Medical certificate
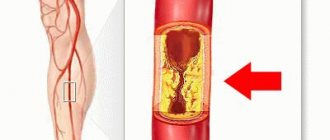
Stroke is neurological in nature. The cause of this terrible disease is an acute violation of cerebral circulation. It is disrupted due to blockage of blood vessels by blood clots or due to embolism of the cerebral arteries. Stroke is most common among residents of developed countries. A sedentary lifestyle is thought to increase the risk of stroke. The brain is poorly supplied with oxygen, which leads to acute brain hypoxia and subsequent death of nerve cells.
Nervous tissue is the most delicate and sensitive. She absolutely cannot tolerate circulatory disturbances: this leads to the rapid onset of ischemia and disruption of the normal functioning of neurons. Just half an hour after the blood flow is disrupted, irreversible changes occur, which forms the picture of the disease. Thus, in case of a stroke, it is important to help the person as soon as possible, before the changes become irreversible.
In medicine, it is customary to divide stroke into two categories:
- ischemic, when there is complete occlusion of the lumen of the vessels;
- hemorrhagic, when the vessel ruptures and hemorrhage occurs into the surrounding tissue. In this case, a cerebral hematoma is observed.
The mechanisms of disease development are approximately the same, but the consequences may be different. Statistics say that in 80% of cases it is the ischemic form of stroke. Both forms of stroke are associated with atherosclerotic changes in the vascular system. Important: hemorrhagic stroke is more dangerous, since when a hematoma develops, a shift in the brain can sometimes occur.
Epidemiology
The incidence of epilepsy has a number of factors that could trigger its development. According to epileptologists, the disease is distinguished by its bimodal nature. Most often, this diagnosis is made to newborns and young children, as well as elderly people over 60 years of age. According to medical statistics, epilepsy is diagnosed most often among older people. This group of patients exhibits seizures that were unprovoked. Sometimes pathology is associated with acute processes occurring in the body.
According to the data obtained, the first seizure among elderly people was recorded in 136 cases among 100 thousand subjects. Active epilepsy among older people occurs in 1.5%. Among patients who are in a nursing home, the active form is observed in 5%. The prevalence of this pathology is growing every year.
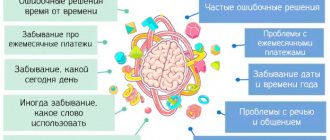
Diagnosing epilepsy in old age is extremely difficult. To establish an accurate diagnosis, the attending physician completely studies the patient’s medical history, analyzes the frequency and nature of complaints. Eyewitness accounts who may have been present during epileptic seizures are also taken into account. Most often, attacks begin when the disease progresses. It is likely that the prevalence rates of epilepsy among people over 60 years of age are lower than those reported. However, the prevalence of the disease among this population group is much higher than among young people. The figure is twice as high.
Causes of stroke
Stroke is a so-called multifactorial disease. It is believed that stroke has many different causes, each of which makes a specific contribution:
- unhealthy lifestyle, which may include overeating and physical inactivity;
- great psycho-emotional stress;
- bad habits, especially smoking;
- hypertonic disease;
- some other factors, including heredity.
These factors can act together or separately.
What are the causes of aggressive behavior in people who have had a stroke? They are:
- damage to areas of the cerebral cortex responsible for emotions, behavior and intelligence;
- extensive brain damage. This is the most common cause of aggression.
One of the common consequences of a stroke is paresis of the facial muscles. The man's face contorts. Important: aggression in people who have suffered a stroke may develop not as a result of damage to areas of the brain, but already during the rehabilitation period, when a person cannot come to terms with the loss of certain functions of his body.
Epileptiform conditions
Diagnosing epilepsy in old age will require a lot of effort and attention from doctors and is often considered incorrect. Very often, epilepsy is confused with other diagnoses that have similar symptoms. The attending physician is obliged to study the patient's medical history, conduct a full diagnostic examination and pay attention to concomitant pathologies.
Some signs and clinical situations at this age mask epilepsy. For example, when falling or fainting, a person has no idea about the development of epilepsy. We are also talking about signs such as cardiac syncope, arrhythmia, disturbed sleep and memory loss.
Manifestations of aggression in post-stroke psychosis
Aggression after a stroke has a number of features. Usually, when inappropriate behavior develops, the patient is dangerous to himself and others. The aggressive state does not develop immediately, but gradually, over two or three months. It is characterized by the following:
- self-criticism disappears;
- the patient withdraws into his thoughts and withdraws from everyone;
- intense psycho-emotional background;
- slurred speech;
- interest in surrounding things and people disappears;
- inappropriate behavior, especially at night;
- weight loss.
In a person who has suffered a stroke, aggression is often accompanied by a depressive state. Aggression is characterized by attacks. Most often it appears at night. Emotional instability leads to increased vulnerability of the patient, and this, in turn, causes him an inferiority complex. A vicious circle arises. Relatives observe with horror that a loved one has become different, distant and aggressive.
Tumors
Convulsive seizures can become a symptom that indicates the presence of a neoplasm among any age group. Seizures are typical for the formation of poorly differentiated primary tumors, and not for highly differentiated ones. Old people often suffer from meningiomas, gliomas and metastatic tumors, which can cause seizures.
Often, seizures indicate the development of metastasis. According to data obtained after the study, it became known that in 43% of cases, metastases were found in patients, the cause of which was the attacks. In general, malignancy is not detected until the onset of epileptic seizures.
A person has become aggressive - what to do?
Scientists have not yet developed a reliable method for fully restoring people after a stroke. Attention from family and friends is of great importance. A person who has suffered a stroke is in great need of support from relatives. The best solution is to avoid the development of post-stroke psychosis and depression. In some cases, psychotherapy may be required. It is important that the victim himself understands the need to combat manifestations of aggressiveness. Then there is a chance for healing. With mild forms of psycho-emotional disorder, love and care from loved ones will be quite enough. Prescription of antidepressants brings good results. In general, treatment after a stroke includes:
- angioprotectors - drugs that strengthen the walls of blood vessels;
- nootropics - drugs that improve cerebral circulation;
- thrombolytics - drugs that thin the blood.
The faster the recovery processes in the brain take place, the sooner a person will get rid of depression and psychosis.
Injury
Old age is the main risk factor for the development of post-traumatic epilepsy. In 20% of cases, neurological pathology occurs among older people after head injury. We are talking about a fall from a height that caused damage.
An increased risk of developing post-traumatic epilepsy appears in the following cases:
- loss of consciousness;
- amnesia for more than a day;
- skull fracture;
- brain contusion;
- subdural hematoma;
Head injuries in old age are more dangerous than in younger people. The risk of subdural bleeding increases, especially if treatment with platelet aggregation inhibitors or anticoagulant treatment is carried out.
Obsessive neurosis
Obsessive-compulsive neurosis is a psychiatric illness that is accompanied by frequent intrusive anxious thoughts. Patients do not have the ability to suppress them on their own. As a result, the problem is only beginning to gradually gain momentum and get even worse. People suffering from this disease often begin to perform peculiar rituals. For example, opening doors a certain number of times, turning lights on and off in a given rhythm. But a person fully understands the inadequacy of his actions and their negative consequences, but at the same time he cannot stop himself, repeating “traditions” again and again.
Obsessive behavior in children
Obsessive behavior in children is a fairly common problem that many parents face. The disorder most often manifests itself when the child constantly bites his nails, twirls the hair on his fingers, and picks his nose. After repeated comments, the situation does not improve at all, repeating itself again and again. In this case, we are not talking about simple habits at all, but about neurosis. Therefore, it is quite difficult to deal with obsessive actions.
There can be many reasons for the manifestation of this type of illness, including divorce of parents, great fear of dog bites, or, for example, a child was once very scared because he almost drowned while swimming. Also, the reasons may be physiological, for example, after sinusitis in an advanced stage, which resulted in chronic intoxication of the body. It is important to start dealing with the situation in a timely manner, since fears that manifest themselves in childhood can develop into severe phobias after reaching adulthood. Therefore, if you notice regular habits in your child, such as tugging at the earlobe, cracking fingers, or any other actions that occur with enviable regularity, it is important to contact a specialist in a timely manner.
Treatment of obsessive behavior
When treating obsessive-compulsive disorders, an integrated approach will be required, which includes psychotherapy, during which a specialist works individually with the patient, drug treatment to correct anxieties and fears, and multiple modern relaxation techniques. Thanks to individual psychotherapy sessions, it is possible to determine the reasons why a person got into this situation. In the case when the patient begins to understand what exactly is the cause of obsession, the situation is much easier to control.
Thanks to cognitive behavioral therapy, you can achieve excellent results after just a couple of sessions. The doctor teaches his patient to detect and change negative attitudes to more optimistic ones. Thanks to this, the patient begins to gradually control his behavior, coping with a stressful situation.
Drug treatment is a last resort. For this type of therapy, patient consent is required. Antidepressants, anxiolics, which help fight anxiety, and sedatives, which can help overcome depression and increased anxiety in a shorter period, are taken as medications. As a result, sleep gradually normalizes and the patient’s general condition improves. Treatment must be carried out until the disease is completely defeated. That is, the course lasts until the patient is unable to independently control the disorder and all symptoms of the disease disappear completely.
If you are faced with this difficult situation, you must definitely contact a specialist. Our Salvation clinic has created the best conditions for a favorable exit from a neurotic state. Our staff consists of qualified psychotherapists who have extensive practical experience. Specialists practice the latest effective techniques, through the use of which you can achieve good results in a short time.
Obsessive behavior in adults
Experts divide manifestations of obsessive actions in adults into several categories, including:
- Classic tics, which are manifested by rapid movements of the head or neck. Also, tics of this type can also manifest themselves in sound, for example, constant mooing, coughing and much more.
- The stereotypical category includes frequent rocking in different directions, tapping fingers on the table surface, and jerking the leg. With such behavioral disorders, there are no prodominal signs that are harbingers of the onset of the disease.
- Behavioral disorders that cause physical harm to the patient - hair pulling, scratching or picking at skin, nail biting.
Such actions are performed unconsciously, since a person involuntarily performs certain actions. The tick stops for a while if requested by loved ones or if a situation arises that will distract from the “procedures.” However, after some time, this situation will certainly repeat itself again and again.