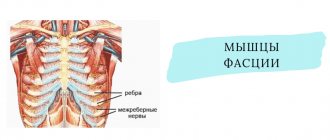
Pain in the region of the costal arches is a fairly common symptom and intercostal neuralgia often has to be differentiated from pain of a cardiogenic nature. The term intercostal neuralgia means the involvement of the intercostal nerves and the presence of pain. The causes of intercostal neuralgia can be various diseases that lead to damage to nerve fibers. First of all, these are degenerative diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, hernia, disc protrusion, spondylosis), rheumatological diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis, infectious diseases (herpes zoster, brucellosis, tuberculosis).
These may be diseases of the nervous system such as multiple sclerosis, polyradiculoneuropathy, systemic diseases (diabetes mellitus, hepatitis), vitamin deficiency due to alcoholism or malabsorption in the gastrointestinal tract. Damage to the intercostal nerves is possible due to intoxication (heavy metals, some drugs).
When the blood supply to the nerves is disrupted, hypoxia of the nerve trunks occurs and this occurs in cardiovascular diseases (hypertension, atherosclerosis) and anemia. Disturbances in the endocrine system can lead to changes in the spine, which in turn lead to intercostal neuralgia (thyrotoxicosis, adrenal diseases, endocrine system disorders in postmenopausal women). So there are quite a lot of factors contributing to the development of intercostal neuralgia and, as a rule, a combination of factors is important, and not just one factor. Intercostal neuralgia occurs most often in elderly people, when there are involutional changes in the spine and in the body
Symptoms
The main symptom of intercostal neuralgia is pain in the ribs, which has an acute burning character, sometimes dull. The pain can develop in paroxysms or appear periodically. During attacks, the pain can be intense and intensify with coughing, sneezing, and body movements. The pain is usually localized in the area of the lower ribs and can radiate to the shoulder or arm, which often makes such attacks of pain similar to cardialgia. Pain with intercostal neuralgia from pain in the heart in the more constant nature of the pain intensity, and in the absence of changes in the cardiovascular system (changes in pulse, pressure). In addition, cardiogenic pain does not increase with trunk movement and there is no local tenderness in the rib area. Pain during intercostal neuralgia may be accompanied by vegetative manifestations (pallor or redness of the skin, sweating), fasciculations of muscle groups, impaired sensitivity in the area of pain (numbness). Palpation of the area of paravertebral points in the intercostal spaces in the area of attachment of the ribs to the sternum can be painful. Sometimes pain with intercostal neuralgia can radiate to the lower back and simulate renal colic.
Intercostal neuralgia: symptoms and treatment
→
Information
→
Neurology
We work seven days a week and holidays
COVID 19: antibody tests
The main symptom characterizing the occurrence of intercostal neuralgia (neuritis) is severe pain, which appears as a result of compression of the spinal nerve roots. The cause of compression and, as a consequence, the appearance of pain is the development of infectious diseases, intoxications, injuries, degenerative and inflammatory processes, the presence of tumors, etc.
Intercostal neurosis often accompanies diseases such as herpes zoster or osteochondrosis. The different zones of localization of the above changes determine the nature of the pain syndrome.
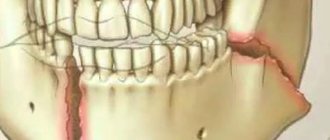
The inflammatory nature of damage to the intercostal nerves usually occurs after previous hypothermia or against the background of infectious processes. The cause of the infectious nature of intercostal neuralgia is mainly a herpes infection (herpes zoster). In certain cases, compression of the spinal nerve roots occurs due to their injury due to chest injuries, bruises, rib fractures and other spinal injuries. With physical overexertion, work associated with tension in the muscular frame, chronic vertebrogenic syndrome, pleurisy, muscular-tonic overexertion (syndrome) develops, which also leads to compression of the nerves. In children and adolescents, the appearance of intercostal neuralgia can occur during a period of intensive growth of the bone skeleton.
The main symptom of intercostal neuralgia is the appearance of acute unilateral piercing pain in the chest (thoracalgia), which runs along the intercostal spaces and has a “girdling” character. Patients describe it as a “shooting sensation” or “passing electric current.” The pain spreads along the intercostal space from the spine towards the sternum. Thoracalgia is of an increasing nature, starting with a slight tingling sensation, and then intensifies and becomes unbearable. Depending on the location of the affected nerve, pain can radiate to the area of the scapula, heart, stomach (epigastric region). When intense, neuralgia may be accompanied by redness (hyperemia) or blanching of the skin, local hyperhidrosis, which is caused by damage to the sympathetic fibers of the intercostal nerves.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia includes a set of measures. To eliminate muscle-tonic overstrain, centrally acting muscle relaxants are used. For edema syndrome, diuretics and venotonics are prescribed. Improving the functionality of the affected nerves is achieved through the parenteral use of ascorbic acid and B vitamins. In the absence of contraindications (gastritis, peptic ulcer), NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are used. Treatment of herpes infection is carried out with antiviral and antihistamines. Local use of antiherpetic drugs in the form of ointment is indicated. Women are not recommended to wear tight underwear. Additionally, sedatives, antidepressants, vitamin complexes are prescribed, and mustard plasters, compresses, and anti-inflammatory ointments are also used locally in the area where the pain is localized. Patients are advised to avoid stress, stress, and alcohol for the entire period of treatment.
Diagnostics
With classic manifestations, the diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia is not difficult (for example, with the consequences of herpes zoster). But given the possibility of pain in the rib area due to numerous diseases, it is often necessary to conduct a thorough examination. The diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia can be made based on the patient’s history of complaints (nature of pain, localization, intensity, duration of pain, presence of irradiation, increased pain with body movements), external examination (presence of spinal deformities), presence of pain on palpation in the area of attachment of the ribs to the sternum or paravertebral points in the thoracic spine. If it is necessary to differentiate with the cardiac nature of pain, an ECG is necessary. To identify degenerative changes in the spine, instrumental research methods such as radiography, CT, and MRI are used. In addition, densitometry is necessary to diagnose osteoporosis. EMG can be used to determine the extent of nerve fiber damage. Laboratory tests and ultrasound may be ordered to diagnose both rheumatological diseases and endocrine disorders or kidney diseases. The approach to diagnosing intercostal neuralgia should be based on the exclusion, first of all, of somatic causes of pain (heart disease, kidney disease, endocrine diseases).
Intercostal neuralgia
Complex therapy is carried out aimed at eliminating the causative pathology, relieving thoracalgia, and restoring the affected nerve. One of the main components is anti-inflammatory therapy (piroxicam, ibuprofen, diclofenac, nimesulide). In case of severe pain, drugs are administered intramuscularly, therapy is supplemented by therapeutic intercostal blockades with the administration of local anesthetics and glucocorticosteroids. An auxiliary means in relieving pain is the prescription of sedatives, which reduce pain by increasing the threshold of excitability of the nervous system.
Etiotropic therapy depends on the genesis of neuralgia. Thus, for herpes zoster, antiviral agents (famciclovir, acyclovir, etc.), antihistamine pharmaceuticals and local use of antiherpetic ointments are indicated. In the presence of muscular-tonic syndrome, muscle relaxants (tizanidine, tolperisone hydrochloride) are recommended. If the intercostal nerve is compressed at the exit of the spinal canal due to osteochondrosis and displacement of the vertebrae, gentle manual therapy or spinal traction can be performed to relieve the compression. If nerve compression is caused by a tumor, surgical treatment is considered.
In parallel with etiotropic and anti-inflammatory therapy, neurotropic treatment is carried out. To improve the functioning of the affected nerve, intramuscular administration of B vitamins and ascorbic acid is prescribed. Drug therapy is successfully complemented by physiotherapeutic procedures: ultraphonophoresis, magnetotherapy, UHF, reflexology. For herpes zoster, local UV irradiation on the area of the rash is effective.
Forecast and prevention of intercostal neuralgia
In general, with adequate treatment, intercostal neuralgia has a favorable prognosis. Most patients experience complete recovery. In the case of herpetic etiology of neuralgia, relapses are possible. If intercostal neuralgia is persistent and cannot be treated, you should carefully reconsider its etiology and examine the patient for the presence of a herniated disc or tumor process.
Prevention measures include timely treatment of spinal diseases, prevention of spinal curvature, and adequate treatment of chest injuries. The best protection against herpes infection is a high level of immunity, which is achieved by a healthy lifestyle, hardening, moderate physical activity, and active recreation in nature.
Methods for diagnosing and treating neuralgia
The basis for making a diagnosis is the data from a survey and examination of the patient, as well as the exclusion of other possible causes of pain attacks. As a rule, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are used - blood and urine tests, computed tomography, MRI.
Treatment of neuralgia is complex and is aimed at relieving pain symptoms and stimulating the body's natural defenses. Modern analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs, injections of B vitamins, physiotherapy, and acupuncture are widely used. In some cases, psychotherapy and the use of homeopathic medicines provide a good therapeutic effect.
If there is an underlying disease that caused neuralgia, efforts should be directed toward its treatment. The sooner therapy is started, the sooner a person’s ability to work and quality of life will be restored. If you do not contact a neurologist in a timely manner, the process can progress and lead to the appearance of signs of organic damage to nerve fibers. During the therapy period, the patient needs complete rest and bed rest.
What treatments are there for this disease?
- Medication . These are, first of all, anticonvulsants. Neuroleptics, antidepressants, and tranquilizers are of no small importance.
- Physiotherapeutic . Acupuncture, pharmacopuncture (introduction of drugs into bioactive points), laser puncture, the use of pulsed currents of low voltage and low frequency, magnetic and electromagnetic fields, infrared and ultraviolet radiation, ultrasound, electrophoresis of medicinal substances.
- Surgical. There are a large number of surgical methods for treating trigeminal neuralgia. This may be a separation of the nerve root and the vessel compressing it; intersection of individual large branches of the trigeminal nerve, destruction of pain fibers in the nerve root. The choice of surgical tactics depends on the patient's condition.
As a rule, at the initial stage of the disease, the patient is recommended to undergo medication and physiotherapy, as well as trigeminal nerve blocks. Neurosurgical treatment methods are indicated only after the above-mentioned treatment methods have failed.
Causes and symptoms of neuralgia
With primary neuralgia there are no concomitant diseases. If neuralgic pain is a consequence of tumor, infectious or inflammatory processes, they speak of secondary neuralgia. This condition can result from circumstances such as:
- traumatic injuries;
- past infectious diseases, foci of chronic inflammation, for example, decayed teeth or sinusitis;
- hypothermia, alcohol abuse;
- osteochondrosis of various parts of the spine;
- the presence of tumors, including malignant ones.
A characteristic symptom of neuralgia is a burning, paroxysmal pain that tends to spread along the peripheral branches of the affected nerve. For example, with trigeminal neuralgia, acute pain radiates to the upper and lower jaws, as well as to the forehead, and with intercostal neuralgia, pain occurs during breathing and is localized in the intercostal spaces. A reflex twitching of the muscles may be observed, as well as a change in the color of the skin over the affected nerve fragment.
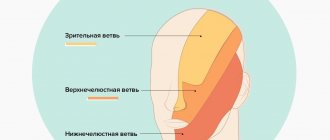
What is the cause of trigeminal neuralgia?
Neurologists believe that it consists of compression of the trigeminal nerve root by a nearby vessel. The causes of compression may be:
- tumors
- adhesions after injuries, infections,
- dilatation of convoluted cerebellar arteries, veins,
- aneurysm of the basilar artery.
The development of the disease can be caused by various vascular, endocrine-metabolic, allergic disorders, as well as psychogenic factors.
Causes of development of intercostal neuralgia
Neuralgia occurs as a result of inflammation of the tissue that makes up the nerve when it is irritated or compressed. There may be several reasons for the development of inflammation:
- complications from viral diseases (colds, flu, herpes);
- injuries, operations, hernias;
- osteoporosis, osteochondrosis, back diseases;
- inflammation of joints and ligaments;
- dysfunction of the rib joints.
These are the most common causes of the disease, but it can also occur in healthy people. For example, if a person was in an uncomfortable position for a long time and made a sudden movement, stood in a draft, or did heavy physical labor.