If you have breast neurosis, you need to get qualified medical help as soon as possible.
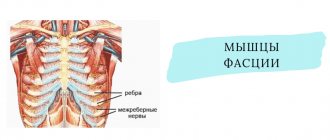
The pathology is characterized by pain in the chest area and between the ribs. In terms of its course, it resembles intercostal neuralgia. Can progress quickly and lead to complications. If you have symptoms of thoracic neurosis, call 8(969)060-93-93 and make an appointment at the Leto mental health center. Our specialists will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis, which will allow you to make the correct diagnosis and select effective treatment.
Where does chest neurosis come from?
The main cause of the disease is prolonged exposure to stress. If a person is under constant tension, his muscle tone increases. Movements become constrained. The muscles periodically spasm, which causes painful cramps. Then any sudden movement causes severe pain.
Negative symptoms persist on an ongoing basis or recur periodically. It often worsens during deep inhalation or exhalation, coughing, or when trying to perform any physical exercise. The patient's condition worsens if he has:
- Diseases of the spinal column. The problem may be associated with inflammation of the roots and joints of the spine, loss of elasticity by the intervertebral discs, etc.
- Curvature of the spine. Lordosis, kyphosis, scoliosis are diagnoses that are more often encountered by people leading a sedentary lifestyle. They slouch and make no attempt to strengthen the muscle corset of the shoulder girdle.
- History of rib fracture. The remaining deformation in the sternum area creates the prerequisites for clamps.
Among the factors complicating the course of breast neurosis:
- general hypothermia of the body;
- pneumonia;
- viral and bacterial diseases;
- pathologies of cardiovascular activity;
- oncological neoplasms in the mammary gland in women;
- diseases of the stomach and intestines.
It will not be possible to heal by eliminating only the physical component of the disease. It is imperative to stabilize the patient’s emotional background. Otherwise, a relapse of the disease will not be long in coming.
Intercostal neuralgia: symptoms, treatment, prevention
What is intercostal neuralgia? It is also called neuralgia of the back. The most important and clearly noticeable symptom of the disease is severe pain. Its main locations are the lower back, back and chest. Other distinctive signs are less pronounced, which is why neuralgia is often confused with other diseases such as heart attack or kidney failure. Although, with a detailed study and thorough examination, it is possible to make the most accurate diagnosis, which means starting treatment in a timely manner and increasing the chances of recovery.
Symptoms
A characteristic symptom of neuralgia is pain. It can be aching, pressing, encircling and even burning. Acute attacks “shoot” at the location of the inflamed nerve. The area may become numb. The skin often experiences tingling and redness. The muscles contract spontaneously. Body temperature rises.
Increased pain is associated with the patient’s physical activity, its level and specificity. With neuralgia of the back, not all exercises cause discomfort, but only those that involve the chest. For example, breathing exercises. Even simple coughing and sneezing, laughing and screaming can cause inconvenience.
The importance of therapeutic measures
Treatment should be prescribed immediately. Otherwise, the patient's quality of life will deteriorate sharply. With the disease, it is impossible to do even simple work - constant pain interferes. Even breathing hurts. Inhalations become less deep, which means less oxygen is supplied. The result is hypoxia. It can lead to such serious consequences as hypertensive crisis, myocardial infarction, and angina pectoris.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the etiology of the disease, and only then can medications and procedures be prescribed.
Etiology of the disease
Intercostal neuralgia appears due to the presence of certain diseases (osteochondrosis, multiple sclerosis, lung damage, colds). Factors that provoke its development are infection, allergic reactions and hypothermia. Stress and injuries to the spinal column, as well as being in an uncomfortable position for a long time, have a negative impact. The situation is aggravated by wearing restrictive lingerie and alcohol abuse.
An integrated approach to treatment
The disease is diagnosed by a neurologist, who also develops a treatment regimen. Its integral part is drug therapy. It includes tablets and injections. With their help, the patient relieves inflammation and eliminates pain. Other treatments include:
- massage (including acupressure);
- electrophoresis (subcutaneous injection of medication with a direct electric current) and phonophoresis (complex medicinal and physiotherapeutic action - ultrasound is done with a special drug, and not a regular gel);
- acupuncture;
- sticking patches (warming, painkillers);
- rubbing in ointments.
Treatment of advanced neuralgia is impossible without tranquilizers and drugs that reduce muscle tone. If the situation requires it, the back muscles are immobilized.
Goals of therapy
The course of treatment is aimed at increasing immunity, eliminating muscle spasms, improving living standards, bringing hormone levels back to normal, restoring the functioning of blood vessels and the heart, eliminating inflammation, developing physical capabilities, reducing discomfort in the back and chest, preventing deformation of intervertebral discs and preventing the development of complications of osteochondrosis.
Prevention measures
Do not aggravate the situation during treatment and after it, monitor your health - try not to get sick during the recovery period, when the body is not stronger.
Avoid hypothermia, frostbite, and drafts. Spend more time outdoors: give preference to walking. Do physical therapy exercises. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Types of pathology
Taking into account the location of the painful area, neurosis is classified into:
- left-handed;
- right-sided;
- bilateral.
The first option is found in medical practice more often than others. When faced with it, people often begin to think that their heart is “naughty.” Therefore, it is important not to delay visiting the doctor. Only differential diagnosis will make it possible to understand the characteristics of unpleasant symptoms and the nature of its origin.
With a right-sided disorder, it is easier to make a correct diagnosis - the doctor and the patient do not have associations with cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, the doctor can immediately assume muscle tension.
The bilateral form is the most painful. The pain has a girdling character and is excruciating. It is necessary to start treatment urgently.
Read also
Fainting
The term “fainting” (syncope, syncope) comes from the Greek word syncope, which means “to interrupt”, “to turn off”.
Fainting is a spontaneous loss of consciousness with a rapid onset associated with a decrease in… Read more
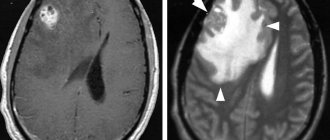
Intracranial hypertension on MRI
Intracranial hypertension is an increase in intracranial pressure. Normal intracranial pressure is 15 mm Hg. When blood pressure doubles, a stroke occurs. At a pressure of 50 mm Hg, the patient can...
More details
Encopresis
Encopresis is a condition in which a person does not control or feel the urge to defecate, and also cannot control the act of defecation itself; Fecal incontinence significantly impairs the patient’s quality of life,...
More details
Myositis
Myositis is a group of diseases characterized by an inflammatory process in skeletal muscles. Depending on the cause of the disease, there are several forms of myositis: Autoimmune…
More details
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease, contrary to popular belief, completely unrelated to attention disorders and senile sclerosis. In this case, the term “sclerosis” means...
More details
How it manifests itself
Signs characteristic of the disorder:
- uncontrolled muscle contractions in the chest area;
- severe pain between the ribs on the right, left or both sides at once;
- discomfort in the lower back, between the shoulder blades;
- numbness of the chest, a strange sensation of “goosebumps”.
When palpated, the pain intensifies. It also becomes more pronounced when sneezing, laughing, coughing, or making sudden movements. If the patient takes painkillers, his condition will hardly improve.
Symptoms of neurasthenia
Neurasthenia, the symptoms of which consist of the main stages of its course.
Neurasthenia is accompanied by irritability, short temper, tearfulness, aggressiveness, which is replaced by fatigue, insomnia, intolerance to noise, sound or light. Neurasthenia, the symptoms of which culminate in the development of apathy, is a cyclical functional disorder.
Neurasthenia may include memory impairment, memorization, and complaints of indifference to the outside world.
Why does chest neurosis need to be treated?
The disease can have various complications. The earlier therapy is started, the lower the risk of their manifestation. Among the most common consequences of untreated breast neurosis:
- Chronic pain in the ribs and back. It deprives a person of the opportunity to lead an active lifestyle, move, play sports, dance. There is a decrease in quality of life. In some cases, advanced pathology leads to loss of ability to work.
- The range of motion in the shoulder girdle is sharply reduced. A person constantly suffers due to stiffness and muscle weakness.
- Lung diseases - bronchitis, pneumonia, obstruction - become frequent. Respiratory arrest, which can lead to death, is also possible.
- Intervertebral hernias form. This is a common complication of curvature of the spinal column, osteochondrosis. Therefore, people with thoracic neurosis who are diagnosed with these diseases should be very attentive to their health.
Symptoms of obsessive-compulsive neurosis
A neurosis whose symptoms may include obsessive thoughts and corresponding compulsive actions or rituals is called obsessive-compulsive neurosis.
Neurosis, the symptoms of which are manifested by unwanted ideas, thoughts, fears, accompanied by stereotypically repeated actions, is called obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The causes of neuroses can consist of psychodynamic and organic-brain ones.
Examination and diagnosis
If there is discomfort in the chest, the patient is examined by a neurologist. Since the symptoms may be related to the stress experienced, a psychiatrist is involved in the work. The patient is interviewed and examined. Specialists:
- palpate the hypochondrium to determine trigger points;
- study the nature of the pain;
- exclude the presence of other diseases with similar symptoms;
- carry out CT or MRI of the chest, radiography, EEG and other instrumental examinations (as indicated).
Based on the diagnostics performed, a diagnosis is made.
Signs of psychosis and neurosis
Symptoms of psychosis
Recognizing warning signs is sometimes not easy, but you should pay close attention to any changes that appear in the character and habits of a loved one.
Characteristic symptoms of psychosis are:
- decreased performance or febrile activity;
- mood swings;
- irritability, suspicion;
- desire for self-isolation;
- unexplained change of interests;
- sleep disturbances, decreased appetite;
- careless attitude towards one's appearance;
- increased vulnerability and other atypical reactions to events and phenomena;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- incoherent speech;
- hallucinations, delusions.
Symptoms of neurosis
It is quite difficult for a non-specialist to identify a nervous disorder. And yet the clinic of neurosis has characteristic features.
Neurosis may be indicated by:
- decreased cognitive abilities;
- depressed mood, tearfulness;
- self-doubt, low self-esteem;
- irritability, dissatisfaction;
- frequent changes of mood;
- obsessive thoughts;
- fixation on bad news and events;
- unmotivated anxiety states;
- poor appetite, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;/li>
- cardiovascular symptoms;
- insomnia and other sleep disorders;
- violations in the sexual sphere;
- increased sensitivity to noise, light, vibrations, etc.
1 Diagnosis and treatment of neurasthenia
2 Diagnosis and treatment of neurasthenia
3 Diagnosis and treatment of neurasthenia
Children's fears and facial tics are also symptoms of neurosis.
Very often in everyday life people confuse the concepts of “neurosis” and “neurasthenia”. Let us repeat once again: neurasthenia is a type of neurosis, one of its most common forms.
Characteristic symptoms of neurasthenia are:
- decreased intellectual abilities;
- dizziness, headaches (the so-called neurasthenic helmet);
- increased fatigue;
- sleep disorders;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
- chest pain;
- mood swings;
- low self-esteem;
- decreased potency and libido.
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 6,000 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 7,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 30,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 60,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!
Treatment of sternal neurosis at the Leto clinic
What procedures the therapy will include depends on the stage of the disease and the dominant symptoms. As a rule, the treatment course is aimed at:
- relieving muscle spasms;
- pain relief;
- improvement of the patient’s mental state and emotional background;
- increasing overall physical activity;
- stimulation of blood circulation.
Relieving muscle tension caused by severe nervous shock includes:
- Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If they prove ineffective, a blockade is carried out. It does not eliminate the root cause of the disease, but it allows a person to be relieved of severe pain for several days.
- Steroid injections. They are used only in extreme cases, for example, if neurological symptoms are accompanied by radiculopathy.
- Physiotherapy. Good results can be obtained by ultraphonophoresis, magnetic and microwave therapy, UHF, and darsonvalization. Physiotherapy makes it possible to reduce the dose of medications used and speed up the day of recovery.
- Exercise therapy. Performing physical exercises is aimed at correcting muscle tension, improving local blood circulation, and relieving existing spasms. Particular attention is paid to stretching the back.
- Vitamin therapy. Patients are shown B vitamins and ascorbic acid. They provide support to nerve fibers and have a positive effect on the functioning of the immune system and the central nervous system.
- Massage sessions. During them, the doctor works on the chest, cervical region, and shoulder girdle. The emphasis is on relaxing cramped muscles, which ensures improvement in the client's condition.
Since the root cause of the disease is stress, observation by a psychotherapist is mandatory. The doctor helps eliminate nervous tension and overcome difficulties that arise. For this purpose, she uses individual psychotherapy sessions, cognitive-behavioral practices, trainings, relaxation sessions, etc.
We treat breast neurosis comprehensively, paying attention not only to relieving symptoms, but also to eliminating the cause and preventing complications. If you are interested in a complete recovery and no longer want to endure cramping chest pain, call - 8(969)060-93-93 . We know how to help you.
Symptoms of hysterical neurosis
Hysterical neurosis is a state of expressed emotion, which is accompanied by emotionally charged theatrical reactions in the form of laughter, crying, screaming, as well as convulsive motor manifestations, the possible development of temporary blindness, deafness and muteness.
The main symptoms of hysterical neurosis will be: hysterical attacks or paroxysms that occur after severe stress or experience.
During such an attack, patients moan, cry, and may commit self-mutilation.
Impaired sensitivity by type of anesthesia, hypo- or hyperesthesia.
Disorders of the function of the sensory organs, speech disorders, movement disorders and disruption of the functioning of internal organs.