Parkinson's disease is the name of a slowly developing pathology of the central nervous system. The main symptoms of the disease include movement disorders, muscle rigidity (increased tone), tremors at rest.
Carriers of the pathology experience not only vegetative, but also affective disorders. Neurologists diagnose patients with true parkinsonism - Parkinson's disease - and parkinsonism syndrome. The latter becomes a complication of other neurological diseases: malignant brain tumors, strokes, encephalitis, etc.
Classification of pathology
The most widespread approach in neurology is based on the patient’s age at the time the first symptoms of Parkinson’s disease were detected. Based on this data, the following are distinguished:
- juvenile parkinsonism;
- pathology with early onset;
- disease with late onset.
An alternative approach to the classification of Parkinson's disease is based on the pattern of changes in the kinematics of movements of the upper and lower extremities of patients. In this case, parkinsonism syndromes are divided into tremulous, tremulous-rigid, rigid-tremor, akinetic-rigid and mixed.
Both classifications given are conditional. Neurologists still have not developed a unified approach to the types and forms of Parkinson's disease.
Symptoms of pathology
Destructive processes in the central nervous system provoke the development of the main symptoms:
- tremor;
- rigidity;
- hypokinesia (limited mobility);
- violations of translational regulation.
True parkinsonism is characterized by recurrent or constant episodes of tremors. The pathology is characterized by a looped movement of the patient’s limbs at rest.
In the early stages of the syndrome, muscle rigidity remains relatively unnoticed. As other symptoms develop, constant muscle tone causes more and more discomfort to the patient. Asymmetry in muscle tension remains one of the main diagnostic markers in the early stages of Parkinson's disease.
Neurologists distinguish several stages in the development of pathology. In the educational literature for medical universities, the classification of Hoehn and Yahr is often given. Its basic provisions are presented in the table.
| Stage | Description |
| Zero | There are no motor symptoms of parkinsonism |
| First | Pathology manifests itself unilaterally |
| Second | A complex of bilateral symptoms is formed |
| Third | Noticeable translational instability develops, but the patient retains the ability to care for himself independently |
| Fourth | Rapid degradation of motor activity, the patient can only stand and move short distances without assistance |
| Fifth | The patient cannot leave the chair or bed without the help of doctors or relatives |
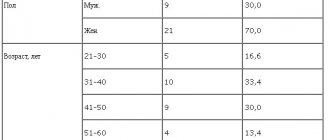
Symptoms and signs of Parkinson's disease are the same in women and men. Gender and age differences in the diagnosis of pathology turn out to be insignificant.
Are you experiencing symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
What are the manifestations of drug-induced parkinsonism?
The incubation period for the onset of development of this phenomenon ranges from several days to months. In almost 90% of LA lesions, it begins in the first three months of therapeutic measures. Since recognizing the first signs is a difficult process, the patient continues to use prescribed medications, which ultimately causes an increase in the symptoms of the disease. Clinical indications are similar to complaints in Parkinson's. Often, in certain situations, the only problem is the presence of hypokinesia. In addition, experts identify the following symptoms:
- General weakness of the whole body.
- Decreased motor activity of the body and facial expressions.
- No friendly hesitation.
- Sluggish ability to gesture.
- Coordination problems in the wrist.
- Change in gait.
- Some people experience numbness while moving.
- Formation of rigidity in muscle areas.
- Formation of a typical resting tremor.
- Trembling of the arms and legs, chin and perioral region.
- The likelihood of hearing loss and some types of cognitive manifestations.
Consequences
When the body is affected by the LP in older people, their general health begins to deteriorate. As a result of postural instability, pensioners often fall, resulting in various injuries and damages (in some cases even fractures, since many develop osteoporosis). If all the symptoms of the anomaly are ignored, the lesion begins to spread to the motor elements, which can cause complete inability to move independently. In addition, doctors diagnose a decrease in positive attitude and the formation of isolation, which flows into a depressive state.
Diagnostic measures
The diagnosis is made by a neurologist. It may take the doctor a significant amount of time to differentiate the diagnosis and conduct various functional tests.
Early-onset parkinsonism is characterized by severe limitation in movement with regular attacks of tremor (the frequency of oscillations of the limbs of patients is 4-6 Hz). The clinical picture is complemented by postural instability, which is not associated with cerebellar disorders or injuries received by the patient.
Diagnostic procedures include:
- EEG;
- rheoencephalography;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment strategies for Parkinson's disease depend on the stage at which the patient begins receiving the necessary therapy. For this reason, neurologists prefer to separate therapeutic approaches aimed at relieving early and late symptoms.
Treatment in the early stages involves the use of medications that stimulate the synthesis of dopamine in the brain. The therapeutic effect is achieved by stimulating dopamine releases and blocking reuptake. Thanks to this, it is possible to reduce the rate of neuronal death. Basic drugs can be used as part of complex treatment or as monotherapy. The combination of necessary substances is selected by a neurologist based on the clinical picture of parkinsonism and the individual characteristics of the patients.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease in the later stages remains an inevitable stage, since drug therapy can only slow down destructive processes. Progressive pathology is complemented by new symptoms that are difficult to relieve. At a certain point, the usual effectiveness of medications decreases. The patient experiences hypersensitivity of dopamine receptors and a kind of withdrawal syndrome due to the body's resistance to substances taken for a long time.
Against this background, doctors are forced to prescribe constantly increasing doses of medications to patients by reducing the intervals between doses. An alternative solution is to switch to a combination treatment regimen, which uses drugs from several groups. In some cases, surgery may be possible to implant an electrode into the patient that provides deep brain stimulation. This method allows you to stop resting tremor and restore motor activity in people suffering from Parkinson's disease.
Main sources of drug-induced parkinsonism
The etiological cause that provokes the dosage form of PS is the long-term use of medications that have a blocking effect on the receptors involved in the production of the hormone dopamine. Typically, many people associate LP with therapeutic treatment of antipsychotic medications. However, the list of other pathogens that cause active disease is extensive. This includes:
- Sympatholytics of central use - used as a therapeutic technique for hyperkinesis and other variants of such pathological processes (the provocative effect of the described disease occurs due to the depletion of dopamine reserves in the cavities of the synaptic sections).
- Metoclopramide - often prescribed by specialists for regular vomiting (it is structurally similar to the drug chlorpromazine, which has a blocking effect on the postsynaptic endings of dopamine receptors).
- Calcium antagonists - accompanied by blocking of dophreceptors, a decrease in the amount of neurotransmitter in the presynaptic sections (as a result, the patient begins to lack dophrase transmission).
- Anticonvulsants have an adverse toxic effect on hormonal structures.
- Other types of medical elements - there are rare variants of the development of LP when taking certain components, for example: amiodarone, phenytoin, etc.
Possible cases of complications in treatment may arise in a situation where the patient has used large dosages of the described substances for a long time. In addition, the direct factors of the disease include provoking factors that have the ability to significantly increase the degree of progression. Such pathogens include:
- The patient has disorders of an extrapyramidal nature.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Presence of depression.
- HIV infection.
Doctors included elderly female people with some painful lesions, patients with a limited form of brain abnormality (for example, after a stroke, TBI, degenerative disorders, etc.) into the high-risk group.
Questions and answers
Can true parkinsonism be cured?
Modern pharmacology and medicine do not have the means to completely cure Parkinson's disease. The treatment regimens used are aimed at slowing down destructive changes, relieving the main symptoms and improving the quality of life of people suffering from parkinsonism. Treatment methods for Parkinson's disease and the causes of this pathology are still being closely studied by the world's leading scientists. It is possible that in the foreseeable future there will be a breakthrough in medicine.
How to predict the life expectancy of a patient with Parkinson's disease?
The prognosis is formed by the attending physician based on the clinical picture, chronic pathologies of the patient and the results of diagnostic procedures. Assessing the prospects for treatment is a difficult task, since neurologists cannot predict in advance the human body's response to drug therapy.
Is it possible to eliminate the possible causes of Parkinson's disease in youth and avoid the development of pathology in adulthood?
Neurologists believe that parkinsonism is a genetically determined pathology. For this reason, the development of an effective set of preventive measures is not possible. Note that the symptoms and signs of Parkinson's disease in the early stages remain insufficiently pronounced to take emergency measures.
Etiology
The main reasons for the development of parkinsonism include:
- medications (neuroleptics, metoclopramide, prochlorperazine);
- intoxication;
- viral encephalitis;
- structural changes in the brain matter after strokes, tumors and other cerebral pathologies;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- vascular disorders;
- Wilson-Konovalov disease.
Parkinsonism can also occur against the background of other neurodegenerative diseases: Alzheimer's disease, multifocal system atrophy, dementia with Lewy bodies, etc.