What is the trigeminal nerve
The human face has many muscles and nerve endings. Not only the mucous membranes of the nose, pharynx, and conjunctiva, but also the nerve endings can become inflamed. This is most often associated with neurological disorders that change the sensitivity of the fibers that conduct impulses.
With neuropathy of the facial area, acute shooting pain occurs on the right or left. Mirror inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is extremely rare. It is located in the temporal region, near the base of the auricle. And from it there are branches along the entire half of the face:
- jaw nerve (upper and lower);
- optic nerve;
- infraorbital nerve.
The trigeminal nerve passes through the bone tissue in several places, which plays an important role in the occurrence of inflammation associated with pinching. Thus, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can result in acute pain both in the upper and lower jaw, and in the forehead area, covering the eye sockets.
Types of localization operations
Surgical interventions can be performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. The patient must undergo a standard preoperative examination: do an ECG, fluorography, take tests, visit a therapist and an anesthesiologist. The last meal is 12 hours before the intervention.
Trigeminal nerve surgery
Neurotomy is performed when conservative methods are not indicated due to their ineffectiveness in a particular case. Indications: trigeminal neuralgia, malignant neoplasms, increased sweating on one side of the face. The essence of the technique is the intersection of nerve fibers in the place where they exit onto the face.
Sciatic nerve surgery
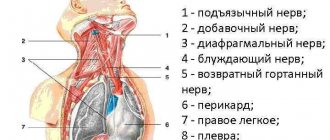
The sciatic nerve is one of the largest; it is an “arch”, the ends of which are at the bottom of the lower extremities, and the top is along the upper edge of the buttocks. A blockade of this nerve trunk is often performed, that is, neurotomy with anesthetics. This is necessary when pinched with very severe pain. This pathology is called “sciatica”. The blockade is indicated for severe back pain and osteochondrosis. It allows you to numb the knee joint, the entire leg, ankles or feet.
Optic nerve
Interventions on it are carried out in cases of nerve fiber atrophy, glaucoma, and to relieve nerve compression. In case of glaucoma, its canal is widened and plastic surgery is performed both on the nerve fiber itself and on the vessels and muscles. In case of atrophy, an alloplant is placed on the nerve, which helps improve blood flow and prevents further atrophy.
Radial nerve surgery
Microsurgical intervention is indicated when conservative treatment is ineffective and compression of the nerve fiber persists, and the cause and timing of the pathology is known. For example, it could be a recent fracture. If microsurgical intervention does not restore limb function over the next few months, then orthopedic surgery is performed.
Median nerve surgery
The median nerve is one of the three main nerve fibers of the arm. It supplies sensitive fibers to the palm, thumb, index, ring finger, some muscles of the hand, and is responsible for the coordination of movements and the functioning of the sweat glands. The most common disease is carpal tunnel syndrome, a type of carpal tunnel syndrome. The nerve fiber is compressed between the dense ligament and the bone walls. Women are more often affected by the disease; its main cause is constant work at the computer. The operation is aimed at opening the carpal tunnel. It is recommended if symptoms persist for six months or more. The intervention may be:
- Open, that is, traditional. An incision up to 5 cm long is made on the wrist. After this, the ligament is divided to increase the volume of the carpal tunnel.
- Closed endoscopic. The surgeon makes only two incisions, 1-1.5 cm long, in the palm and wrist to insert the endoscope and instruments. This procedure provides less postoperative discomfort and faster recovery.
Auditory nerve surgery
Acoustic neuroma occurs in one case in 100,000. In 95% of cases, it is a unilateral tumor. Neuromas are more common in women, in a ratio of about 3 to 2 with men. Tumors are localized in the internal auditory canal. The growth of the tumor is directed towards the direction of least resistance, that is, towards the nerve root in the middle part of the cerebellopontine angle. The tumor can spread to the cranial nerve trunks. The goal of the operation is radical removal of the tumor while maximally preserving the function of nerve fibers and a good quality of life for the patient.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
There are several reasons leading to inflammation of the nerve ducts:
- Poor blood supply associated with physical compression of the nerve. First of all, this is swelling caused by diseases of the ENT organs. The resulting tumor can also pinch the nerves.
- Inflammation associated with dentistry. This includes gingivitis, periodontitis, caries, pulpitis, and eruption of wisdom teeth. Each of these diseases can lead to suppuration, abscesses, swelling and bacterial infections of tissues.
- Medical error by an anesthesiologist - if the injection was given unsuccessfully and the needle got into a nerve, pain cannot be avoided.
- Hypothermia causes muscles to lose their elasticity, which leads to pinching of the nerves passing between the fibers.
- Bacterial infections, in particular tetanus and polio.
- The cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, which is difficult to diagnose, is the psychological state of a person - frequent experiences, stress, and nervous disorders.
To determine the cause of inflammation, you need to consult a specialist.
Treatment methods
Depending on what caused the inflammation, a course of treatment is prescribed. For bacterial lesions, the emphasis is on antibacterial therapy through systemic administration of drugs.
However, regardless of the reasons, the doctor prescribes painkillers to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. It could be:
- ibuprofen;
- paracetamol;
- analgin;
- ketorol;
- diclofenac.
All of the listed drugs can be prescribed either in the form of tablets for oral administration, or prescribed in the form of solutions for intramuscular administration.
When conservative methods are not possible, the help of a surgeon may be needed. This primarily concerns abscesses due to the eruption of wisdom teeth, pulpitis or other dental diseases. In this case, the abscess will be opened, pus will be removed, the wound will be treated with antiseptic, and the tooth will be removed, if necessary. If a pinched nerve occurs as a result of pathologies in the structure of the skull, the surgeon will perform an operation to correct the situation and free the nerve bundles.
As a complex therapy, massage, heating or exposure to a magnetic field and electric current can be prescribed. You cannot massage or warm the inflamed area yourself, because this can lead to complications associated with rupture of the purulent capsule, blood poisoning and paralysis of the facial nerve.
Separately, you may need to consult a neurologist who will determine the cause of the inflammation if other specialists have not found obvious foci of infection and abscesses.
Traditional methods of treatment are permissible only as an addition to the main therapy. For example, rinsing with chamomile decoction will relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. But you can resort to such procedures only with the permission of the attending physician.
Long term forecast
With treatment (and in rarer cases, without it), remission - the symptoms of trigeminal neuritis do not bother you for several months or even years. Many patients are helped by medications, but over time they begin to act weaker, and they have to resort to surgical treatments.
Frequent and severe pain attacks can reduce performance and quality of life. In young patients, the prognosis is more favorable, in older people (and it is in them that the disease occurs more often) it is more serious.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The cause of trigeminal neuritis is not always found. In this case, the disease is called idiopathic . If the damage to the nerve trunks is caused by some other disease, they speak of symptomatic , or secondary , neuritis.
Most often, the disease develops as a result of compression of the nerve by improperly located vessels. In most cases, the superior cerebellar artery is to blame.
Modern medicine sees the mechanism for the development of inflammation and pain as follows. Chronic compression causes the trigeminal nerve to lose myelin , a sheath that is made of fat and is important in conducting nerve impulses. An inflammatory process develops. Subsequently, degeneration of axons - the long processes of nerve cells that make up the nerve fiber.
Possible complications
Doctors call facial paralysis the first complication that appears in the absence of adequate treatment. This means that a person who does not receive medical care in a timely manner is deprived of the opportunity to express his emotions through facial expressions on one side of his face. This condition can no longer be corrected, which will certainly affect the quality of life. Distortion of facial expressions will lead to the development of depression and constant dissatisfaction with one’s appearance. Not every patient can come to terms with irreversible changes in their appearance without deep distress.
One of the most unpleasant manifestations of paralysis is the inability to close the eyelids on the injured side of the face. In this case, the eye will have to be regularly instilled with artificial tears to prevent the cornea from drying out, since natural hydration through blinking becomes unavailable for this eye.
Diagnostics
Based only on a survey, a doctor can distinguish tertiary neuralgia from Sjostad syndrome (with this syndrome, longer attacks), post-herpical pain, and typical migraines. To understand the full picture, it is important to carry out a comprehensive diagnosis:
- Tomography. For accurate diagnosis and correct treatment, the most complete data on the state of the brain and the selection of a detailed scheme (the scheme is important for accurate positioning) when performing magnetic resonance imaging of the ternary nerve are extremely important. The most accurate data can be obtained from MRI with contrast.
- Tomography (scanning) scan of the trigeminal nerve. Makes it possible to create layer-by-layer images, identify neurovascular conflict, signs of destruction of the myelin sheath of nerves. The scan allows the doctor to get a complete picture of what the nerve being examined looks like and what is happening where it exits the brain stem.
- It is extremely important that tomography allows not only to identify that there is a neurovascular conflict, but also to understand its cause. This may be a conflict of the cerebellar arteries, a neuroma (neoplasm) of the nerve. In many cases, the trigeminal nerve scan is performed with a simultaneous scan of the facial nerve.
- X-ray of the jaws (if you suspect that the main problem is dental).
- Angiography. Important for verification (confirmation) of the vascular origin of compression with an impressive size of the aneurysm and vascular loop or aneurysm.
Also, in most cases, blood and urine tests are prescribed (the role of these studies is especially valuable in pathologies that arise as a result of infectious diseases).
Prevention of inflammation
To prevent the risk of developing inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, it is recommended to follow a number of measures:
- monitor oral hygiene and consult a dentist in a timely manner;
- do not stay in the cold for a long time or protect your face from freezing with a scarf;
- do not self-medicate otitis media.
At the first manifestations of pain on the face, you should immediately consult a doctor. This will stop the development of inflammation. In addition, early diagnosis allows for conservative treatment methods.
How does the treatment of neuritis depend on the causes?
If the cause of trigeminal neuritis is not known, all that remains is to deal with its main manifestation – pain. The neurologist prescribes various medications, and if they stop helping, he recommends surgery.
If the cause of the disease is known, you need to try to eliminate it. For example, if a patient is diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, special therapy is prescribed that helps slow down the progression of the pathology. If the nerve is compressed by an artery or the walls of a bone canal, the compression must be removed.
Get a consultation with a doctor
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Sometimes, before the correct diagnosis is finally established, a patient suffering from trigeminal neuritis has to see more than one doctor. It is extremely important to start treating the disease as early as possible. It has been proven that the longer a person suffers from trigeminal neuralgia, the more difficult it is to cope with the pathology.