Problems with using or understanding language (aphasia) appear, according to statistics from studies conducted by NABI (National Stroke Association), in 25 patients out of 100. Every fourth patient experiences difficulties associated with verbal communication - the ability to speak, write or understand spoken language. and written language. This indicates that acute cerebrovascular accident affected one or more language control centers.
Aphasia is a symptom of brain damage, not a disease. As individual as the picture of damage is, the manifestation of aphasia in each patient is as individual. This condition determines the individual nature of the selection of speech restoration techniques after a stroke for each patient.
The process of speech restoration after a stroke
Content
The process of speech restoration is very long
Restoring speech after a stroke is a process that should begin immediately after the condition after the stroke has stabilized. You need to be prepared for the fact that it will take longer than the restoration of motor functions. Everything can drag on for up to six years, although even after such a period of time, speech may not fully resume. The patient must be reassured that the success of treatment primarily depends on his own efforts.
A speech therapist should monitor the improvement of speech functions. He may prescribe both medication and speech therapy exercises. If you try to treat a patient yourself, you can cause great harm, then the chances of recovery will be significantly reduced. It is worth noting that there are two types of speech disorders, each of which requires separate treatment.
Forms of disorders
Let us first consider the manifestation of each form, and then the treatment required in each form.
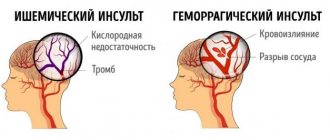
- Aphasia. The very phenomenon of speech as a manifestation of higher nervous activity is disrupted. The patient is unable to recognize written or spoken language, but he hears sounds and words. This is sensory aphasia. Due to the fact that the necessary impulse is not formed in the necessary parts of the neocortex, the patient cannot pronounce a word. This is the so-called motor aphasia or apraxia of speech. There is total aphasia, in which a person not only cannot speak himself, but also does not understand what is being said to him.
- Dysarthria. This is a defect in the pronunciation of words and sounds. A person understands perfectly well what is said to him, can write and read, but is not able to speak, since the work of the muscles that are responsible for the pronunciation of sounds is impaired. This is also called articulation disorder, which affects parts of the subcortical structures and frontal lobes.
Now is the time to discuss which treatments are used in each type.
Treatment of aphasia and dysarthria
- Speech therapy method. In this case, speech, reading and writing are restored by training and consolidation of linguistic skills. Melodic intonation therapy is also used, which is aimed at activating the functions of the right hemisphere of the brain. Cognitive functions and speech can be restored using computer technology. The speech therapy method is most beneficial when interacting with pharmacological methods that are aimed at bringing the damaged hemisphere back to normal. Although for severe aphasia other methods are still used.
If there is a stroke on the right side, is there a chance of recovering memory?
Right-sided paralysis of the limbs occurs when the focus of hemorrhage or ischemia is located in the left hemisphere of the brain. In this case, patients experience disruption of the functions for which this area is responsible:
- speech,
- logical thinking,
- establishing a cause-and-effect relationship,
- math skills,
- the ability to write and read.
Memory loss accompanies various forms of acute cerebrovascular accidents. There is a pattern of such a violation - first current events are forgotten, then the immediate past, and the long past is preserved for the longest period of time. Restoration occurs in reverse order. In this case, the patient can fill in the lost periods of time with fictitious ones.
The possibilities for rehabilitation of lost abilities depend on the degree of brain damage, age, the presence of vascular diseases, and concomitant pathology. Full recovery occurs in the following cases:
- a relatively young patient without chronic diseases;
- small area of brain destruction;
- early diagnosis and hospitalization;
- a full range of drug treatment;
- help from a speech therapist;
- psychotherapeutic sessions.
Folk Means.RU
Folk Remedies » Blood » Restoring speech after a stroke
Restoring speech after a stroke
More than a third of stroke patients experience speech disorders. I offer exercises to restore speech.
Start your classes with exercises that engage the muscles involved in pronouncing sounds. On the first day, it is enough to do the exercises 2 times, and then add one approach every 3 days. Bring the repetition of each exercise up to 5-7 times. Do the whole complex 5 times a day.
1. Pull your lips out with a tube for 3-5 seconds, then rest for 3-5 seconds, repeat the exercise.
2. With your lower teeth, grab your upper lip with tension for 3-5 seconds, then rest for 3-5 seconds, and then repeat.
3. With your upper teeth, grab the lower lip with tension for 3-5 seconds, then rest for 3-5 seconds, repeat.
4. Stick out your tongue as much as possible and at the same time slowly stretch your neck forward for 3 seconds, return to the starting position within 3 seconds.
5. Lick your lips: first from right to left the upper lip, then from left to right, and then lick the lower lip in the same order.
6. Lick your lips in a circle: first clockwise, then counterclockwise.
7. Try folding your tongue into a tube and stretching it out. Stay in this position for 3 seconds.
8. Open your mouth slightly, try to cup your tongue and hold it there for 3 seconds.
9. Lift the tip of your tongue up and reach the soft palate.
10. Teeth are open, lips are closed. Run your tongue between the upper gums and cheeks to the lower gums clockwise and in the opposite direction.
The next exercise is performed with an assistant. Have your assistant start saying a word and you finish it. For example, an assistant says: “Now a dog is running down the street...”, and you add: “ka.” Start with one syllable, then move to two syllables. For example, the assistant says: “Across the sky
white floats about...”, and you add: “varnish.”
Have your assistant sit next to you and sing the song quietly, in an undertone. Try to pick up the words and join in the singing.
Pronouncing tongue twisters gives a very good effect.
Tongue twisters with the sounds b-p: “The bull is blunt-lipped, the dumb-lipped bull”, “The bull had a white lip and was dumb.”
Tongue twisters with the sounds l -v: “The queen gave the gentleman a caravel, the queen and the gentleman retired to the caravel.” “The cap is sewn, but not in the Kolpakov style; the bell is poured, but not in the Kolokolov style. It is necessary to re-cap and re-cap. We need to re-bell the bell, and re-bell it.” “The butt is on the head, the cap is on the butt. A shock under the butt, a priest under the cap.”
Improve the articulation of tongue twisters with the sounds r and v. “There is grass in the yard, there is firewood on the grass, don’t cut wood on the grass in the yard.”
Alexander Vladimirovich Goyaovkov.
How speech can be impaired
By the end of the acute period of stroke, 35% of patients remain with a speech defect in the form of aphasia. It comes in several forms, since different areas of the brain are responsible for speech:
| Brain zones | Brief description of aphasia |
| Inferior parts of the frontal gyrus, Broca's area | it is impossible to switch from the pronunciation of one sound to another, the patient communicates with sounds, but can write and read; |
| Temporal region | do not understand the addressed speech; |
| Middle temporal gyrus | do not perceive the meaning of words by ear and cannot name the objects depicted in the pictures; |
| Parietal zone | do not remember the names of objects or actions, cannot construct complex speech structures; |
| Frontal lobes | unable to formulate and pronounce a sentence, communication with others is impaired. |
If the sensory (perceptive) and motor (motor) speech zones are damaged, then a mixed form develops - total aphasia, in which the patient cannot speak and does not understand speech.
If the cerebellum, brainstem, cortical and subcortical zones are damaged, dysarthria may also occur. It is due to the fact that the muscles involved in pronouncing words weaken. In this case, the patient hears well, sees and is fully aware of the meaning of what was said, but cannot speak. This disorder is characterized by a more favorable course.
Speech defects are not necessarily expressed in complete or partial absence of speech. With damage to the cerebral cortex, the patient may become verbose, but confuses the meaning of words, replaces them with similar sounds, or loses the ability to remember a name, the name of an object or an action. It is impossible to understand such people, despite the fact that they pronounce words normally.
Watch the video about speech impairment (aphasia) after a stroke:
The work of a speech therapist to restore speech
The beginning of classes takes place with the passive participation of the patient. In the acute period, the speech therapist determines:
- possibility of contact,
- speech abilities,
- preservation of intellect,
- emotional background.
The first sessions are predominantly psychotherapeutic in nature and are conducted to instill in the patient faith in recovery. The specific form of speech loss becomes clear by 20–25 days from the onset of the stroke. From this moment until the sixth month, the most productive work on recovery takes place. It includes:
In a later period, work is carried out to distinguish the meaning of similar-sounding words, develop vocabulary, restore literacy, speech memory, and write texts. The advantage of classes with a speech therapist is the correct technique, which allows you to use various functions of the brain; if complete rehabilitation is not possible, it helps to compensate for speech impairment for effective communication.
In addition, the emotional background has a great influence on the patient. It is difficult for the layperson and loved one to remain completely neutral and not show frustration or impatience. Classes last from 15 to 40 minutes at least 2 times a week for 2 - 3 months, then you can stop the process for 1 - 2 months, and then resume again.
Practical exercises at home for speech, memory
If it is not possible to study with a speech therapist, then classes can be done at home on your own. They are less effective, but with some persistence they help make progress. It is first necessary for a speech therapist to examine the patient and recommend the necessary exercises.
They may involve selecting part of a word, folding cubes or cards with syllables, learning words and then texts, naming depicted objects or describing actions based on a picture. In addition, pronunciation training is recommended for all patients. Each exercise is repeated from 7 to 10 times:
- stretch your lips into a tube;
- grab your lower lip with your upper lip;
- open your mouth and stick out your tongue as much as possible, try to reach their chin;
- lick your lips with your tongue in a circle (outside and inside the oral cavity);
- turn the tongue towards the soft palate;
- smile broadly.
Causes of aphasia
When a person loses the ability to speak, this phenomenon is commonly called aphasia in medicine. Pathology makes itself felt due to impaired blood flow in the brain. This process, in turn, provokes tissue atrophy, especially the departments responsible for the perception and processing of incoming information.
Reference! Usually, immediately after an acute attack, there is a lack of speech. The site of the lesion itself is in the prefrontal areas of the brain.
In order to fully restore speech function, a lot of time must pass. This period depends on the following factors:
- degree of neglect of the disease;
- type of memory loss;
- timeliness of starting the fight against the disease;
- localization of the lesion;
- volume of cerebral blood flow.
It is worth understanding that after a stroke there is a chance of regaining normal speech. However, it is very difficult to predict what the period of speech rehabilitation will be, because it depends on each specific clinical case. A patient who has lost speech must make great efforts to recover. They should be aimed at implementing all the recommendations of relevant specialists, which will be discussed below.
What is the likelihood of recovery for young people?
Resuming speech usually requires a fairly long period, since it is necessary not only to teach a person to pronounce sounds and words correctly, but also to fully communicate with others. The earlier the restoration of speech function begins, the greater the chances of success.
At a young age, the rehabilitation process proceeds much faster, this is due to the fact that usually one area of the brain is damaged, and the hemorrhagic form of stroke is more common. With this type of disease, the cerebral cortex is less often affected, and the perception and understanding of speech and intellectual abilities are not affected.
As a rule, this will take 4 - 5 months. With a major stroke, improvement in this function continues throughout the year; there are known cases of complete rehabilitation at a later date.
Restoring speech abilities
How to restore lost function and teach a person to speak again?
Like any lost brain function, speech loss does not return immediately.
In 70% of cases this process is very slow.
The maximum recovery period can reach 3-5 years.
If the disturbances do not go away within this period, then speech most likely will not return.
Basic rules to follow:
- constant work on oneself;
- alternation of periods of active exercise must be observed;
- gradual increase in lesson time;
- contact specialized specialists: rehabilitation specialist, neurologist, speech therapist.
Important! Treatment should be based solely on a systematic approach.
Use of medications
Some may question how a person can be taught to speak using drugs.
However, they play a big role in restoring brain function, and this means speech.
The drug therapy prescribed by the doctor will depend solely on the severity of the patient’s condition.
If the disorders are not global, then the following types of drugs are used:
- anticoagulants , which help reduce blood clotting;
- nootropics that restore full brain activity;
- antihypertensive medications that reduce blood pressure;
- diureticsprescribed to relieve swelling of the brain, fluid is removed from the body faster.
If the rehabilitation process is very complex, then doctors move on to therapy with more serious drugs:
- Gliatilin;
- Ceraxon;
- Actovegin;
- Maxidol.
All of the above drugs provoke rapid regeneration of dead neurons. In addition, a method associated with stem cells is often used. For these purposes, doctors take biomaterial from the patient, grow it under artificial conditions, and then gradually introduce it into the patient’s body.
Classes with a speech therapist
The first thing you need to do before starting to restore speech is to contact a speech therapist who specializes in post-stroke patients. He will determine the nature of the loss of abilities and create a personal program suitable for this particular patient. With an appropriate approach, already a third of patients begin to talk at the stage of discharge from a medical institution.
Attention! You need to practice on your own at home. From time to time you will have to visit a specialist for speech correction.
Speech therapy classes can also be carried out at home, but then a speech therapist will have to be called privately.
Next, we’ll talk about the key techniques and principles of a specialist’s work:
- identifying the patient’s reaction to a weak voice and a fairly loud sound;
- increasing the load should be carried out in stages;
- only after mastering simple functions, you need to move on to studying more complex ones;
- It is necessary to monitor not only diction, but also how the patient understands the meaning of phrases and words;
- technique is used: the specialist starts, the patient finishes;
- musical techniques are used. The patient tries to sing along to his favorite songs;
- Pronunciation training should be combined with drawing. What the post-stroke patient is unable to say out loud, he depicts on paper.
All data received have a positive effect on speech restoration.
Exercises
Is it possible to restore speech without contacting a specialist?
It's practically unrealistic.
It is the speech therapist who must outline the stages of rehabilitation and monitor the process.
However, the patient can train himself in front of the mirror every day, performing various exercises, and from time to time conducting control sessions with a specialist.
How to restore speech with the help of exercises, even at home? Regardless of the type of speech loss, a person needs to perform special movements with the speech apparatus. This is due to the fact that a mixed type of aphasia is often recorded.
Effective techniques include the following:
- doctors advise stretching both lips so that they take the shape of a tube and remain in the corresponding position for 7 seconds. The number of repetitions is 5-10 times;
- the upper lip usually tightens the lower lip, it is recommended to hold in this state for 5 seconds and repeat the exercise up to 10 times;
- you need to open your mouth , and try to stretch your neck and head a little forward, your tongue extending out of your mouth as much as possible. The person lingers in the corresponding position for several seconds. The number of repetitions is the same as in the previous two methods;
- You should lick your upper and lower lips . First this is done from right to left, and then in the opposite direction;
- to lick your lips with your tongue several times , following a circular direction in different directions;
- the tongue is curled into a narrow tube and in this position is pulled out;
- with your mouth closed, experts advise turning your tongue up and trying to reach the roof of your mouth;
- It is recommended to cover your mouth so that your lips are closed. Between them and the teeth it is necessary to carry out circular movements in different directions;
- It is recommended to click your tongue on the hard palate. When done correctly, the sound resembles the noise of a fast galloping horse;
- from the mouth and moves forward as much as possible , emitting a somewhat hissing sound reminiscent of a snake;
- It is recommended to blow a kiss with a smack;
- the tongue protrudes and alternately reaches up to the tip of the nose;
- you need to try to smile with your mouth closed , and then open your lips and show your teeth.
Important! Any exercise to develop the speech apparatus should be performed 5-10 times, depending on how you feel.
Useful video
We invite you to watch the exercises for speech restoration on video:
Tongue Twisters
Tongue twisters help people restore speech not only after a severe form of stroke, but also after other diseases.
The sounds that are emphasized are determined by a specialist after a preliminary examination of the patient.
Tongue twisters for speech development will be an excellent solution for practicing at home without a speech therapist.
Here are examples of some of them:
- Alyosha gives a signal to Alena. Alena will hear and find Lesha.
- Arina and Agrafena's dahlias are growing.
- Borya gave Ira toffee, Ira Borya gave barberry.
- All beavers are kind to their cubs. The beavers go to their forests.
- Marusya was bought beautiful beads by her beloved grandmother.
- The bull is fed with the bull, they run around in a circle, take care of the runner's sides from the aggressive bull.
- The barrel rested for itself.
- The crow missed the little crow.
- Thieves stole all the firewood from the widow Varvara's yard. The widow got angry and removed all the wood. In the stable with the wise men, the magician practiced magic.
It is recommended to repeat tongue twisters several times on a systematic basis.
How tongue twisters can help
For the treatment of patients with dysarthria, along with gymnastics and myostimulation, exercises for pronouncing tongue twisters are indicated. These speech forms are aimed at pronouncing a letter or combination; they help eliminate articulation disorders. Only a speech therapist or neurophysiologist can choose the right type of sayings correctly.
For independent training, you need to change the letter that is most often found in the phrase every day. Some patients find it easier to sing tongue twisters at first.