Hemiparesis in children is one of the forms of cerebral palsy, cerebral palsy. The prefix “hemi” indicates the right or left half of the body; “paresis” is incomplete damage to the nerves with partial loss of function. The term “hemiplegia” is complete paralysis of half the body. It must be said that this is not the most severe form of the disease, but it also depends on the severity of the brain damage. With a mild lesion, an adult child may not understand that he was given such a diagnosis. In severe cases, the child cannot use the right or left half of the body, i.e. the arm and leg are constrained by spasticity and movements in them are extremely limited. With such a diagnosis, there may be disturbances not only in the muscles of the limbs and torso, but also in the speech apparatus and intellect. Based on localization, left-sided and right-sided hemiparesis are distinguished. Causes of hemiparesis in children : usually this diagnosis is caused by brain injuries during childbirth through hemorrhage, prolonged or acute intrauterine hypoxia, asphyxia, ischemia, and combinations of these conditions. Often the cause may be infections, viruses, medical errors during childbirth, fetal development abnormalities, and brain underdevelopment. Extremely premature and low birth weight babies are at risk. The human brain is very sensitive to the lack of oxygen; if it is not supplied through the blood within 15-20 minutes, then the brain cells begin to die. Therefore, states of oxygen starvation are very dangerous for humans, and especially for the developing fetus. We can distinguish the main groups of factors leading to oxygen deficiency:
- mechanical, compression of the arteries by the umbilical cord when passing through the birth canal.
- hemorrhagic, with rupture of blood vessels in the brain.
How can you tell if your child has hemiparesis?
What symptoms may alert parents and become a reason to see a doctor? Upon examination, the specific posture of the child immediately attracts attention; on one side, the limbs are more tense, tucked in, brought closer to the body, less mobile, lagging behind the Moro reflex (this is when the child suddenly throws his arms to the sides and back, as if he was scared) Palpation and In passive movements of the limbs, tension and resistance from the muscles are felt. The child manipulates the tense half of the body much less. In such cases, you need to consult a doctor and explain the cause of your concern. It is the neurologist who makes such diagnoses; in other cases, these are only suspicions that need to be checked. Hemiparesis is similar to hemisyndrome, so the doctor will make this diagnosis last. Usually, a diagnosis of cerebral palsy is not made until one year of age; if the baby is at risk, then before the diagnosis is made, he is actively rehabilitated with medication, massage, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, etc. As a rule, specialists even before a year can already understand that making a diagnosis is a matter of time, but they write the threat of cerebral palsy as a type of hemiparesis. Experienced massage therapists can distinguish spasticity from tone, but according to the rules, you must first carry out therapeutic measures in order to eliminate the (so desired) error. At such moments, the doctor really wants to be wrong in his suspicions and the parents really hope for this.
Treatment of spastic hemiparesis in children
Therapeutic measures will be somewhat different in the early recovery period, late, and in the period of residual effects. The greatest intensity of treatment is in the first 2-3 years, hence the prognosis for future prospects. Many sources repeat that the earlier treatment is started, the greater the results. Of course this is true, but no less important is the correctly selected treatment methods and the quality of their implementation. You also need to understand that hemiparesis is not completely cured; it is only possible to partially restore lost functions. For most people, the diagnosis of cerebral palsy sounds scary, like a death sentence, in part this may be so, but I recommend that parents do not waste time and energy on despondency, but focus on the quality and regularity of treatment. Treatment of spastic hemiparesis in children is a long and expensive matter. The rehabilitation process is complex, usually in the first stages it is carried out in neurological hospitals, but after discharge it continues at home as prescribed by a doctor. Treatment is medicinal, massage, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, after 1.5-2 years speech therapists, psychologists, speech pathologists, orthopedic solutions are added.
Rehabilitation of patients with movement disorders after ischemic stroke
Patients with movement disorders make up a significant portion of all patients in the neurological rehabilitation department; these patients are least adapted to active activities, including self-care, and most often require outside care. Restoring motor functions in patients with diseases of the nervous system, in particular those who have suffered an ischemic stroke, is an important part of their rehabilitation. Neurology as a field of medicine sets itself the goal of primarily restoring their motor function during the rehabilitation treatment of patients suffering from diseases of the nervous system.
With pathology of the nervous system, in particular with cerebral ischemia, two types of motor functions are formed: maintaining position (posture) and movement itself. The systems that regulate movement include the pyramidal system, the extrapyramidal system, and the structures responsible for regulating the coordination of movements: the basal ganglia and the cerebellum. The resulting movement disorders depend on the level of localization of the pathological process and the degree of damage to certain brain systems.
Post-stroke movement disorders are characterized by significant clinical polymorphism. Among them are hemiparesis, which is often accompanied by sensory conduction disturbances, ataxic disorders of various types, and extrapyramidal disorders (chorea, tremor, dystonia). A significant proportion of patients have a “combined” motor defect, varying in nature and severity, leading to the development of postural disorders.
The most active restoration of motor functions occurs in the first 3 months, but functional improvement can last up to 6–24 months. It is believed that rehabilitation measures can be effective in 80% of people who have suffered a stroke (the remaining 10% experience spontaneous motor recovery, and in another 10% of patients, rehabilitation measures are futile). Spasticity, accompanied by a decrease in muscle strength and lasting more than 3–4 weeks, can lead to structural changes in the segmental apparatus (shortening of the dendrites of a-motoneurons and collateral sprouting of afferent fibers that are part of the dorsal roots), which contributes to the progression of motor disorders. Secondary changes may also develop in paretic muscles, tendons and joints, which aggravate movement disorders and increase the resistance in the muscles that occurs when they are stretched.
The restoration of “deficient” functions, that is, the basis of rehabilitation therapy, is based on the processes of neuroplasticity, the morphological basis of which is the reorganization of cortical and subcortical sections, increasing the efficiency of functioning of the remaining structures, as well as the active use of alternative descending pathways. Understanding that the restoration of neurological functions is associated with processes of neuroplasticity, it is promising not only to develop methods of motor rehabilitation, but also to search for effective and safe medications created on the basis of endogenous regulators of the body involved in the processes of neuroplasticity, which include regulatory peptides of a multicomponent type actions [1, 2], for example, the drug Cerebrolysin, which is a complex of low molecular weight neuropeptides (<10 kDa) and free amino acids. Numerous experimental studies have proven the neuroprotective effects of Cerebrolysin: the drug effectively reduces excitotoxicity, suppresses the formation of free radicals, microglial activation/neuroinflammation and calpain activation/apoptosis and, in addition, it exhibits neurotrophic activity, promoting the sprouting of neurons, increases cell survival, stimulates neurogenesis [3- 7].
The effectiveness of the clinical use of Cerebrolysin has been studied in a large number of studies in patients in the acute period of ischemic stroke.
In 2015, the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter clinical trial “Cerebrolysin and Recovery after Stroke (CARS)” was completed [8]. The purpose of this study was to study the effectiveness and safety of the use of the drug Cerebrolysin in the acute and early recovery period of stroke as a support for the rehabilitation of motor function of the upper limbs. Treatment with Cerebrolysin/placebo was prescribed within 24–72 hours after the onset of stroke. Cerebrolysin was prescribed 30 ml diluted in 70 ml saline as an intravenous infusion for 21 days. A standardized rehabilitation program was prescribed for 21 days, 5 days a week, 2 hours a day and included massage, passive and active motor exercises involving the upper and lower extremities. After discharge from the hospital, patients continued to do active exercises 3 days a week, 2 times for 15 minutes per day for 3 months. The primary endpoint was the relative change from baseline in the ARAT to study day 90.
The Arm Assessment Test (ARAT) evaluates the recovery of hand motor function by the patient's ability to hold objects of varying sizes, weights, and shapes.
Combination therapy using Cerebrolysin showed a significant improvement in the motor functions of the upper extremities - the dynamics of the ARAT score on the 90th day (primary end point) showed that treatment with Cerebrolysin leads to an improvement in the motor function of the hand - a significant reduction in disability. The improvement in ARAT test scores on the 90th day of observation (primary end point) ranged from 10.1 to 40.7 (p<0.0001) - 88% compared to the control group. In the group of patients receiving Cerebrolysin, there was also a significant decrease in the percentage of disability [8].
Thus, the use of Cerebrolysin as a drug treatment carried out in addition to a rehabilitation program can be considered as an important pharmacological approach to restoring the motor system in patients with motor disorders in the acute period of ischemic stroke.
Grivennikov I.A., Dolotov O.V., Goldina Yu.I. Factors of peptide nature in the processes of proliferation, differentiation and maintenance of cell viability of the mammalian nervous system. Molecular biology. – 1999. – T. 33. P. 120–126.
Romanova G.A. Shakova F.M. Peptidergic regulation of cognitive disorders during focal ischemia of the prefrontal cortex of rats. Pathogenesis. – 2008. – T. 6. – No. 4. – pp. 49–52.
Masliah E., Diez-Tejedor E. The pharmacology of neurotrophic treatment with Cerebrolysin: brain protection and repair to counteract pathologies of acute and chronic neurological disorders. Drugs Today. 2012; 48: Suppl A: 3–24.
Hartbauer M., Hutter-Paier B., Skofitsch G., Windisch M. Antiapoptotic effects of the peptidergic drug cerebrolysin on primary cultures of embryonic chick cortical neurons. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2001; 108:459–473.
Zhang L., Chopp M., Meier D.H., Winter S., Wang L., Szalad A., et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway mediates cerebrolysinimproved neurological function after stroke. Stroke. 2013; 44: 1965–1972. doi: 10.1161/ STROKEAHA.111.000831.
Gutmann B., Hutter-Paier B., Skofitsch G., Windisch M., Gmeinbauer R. In vitro models of brain ischemia: the peptidergic drug cerebrolysin protects cultured chick cortical neurons from cell death. Neurotox Res. 2002; 4:59–65.
Darsalia V., Heldmann U., Lindvall O., Kokaia Z. Stroke-induced neurogenesis in aged brain. Stroke. 2005; 36: 1790–1795.
Dafin F. Muresanu, Wolf-Dieter Heiss, Volker Hoemberg, Ovidiu Bajenaru et al. Cerebrolysin and Recovery After Stroke (CARS). A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Multicenter Trial. Stroke. 2016;47:151–159
Massage and exercise therapy for hemiparesis in children
Massage for hemiparesis is done classically, has its own characteristics in plan, and the procedure also includes techniques from exercise therapy, passive ones aimed at stretching spastic muscle groups, and active ones aimed at strengthening the healthy half of the body and developing skills. The duration of the procedure depends on the age of the child. It is better to rely on the child’s patience, but even if the baby is able to endure a long procedure, I still do not recommend doing it for more than 40-50 minutes for children under one year old and 60-70 minutes for babies after one year. The massage is done every day, you can stop on weekends, the course is up to a maximum of 25 sessions, then a break for at least 2-3 weeks. Exercise therapy can be done every day without breaks. The massage can begin with the back and neck area, in order to work on the reflex zones and segments innervating the limbs. We use classic techniques. In tense areas such as the shoulder girdle, buttock area, the massage is done deeper and more slowly. We carefully process the paravertebral lines from bottom to top using spiral rubbing. The child should not be in pain, but the pressure must be strong to achieve the effect. In a position lying on his stomach, it is advisable for the child to lie supported on his elbows; if the baby does not succeed in this, then the mother sits and holds the child’s hands in this position. Reliance on the elbows is practiced for children up to 5 months old; older children, who can already lean on their elbows without support, can, if desired, place their heads on the table. Massage of the arms and legs for hemiparesis in children is done in a classic way, but passive movements in the joints are necessarily added in order to stretch tense muscles. Kneading at a slow pace and deeply in spastic areas. To improve the quality of kneading, the muscle can be stretched by movement in the joint through which it is thrown, and massaged in a stretched position. Physical therapy (physical therapy) for hemiparesis in children is of great importance in rehabilitation in all age groups. For infants there is a lot of passive and reflex gymnastics, but less active, due to the newborn’s inability to perform many active exercises. As they grow older, the emphasis and set of exercises gradually changes towards more complex ones that require the involvement and active participation of the child in the process.
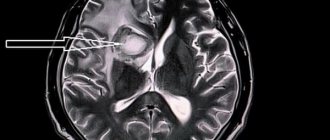
Diagnostics
Determining the cause of hemiparesis is the responsibility of a neurologist. During the interview, the specialist finds out the time of occurrence and rate of progression of the symptom, and establishes the presence of other complaints. To clarify the diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- Neurological examination
. The doctor examines reflexes, assesses the sensitivity and strength of muscles on the healthy and diseased sides, and detects other neurological manifestations. - Echoencephalography.
A basic method used for the primary diagnosis of tumors, hematomas, abscesses, parasitic lesions, and confirmation of displacement of brain structures. - Vascular Research
. Rheoencephalography and vascular ultrasound are performed to assess the state of cerebral circulation. - X-ray of the skull.
Included in the mandatory examination program for TBI, it is prescribed to determine the nature and severity of fractures. Informative for abscesses that have arisen against the background of osteomyelitis of the skull bones. - CT scan of the brain.
It is used for a detailed study of space-occupying formations, differentiation of strokes, and clarification of the nature and prevalence of inflammatory changes. Can be native or contrasting. - MRI of the brain.
Performed at the final stage of diagnosis. Recommended for head injury, neoplasia, stroke, abscesses, aspergillosis. If indicated, it is supplemented with MR angiography. - Lab tests
. Necessary for establishing the etiology and severity of inflammation, assessing the state of the body during tumors and purulent processes. In some cases, to determine the type and degree of differentiation of neoplasia, a morphological study of the material obtained during stereotactic biopsy is performed.
Exercise therapy for hemiparesis
What should be the result after massage and exercise therapy for hemiparesis?
Of course, these methods are not a panacea. The benefits of massage with gymnastics in the prevention of contractures, the consequences of congestion, atrophy, training and maintaining muscles, nerves, blood vessels, bones and ligaments. After all, without stress, muscles weaken, ligaments become thinner, bones become thinner and more fragile. The functions of the musculoskeletal system must be preserved at least until the child grows to an age when he will more consciously work with a physical therapy instructor and perform increasingly complex exercises that will form the skills necessary for life.
Forecasts
So far, no supermethods or specialists have cured a single child from cerebral palsy with deep damage and, as a consequence, central spasticity. The diagnosis can be removed, but if the child had a mild degree of brain damage, in which many functions are preserved. If we are talking about deep and extensive damage to the brain tissue, then nothing can be done to force the brain to restore dead cells again, too many of them die, the structure is complex, and besides, the body quickly replaces the dead areas with connective tissue. Therefore, everything that can be restored bypassing the lost areas in childhood will be the result of treatment for hemiparesis. But with this form, one half of the body is working and this means a lot for the future formation of skills.
Characteristics of hemiparesis
Hemiparesis is a decrease in muscle strength in the right or left half of the body due to damage to cortical neurons or pathways.
During the transition from the brain to the spinal cord, the nerve tracts intersect, so hemiparesis in most cases develops on the side opposite to the pathological focus. May develop acutely or gradually. It is often combined with aphasia, cognitive disorders, and pelvic dysfunction. With simultaneous involvement of the brain stem and cranial nerve nuclei, alternating syndromes are formed - conditions in which hemiparesis on one side is combined with loss of function of one or more cranial nerves on the other side.
How to select specialists for the rehabilitation of a child with hemiparesis?
Usually the parents of such children are ready to do anything and believe everything in order to restore their children’s health. Unfortunately, there are unscrupulous people who try to sell useless services to parents who find themselves in difficult life situations. We have accumulated some experience in interacting with such children and their parents. Based on this, we would like to give advice to parents: for medical rehabilitation, select specialists with medical education, massage therapists, exercise therapy instructors, etc. From time to time it is advisable to undergo complex treatment and rehabilitation in specialized medical facilities. centers, hospitals. During the break between such courses of treatment, you can work with the child by inviting specialists to your home. If it so happens that your baby has hemiparesis and you don’t know anything about it, don’t hesitate to ask mothers who already have experience in the rehabilitation, care and education of such children. They can be found on the Internet on forums and social networks. Children with the same diagnosis are still individual and have their own characteristics. But in general, information exchange with such parents will help you choose suitable correctional teachers-speech pathologists for your child, a feeding system, a diet, developmental activities, gradually trying what was useful for others, you will select for your baby the most effective activities, methods, and methods in your case. etc. It is better to look for speech pathologists and other teachers in specialized institutions where such children are cared for. For questions about massage and exercise therapy for children with hemiparesis, write to me on WhatsApp +79266057470 Alexey. The author of the article is massage therapist Alexey Matrosov.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Treatment tactics are determined by the stage of the disease and the duration of hemiparesis. In the acute period, pathogenetic and symptomatic measures are carried out, and complications are prevented. In the future, restorative techniques play a leading role. The treatment plan includes:
- Drug therapy
: antibiotics, muscle relaxants, anticonvulsants and vascular drugs, drugs to stimulate local metabolism, neuroprotectors, B vitamins. - Physiotherapeutic procedures
: electromyostimulation, reflexology, electrophoresis, diadynamic therapy, ultrasound, water procedures, mud applications. - Manual influence
: various types of massage and manual therapy. - Active rehabilitation
: exercise therapy, programs for restoring motor skills during self-care, mechanical therapy, swimming, use of special exercise equipment. - Psychotherapy:
individual sessions with a psychologist are aimed at adapting to changes in health status and preventing depression. They are supplemented by group trainings to improve everyday and social skills. - Working with a speech therapist
: speech therapy sessions are recommended for patients with speech disorders.
Surgery
Taking into account the etiology of hemiparesis, the following operations are performed:
- Circulatory disorders
: thrombolysis, extra-intracranial anastomosis, vertebral artery reconstruction, carotid endarterectomy, AVM removal, aneurysm occlusion. - Tumors
: removal of intracerebral tumors and brain stem neoplasms, excision of metastatic neoplasia, stereotactic surgery, embolization. - Trauma
: transcranial, stereotactic or endoscopic removal of hematomas. - Purulent processes
: drainage of abscesses and empyemas, transcranial excision of the abscess along with the capsule.
In the long-term period, orthopedic interventions may be indicated for patients. Joint redress for contractures, arthrodesis in a functionally advantageous position, and tendon and muscle transplantation are possible.