21.02.2017
Pinchuk Elena Anatolyevna
Deputy chief physician for medical work, kmn, neurologist, doctor of physical and rehabilitation medicine
Maltseva Marina Arnoldovna
Head of the consultation department - neurologist, specialist in the field of extrapyramidal pathologies, doctor of the highest category
Kritskaya Olga Pavlovna
Neurologist, highest category
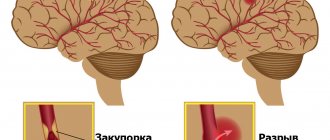
The term stroke is understood as an acute disorder of cerebral circulation with a persistent decrease or complete loss of certain body functions. A stroke can be a focal stroke (micro-stroke) or extensive, in which paresis can occur, most often of one half of the body. A condition in which a person experiences weakness or complete lack of movement in the left or right half of the body is called hemiparesis. Paralysis of the left side or paralysis of the right side during a stroke often occurs as a result of rupture of a cerebral artery, if qualified help is not sought in a timely manner.
Recovery from paralysis after stroke
Paralysis after a stroke indicates that ischemia or even necrosis of a large area of the cerebral cortex has occurred. If paralysis develops, the victim needs immediate, highly qualified medical care, which can be obtained at the Clinical Institute of the Brain, which employs highly qualified neurological and vascular specialists. Treatment largely depends on topical diagnosis and determination of the form of stroke. Treatment can be carried out conservatively or operatively (surgically).
Often, a paralyzed person after a stroke needs surgery, which consists of making a burr hole in the skull to avoid serious complications associated with compression and dislocation of the brain.
Symptoms of a left-sided stroke
Please note: Increasing headaches in the evening, which are not helped by analgesics, as well as a sharp increase in blood pressure and tinnitus, are one of the precursors of a hemorrhagic stroke. Common clinical signs of stroke development are also:
- profuse sweating;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- weakening of the pulse;
- loss of touch on the affected side of the body;
- general weakness;
- numbness of the limbs;
- articulation disorder;
- weakening or loss of vision in one eye (if the lesion is localized in the occipital lobe);
- loss of orientation in space;
- loss of coordination (if the pathological process has affected the cerebellum);
- difficulty swallowing;
- disturbance of the respiratory rhythm (if the focus is in the brain stem).
A left-sided stroke often leads to the development of paralysis of the right side of the body, which is manifested by the disappearance of all forms of sensitivity and a sharp change in muscle tone. Damage to the left hemisphere is characterized by motor aphasia (severe speech impairment). In relatively mild cases, the patient pronounces individual nouns (the symptom is called “telegraphic style”), and against the background of extensive damage, speech virtually disappears.
Important: Speech disorders significantly complicate the diagnosis.
When the lesion is localized in the left hemisphere, a disorder of logical thinking occurs. Patients are very often depressed if the neurons of the left temporal lobe are affected.
First aid
This involves hospitalizing the victim as quickly as possible. To do this, when identifying signs of a stroke, you must first report the incident to the emergency medical service and call a specialized team. It is necessary to provide the patient with rest, a supine position and an influx of fresh air. At home, it is unlikely that anything can be done to prevent the progression of a stroke. Only early initiation of drug therapy or surgery can prevent serious health consequences from a stroke.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 3/5 — 11 votes
Share article on social networks
Specifics of treatment of strokes of the left hemisphere of the brain
The main goal of stroke therapy is to restore damaged nerve cells. The basic principles of treatment are:
- urgency;
- complexity;
- phasing.
In clinical practice, there is the concept of a “therapeutic window”. This is a time period during which it is quite possible to fully or at least partially restore potentially reversible pathological changes in brain cells during a left-sided stroke. Its duration is from 3 to 6 hours, during which the patient must be admitted to the hospital.
Hemorrhagic strokes require surgery to remove the hematoma. Treatment of ischemic strokes involves active therapy to quickly restore cerebral blood flow.
Important: For still unknown reasons, nerve cells in the left hemisphere die more slowly than neurons on the right side, and recovery from paralysis on the right side is faster.
Of great importance is the establishment of the mechanism of development of acute cerebrovascular accident and identification of the main etiological factor in order to eliminate it as quickly as possible. In case of a stroke on the left side, recovery requires a timely (as acute symptoms subside) initiation of rehabilitation measures. To prevent the appearance of bedsores, muscle contractures and a number of other complications, the patient is recommended to undergo a complex of physiotherapeutic procedures, selective or general therapeutic massage, electrical stimulation, kinesiotherapy, and reflexology.
Please note: Kinesiotherapy creates favorable conditions for the victim’s rapid adaptation to physical activity. Massage is necessary to influence the receptor zones in order to obtain a general reflex response.
To improve the functioning of the central and peripheral nervous system, vitamin therapy (B vitamins and nicotinic acid - PP) is prescribed. To cope with depression and causeless mood swings, a patient recovering from a stroke on the left side needs the help of a specialist psychotherapist. It is advisable that psychotherapy sessions be carried out regularly, for which a stay in a specialized clinic or rehabilitation center is recommended. Treatment of speech disorders is carried out under the supervision of a speech therapist. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe medication. Some patients are advised to take drugs from the group of tricyclic antidepressants.
With a stroke on the left side, restoration of motor activity can begin 1-2 weeks after the episode of acute cerebral circulation disorder, and the patient requires absolute rest for the first days. If rehabilitation begins a month or more after the stroke, the prognosis worsens significantly against the background of asthenic-depressive disorders.
Please note: For left-sided lesions, approximately every third patient has a parallel development of right-sided sensory impairment and sensorimotor deficit, which significantly complicates the restoration of walking.
Afferent paresis is also often observed, which is characterized by difficulty in performing purposeful movements against the background of complete preservation of the strength and range of movements of the arms and legs. With the so-called thalamic syndrome after a stroke on the left side, which is accompanied by intense pain on the right side of the body, recovery may require the use of opioid painkillers, as well as medications that reduce paroxysmal activity of the central nervous system.
The text was checked by expert doctors: Head of the socio-psychological service of the Alkoklinik MC, psychologist Yu.P. Baranova, L.A. Serova, a psychiatrist-narcologist.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 798-30-80
Call! We work around the clock!
Programs:
Assessment of rehabilitation potential
Movement restoration
Rehabilitation after stroke
Restoration of cognitive functions
Early (resuscitation) rehabilitation
What you need to know
The disease entails severe complications. The main condition is rest and minimal activity, this in turn contributes to the development of bedsores, pneumonia, thrombosis, loss of sensitivity, and mental disorders. Therefore, care for the patient must be taken responsibly. A comprehensive rehabilitation program is required:
- Drug treatment (drugs: nootropic, erythrocyte, platelet, vasoactive, angioprotective).
- Vitamins . Taking vitamins plays an important role in restoring the body and restarting metabolism. For a speedy recovery, you need to establish a balanced diet, and if necessary, consult a nutritionist to reduce body weight.
- Physiotherapy. One of the successful areas in the fight against the disease is physiotherapeutic procedures. Having diagnosed paralysis of the left side after a stroke, treatment with physiotherapy is simply necessary. With the help of modern equipment, it is possible to restore the functioning of nerve endings and make the remaining parts of the brain function. Achieve activity of the affected parts using artificially created impulses. The following physiotherapy procedures are effective:
- kinesitherapy;
- magnetic stimulation;
- physiotherapy;
- micropolarization;
- neuromyostimulation.
- Psychological support.
Treatment of disorders is a long process; relatives need to be patient and strong. The center’s specialists successfully cope with the most complex diseases. Modern equipment, successful experience, participation in world scientific conferences, the use of innovative methods, and most importantly, a sincere interest in achieving results - all this allows us to return to a full life, including patients who have suffered complete paralysis after a stroke.
Features of patient care after a stroke
Features of patient care after a stroke.
Stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, most often developing as a complication of hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, cerebral vascular abnormalities, aneurysms, and diabetes mellitus.
If your ward has one of the diseases listed above, there is a risk of stroke. We will analyze the symptoms of the disease in order to provide first aid in a timely manner during an attack.
There are hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes (cerebral infarction), as well as subarachnoid hemorrhage.
| Hemorrhagic stroke | Ischemic stroke |
| The development of a stroke may be accompanied by emotional distress or physical stress. | Provoking factors include emotional stress, fatigue, and infectious diseases. |
| This is a cerebral hemorrhage. Occurs as a result of rupture of an artery due to fluctuations in blood pressure or the functional state of blood vessels. | Occurs in old age as a result of blockage (thrombosis or embolus) or sharp narrowing of atherosclerotic cerebral vessels. |
|
|
There is also a subarachnoid hemorrhage, which occurs when a cerebral aneurysm ruptures. Characteristic
| |
Home care for patients after a stroke
No matter how severe the stroke may be, with proper treatment and the patient’s active participation in rehabilitation procedures, most of the body’s functions are restored.
The patient needs a full range of procedures for rehabilitation, including therapeutic exercises and massage.
Turn a bedridden patient every two hours to prevent the formation of bedsores. Properly position the patient's paralyzed arm and leg:
In the supine position:
1. To prevent the development of stiffness in the shoulder joint and the appearance of pain in it:
• Place a stool next to the bed, on the side of the paralyzed side, and place a large pillow on it so that the corner of the pillow is under the patient’s shoulder joint.
• Extend your client's arm at the elbow. Place it palm up, straighten your fingers, apply a splint and bandage it to your arm. The longueta should reach the middle of the forearm.
• Move the patient's arm to the side 90° (maintaining a palm-up position) and place it on a pillow so that the shoulder joint and the entire arm are at the same level horizontally.
• Place a roller between your arm and chest so as to fix the arm in the correct position; if necessary, place a 0.5 kg sand bag on the roller.
2. Bend the patient’s paralyzed leg at the knee 15-20°. Place a cushion under your knee.
3. Place your foot in the middle position between flexion and extension and secure it with a stand.
In the “healthy side” position:
• bend the patient’s paralyzed arm at the shoulder and elbow joints and place a pillow under it;
• bend the paralyzed leg at the hip, knee and ankle joints and place a pillow under it.
In the “lying on the paralyzed side” position:
• tilt the patient's head down slightly;
• Stretch the patient’s paralyzed arm forward at a right angle to the body and turn it palm up;
• place the patient’s healthy arm to one side or move it back (but not forward!);
• slightly bend the patient's paralyzed leg at the knee joint, but straighten it at the hip;
• Bend your healthy leg at the hip and knee joints and place a pillow under it.
To maintain mobility of the joints in the paralyzed arm and leg, perform “passive exercises” with the patient: first take the patient’s hand and carefully make certain movements, and then make movements with the patient’s paralyzed leg.
Perform a set of therapeutic exercises with your ward every 4 hours.
Make sure that the movements are smooth and do not cause pain.
Make sure that the patient does breathing exercises. Breathing affects muscle tone.
Keep in mind that the behavior of patients with right-sided paralysis differs from the behavior of patients with left-sided paralysis.
| Right-sided violation - paralysis of the left side of the body | Left-sided violation - paralysis of the right side of the body |
| Underestimating the scale of movement disorders, the patient is indifferent to his situation. | Lethargy, passivity, loss of complex emotional experiences. |
Characteristic:
| Characteristic:
|
|
|
Restoring motor activity after a stroke.
Exiting bed rest should be done gradually and only in consultation with a doctor.
First, they teach the patient to sit down, then do exercises for the legs, then stand up, and only then walk.
If the person in your care cannot sit up independently:
1. Help him sit up first.
2. Then he needs to learn to sit in bed.
3. Provide the bed with special devices so that the patient can sit up without your help.
4. Teach the patient to lower his legs from the bed and transfer to a nearby chair or wheelchair.
5. Gradually teach the patient:
1) stand;
2) transfer the weight of the body from one side of the body to the other;
3) take steps on the spot;
4) to learn to walk, purchase a walker.
6. When teaching walking, stay close to the patient on the affected side.
Helping patients eat after a stroke.
The physician should assess the patient's ability to swallow and chew and prescribe an appropriate diet.
It is easier for a patient with impaired chewing and swallowing functions to swallow soft food than liquid food.
If you are drooling from the paralyzed side of your mouth, make sure your face is dry and clean. Lubricate the skin near your mouth with a protective cream.
Always serve food to your client from the side, on the uninjured side, and place it on the side of the mouth that is not affected.
After eating, make sure that there is no food left in the patient's mouth.
Monitoring the patient.
Watch your skin and take all measures to prevent bedsores.
Such patients often have urinary and fecal incontinence; take proper care of the patient.
To restore a normal sleep cycle:
• lower the air temperature in the patient's room at night;
• reduce the calorie content of food and its temperature (after a hot, hearty meal a person falls asleep);
• organize your ward's daytime so that he has something to do all the time.
Call a doctor if
• there was an increase in temperature, severe pain in the side. Bedridden patients have a high risk of pneumonia;
• swelling appears on the paralyzed side - this may be a sign of vein thrombosis.
Provide your client with emotional support. Reassure him that his family loves and appreciates him regardless of his condition.
https://schule.bz/osobennosti-uhoda-za-bolnimi