A young woman named Irina approached the doctor and began her story with a complaint that she was afraid to live because of oppressive hatred. The subject of this feeling was a mother suffering from dementia. She waited with horror and impatience for its end, so that she could finally live like a human being. Such situations are not uncommon. Dementia also drives the relatives of the sick person crazy. But still they find the strength to take care of him. This is what Irina said about her mother.
“One late evening my mother’s neighbor called me and asked me to urgently come to her. I immediately rushed over. Mom sat in the corridor with a knife in her hand, in some rags, with her face wrapped in a scarf, and claimed that bandits were breaking in on her. They allegedly release sleeping gas into the apartment through the keyhole in order to get inside, rob and kill her. Before this incident, I believed my mother that someone was trying to break into her house, and I even changed the locks on the front door. Now it became clear that it was time to see a doctor. The diagnosis became a death sentence: Alzheimer's. Mom was admitted to a psychiatric hospital for a long time. The antipsychotics worked, she became calmer and I took her home. But I soon noticed that my mother began to walk somehow strangely and I stopped giving them to her without consulting doctors. At first everything was fine, she went out for walks and closed the door behind her. Then she told me that she had met some friends and was going to go home with them. A week later, trouble happened again. Left alone at home, my mother suddenly began destroying everything around her in the apartment, banging on the door, screaming that she was being beaten and raped. The psychiatric team took her to the hospital. There she stopped recognizing me and claimed that I was an impostor who had kidnapped her own daughter. She demanded that her relatives be found and protected from thieves who were robbing her of money. Now my mother lives with me. He takes medications regularly, but there is no improvement. All that was left of my loving mother was the outer shell; she tormented me with frequent whims, reproaches, and began to have difficulty moving. My life has turned into a nightmare. I am afraid to go home, not knowing what awaits me there: “poisoned” food thrown out the window, cabinets emptied in search of “bandits,” a saucepan that was used as a toilet, etc. But I hold on, believing that this is my cross, my daughter’s duty. I’m just scared for my children, will they be able to bear all this if something similar happens to me?”
This fear is not groundless. Predisposition to Alzheimer's disease is inherited, so in such a situation you need to pay maximum attention to your health and consult a doctor at the first symptoms. In the early stages of dementia, its progression can be slowed down and a person's sanity can be extended for years. Progress does not stop; new drugs and treatment methods are emerging. Remember how many people died from AIDS in the 80s? And now, taking new drugs, HIV-infected people live to old age.
Dementia in older people and its forms can be divided into three main stages:
- Early.
- Moderate.
- Late.
It should be taken into account that the progression of dementia in pensioners occurs in stages and may not make itself felt for some time . Moreover, treatment of this disease, as a rule, is most effective in the early stages of development. Therefore, it is so important to systematically undergo examination and diagnostic procedures in specialized institutions.
Home care for people with dementia
Caring for older people with dementia is based on the constant presence of a caregiver next to the patient. Considering that a loved one is losing most life skills, the support of a caregiver is required throughout the day in all activities.
Care for mild dementia
The patient is helped to perform morning hygiene procedures, get dressed, and get himself in order. Food is prepared for him and he is fed 5 times a day. Correlate diet and medication schedule. Physiological functions are monitored. If the elderly person does not maintain control of the toilet, a diaper is put on him and changed when he is full.
If motor skills are preserved, the ward is taken for a walk. Fresh air stimulates the functioning of the whole body, filling the lungs with oxygen.
It is advisable to conduct classes on the development of cognitive abilities in the first half of the day. At this time, the brain is more active. The materials used for classes are:
- Crosswords;
- Board games;
- collections of exercises.
Physical exercise is also beneficial for the patient. It is recommended to do gymnastics in the morning, breathing exercises, and accustom the ward to Nordic walking.
Treatment of the disease should be under the supervision of a physician. Periodically, a psychiatrist is called to the patient’s home so that the doctor can assess the elderly person’s condition and make timely adjustments to the treatment regimen.
Care for severe dementia
When a patient with dementia loses the ability to move, it is necessary to care for him as for a bedridden patient. Much attention during care is paid to preventing the occurrence of bedsores. The patient's position is regularly changed: they are turned over on the right and left side, on the back, placing the limbs comfortably. They massage those places where the patient has been lying for a long time, avoiding tissue atrophy. The bedding is changed frequently, even if there are small areas of soiling.
For an elderly person, choose comfortable clothes without rough seams made from natural cotton. The lower part of the kit must be securely fastened so that the patient cannot tear off the diapers on his own. In an unconscious state, the patient can stain himself and the bed with the contents, scratch his skin, and cause an infection.
You may also be interested in the article: Proper care for bedridden patients
Food for an elderly person with dementia should be of a liquid consistency: problems arise with chewing and swallowing food. When feeding, the patient is seated, placing pillows under his back. For drinks, closed sippy cups are used. The food is served at a warm temperature. People with senile dementia will not be able to cool it down on their own. And cold dishes cause aversion in a seriously ill person.
Early stage dementia
Patients are practically no different from healthy people at this stage of development of the disease . Only minor manifestations may be noticed, which are usually associated with the natural aging process. An elderly person does not have significant negative changes in spatio-temporal orientation, he can take care of himself and demonstrates adequacy in behavior.
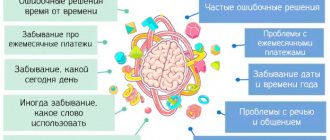
Symptoms of the onset of the disease:
- Slightly reduced performance.
- Some loss of interest in your hobbies and social circle.
- Strict adherence to traditions progresses, excessive importance is attached to the past and everything new is denied.
- Deviations in memory functioning.
- Decreased alertness or excessive concentration.
- Attacks of irritability, aggressiveness, touchiness and self-isolation appear.
- Physical activity decreases somewhat.
Prognosis of the disease in women
Alzheimer's disease and dementia are defined as steadily progressive neurodegenerative diseases. Everything is individual: for some women it is 5-8 years, others with this diagnosis can live to a ripe old age. It all depends on the resistance of the nervous system, its stability, living conditions, and family environment.
All over the world, scientists are working hard to create a means to combat the disease. Humanity needs a medicine for a long and full life of the brain. Much has already been achieved: the biochemistry of dementia, which develops due to mutations in pathological protein compounds that destroy brain neurons, has been worked out. It was found out where these proteins are formed and undergo mutations. Scientific laboratories around the world are searching for a substance that can break down amyloid proteins and remove them from the brain. At the same time, methods are being studied to recreate new healthy neurons and replace damaged nerve tissue with them. Researchers from different countries predict that these funds will be found.
Moderate stage of dementia
Symptoms of the disease:
- The ability to care for oneself is lost: a person has difficulty getting dressed and using household appliances.
- There is an irresponsible attitude towards personal hygiene.
- Memory deteriorates: the patient may forget recent events, the names of loved ones, and may not recognize himself in the reflection of the mirror.
- Sleep disorders.
- Difficulties arise with orientation in space, so a person should not be left alone on the street.
- Personal qualities change, and with them character.
- There is a process of degradation of intellectual abilities.
- The physical condition changes: an unsteady gait, the patient may mince, muscle tissue weakens, tremors of the limbs and muscle stiffness appear.
Symptoms and signs
What dementia looks like in older people: symptoms that are mild at first gradually get worse.
- Motor skills deteriorate and tremor appears.
- Ideas about hygiene become dull: the patient is careless in caring for himself, does not use the shower, does not brush his teeth, and stops dressing.
- Speech and thinking are qualitatively deteriorating.
- Psychomotor skills are disrupted - the body’s response to a signal from the outside.
- Dangerous forgetfulness. The patient may get lost or forget simple information about himself. Over time, this symptom can develop into complete disorientation. A type of memory loss is fixation-type amnesia - an elderly person does not remember immediate events, but retains a clear idea of what happened many years ago. But these memories fade over time. Another option for the loss of spatiotemporal concepts is paramnesia: the memory of an elderly person reproduces missing memories.
The described signs, mild at first, will help recognize the onset of the disease. Over time, the deviations expand and deepen, and new symptoms appear. The degree of brain damage determines the severity of pathologies. Specialists from a boarding house for the elderly classify dementia according to symptoms of atrophic and vascular type.
Vascular type symptoms
Vascular types of dementia include:
- atherosclerotic;
- senile;
- consequences of hemorrhagic stroke, ischemia.
In the first months of the disease, the following signs are detected:
- deterioration of concentration, absent-mindedness, dispersion;
- decreased short-term memory;
- dulling of interest in everyday events;
- cognitive distortions, asociality, apathy, loss of motivation for something;
- irritability, anxiety;
- sleep disturbances, confusion of day and night.
Gradually, the symptoms change qualitatively, moving to an in-depth phase: More serious memory impairment.
Names and dates are erased, current moments are immediately forgotten, but the elderly person focuses on the events of his youth - first, fixation amnesia appears, then a complete loss of memories.
Personal deformation:
the worst traits appear or worsen: greed, grumpiness, aggressiveness, capriciousness, etc.;
Self-care is completely devalued:
a person with dementia does not pay attention to this aspect at all;
urinary incontinence may occur; Degeneration of consciousness
and understanding up to complete disorientation, incompetence, inability to plan and act consistently;
Deterioration of gross motor skills:
poor gait, falls, muscle atrophy, and in the most acute form, paralysis.
Signs of atrophic type
Atrophic disorders, which include Huntington's chorea, Pick's disease, Parkinson's, and Alzheimer's, are characterized by gradual disruption of neural connections, loss of functionality, and complete death of brain cells.
It is more difficult to recognize this group: at the initial stage, the disease is often asymptomatic; their total development time is up to 8 years. Signs of the development of atrophic dementia are:
- Memory impairment. Fresh information is not remembered. The meaning of concepts and words is erased, skills and everyday habits are forgotten. An elderly person ceases to recognize loved ones.
- Decreased activity of cognitive processes. Mental work is dulled, spatiotemporal disorientation appears.
- Perception - vision, hearing, smell, tactile sensations - goes out. In the extreme stage it disappears completely.
- Emotional problems: the patient is overcome by depression, apathy.
- Loss of self-care ability: an elderly person is not able to dress himself, eat food, or maintain hygiene.
- Communication becomes difficult: the elderly person forgets and confuses words, forgets how to read and write.
- The muscles are overly tense, movements slow down, and hunching appears.
- Epilepsy – its occurrence is associated with damage to parts of the brain.
- Personal destruction: aggressiveness, rudeness, grumpiness, irritability and other similar conditions.
- As the situation worsens, serious mental deformations arise: visions, delusions.
Diagnosing dementia
A qualified doctor must study the patient’s condition, his clinical picture along with the medical history, and interview relatives. To accurately diagnose dementia, a questionnaire is used using a specific neuropsychological scale.
The following number of factors need to be taken into account:
- Symptoms appear for at least six months.
- Problems with emotions: unstable behavior, attacks of apathy and irritability.
- Impaired cognitive functions.
- Medical meanings of deviations and how they affect a person’s quality of life.
To obtain the most complete picture of the disease, additional brain examinations, blood samples for hormonal studies, and MRI may be prescribed.
Signs in old age
The causes of dementia in women are identified within all types of the disease:
- Atrophic or degenerative form. It occurs with organic lesions of the brain, when cells of the nervous tissue die from various damage to the central nervous system: infectious, toxic, parasitic, trauma, inflammatory diseases of brain structures, the presence of oncological foci in them, etc. Atrophic and degenerative forms occur more acutely, with increasing symptoms of dementia. MRI studies reveal diffuse lesions of the cerebral cortex;
- Vascular form. The functions of the central nervous system change due to the pathological state of blood circulation, which is unable to ensure normal metabolic processes and trophism of the brain due to atherosclerosis and other lesions of the vascular network. The same reasons include heart disease: ischemia, valve insufficiency, and previous heart attacks. The largest percentage of causes of vascular dementia are strokes. It significantly aggravates the course of dementia and often becomes an independent cause of neurodegenerative degeneration of brain tissue. The vascular form is more typical for men.
- Mixed form. Combines many diverse causes of senile dementia from the field of endocrinology, psychiatry, narcology and other medical areas. Disorders of the thyroid, pancreas, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, pineal gland, and reproductive organs in combination with vascular and cerebral pathologies often become the cause of dementia in women.
Foci of brain damage can be located in different areas and levels of the central nervous system:
- Cortical lesions;
- Subcortical lesions (pathology of the substantia nigra with muscle rigidity, stiffness, tremor);
- Cortical-subcortical lesions. Most often occur due to vascular causes;
- Multifocal lesions. Pathological multiple foci occur in the spinal cord and other parts of the central nervous system.
The patches spread over time, causing the severity of age-related dementia in women to worsen along with a variety of neurological symptoms.
Signs of Alzheimer's disease in the elderly depend on the severity of the pathological process and the duration of its impact. The main symptoms characteristic of various forms of the disease are noted:
- Loss of a critical attitude towards one’s condition;
- Memory problems;
- Decreased intellectual abilities, changes in speech, handwriting;
- Persistent depression;
- Anxiety, phobias, insomnia;
- Paranoid suspicion;
- Feeling of irritability, rudeness, dissatisfaction;
- Problems with choosing words and forming complete phrases;
- Difficulty communicating even with loved ones;
- Loss of moral and spiritual values.
Gradually, in the later stages of the disease, phenomena of confusion, loss of basic self-care skills, complete apathy, and personality disintegration develop.
Diagnosis and identification of the stages of Alzheimer's disease and subsequent total dementia, even for experienced neurologists, presents certain difficulties due to the diversity of individual manifestations. Modern diagnostic equipment comes to the aid of doctors, which allows them to differentiate the forms and stages of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The material and technical base of the Yusupov Hospital has a constantly updated fleet of diagnostic and therapeutic equipment produced by the world's leading companies for making accurate diagnoses.
Symptoms of the disease in young people
In the modern world, Alzheimer's disease is no longer considered a disease of old age. Every year, out of every 100,000 thousand, 90 people under 40 years of age fall ill. In studies of genetically predisposed patients, only 4.5% were found among young people. For others, the disease is considered acquired. For what reasons? Scientists all over the world are struggling with this mystery. It has been found that early Alzheimer's disease is caused by mutational processes in intracellular components that contribute to the death of nerve cells. Often these changes are triggered by the presence in the pedigree of a person with Down syndrome and other genetic disorders. The clinical picture of Alzheimer's in the young is extremely difficult to identify. The symptoms have long been similar to the manifestations of neuroses, chronic fatigue, and prolonged depression. But when characteristic signs appear: loss of short-term and then long-term memory, problems with assimilation of new information, difficult orientation in time and space, difficulties with speech, sudden weight loss, then the diagnosis of a neurodegenerative disease becomes obvious. Young people with Alzheimer's need intensive treatment and regular rehabilitation courses in order to delay the development of severe consequences for as long as possible.
Treatment of dementia in older people
The treatment program for this disease should include a course of medication, certain rules and psychotherapy.
Drug treatment for dementia
Dementia can be classified as a mental illness, but therapy is somewhat different. Treatment uses methods of influencing the head vessels, and this requires paying attention to the cardiovascular system, and only then considering the manifestations of disorders.
Prevention of stroke and heart attack requires the use of ACE inhibitors, diuretics, perindopril and lisinopril. Cerebrolysin, various tranquilizers or nootropics may also be prescribed for treatment.
The prescription of psychotropic drugs occurs only in cases where a person is observed to have depression, anxiety and problems with sleep patterns.
Vinaigrette on Thursdays, sauna day on Fridays
Photo: Andrea Piacquadio/Pexels
Routine is very important. More and more literature, mostly translated, is being published on this subject. In the West there are a lot of books dedicated to caring for people with dementia. And the idea of maintaining some principles of daily routine is generally accepted. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of such a routine.
A lifestyle that is as ritualized, predictable, and structured as possible will prolong the patient’s adequate behavior and independence. That is, there is a certain routine that must be followed. The patient knows that every day in the morning we first brush our teeth, then have breakfast, then go for a walk, then call a friend, then read aloud, and then listen to music, and since today is Friday, today is also a bath day.
And the more ritualized the lifestyle, the longer the patient will be able to stick to it. For example, he knows that “we always make vinaigrette on Thursdays.” And he will be able to make the vinaigrette longer than if he just made it occasionally.
The patient should be included as much as possible in those types of activities that he is capable of, this will help maintain the remnants of independence.
A common mistake that caregivers make is when they take on all the functions. On the contrary, it is necessary to use as much as possible all the remaining functions of the patient. For example, he cannot cook, but he can peel potatoes. He can cut the salad when you tell him: first this, and now this. He doesn't wash dishes well and needs to be washed after him. But he washes, he still knows how to do it. And it’s better to wash him up later, but give him the opportunity to do as much as possible on his own.
Treating dementia at home
An extremely important factor in home treatment is the environment in which he lives, as well as his activities and lifestyle.
Recommendations for older people with dementia
- Follow the regime . It is necessary to strictly follow the diet, rest and activity regimes. It will be useful to do moderate work, but it is not recommended to overwork yourself. It is better to eat a little food up to 6 times a day.
- Train and exercise . You need to support both your brain and your body. Moderate physical activity in the form of helping around the house, walking and therapeutic exercises will be useful. You can also use yoga classes.
- Effective treatment requires mental development . Reading printed publications, poems, crosswords, memory tests - everything can bring significant benefits. Creative activities have proven themselves to be excellent: hobbies, embroidery and knitting.
- A person with dementia should be provided with love and pleasure . Pets, communicating with family members, looking through family photo albums, listening to beautiful music, etc. can help with this.
Basics of preventing aggressive behavior in dementia
Most often, aggression occurs after the same situations. If you understand their pattern, you will easily begin to predict the moments of the next attack. Patient irritation often occurs when:
- there is stress or fear caused by the fact that it is not possible to implement usual tasks;
- there is a need to accept outside help when performing intimate procedures;
- relatives express their indignation at the mistakes and blunders made by the elderly person when he does something in everyday life;
- orientation is disturbed and excessive irritability appears due to the fact that guests have come to the house or the patient is in a public place where it is too noisy;
- something hurts or bothers you, there is discomfort and fatigue.
Relatives need to determine the reasons for the aggressive behavior of an elderly person as early as possible, and then they will be able to avoid the psychosis that occurs with dementia. Accept the new reality in which your relative can no longer perform everyday tasks. React calmly to the fact that he is now thinking for a long time about completely simple actions.
If there is little negativity, then manifestations of aggression will significantly decrease. With senile dementia and psychosis, it is important to unobtrusively help with everyday life and hygiene. Do not criticize the patient under any circumstances; try to avoid situations that demonstrate his helplessness.
If you notice signs of some kind of anxiety or fear, then immediately begin to distract the elderly person with something that may seem interesting to him.
We recommend
“Elderly dementia: symptoms, prognosis, treatment options” Read more
Treatment of dementia with psychotherapy for older people
Psychotherapy plays a significant role in rehabilitation and proper socialization . Specialists will help you restore faith in your strength and spirit for a decent future life, as well as a positive recovery outcome. Psychologists help the patient change his views on situations and pay more attention to the positive aspects of life.
Recommendations for the patient's relatives
An elderly patient with dementia should be provided with constant care, care and control. The responsibilities of loved ones include caring for the patient. For quality assistance, it is possible to use the services of professional nurses who work in private boarding houses, such as Eden.
It is also important to understand all the intricacies and nature of the illness of an elderly relative and be prepared for predicted events. A person can be determined to have a disability and be assigned guardianship.
The process of communicating with the patient should be as simple as possible . It is worth speaking with utmost clarity and clarity, with simple turns of phrase. You need to prepare to repeat and remind the patient many times, and also, if possible, not to rush him or get irritated. To do this, you need to remember that such behavior is not his whims, but manifestations of dementia.
It is necessary to create the most calm conditions surrounding the patient and facilitate his daily activities . Comfortable furniture, good lighting, and avoidance of noise – all this will contribute to treatment.
Monitoring the patient's condition is mandatory . It is necessary to teach him to control his regime, personal hygiene and the use of medications.
Support any of his activities: let him participate in the cleaning process, walks, communication and hobbies. You should not force a person by force: such coercion will only increase the manifestations of depression and apathy.
People caring for older people with dementia need social and emotional support. Caregivers are 20% more likely to develop the disease than others. Don’t neglect yourself for the sake of care – take care of yourself too.
Causes
Scientists have not yet established the exact cause of the development of senile dementia. The brain processes that cause dementia are not the result of natural aging. Neurologists identify the following causes of senile dementia:
- Compounded heredity - the disease more often develops in people whose relatives suffered from dementia in old age;
- Autoimmune reactions - age-related changes in the body activate autoimmune processes in the human body, which negatively affect nerve cells and destroy the structure of neurons in the brain;
- Concomitant somatic pathology - senile dementia develops more quickly against the background of cerebral atherosclerosis, acute cerebrovascular accident or frequent transient ischemic attacks, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension;
- Oncological pathology - space-occupying formations compress the structures of the brain, causing the development of symptoms of dementia:
- Intoxication – smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Suffered traumatic brain injuries;
- Chronic stress.
Diseases that can cause dementia include Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (dystrophic disease of the basal ganglia and cerebral cortex, spinal cord), Gaye-Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (damage to the hypothalamus and midbrain due to vitamin B1 deficiency). Dementia develops in patients suffering from Pick's disease (a disease of the central nervous system, which is characterized by destruction and atrophy of the cerebral cortex), neurosyphilis, and multiple sclerosis.
Dementia of the brain is a consequence of the disease. Timely examination and treatment of pathology in some cases helps prevent the development of dementia. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients receive a full range of services, including prevention, diagnostics, outpatient care, inpatient treatment and subsequent rehabilitation.
Expert opinion
Author: Polina Yuryevna Vakhromeeva
Neurologist
Dementia is often called “senile dementia,” but this is not always true. Although in the case of senile dementia, the main factor is age. The disease develops very slowly, so in the first stages only the patient himself can notice the changes. It is worth paying attention to such disorders as memory loss, tremors, changes in gait, muscle atrophy, and changes in character.
The average age of life is increasing, and, accordingly, more and more people are suffering from dementia of various types. Almost 50 million people worldwide have been diagnosed with the disease. According to WHO, in 40 years the number of people with dementia will triple!
Dementia is a multi-etiological disease. The most common cause is Alzheimer's disease. Less than 1% of cases of Alzheimer's disease are officially registered, and only 5% of them receive treatment, and this treatment is not at the expense of the state (only 10-15% of expenses are financed).
In our country, the system of care for such patients is just beginning to develop. Currently, there are many drugs that can significantly improve the condition of patients and their quality of life. It is important to remember: the sooner you contact specialists, the higher the likelihood of slowing down the course of the disease.
Preventing dementia in older people
During the natural aging process, as you approach age 50, it is worth considering dementia prevention . The tips described below will significantly reduce the risk of the onset and progression of dementia, as well as remain healthy, happy and full of strength in old age.
- Maintain interaction with pleasant friends . It’s worth communicating more with your loved ones, meeting like-minded people, taking part in interest groups, etc. You shouldn’t be alone for a long time.
- Move . Any type of systematic activity that is enjoyable and not stressful will play a positive role in the prevention of dementia. Walking in the fresh air, swimming and cycling have significant benefits.
- Maintain proper nutrition . It is worth eliminating any junk food from your diet. You should eat small amounts several times a day. You can also include vitamin complexes in your diet.
- Don't stop learning new things and training your memory . The development of intellectual activity, mental exercises, etc. will help maintain brain function at the proper level.
- Completely give up harmful addictions . It is worth eliminating the use of alcohol and tobacco from your life, as they negatively affect the condition of blood vessels in the brain and health in general.
- Learn to react calmly . Methods of relaxation, meditation, yoga and psychotherapy help maintain physical and psycho-emotional health.
- Get treatment in a timely manner . It is worth timely treatment for various possible diseases, especially infections and problems in the cardiovascular system.
We hope that after reading this article you have a more complete picture of the disease such as dementia in older people. If you use all the material provided, you can prevent the disease, or learn to maintain a good standard of living when the diagnosis has already been made.
Stages of the disease in women
Forms of dementia go through their successive stages:
- Predementia. Occurs 7-8 years before the full clinical picture develops. It is expressed by weak negative cognitive manifestations, minor impairments in memory of recent events.
- Moderate stage. There is increased irritability, a tendency to attacks of headaches and dizziness. It is difficult to assimilate new information. Memory fails significantly, especially short-term memory.
- Difficult stage. It occurs individually for everyone. There are patients who progress from the first to the last stage in 3-4 years (mostly young or middle-aged women). There are also many who live with moderate dementia for another 18-20 years and manage to raise children and care for grandchildren. Age-related dementia in women, the rate of its progression may vary depending on genetic burden, the stability of the nervous system and the plasticity of the brain.
In the severe stage, the process of personality disintegration continues, the entire range of cognitive abilities is lost. There is physical and mental exhaustion, difficulty moving even within one’s apartment, simple everyday activities are performed with tension, and patients prefer to stay in bed all day. Due to congestion, infections of the urinary tract, bronchopulmonary system, bedsores and trophic ulcers develop. At this stage, the patient needs constant care.
What it is?
Dementia is acquired dementia, a persistent decline in cognitive activity with a loss to varying degrees of previously acquired knowledge and practical skills and difficulty or impossibility of acquiring new ones.
In contrast to mental retardation (oligophrenia), congenital or acquired dementia in infancy, which is an underdevelopment of the psyche, dementia is a breakdown of mental functions that occurs as a result of brain damage, often in youth as a result of addictive behavior, and most often in old age ( senile dementia; from Latin senilis - senile, old man).
Popularly, senile dementia is called senile dementia.
Clinical picture of senile dementia
It occurs in old age and is characterized by progressive mental disorders and the gradual development of total disability. On average, 4.5–5% of people over 65 years of age suffer from the disease ; women are diagnosed twice as often.
A specific symptom is the so-called “senile psychopathization.” What does it mean? Signs of rigidity and coarsening of the personality, narrowing of interests and horizons in general come to the fore in the patient’s behavior and actions. Responsiveness, the ability for emotional empathy, and sympathy are lost. Typical:
- gullibility and suggestibility, the patient quickly succumbs to the influence of others, and we are talking about complete strangers, which is often used for fraudulent purposes;
- wariness, mistrust and suspicion towards relatives and friends;
- absent-mindedness, inattention, forgetfulness;
- changes in behavior: the patient may constantly walk around his home, checking door and window locks, listen to extraneous sounds, not sleep, fearing burglars;
- sleep disorders: insomnia at night and irresistible drowsiness during the day (a person sometimes falls asleep while eating, while talking, etc.);
- disinhibition, sexual promiscuity (in severe cases, attempts at sexual violence are not excluded);
- frequent falls, fainting, tremors, shuffling gait (typical of Lewy syndrome);
- speech disorders (the occurrence of stereotypies, when the patient repeats the same thing several times with the same intonation, reluctance to speak, etc.);
- impaired coordination of movements, etc.
One of the main symptoms of senile dementia is memory impairment. At the initial stage of the disease, the ability to remember is partially preserved, but over time, it becomes more and more difficult to consolidate new information. Fixation amnesia gradually develops (the patient does not remember recent events), then the patient ceases to navigate in time, in the surrounding space, and at the final stage of the disease, in his own personality. Memory loss occurs in the reverse order, and sooner or later a moment comes when a person, in principle, does not remember anything about himself.
False recognitions are common. A kind of “shift into the past” is possible: a person considers his children to be brothers/sisters or parents, says that he is in school, etc. This is due to the fact that relatively recently acquired events are forgotten, and earlier episodes from life come to the fore.
Sometimes senile delirium develops, but unlike senile and other forms of psychosis, in this case the awareness of what is happening is impaired not due to hallucinations, but due to a general distortion of the perception of reality.
At the terminal stage of senile dementia, the patient is completely immobilized, mainly lies in the fetal position and leads an almost vegetative lifestyle. But there are no neurological disorders (in particular, various automatisms).