PET/CT examination - what is it?
The deciphering of the abbreviation sounds like positron emission tomography - computed tomography. This diagnostic method combines the study of the structure and functional characteristics of tissues. The technology is especially widely used in oncology to identify and determine the degree of development of malignant tumors.
Why?
Today, up to 90% of PET/CT studies in the world are performed on people suffering from cancer. The study is important from a number of perspectives:
- The study is important from the point of view of determining the degree of development and spread of the tumor process, detection of metastases, both regional and distant.
- In medical practice, there are situations when doctors are unclear about the nature of the process occurring in a particular organ. The study allows you to differentiate the process, distinguish between benign and malignant.
- The study helps to understand whether the treatment is effective.
- The study can be used to diagnose relapse of the disease.
When it comes to diagnosis, many cancers have the ability to actively accumulate fluorodeoxyglucose. This substance is used during the study. However, some types of cancers have low metabolism.
These types include:
- Highly differentiated cancerous neoplasms of the thyroid gland; Benign tumors of any location;
- Some kidney tumors;
- Some bone tumors;
- Liver tumors;
- Prostate tumors;
- Some types of sarcomas, lymphomas.
Having a low metabolic rate, they are poorly visualized by PET/CT. This means that other diagnostic methods are required.
Whole body PET scan
It is the most common type of research in positron emission tomography. The main patient population is cancer patients. The principle of the method is based on the fact that the tumor cell, due to the fact that its metabolism is accelerated, absorbs the radiopharmaceutical much more intensively (compared to normal cells of the body). In addition, 18F-FDG, after entering the cell, does not participate in oxidation processes and, thus, ends up in the so-called metabolic trap.
As mentioned earlier, the object of research is the human organocomplex. As a rule, they look in the range from the earlobe to the middle third of the thigh.
The main diseases that are studied using 18F-FDG PET-CT are lymphomas, breast cancer, thyroid cancer, esophageal cancer, colorectal cancer, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer and many others.
It is important to say that 18F-FDG PET should not be used for fibroadenomas, neuroendocrine tumors, prostate cancer, and some types of renal cell carcinoma, since these types of tumors do not accumulate 18F-FDG radiopharmaceuticals.
With 18F-FDG PET, the extent of the tumor process (primary tumor, regional metastases, distant metastases) is primarily assessed. It should be noted that in some cases, with a widespread tumor process and an unperformed biopsy with morphological (histological) examination, it is not possible to establish the primary tumor.
Whole body PET-CT with 18F-FDG focus of pathological accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals
The 18F-FDG PET method also makes it possible to evaluate cancer treatment, i.e. say whether the treatment helps or not. But it is important to know that in order to conduct a high-quality study and eliminate errors, it is necessary to observe certain periods between the treatment session and the PET study: a) 3 months after surgery for an adequate assessment of the surgical area, b) 4 weeks after the last radiation therapy session, c) at least 3 weeks after the last administration of chemotherapy.
Preparation for PET examination:
- On the day of the study, the patient must be hungry.
- 6 hours before the test you can eat 2 boiled eggs.
- You can drink plain unsweetened and still water without restrictions, tea, coffee without sugar and without milk (this is also possible).
- In patients with diabetes mellitus, glucose-lowering medications are discontinued on the day of the study. IMPORTANT: the blood glucose level should not be higher than 11 mmol/l, otherwise the study will be refused.
The patient should expect that he will spend at least 4 hours in the department (usually 4-6 hours). Of this time, 30 minutes are allocated for measuring the patient’s height and weight, as well as for filling out documents: a contract for the provision of medical services, informed consent for the study, etc. After registration, the patient is taken to the treatment room, where he is administered the 18F-FDG radiopharmaceutical. After administration of the radiopharmaceutical, the patient is given 1 liter of water and sent to the waiting room for 1 hour 30 minutes (minimum). After the designated time has passed, the patient is invited to a tomograph scan, which lasts on average 30 minutes. After the scan, the patient either remains to wait for the report or goes home to pick up the report the next day.
Some aspects of interpretation of the conclusion
The main concept used in the description of PET studies with 18F-FDG in the conclusions is the “focus of pathological accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals” as well as its characteristic such as Standard Uptake Value or SUV, in addition, you can often find such concepts as focal hypermetabolism, zone of hypermetabolism etc. Let's look at these concepts in more detail.
The focus of pathological accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals is an area of living tissue with a high accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals. As a rule, these are tumor nodes, metastases, and foci of inflammation.
Standard Uptake Value is a dimensionless value that quantitatively characterizes the level of radiopharmaceutical accumulation in the area of interest (usually in the focus of pathological accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals, but normal tissues can also be assessed, for example, in lymphomas). It is important to note that different tomographs calculate this indicator differently. The author of these lines knows at least 5 formulas for its calculation. Therefore, dynamic monitoring (repeated PET study) should be performed on the same tomograph, and ideally by the same doctor.
Description of research technology
The basis of the research technology is the study of tissue characteristics, structural and functional. Functional characteristics can be assessed through metabolism. Let's take the following example. We choose a substance that is necessary for all cells of the body. We mark it with a radioactive label, introduce it into the body and observe the places of its maximum accumulation.
Glucose is a universal substance in the human body. With the help of glucose, almost all tissues and cells are nourished. In malignant tumors, the greatest consumption occurs, since the growth and reproduction of tumor cells requires a lot of energy.
In a PET/CT scan, glucose is labeled with radioactive atoms with a short half-life. Once in the body, glucose actively accumulates in tissues with the most intense metabolism, i.e. in cancerous tumors.
The tag disintegrates, emitting energy in the form of gamma rays. A special device records this process. The data that the doctor receives creates a visual model showing the location of the tumor, its size and metastases.
Radioactive tracers accumulate only at the location of atypical cells; healthy tissues are not visualized.
When the doctor needs to examine both healthy and changed structures, CT comes to the rescue, allowing you to obtain a detailed picture with millimeter accuracy.
After data from both scanning systems is received, they are superimposed on each other, thereby achieving an image that gives a clear picture of the location of tumor foci.
PET/CT with glucose and methionine. What is the difference?
The principle of operation of a PET scanner is to construct a color image of the organs and anatomical structures of the patient’s body based on the data received from the radiopharmaceutical. The color of different tissue areas depends on the radiopharmaceuticals accumulated in them. Tumor foci in such images are marked in bright red, since they have accumulated the largest amount of radiopharmaceuticals.
Labeled glucose (fluorodeoxyglucose) is used as a radiopharmaceutical in 9 out of 10 cases. This choice is explained by the fact that for the intensive development of malignant tumors, sugar is vital, which they accumulate faster than normal tissues.
But the difference in the volume and rate of accumulation of radiolabeled glucose in the brain is not so significant. The thing is that accelerated absorption of glucose for the central nervous system is a physiological norm. There is certainly a difference, but it may not always be noticeable.
Therefore, another radiopharmaceutical, 11c-methionine, is currently used for brain research. This drug also effectively accumulates in malignant neoplasms, while healthy brain tissue practically does not absorb it. Years of research have shown that methionine PET/CT is a more accurate and informative method for diagnosing the brain than glucose PET/CT.
Types of drugs used
The potential of a study depends on the arsenal of radiopharmaceuticals used in it. These drugs are labeled with unstable isotopes that make them radioactive.
Today, isotopes of such elements as:
- Nitrogen-13;
- Oxygen-15;
- Carbon-11;
- Fluorine-18.
In oncology, fluorine is most common, since it has the longest half-life and at the same time the lowest radiation energy.
These advantages of fluorine make it possible to obtain high-quality images with high spatial resolution. In addition, the relatively long half-life makes it possible to transport the drug from the site of production to the clinic.
The most common drug used is fluorodeoxyglucose. It is an analogue of glucose. Atypical cells absorb it faster, it actively accumulates, and this is ideal for scanning.
The downside of fluorodeoxyglucose is that it accumulates in brain tissue and nephrons, which in turn can cause these organs to glow, even when they are healthy.
This drawback stimulated the search for other, more advanced drugs, and now such drugs have been created.
An example of a modern drug is 18F-FET. It is intended for the brain and contains the amino acid tyrosine, labeled with the fluorine-18 isotope. Tyrosine has a very high selective accumulation in brain tissue, which is important for imaging neurotumors.
The drug is also used to diagnose oropharyngeal tumors, to detect metastases and to diagnose lesions of the cervical lymph nodes.
Where can I get a positron emission tomography scan?
Not so long ago in our country the method was little known not only to patients, but also to doctors. Today in Russia, every self-respecting doctor knows what a PET/CT examination is, and modern PET centers operate or are actively being built in most large cities.
How to get tested for free under compulsory medical insurance
According to compulsory medical insurance, PET/CT can be done upon referral from the attending physician. This diagnosis is included in the list of services provided as part of compulsory health insurance. In most regions, examination under compulsory medical insurance requires a referral from the attending physician, and the service is provided on a first-come, first-served basis. The waiting time, depending on the region, ranges from 5 working days to two weeks.
Indications for the study
- Search for the primary tumor site when metastases are detected;
- Determination of the stage of the oncological process;
- Differentiated diagnosis of relapse and post-treatment changes;
- Monitoring the course of the disease, detecting relapse;
- Planning of radiotherapy and surgical manipulation;
- Planning a biopsy and finding the most aggressive area of the tumor.
Radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases
Diagnostic results
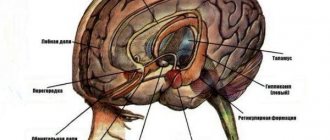
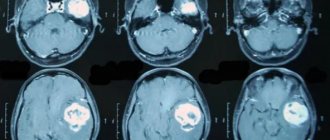
How informative is PET CT for brain tumors?
- The tumor site in the brain is being identified.
- The dynamics of the tumor and its relapse are observed.
- The extent of the tumor is determined.
- Metastases are visible in the lymph nodes.
The doctor makes an accurate decoding of the PET CT scan of the brain. It allows you to see pathologies and identify serious diseases. In cases of mental illness, the difference between the brain of a healthy person and one with depression is clearly visible.
For PET CT scans of the brain, decoding is necessary to make a correct diagnosis and timely treatment.
Preparation
When preparing for the examination, you must adhere to a number of rules:
- The day before your scheduled procedure, follow a low-carbohydrate diet.
- Come to the examination on an empty stomach.
- On the eve of the study, avoid heavy physical activity.
- On the day of the procedure, drink plain water.
- Stop chewing gum.
- Come to the procedure in comfortable, comfortable and preferably warm clothing.
It is recommended to bring information about the disease, diagnoses, extracts from other hospitals, results of other studies, etc. to the research procedure.
Preparation for the brain PET/CT procedure
First of all, the day before a PET CT scan of the brain, it is forbidden to engage in physical exercise. You should not drink alcohol, caffeine or smoke cigarettes. This also applies to nicotine patches, hookah and chewing tobacco. You cannot ignore these recommendations, as you can harm your health, because the reaction can be the most unpredictable.
Before a PET CT scan of the brain, it is advisable to eat a light dinner, which should include fermented milk and cottage cheese products. 6-7 hours before the procedure, it is not advisable to eat, chewing gum or sweets. Drinking before PET CT scan of the brain is recommended; the patient should drink at least 0.5 liters of water or weak tea and coffee, without sugar or any sweeteners.
It is worth noting that the patient’s clothing should not contain metal buttons, fasteners, zippers, hooks or snaps. Clothing for a PET CT scan of the brain should be as comfortable and warm as possible. This is necessary for good muscle relaxation, and as a result, a high-quality image.
It is strictly prohibited to take watches, keys and other metal objects for a PET CT scan of the brain.
Carrying out
The procedure itself takes about an hour, but it is necessary to keep in mind the preparation, preparation of the necessary papers and post-procedure rest.
The procedure is carried out in comfortable clothing; it is necessary to remove everything containing metal.
It is necessary to inform your doctor about the pain that may arise from prolonged immobility. Taking this into account, he will be able to select an individual procedure for the procedure.
After the injection, you must lie silent, motionless and relaxed. Immobility has a beneficial effect on the correct distribution of the administered drug. This is important for image quality.
The first stage of the examination is the administration of the drug. It lasts about an hour. The drug is administered intravenously. Sometimes the patient may feel fever, nothing more. The distribution of the drug among the cells lasts about an hour.
The second stage is scanning. Patient in a tomograph. CT is performed first, then PET. If required, an additional contrast agent is administered. The duration of this stage varies from twenty to forty minutes.
Upon completion, the CT and PET images are superimposed.
How is it going?
The subject is injected intravenously with a solution containing labeled methionine 1 hour before the start of the procedure - this is exactly the amount of time the radiopharmaceutical needs for uniform distribution.
distribution throughout the body.
After this, the patient is positioned on the table of the tomograph, which will slowly move through an arch with a scanner receiving information from the radioisotope. The PET scanner and CT scan operate simultaneously, and the resulting data is combined by special software into a color 3D image.
Throughout the entire procedure, the patient is alone in the diagnostic room. Scanning duration is from 30 minutes to 1.5 hours.
What after?
Afterwards, it is not recommended to be in crowded places for 24 hours, especially to have contact with pregnant women and children. In the family, it is necessary to maintain a social distance of 1 -1.5 from each other.
It is necessary to consume a lot of fluid, two and a half liters or more. This is necessary to remove contrast and radiopharmaceuticals faster and safer.
You can drink any decaffeinated drinks, not just water.
Indications and contraindications for PET/CT.
PET/CT is used in the presence of diseases such as:
- brain tumors of various types;
- stroke;
- dementia;
- epilepsy;
- multiple sclerosis;
- schizophrenia;
- Parkinson's disease;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- cerebrovascular pathology;
- primary progressive aphasia;
- Pick's disease.
Contraindications:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- decompensated and subdecompensated forms of diabetes mellitus;
- chronic diseases with exacerbations;
- general serious condition of the subject;
- inability to lie down and remain motionless for a long time.
Complications
Complications during the examination procedure are mainly associated with the administration of contrast.
It could be:
- Allergy caused by vein puncturing;
- Damage to blood vessels;
- The appearance of a hematoma;
- Neuritis
A very rare complication is renal dysfunction.
Oral administration of contrast may cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
After the procedure, dizziness and weakness may occur due to the fact that the stomach is empty.
Technology development
Initially, PET examination was used in diagnostics as a separate technique. Due to the above-described features of the resulting images, its results were not informative enough. Therefore, all modern diagnostic systems are equipped with two types of scanners: positron emission tomography and computed tomography.
Each next generation of devices surpasses the previous one in accuracy of results and safety due to:
- equipped with innovative sensors and electronic units;
- increasing noise immunity;
- other engineering, technical and software solutions.
Recently introduced PET MRI complexes allow unhindered visualization of soft tissue tumors, including in organs blocked from the scanner by skeletal bones. In addition, this technique makes it possible to significantly reduce radiation exposure, since, unlike CT, MR imaging does not use ionizing radiation.
Radiation exposure to the patient during examination
The choice of radiation dose is influenced by the radiopharmaceutical used and the scope of the study. So scanning the head requires less radiation than scanning the whole body. Minimizing harm from using the method is achieved if the following requirements are followed:
- Use isotopes with a half-life of several minutes or hours;
- Calculate the dose individually for each patient, taking into account his age, height, weight;
- Use special filters on scanners, as well as programs that reduce radiation doses;
- Consume the required amount of fluid, this will allow you to quickly remove the radiopharmaceutical from the body
By contacting the Onco.Rehab integrative oncology clinic, you will find out where it is best to undergo the study that we told you about in this article.
PET CT examination: what is it from a scientific point of view
Positron emission tomography is based on the principle of capturing gamma radiation from isotopes with special sensors. These signals are interpreted using a special program that converts them into multi-colored luminous zones. The color of the luminous foci changes depending on the amount of isotopes captured by the tissues and, accordingly, on the intensity of the radiation.
Dependence of radiopharmaceutical accumulation on the degree of malignancy of tumor cells
The more radiopharmaceuticals accumulate in the lesion, the “hotter” it is, that is, the brighter it glows. However, such luminous zones do not have clearly defined boundaries. Superimposing images obtained using computed tomography onto positron emission tomogram images eliminates this drawback.
What is the difference from other visual diagnostic methods?
No other imaging method except positron emission tomography allows one to see changes in metabolic processes at the cellular level, and in combination with a clear image of the lesion on a computed tomogram, this makes it possible to most accurately plan laparoscopy or targeted radiosurgery, determine metastases in the bones and solve other complex diagnostic problems. tasks.
What is 11C-methionine
This substance is an essential amino acid found in many peptides and proteins. It is safe for the body and does not cause allergic reactions.
For PET CT, it is labeled with carbon 11. This radiopharmaceutical can detect the metabolic characteristics of structural brain damage. The main indicator of the tumor process is the high accumulation of 11C-methionine in the area where the primary tumor is located. The diagnostic method allows you to track changes in dynamics, including after treatment. In the place where radiation excision of the tumor took place, an increased content of the drug is not observed; in areas of necrosis it is even reduced.
Where to sign up for testing
There are several diagnostic centers in Moscow licensed to provide this service. The most convenient way to view information about them is through our service. There is comprehensive information about the infrastructure of these clinics and the ability to receive patients with limited mobility. The website contains telephone numbers and addresses, the availability of free coupons, and possible appointment times. The easiest way to book a ticket is by calling +7(495)236-74-72. Our operators will answer all questions, provide a detailed description of preparations for the study, and tell you what to take with you. When registering through the service, a discount on diagnostics is up to 1000 rubles.