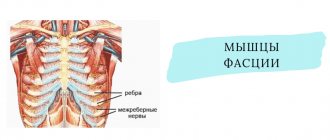
Intercostal neuralgia is a disease that is accompanied by pain in the ribs, chest or back due to inflammation of the nerve endings in the intercostal space. This diagnosis can be made only after other diseases with similar symptoms - namely, pneumonia, tuberculosis or cardiovascular pathologies - have been excluded. The pain with this disease is acute and appears suddenly. In most cases, it is difficult for the patient to take a breath, since this causes unpleasant sensations, reminiscent of those that accompany a heart attack, to intensify several times.
Intercostal neuralgia
This is a pain syndrome caused by damage to the peripheral nerves of the chest. Appears due to inflammation, irritation or pinching of the nerve roots in the intercostal space. Intercostal neuralgia is not a disease - it is a syndrome that can appear against the background of various pathologies. Vertebrogenic thoracalgia (as intercostal neuralgia is called) is a general concept that refers to pain that occurs in the chest area. They can appear for no particular reason, or can serve as a sign of various diseases.
Symptoms may resemble pain from a heart attack, pneumonia or pleurisy, diseases such as pancreatitis and others. A characteristic symptom is an increase in pain when coughing, laughing, moving, bending the body and decreasing at rest and with muscle relaxation. This is a distinctive feature of intercostal neuralgia, which allows it to be differentiated from symptoms of heart disease or other pathologies. But you shouldn’t take risks and try to diagnose yourself. The cost of a mistake can be higher than the prolonged pain syndrome.
The principles of treatment and symptoms of intercostal neuralgia in men and women are similar. The main manifestation is pain:
- Paroxysmal, occurring on its own.
- Monotonous, aching.
- Intensified by movement, deep breathing and exhalation, laughter, coughing.
- Occurs when pressing on individual points on the front of the chest or side.
- A burning sensation in the area where the nerve is damaged.
- Numbness, “pins and needles” sensation.
The pathology is more common on the left side of the body, and in women, intercostal neuralgia is a fairly common companion to pregnancy. During this period, the growing fetus puts pressure on the organs in the abdominal cavity, which can lead to pinched nerves.
Symptoms and diagnostic features of intercostal neuralgia on the right
The signs of intercostal neuralgia on the right are typical: severe pain, aggravated by inhalation and exhalation, coughing, sneezing, uncomfortable posture, and physical activity. Local pain is more common, its localization is easy to determine: intercostal spaces, lower back, shoulder blades .
It also increases with palpation of the corresponding areas of the ribs and spine. Severe attacks can continue for a long time.
This pathology is also characterized:
- Trembling and twitching of the intercostal muscles. They can be easily noticeable and strong or barely noticeable. This reflex reaction to pain occurs due to the fact that the motor areas of the nerve fibers are affected or due to a disruption in the blood supply to the nerve tissues.
- Numbness of the skin, tingling and burning near the affected nerve due to impaired sensitivity of part of the intercostal nerve.
- And if the autonomic part of the nerve is located, sweating, a change in color of the corresponding part of the skin (pallor, redness or cyanosis), a feeling of cold in this area and a local decrease in temperature are observed.
- A forced position of the body when the spine and chest are slightly tilted to the left, protecting the right side from compression of the nerve endings.
- Sleep disturbances due to constant and unbearable pain.
- Poor filling of the lungs, resulting in rapid and shallow breathing and shortness of breath.
Causes
Intercostal neuralgia can be caused by various reasons. Basic:
- Poor posture, injuries, intervertebral hernias, osteochondrosis.
- Hypothermia, which led to poor circulation.
- Infectious and other diseases that lead to nerve damage. For example, destruction of the nerve sheath in multiple sclerosis.
- Neoplasms that compress nerve roots.
- Muscle spasms, prolonged tension during sudden movements or prolonged uncomfortable body posture.
- Operations.
- Pathologies of internal organs.
2. Reasons
The list of factors that can cause pain in the right hypochondrium far exceeds the scope of a short article, so we have to combine these causes into large and most common categories:
- liver pathology (hepatitis and hepatosis, cirrhosis, parasitic infestations, oncopathology, intoxication, etc.);
- gallbladder pathology (cholecystitis, stones, dyskinesia, etc.);
- pathology of the right kidney, adrenal gland, ureter (various inflammatory processes, cancerous tumors, renal tuberculosis, urolithiasis);
- various types of inflammation, irritation and/or ulceration of the intestine (specific and nonspecific ulcerative colitis, infections, oncopathology);
- certain types of cardiac pathology (eg, abdominal myocardial infarction);
- inflammation and tumors of the diaphragm on the right side;
- vascular pathology (eg, thrombosis) in the systemic circulation;
- shingles;
- rib injuries and intercostal neuralgia.
Finally, pain can be localized in the right hypochondrium in a life-threatening condition of the abdominal cavity, known in medicine as an “acute abdomen” (ulcer perforation, acute forms of pancreatitis or cholecystitis, bleeding and hemorrhage due to severe injury or pathology, intestinal obstruction, etc.).
Visit our Therapy page
Diagnostics
Intercostal neuralgia can be a symptom of many diseases - from cardiovascular pathologies to diseases of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity and chest. It is impossible to independently determine the cause only from existing complaints. A consultation with a neurologist and a comprehensive diagnosis is necessary to ensure that there are no diseases of the heart, lungs, or digestive system.
Particular attention is paid when diagnosing and treating intercostal neuralgia on the left side. Acute pain in the heart may be a sign of a heart attack. Symptoms usually differ - for example, with heart problems, cold sweat appears and shortness of breath bothers you, the pain does not decrease with rest when the muscles relax. But making a diagnosis based only on symptoms is wrong. The doctor is responsible for the life and health of the patient, which means he needs confidence in the diagnosis and correctness of treatment.
The procedure for examining a patient with suspected intercostal neuralgia is as follows:
- Questioning the patient about complaints and the characteristics of their occurrence.
- Examination to find the location of the pain.
- Setting up a preliminary diagnosis.
- Carrying out examinations to confirm intercostal neuralgia, its causes and prescribe the treatment that will be required in a particular case.
The following diagnostic methods can be used:
- Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography is a study that will provide detailed and highly accurate images of tissues and pathology in them.
- ECG – monitoring of heart function to exclude cardiovascular diseases.
- Ultrasound of the heart or other internal organs, diseases in which may have similar symptoms.
- X-ray of the lungs to exclude pneumonia, pleurisy and other diseases in which there are complaints of chest pain.
Diagnostic methods are selected individually depending on the nature of the pain and its location, and the patient’s condition. In some cases, other specialists are involved in diagnosis and treatment - a cardiologist, gastroenterologist, pulmonologist.
1.General information
From the school course of human anatomy and physiology, we remember how important the pain mechanism, formed and fine-tuned during evolution, is for humans. Pain is an alarming electrochemical signal to the brain; it is a neuronal lightning telegram about dysfunction or damage to an organ. If humanity didn’t have this alarm system, our species would have died out a long time ago, and in most cases without knowing what kind of blockages, inflammations, perforations and injuries.
However, a person in pain has no time for theory and, by and large, no time for evolution; The main thing for him is that he stops getting sick. It is also obvious that pain is different, and in some cases this “panic button” simply needs to be turned off artificially - with analgesics, anesthetics, or even life-saving general anesthesia. However, we cannot brush off pain in any case, especially if it hurts “somewhere inside” and we don’t really know why. Areas of particular importance, the pain in which is never trivial or unimportant, include the so-called. hypochondrium - areas above the border between the abdominal cavity and the ribs, which serve as a natural shield for life-sustaining internal organs.
On the right side, as we know from the same school textbooks, we have the liver, gall bladder, one of the kidneys with the adrenal gland and one lung, half of the diaphragm, as well as some of the intestinal loops. And all this can hurt, and in completely different ways and under the influence of a huge variety of possible reasons.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Treatment
The goals of therapy for intercostal neuralgia: reduce pain, eliminate the cause of pinching or inflammation.
For this purpose, drug treatment is prescribed using:
- Muscle relaxants to relieve muscle spasms.
- Neuroprotectors for the protection and restoration of nerve cells.
- Painkillers and injection therapeutic blockade with various drugs. It has a strong analgesic effect, relieves swelling and eliminates muscle spasms.
Drug treatment of intercostal neuralgia is complemented by physiotherapy. The following physiotherapeutic procedures can be used:
- Exercise therapy is an individually selected set of exercises to relax spastic muscles, improve blood circulation and lymph flow in the problem area. Exercise therapy is effective for the treatment and prevention of neuralgia, but it can only be done if there are no contraindications. It is important not to cause harm, which is possible with home exercises. What exercises will be effective, how exactly to do them, the number of repetitions - all this will be advised by a physical therapy doctor. The safest and most effective classes are under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor in individual or group classes.
- Laser therapy uses light energy to increase blood circulation, relax muscles, and reduce pain and inflammation.
- Magnetotherapy - the effect of an electromagnetic field on the body leads to the elimination of congestion, improvement of blood circulation, and reduction of pain syndromes.
- Diadynamic therapy, galvanization, exposure to interference currents and other procedures with electric current of varying power and frequency. They have a healing effect on soft tissues, improving blood circulation and lymph outflow, relaxing muscles and providing an analgesic effect.
- Electrophoresis is a procedure that improves the penetration of drugs into soft tissues and accelerates their action.
- Therapeutic massage and manual therapy are methods of influencing the body with the hands of a doctor. They allow not only to reduce or completely relieve pain, but also to treat the causes of intercostal neuralgia - pathologies of the spine, functional blocks in its work. What exactly to use - acupressure, segmental or other types of massage - is decided by a chiropractor or massage therapist.
- Acupuncture (acupuncture) – injections with thin needles into biologically active points on the body to relieve pain and normalize the functioning of internal organs.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia on the right or left side of the chest, in the side with the help of physiotherapeutic procedures is carried out in several procedures. A full course usually consists of 10-15 sessions. Appointments are always individual.
4.Treatment
To paraphrase Hippocrates, the basic principle of modern medicine can be defined as follows: “It is not the symptoms that need to be treated, but their cause.” Of course, etiopathogenetic (aimed at eliminating the cause) therapy is not possible in all cases - unfortunately, medicine today is not yet omnipotent, and sometimes we have to limit ourselves to symptomatic, palliative treatment - however, for pain in the right hypochondrium, the primary task is to find out what it is the organ that gives the distress signal, what is the nature and extent of the damage, prognosis, advantages and disadvantages of surgical or conservative approaches. These findings determine the therapeutic strategy in each individual case. It is more important for patients to understand and remember that for any discomfort in the subcostal area, especially if the pain has become chronic, paroxysmal or progressive, consulting a doctor is not only mandatory, but sometimes life-saving. As a rule, patients with such complaints initially turn to a therapist or gastroenterologist, but in some cases specialized treatment may be required from an infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist, cardiologist or other specialist. According to statistics, every third adult is more or less familiar with pain in the right hypochondrium, i.e. the phenomenon is very widespread (which is not surprising, given the list of possible causes). However, this does not mean that such pain can be ignored or endured indefinitely: it is unlikely to disappear on its own, but if you seek help too late, it can result in very, very serious consequences. Don't procrastinate or persuade yourself. It hurts under the ribs - go to the doctor.
Prevention
The following recommendations help to avoid the appearance of intercostal neuralgia:
- Moderate physical activity to strengthen the muscle frame and maintain their elasticity.
- Maintaining correct posture.
- Healthy eating.
- Daily routine and alternation of work and rest time.
- Protection against hypothermia.
You should not endure the pain of intercostal neuralgia and worry about its causes - consult a doctor to be sure that there are no serious pathologies and for quick relief of symptoms.
Complications
The insidiousness of intercostal neuralgia is that its symptoms can be confused with many other diseases. Sometimes the patient is in no hurry to get an appointment and begins to treat intercostal neuralgia with ointments, tablets or herbs. For any form of the disease, even mild, the patient must be examined by a doctor. In no case should you independently diagnose yourself and prescribe treatment - the lack of medical intervention for serious diseases mistakenly mistaken for intercostal neuralgia can cost the patient’s life.
After identifying the cause of the disease, the doctor will prescribe adequate treatment to minimize the risk of complications.
The main complication of intercostal neuralgia is the transition of the disease to a chronic form with frequent exacerbations.