of yourself and them becomes fragmentary or disappears completely.
Depending on the type of illness, different symptoms occur:
● Memory loss; ● Deterioration of attention; ● Sleep problems; ● Dizziness; ● Disconnected thinking; ● The appearance of visions, hallucinations; ● Apathy; ● Loss of concentration; ● Speech impairment.
️ Allopsychic disorientation means a lack of understanding of where a person is, the present place and time. The sufferer cannot name his location, is confused about calendar dates and time of day, and also does not know what year it is.
️ Sexual disorientation manifests itself as same-sex attraction, hatred of the opposite sex, and transgenderism. The reasons for such disorientation may be different, and this phenomenon is in the process of being studied. As an assumption, a hypothesis was put forward about a genetic predisposition, and there are also examples that sexual disorientation appears as a result of mental trauma and violence experienced.
️ Errative disorientation means speech impairment when pronouncing and writing words. People sometimes tend to be errative deliberately, creating slang expressions, but distorted speech can also be a symptom of a neurological and mental disorder.
️ Topographic disorientation means a lack of understanding of where a person is at the moment; he cannot name the locality, country, address and place of residence. It is this type of illness that most often occurs in elderly people who leave home in light clothing and wander the streets, not understanding where they are.
Disorientation in time and space, manifested due to brain damage due to trauma, concomitant illness or due to age. The patient cannot name the date, time, time of day, year, time of year and his location, as well as remember his own address, or go to the place where he lived for some time, but has long since left.
Loss of disorientation, or rather orientation, can occur suddenly and be temporary or develop gradually, conquering a person’s perception and depriving him of his usual guidelines in life. In this case, they say that complete disorientation has occurred and the patient disappears as a person. He falls into a confused state, becomes sedentary and withdrawn, does not speak, and performs a minimum number of actions, because he no longer understands what and when to do. Needs constant supervision and care.
Risk factors
By reviewing the main symptoms, people will learn useful information that will help them anticipate the possible occurrence of a disorder. However, there are certain risk factors that are long-term reminders of the brain. Having received data about them, you can evaluate your own life in order to find errors or necessary treatment.
- Age;
- Hypertension;
- Heart diseases;
- Bad habits;
- Diabetes.
The first question that arises in people is at what age does a stroke occur. Typically, poor circulation is considered typical for people over 50 years of age, but in recent years the statistics have changed, gradually forcing one to come to terms with the early manifestation of the disease. For this reason, you need to think about other risk factors.
Although hypertension, diabetes and heart disease cannot be changed, you can still undergo regular examinations and procedures to eliminate complications. Through simple actions and constant medical supervision, it will be possible to get rid of the preconditions for impaired brain function. For this reason, doctors advise staying under the supervision of doctors and not missing any dangerous symptoms.
In addition, bad habits are an important point. Now the characteristics of a stroke necessarily include their description. Because of this, the fight against smoking and alcoholism is being waged everywhere. A person should remember that such an attitude towards one’s own life gradually results in dire consequences.
What is a confused state?
In this process, the ability to think at an average speed disappears, the clarity and consistency of thoughts is significantly destroyed.
- What is a confused state?
- Causes
- Symptoms
- What is disorientation?
- Current of development
- Medical classification
- Symptoms of the disease
- Benefits of diagnostics
Signs of the disorder are problems with orientation in space and deterioration of attention. Logical thinking disappears and memory is degraded. The highest signs of the psyche change one by one. For example, only speech recognition may be affected. Memory problems are noted, spatial orientation is impaired. There are two types of confused consciousness, depending on the cause of its occurrence - fast and slow.
Manifestations can be one-time or permanent. Dementia and delirium are signs of the latter condition. The integrative function of thinking at the moment of confusion is absent. Along with the expected change, the patient is often silent, moves little, and is depressed outwardly. Illusions and hallucinations accompany the disease. The first arise because the body incorrectly perceives the stimulus, while hallucinations manifest themselves independently. Each individual suffers from the disease differently - the determining factor is the root cause of the development of the disorder. Slowness of thinking and inconsistency of logical series are emphasized during the first minutes of conversation. Even non-professionals can notice the initial symptoms.
Psychotherapists divide delirium into several classifications: hallucinatory (the ability to see non-existent information); manic (obsession with aggression); catatonic (inability to fully move); confabulatory (twisting of an obvious fact).
Symptoms of the disease
Most often, there is a disturbance in orientation in space (the patient is not aware of where he is) and in time (he forgets dates and days). Both options can be combined.
True confusion is usually the result of illness, injury, or a side effect of medications.
Children and adolescents may experience social disorientation due to major life changes. Young children have difficulty distinguishing between gender and occupation, and they are disturbed by the company of strangers. This is considered a normal physiological phenomenon that goes away during adolescence.
In other conditions, disturbances of consciousness require specialist consultation, since they may be a sign of serious diseases (dementia, mental retardation).
Early signs of a pathological condition are deterioration of attention and memory. A person’s perception of the world changes, disturbances are observed at the emotional level and problems with speech begin.
Sometimes illusions are added - incorrect perception of current events or hallucinations - visual and auditory sensations that do not actually exist. The patient is gloomy, silent, depressed, and inactive.
For a primary diagnosis, it is necessary to detect the active progress of processes:
- shallow memory lapses (information is lost within a few minutes);
- the patient cannot recognize his loved ones, as well as basic passport data;
- there is no memory of the person’s information field;
- disorientation;
- unconditional changes in mood (an aggressive mood can be used even on close people);
- there is no logical chain in the pronunciation of phrases (pronunciation speed is below average);
- lack of control over the bladder and sphincter (constant urination and defecation);
- Normal sleep is completely disrupted.
Due to internal bleeding, additional aspects appear: increased volume of sweat; bleeding of the skin; black defecation products; high blood pressure; worsening breathing; tachycardia.
Psychological disorder, in turn, contains the presence of inadequacy in behavior, aggressive attacks, lack of normal sleep, terrorizing the immediate environment, the emergence of helplessness and the collapse of a clearly established internal model of behavior.
Changes that help establish the diagnosis are pronounced dizziness, variable mood, disturbed sleep, problems with remembering facts, inability to identify a person, internal psychological anxiety without outside provocation.
Spatial symptoms stand out: a sharp change in mood - an apathetic state changes to an aggressive one.
Help in this situation can only be found in a specialized institution that works with psychologically unbalanced people.
A separate category is social disorientation, which cannot be classified as a mental disorder. Its specific features: unclearly pronounced age, long-term adaptation to society, anxiety in an unusual situation.
The diagnostic complex involves an initial consultation with a psychotherapist and a neurologist. The doctor carries out manipulations with the patient, a full physical examination, with questions that help establish the correct diagnosis. From the point of view of physical manipulations, there is blood sampling for biochemistry and general clinical analysis.
Confusion and temporary loss of orientation can be symptoms of very serious illnesses. If disorientation is accompanied by weakness in the limbs and slurred speech, we can talk about a transient ischemic attack or stroke.
If disorientation is accompanied by a high temperature, there is likely a severe infection in the body.
In any of the above cases, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Current of development
To correctly establish the primary diagnosis, it is necessary to note the causes of the anomaly. Fundamental experts identify the following factors:
- psychological disorders leading to a serious disorder in consciousness;
- stress, nervous overstrain;
- exceeding the norm of ppm alcohol in the blood;
- drug intoxication;
- medications: tranquilizers, antidepressant tablets, sedative drops;
- long-term exposure to increased background radiation;
- period of recovery from anesthesia;
- progressive depression;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- senile pseudosclerosis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- schizophrenia;
- hypoglycemia;
- senile dementia;
- lack of water resources in the body;
- insufficient kidney function;
- epileptic disease;
- malignant brain tumor;
- benign brain tumor;
- hyperthermia;
- infection with encephalitis tick.
Disorientation can be observed during a high-power impact and in a large emotional outburst. With this development, fainting often occurs. A one-time case is not a consequence of the occurrence of pathological processes. However, to be on the safe side, a consultation with a psychotherapist is necessary.