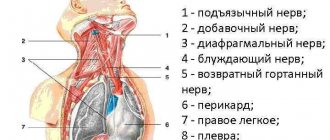
The trigeminal nerve is a ganglion that gives rise to three “branches” that exit directly from the brain stem. Three “branches” reach directly to the human face, supplying it with nerves and connecting it with the central nervous system.
The trigeminal nerve exits the skull through three different foramina. The first “branch” comes out through symmetrical points that are located slightly above the person’s eyebrows (the so-called ocular process). The second, emerging, passes along both sides of the nose (just below the eye area and close to the cheeks) and is therefore called the maxillary, the third “branch” exits in the lower jaw (mandibular) in the direction from the corners of the mouth to its center.
With inflammation of various processes of the trigeminal nerve, pain is observed, localized in various places of the face. When the first “branch” is inflamed, pain occurs above or below the brow ridge, in the forehead and in the front part of the temporal region of the head. When the second and third “branches” of the trigeminal nerve become inflamed, pain occurs in the upper and lower jaws, respectively, which, in turn, causes severe toothache.
Next, we will talk about the types of neuralgia, causes and methods of treatment. But if you are experiencing unbearable pain right now, make an appointment with us. When making an appointment, tell the administrator that you need emergency assistance, and they will find an appointment for you as soon as possible. An appointment with a dentist can be made by calling 8 or using the online appointment form.
Types of trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is divided into two types. The first, the so-called true trigeminal neuralgia, is a holistic disease caused in most cases by compression of the nerve or disruption of the blood supply. The second type - secondary trigeminal neuralgia - is a symptom of a general disease of the body. It could be a tumor or a serious infection.
In most cases, doctors diagnose inflammation of one of the processes of the trigeminal nerve, but in some situations inflammation of two or three processes occurs at once. Inflammation can affect either one side of the face or both, and in different combinations.
Clinical manifestations of the disease
The main symptom of the disease is severe, current-like, throbbing pain in the face. The place in which it is felt depends on which branch of the trigeminal nerve is involved in the pathological process. The pain syndrome can last from a few seconds to a couple of minutes, which brings unbearable torment to the patient. The chronic course of the disease even causes suicidal thoughts.
Pain from trigeminal neuritis may be accompanied by:
- lacrimation;
- increased salivation;
- facial tics;
- cramps of the masticatory muscles;
- numbness of the affected area of the face;
- difficulty with facial expressions and speech.
Pain syndrome can be provoked by:
- hypothermia;
- eating spicy food and strong drinks;
- active articulation, during a conversation or smile;
- touching the face while applying makeup or hygiene procedures (washing, brushing teeth, shaving).
Women note that just as a migraine attack can cause trigeminal neuralgia, and vice versa.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Doctors believe that the main cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is compression of it either inside the skull or outside it. Inside the skull, the trigeminal nerve can be compressed as a result of the formation of tumors, in most cases resulting from some kind of head injury.
Also a fairly common cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is internal venous or arterial displacement.
Other causes of trigeminal neuralgia include:
- the presence of a chronic inflammatory process, viral or bacterial infection in the body;
- herpes infection (herpes);
- a brain tumor;
- scarring in the brain stem;
- failure of anesthesia during treatment or tooth extraction.
Most often, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve affects women at pre-retirement and retirement age (usually from fifty to seventy years). If trigeminal neuralgia is diagnosed in a young man or girl, then most likely its cause is a change in the arteries of a sclerotic nature or a strong dilatation of blood vessels.
Review of effective drugs
There are a lot of medications used to treat colds of the trigeminal nerve. The most popular of them are the following:
- Anticonvulsant medications. They increase muscle tone and also improve nerve patency. The pain subsides after 1-2 days of taking the drugs, and the period of time between attacks increases. Carmabazepine, Phenytoin, Clonazepam, Lamotrigine;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process in the body. Taking them also helps to get rid of pain. Ibuprofen, Nimesil;
- Painkillers and antispasmodics. Relieves pain. This is a very important group of medications, since in some cases the pain is so severe that the patient cannot lead a normal lifestyle. Baralgin, Ketonal, Baclofen, Ketorol;
- Sedatives and antidepressants. They are taken when necessary, since constantly felt pain can provoke increased anxiety and insomnia. Sodium hydroxybutyrate, Amitriptyline;
- Glucocorticosteroids. They relieve existing swelling and accelerate the process of regeneration of nerve tissue. Alclomethasone;
- B vitamins. Stimulate metabolism, reduce pain, and have a beneficial effect on the immune system. Neurobion, Neuromultivit.
Ibuprofen is prescribed to relieve inflammation in the body.
Additionally, the following may be prescribed:
- Antiviral agents. They are aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process in the body. Rimantadine, Arbidol;
- Antibiotics. Perform similar functions with antiviral agents.
The difference is that this group of medications is used in the presence of a bacterial infection. Levofloxacin, Amoxicillin.
As you can see, in order to prevent trigeminal neuralgia, it is necessary not only to monitor your health, but also not to come into contact with the flow of cold air. This can cause not only a common cold, but also more serious health problems.
How does inflammation of the trigeminal nerve manifest?
The main symptom of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is severe pain that occurs in the facial part. The pain really has a powerful force and shooting character, so it is very difficult for the patient to calmly endure painful attacks. The pain intensifies when performing the slightest actions with the facial muscles and jaws - yawning, chewing, laughing, and performing daily oral hygiene. At the same time, the sensitivity of the skin on the inflamed side of the face decreases.
The next painful attack is accompanied by a rapid dilation of the patient’s pupils and the same rapid contraction of facial muscles. Increased tear production may begin.
Pain with trigeminal neuralgia is severe, but not constant. The pain occurs for a few seconds and is interrupted for a while. But if the intervals between painful attacks are short, then it seems that the pain is constant. Trigeminal neuralgia is dangerous because the interval between attacks can be several weeks, and sometimes even several months. But after this period, the pain will certainly return. A long break does not mean that the disease has passed, so if you have already noticed symptoms of neuralgia once, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Why do teeth hurt when the trigeminal nerve is inflamed?
How is inflammation of the trigeminal nerve related to teeth? The connection here is the most direct. Firstly, severe pain during attacks “radiates” to the upper or lower jaw (depending on which nerve extension is inflamed), and sometimes to both jaws. This causes severe and unbearable toothache.
Secondly, those nerves that are found in the upper and lower teeth and gums are directly connected to the trigeminal nerve. The second branch of the trigeminal nerve innervates the upper teeth and gums, and the third, respectively, the lower jaw and gums.
The trigeminal nerve can also be damaged during a number of dental manipulations. Unsuccessful tooth extraction or improper filling, surgical intervention in the jaw structure that ended unsuccessfully, and injuries can cause trigeminal neuralgia.
It is very important to distinguish inflammation of the trigeminal nerve from other diseases of the oral cavity, in particular pulpitis - inflammation of the internal dental tissues. A characteristic sign of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is that, despite severe pain, the sensitivity of the teeth does not increase when they come into contact with cold and hot foods, and hypothermia or heating does not provoke the onset of a new pain attack. Acute tooth sensitivity is a symptom of pulpitis.
When the trigeminal nerve is damaged in the jaw area, acute toothache, pain in the chin, ears and sometimes in the lower lip occurs. The pain may become increasingly intense, and often the patient continues to feel a dull ache after the attack.
Diagnosis and treatment
The main diagnostic methods include:
- CT or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), which can rule out other causes of pain and identify vascular compression of the trigeminal nerve root;
- radiography of the paranasal sinuses to identify chronic inflammatory and other pathological processes;
- consultation with a neurologist;
- OPTG (orthopantomogram), to assess the width of the bone canals;
- dentist consultation;
- general blood analysis.
Treatment of neuralgia includes the following main methods:
- medicinal;
- surgical treatment.
Drug therapy is selected individually for each patient, depending on the severity of the pathology. Surgical treatment is recommended in the absence of clinical effect from drug therapy.
Treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
The first stage of treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is medication. It is aimed at reducing the strength and frequency of pain in the patient. Most often, doctors prescribe anticonvulsants to a patient suffering from trigeminal neuralgia. Sedatives are also used.
Physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as resorption therapy to relieve the inflammatory process, have a good therapeutic effect. Next, the doctor may recommend the use of laser treatment, in which the laser is directed cutaneously to the area where the processes of the trigeminal nerve exit the skull.
Our clinic is located in the same building as the multidisciplinary clinic “Diamed on Shchelkovskaya”, where special conditions for receiving physiotherapeutic procedures are organized for dental patients. The clinic’s physiotherapy room is equipped with modern equipment, including a laser physiotherapy device, with which you will feel relief after the first procedure. The pain will go away and you can return to normal eating. Make an appointment with a dentist by calling 8 or using the online appointment form. The doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and refer you for treatment.
If you are in severe pain, but for some reason you have not yet made an appointment with us, then it can be relieved with folk remedies. Take one tablespoon of yarrow, pour a glass of boiling water, let it brew for one hour and strain. The tincture should be taken one tablespoon before meals three to four times a day.
Treatment
Your doctor will tell you what to do if you have a cold in the peripheral nervous system. It is better not to self-medicate, since therapy depends on the nature of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Treatment of a cold trigeminal nerve includes physiotherapeutic procedures
Treatment options may include:
- Elimination of the inflammatory process. For this purpose, medications are used in the form of tablets, injections or droppers;
- Blockade. This method aims to completely desensitize the affected nerve. It is carried out by introducing painkillers into the body;
- Surgical restoration of nerve tissue in case of injury;
- Taking antidotes if the cause of neuritis is intoxication of the body;
- Antiallergic therapy;
- Surgical intervention can also be expressed in the form of removal or transfer of vessels pressing on the nerve ending.
Treatment of a cold trigeminal nerve often includes physiotherapeutic procedures using UHF and electric currents. Staying in a hospital for no apparent reason is not required.
If the cause of neuritis is not just hypothermia, but some pathological disease in the body, then treatment may require taking additional medications aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease.