Cerebral edema occurs against the background of blood circulation disorders caused by various diseases or functional abnormalities.
- Cerebral edema: prediction and symptoms
- Symptoms of swelling from hemorrhagic stroke
- Symptoms of swelling from ischemic stroke
- Cerebral edema from stroke and its features
- Reasons for development
- Care and rehabilitation
- Boarding houses for post-stroke patients "Olympia House"
The pathological condition has its consequences and can even lead to death; depending on the symptoms, it helps to determine the type of stroke suffered.
If even minor signs are detected and there is a suspicion of the formation of edema, it is necessary to arrange a visit to the doctor. An emergency call will help diagnose the condition of an elderly patient and promptly provide the necessary assistance, provide decent care and concern.
Diagnosis of acute ischemia during examination by a vascular surgeon
The classic picture of acute ischemia is determined by six symptoms:
- Sudden leg pain
- Pale skin
- Absence or deficit of movement in the affected limb
- Absence of pulse in the affected limb
- Decreased skin sensitivity
- Decreased skin temperature
The pain may be constant or with passive movement of the affected limb. With an embolic blockage, the pain is usually sudden and very intense. With thrombosis, the pain intensity is much less, and sometimes there is a progressive increase in intermittent claudication.
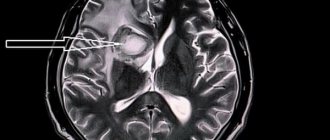
Cerebral edema: prediction and symptoms
Stroke is defined by medicine as a circulatory disorder and this condition leads to oxygen starvation of a certain area of the brain. Cortical cells die, and the patient's condition worsens due to the accumulation of watery secretions that put pressure on certain brain centers.
Watery accumulations are not capable of causing physical harm to soft tissues, but they accumulate in areas of nerve cells. This effect provokes an increase in intracranial pressure, which affects intracranial hypertension, the consequences of which (without providing the necessary assistance) become fatal.
With cerebral edema, a high degree of severity of the consequences of a stroke is determined, because this can cause unstable brain activity. The irreversibility of the impact is determined by real indicators of the extent of the spread and localization of edematous activity.
Without certain knowledge and understanding of the clinical picture, it is impossible to identify the symptoms of a pathological condition. The most difficult cases are considered to be attacks of hemorrhagic stroke, in which cerebral edema develops rapidly, putting the life of an elderly person in serious danger.
Ultrasound duplex scanning
Ultrasound duplex scanning allows you to determine the patency of the arteries, localize the site of blockage of the vessel and the state of blood flow below the site of occlusion. Often, in acute ischemia, this diagnosis is enough to determine treatment tactics and send the patient to the operating table. With an embolism or rupture, the arteries below the blockage are usually empty or thrombosed, and blood flow in them is not detectable. Blood flow in the veins is sharply slowed down. With thrombosis, blood flow can be detected below the site of blockage, but its speed is sharply reduced; most often, blood flow through the main vessels cannot be detected, but blood flow can be seen through collaterals. As a rule, this is due to
Prevention
In order not to worsen the patient’s condition and prevent complications, immediately after a stroke you should take into account the necessary rules and recommendations:
- Fluid intake (in any form) is no more than 1 liter per day. The patient's urine should be excreted in the same volume;
- Diet (allowable amount of salt – 1.5 g per day);
- every 2 hours , at night - every 5 hours;
- It is unacceptable for limbs to hang from the bed (it is better to raise your legs and place them on a thick pillow);
- Massage and exercises should be performed regularly (even simple movements help restore blood circulation);
- In a sitting position, the back should rest on a backrest or support , pillows are placed under the arms, the position of the hands is palms down, fingers extended.
Useful video on the topic:
Angiography
To resolve the issue, surgical tactics require information about the patency of the arteries of the affected limb. The choice of technique for restoring blood circulation depends on the condition of the inflow pathways to the affected limb and the vascular bed below the site of blockage. In addition, angiography can distinguish embolism from thrombosis against the background of atherosclerotic narrowing. During an angiographic examination, endovascular treatment can be undertaken in the form of thrombectomy and angioplasty of the affected segments or local thrombolytic therapy can be performed.
Arterial embolism is an acute blockage of a vessel by a thrombus or other object brought from other parts of the vascular bed. Most often, vascular surgeons deal with thromboembolism from the heart cavity during a heart attack or atrial fibrillation, from the cavity of the aneurysm of the vessel overlying the blocked artery.
Consequences of acute cessation of blood flow
The sudden cessation of blood flow leads to the phenomenon of acute ischemia. The organs and tissues that are supplied by this artery lack nutrition and oxygen, so they begin to slowly die. The most specialized tissues are affected first—nervous, muscle, and finally skin. The body tries to restore blood circulation by opening additional bypass pathways for blood flow, so sometimes tissue death is stopped. But the likelihood of such an outcome is low. In any case, acute ischemia leads either to gangrene or to the development of chronic circulatory deficiency - critical ischemia.
About the disease
Stroke – translated means “strike, attack”, “paralysis” – an acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain. The disease develops suddenly (from a few minutes to 1-2 days), manifests itself against the background of overexertion.
Reference. The first descriptions of the disease were made by Hippocrates back in 460 BC.
There are three types of disease:
- Ischemic stroke (up to 75–85% of cases), affects people over 60 years of age;
- Hemorrhagic stroke (up to 20%) occurs in people with hypertension aged 40–60 years;
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (up to 5%) – rupture of an aneurysm, brain injury.
Important! Every 1-2 minutes, someone in Russia develops a stroke. Up to 80% of stroke survivors become disabled, 20–30% of them require constant care.
Stages of acute ischemia
1. Sudden pain in the leg, coldness, reduction in walking distance. If the collateral vessels are good, ischemia may stop at this stage with the development of intermittent claudication or critical ischemia. Most often, this stage is observed with thrombosis of altered arteries, if their lumen was previously narrowed and collateral circulation developed. At this stage, the operation is carried out after the necessary additional examination and preparation. The color of the leg may be pale or take on a bluish tint (cyanosis). The result of surgical treatment is excellent. Recovery of leg function is most often complete.
2. The symptoms described above are accompanied by weakness in the leg, which gradually worsens to the point of paralysis. However, passive movements in the fingers and other joints are possible. Such phenomena are associated with the death of nerve endings and blockade of nerve impulse transmission along the nerves. This stage of ischemia is an absolute indication for emergency surgery, since independent restoration of blood flow is impossible, and delay in intervention will lead to gangrene. Timely surgery restores blood flow with minimal loss of limb function. Numbness of the foot and fingers remains, and swelling of the leg persists for a long time.
3. Muscle death begins, first there are foci of muscle necrosis, muscle pain, and dense swelling of the lower leg. Then comes numbness of the fingers, ankle joint, and knee joint (muscle contracture). The muscles die completely. If the muscles are partially lost after restoration of blood flow and a long postoperative period, the leg may be preserved, but walking will be difficult. In the case of muscle contracture, amputation is necessary, since restoration of blood flow leads to the death of a person from poisoning with decay products.
Why do limbs swell?
A stroke is a powerful blow to the left and right hemispheres of the brain, disabling not only the central nervous system, but the functioning of the entire organism as a whole.
If the cerebellum and right hemisphere, which is responsible for the physical functions of the body, are damaged, the patient experiences convulsions, swelling, numbness, sensitivity is lost, and paralysis of the limbs is possible.
This is why patients often complain that their legs are swollen.
This disease is terrible precisely because of its consequences - the functioning of the kidneys, heart, and genitourinary system is disrupted. Swelling of the legs (failure of fluid exchange) is a consequence of these disorders.
Important! Swelling of the legs appears within 1-2 hours after a stroke; emergency medical assistance is necessary to prevent a recurrence of the crisis.
Next we will tell you the specific reasons for the violation.
Heart failure
As a result of unstable heart function, limited blood supply to the legs or arms occurs. After a stroke, the heart muscle cannot cope with the volume of blood, and stagnation occurs. Reason: when the right side is affected, the blood, overflowing the veins, penetrates the tissues of the arms, legs and liver.
Varicose veins
After a stroke, the functioning of the entire circulatory system is disrupted - the vessels dilate, the walls fill with blood, become thin, as a result, the legs swell and greatly increase in size.
It is important to prevent the formation of blood clots by increasing the tone of the vessel walls and improving blood flow.
Thrombosis
After a stroke, with temporary paralysis, the patient practically does not move, and is always in a supine position. The blood stagnates and becomes thick not only in small capillaries, but also in the deep veins of the legs and arms. The cells “starve”, the limbs go numb, severe swelling occurs, accompanied by pain and bluish skin. People with varicose veins and other vascular diseases are especially at risk for thrombosis.
It is impossible to cure thrombosis on your own with massage or special exercises; urgent surgery is required (removal of a blood clot or installation of special filter devices that “catch” clots).
Kidney complications
After a stroke, the water balance is disrupted, the body can accumulate water, and dehydration is also possible. A distinctive sign is that not only the legs and arms swell, but also the face. The swelling is pale, warm, soft to the touch.
Possible necrosis and kidney failure; Inpatient treatment, special medications, and massage are required. Kidney prevention is very important.
When paralyzed
After a stroke, temporary immobilization of the right or left side is possible (sensitivity and muscle tone are impaired).
In this case, swelling of the paralyzed leg is a common occurrence.
Reasons why a paralyzed leg swells:
- Clamping of large vessels. When paralyzed, a person does not feel discomfort, cannot roll over, or change body position. And if a bedridden patient lies in one position for a long time, the vascular system is pinched, blood circulation is disrupted, and swelling appears.
- Stagnation of venous blood and lymph. The hanging position of the foot or hand is unacceptable - blood stagnates in the paralyzed limbs. The situation is aggravated by muscle weakness. As you know, muscle work ensures normal blood flow.
- Thrombosis. A distinctive feature is that the leg becomes hot, and pain occurs when lightly pressed. In this case, immediate assistance from a specialist is required.
Diagnosis of thrombosis or embolism
In addition to the clinical picture, it is necessary to use special research methods for diagnosis.
Ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to clarify the nature of occlusion and identify atherosclerotic plaques during thrombosis. Thrombosis differs from embolism in the initial damage to the arteries; in embolism, the arteries are most often not affected.
Angiography is performed on the operating table to clarify the receiving vascular bed and allows you to determine the nature of the surgical intervention
Multislice computed tomography is performed when there is time for a detailed diagnosis and allows you to very accurately identify the nature of the lesions and determine treatment tactics.
Treatment
Treatment of leg swelling is carried out comprehensively; therapy includes taking medications, regular massage, and moderate exercises involving the limb. Only in combination these methods will help get rid of swelling and prevent complications.
Massage
Massage is an additional method of recovery after a stroke. Massage stimulates the functioning of blood vessels, accelerates blood flow, relaxes muscles, restores their strength, and relieves swelling.
Massage is prescribed in the first month of recovery. The course is long, at least 14-30 days, depending on existing complications, type of stroke, etc.
Important! In case of cerebral infarction without complications, massage is performed 2-3 days after the crisis; in case of hemorrhage - after 6-7 days.
Time of implementation : immediately after sleep, in the morning or before therapeutic exercises.
Duration – from 10 minutes, time gradually increases to 30 minutes.
Frequency day .
The entire course and number of sessions are prescribed by the doctor.
Carrying out conditions – air temperature not less than 20 ᵒС; Only the massaged part is exposed, the patient is covered with a blanket; massage is performed before meals or 2 hours after meals; after the massage – rest for 15 minutes.
Massage movements are directed from the foot to the knee, then to the inguinal lymph nodes. To quickly relieve swelling (to narrow blood vessels), massage is done with ice cubes, which include a decoction of oak bark and eucalyptus.
Additional remedies: cool gauze compresses (wrapped around the leg) are applied at night.
Gymnastics
Gymnastics is a prerequisite for relieving leg swelling.
To return the vessels to their previous state and normalize blood flow, feasible physical activity is necessary.
Time : in the morning after the massage.
Duration – at least 20 minutes.
Frequency – at least 2 times a day.
If possible, it is advisable to visit the pool and gym.
In the afternoon, exercise can be replaced by a walk. Fresh air, nature, positive emotions contribute to recovery.
For paralyzed limbs, passive gymnastics is performed.
Medicines
Attention! All medications are prescribed only by a doctor; self-medication is dangerous for the patient’s life.
In the initial stages, medications that thin the blood and prevent blood clotting (heparin, warfarin) are most often prescribed.
Diuretics - furosemide, torasemide, etc. can be used intravenously, intramuscularly and in tablets. Daily dose – from 10 mg. Negative consequences may occur - arrhythmia, exacerbation of heart disease.
For varicose veins, venotonics are added (detralex, phlebodia, etc.). For bedridden patients, an elastic bandage and special underwear are used.
Don’t forget about folk remedies - decoctions, baths, tinctures effectively relieve swelling:
- Carrot, cucumber, lemon juice are diuretics (drink 3 times a day before meals);
- To increase overall tone and quickly relieve swelling, it is recommended to mix the yolk with 3 grams of milkweed (use 2-3 times a day);
- Tincture of mint or flax relieves swelling after 3-4 days;
- Baths of mustard, sea salt and mint tone muscles and increase blood flow (every day before bed for 6 days).
Treatment of gangrene in elderly patients
Therapeutic measures begin with a diagnosis based on examination, biochemistry and blood tests, analysis of biomaterial from the wound, ultrasound, and x-ray examination. Therapy for gangrene involves surgery, during which the affected tissue is excised, therapy using antibiotics and other effective methods. The prognosis is favorable provided immediate medical attention is sought and the correct therapy is chosen for the elderly patient.
Let's look at the steps in detail:
- Surgery. It is important to understand that necrotic tissue cannot be preserved, so its removal is inevitable. Excision of dead areas helps prevent further growth of the gangrenous lesion and makes it possible to start the process of regeneration of healthy tissues. To restore normal blood flow, the vascular surgeon artificially increases blood flow; in severe cases, amputation of the fingers, foot, or entire leg is used. During rehabilitation therapy, skin transplantation is often used; the necessary flap is taken from a healthy area of an elderly patient, and then transferred to the affected area. A bandage or suture is used for fixation; the likelihood of engraftment depends on the blood supply.
- Antibiotic therapy. If necrosis is complicated by an associated infection, therapy must be supplemented with antibiotics, which are delivered intravenously or intramuscularly.
- Oxygen therapy (hyperbaric oxygen therapy). The therapeutic method is used to get rid of gas gangrene; during the procedure, the patient is placed in a special chamber. Under the influence of high pressure (2 times higher than usual), the blood is enriched with oxygen, the growth of pathogenic bacteria is stopped, and wounds heal faster. The duration of the session is about 90 minutes, the course consists of 3-5 days.
Other therapeutic methods include supportive measures aimed at stabilizing the patient’s condition and eliminating symptoms. To combat dehydration, IVs are prescribed, and strong painkillers are prescribed to relieve pain. It is important to begin the treatment process as quickly as possible in order to prevent further spread of the infection and not resort to large-scale surgical interventions.
To establish specific figures, the financial situation of both parties (children and elderly plaintiffs) is assessed, as well as:
- the degree of neediness of the elderly generation (a check is carried out for the presence of extraneous financial charges);
- the level of the cost of living, the amount of pensions and other payments;
- living conditions of the elderly generation;
- marital status of both parties;
- current expenses for treatment, accommodation, covering utilities, obligations on loans, mortgages, etc.;
- maintenance of minor family members, guardianship of incapacitated persons;
- the degree of participation in the educational issue and other key factors.
The size of the amount is influenced by the age of the potential alimony payer, the fact of employment, length of service, and the level of his salary. For example, having a pregnant wife or poor health may ease obligations. In addition to fixed alimony obligations, children may be required to compensate for additional expenses associated with forced repairs of a pensioner’s home, treatment, payment for the services of a nurse for an elderly patient, surgical intervention, etc.
Causes of paraplegia
- Tumors
A tumor of nervous tissue or a brain tumor growing into the lumen of the spinal canal can cause partial or complete loss of motor functions of the limbs. Metastases in the vertebrae and fractures in their background have a similar effect.
- Chronic diseases
And a large group of causes of paralysis are chronic diseases of the nervous system or autoimmune processes, for example, multiple sclerosis. In recent years, the incidence of tertiary syphilis, poorly treated during the epidemic of the early 90s, has increased, and tabes dorsalis, forgotten for half a century, is being diagnosed.
Our expert in this field:
Vasinkina Inna Yurievna
Neurologist
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Symptoms of swelling from ischemic stroke
An acute ischemic condition leads to a functional disruption of the normal reproduction of metabolic processes in neuronal cells.
Their intermediate area is filled with intracellular fluid, which leads to an increase in pressure and the formation of swelling, which has its own symptoms:
- acute headache that cannot be relieved even with strong medications;
- the appearance of vomiting and increased feeling of nausea with frequent convulsions;
- temporary disturbance of spatial orientation and feeling of loss;
- severe shortness of breath without any exertion or physical activity in patients;
- fainting and fainting, a visually determined disturbance of blood circulation.
In ischemic stroke, cerebral edema develops gradually and there is a high probability of prompt provision of the necessary assistance. At a certain level of diagnostic complications, it is important to organize constant monitoring of older people at risk.
Rate of vascular recovery after stroke
Treatment of the consequences of a stroke condition is kept under constant monitoring. The speed of vessel recovery remains an important factor. The resulting stress has an extremely serious impact on their condition.
To prevent constant swelling, it is recommended to monitor the composition of the blood and the accumulation of fluid in the tissues. Stimulating procedures put additional pressure on the arteries.
Without proper treatment, part of the vascular system may not recover at all. A return to normal will occur if you take vitamins and follow the rules of therapy, do massages in a timely manner, and put stress on the damaged areas of the limbs.
At home, some patients try not to use their damaged limbs. This leads to dystrophy of the muscular system. If the rules are followed, the vessels and arteries return to normal after a year and a half, fully beginning to fulfill natural duties.
Clinic of manifestations of vascular blockage
The consequences of a stroke affect the condition of the body's blood vessels. A sharp jolt of blood flow at the time of crisis displaces a mass of tissue fluid, muscle fibers swell. The accumulation of liquid media provokes various pathological processes, especially the legs are modified.
The cause of leg swelling is the blockage of the artery by various types of deposits on the inner walls of the line. The further movement of blood flow becomes difficult, causing swelling of the legs.
Vessel blockage
The process is preceded by changes during a stroke:
- an abundance of hormones is released;
- under the influence of active substances, tissues become inelastic;
- body systems sharply increase the rate of metabolic reactions;
- a large number of chemical compounds are released into the blood;
- the blood flow rushes to the leg, bringing various decay products into the vessels.
At the moment of agony of brain activity, the body, in an attempt to protect itself from stress, dissolves part of the adipose tissue to obtain additional energy. A lot of fluid is released, filling the vessels. The media contain additional substances for the breakdown of fat cells. Cholesterol compounds settle on the inner walls of the blood vessels in the legs.
Mechanisms of fluid metabolism disorders after stroke
After a stroke, the lower part of the body often swells. This is due to the process of damage to blood vessels during the actual impact. An acute transient disturbance in the blood circulation of the brain provokes a number of sudden changes affecting the legs.
Caring for a patient after a stroke
The understanding of metamorphosis lies in the symptoms preceding the impact:
- sudden attacks of weakness - the ongoing increase in the spasmodic state of blood vessels reduces the tone of the walls of the veins and capillaries, a feeling of buzzing in the legs;
- impaired understanding of speech, pronunciation of words - failures in communication pathways occur between parts of the brain, affecting other parts of the brain responsible for the unconscious processes of the body;
- impaired coordination, loss of balance, dizziness - increasing spasm provokes a sharp increase in the speed of movement of water media, synchronization dysfunction in one leg;
- fainting, loss of consciousness - a huge amount of hormones released into the blood provoke synoptic disturbances;
- sharp pain in the head - at the site of spasm, the pressure of fluids on the vessels increases;
- upcoming paralysis of half the face - damage to nervous activity in the area of cerebral hemorrhage, paralysis of the legs is possible.